Abstract
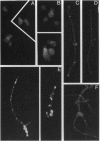
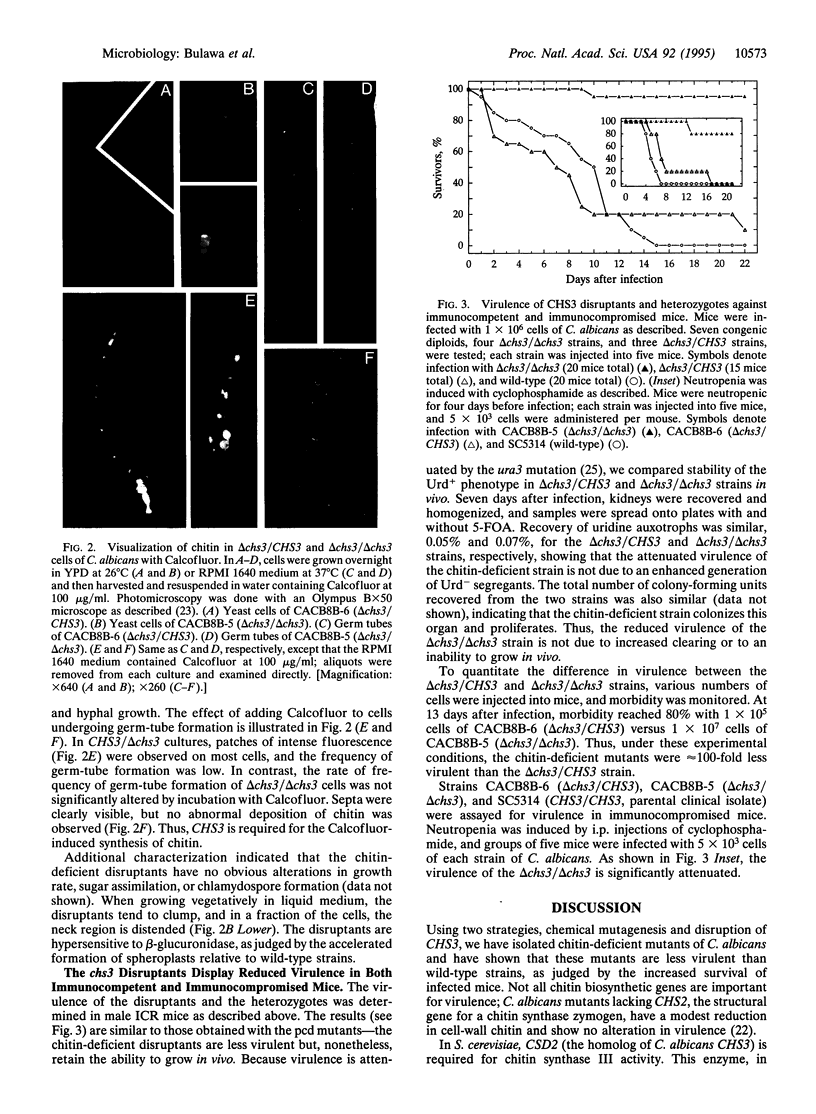
We have analyzed the role of chitin, a cell-wall polysaccharide, in the virulence of Candida albicans. Mutants with a 5-fold reduction in chitin were obtained in two ways: (i) by selecting mutants resistant to Calcofluor, a fluorescent dye that binds to chitin and inhibits growth, and (ii) by disrupting CHS3, the C. albicans homolog of CSD2/CAL1/DIT101/KT12, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene required for synthesis of approximately 90% of the cell-wall chitin. Chitin-deficient mutants have no obvious alterations in growth rate, sugar assimilation, chlamydospore formation, or germ-tube formation in various media. When growing vegetatively in liquid media, the mutants tend to clump and display minor changes in morphology. Staining of cells with the fluorescent dye Calcofluor indicates that CHS3 is required for synthesis of the chitin rings found on the surface of yeast cells but not formation of septa in either yeast cells or germ tubes. Despite their relatively normal growth, the mutants are significantly less virulent than the parental strain in both immunocompetent and immunosuppressed mice; at 13 days after infection, survival was 95% in immunocompetent mice that received chs3/chs3 cells and 10% in immunocompetent mice that received an equal dose of chs3/CHS3 cells. Chitin-deficient strains can colonize the organs of infected mice, suggesting that the reduced virulence of the mutants is not due to accelerated clearing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel G., Czop J. K. Stimulation of human monocyte beta-glucan receptors by glucan particles induces production of TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1992 Nov;14(8):1363–1373. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(92)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au-Young J., Robbins P. W. Isolation of a chitin synthase gene (CHS1) from Candida albicans by expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):197–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barki M., Koltin Y., van Wetter M., Rosenberg M. A Candida albicans surface antigen mediating adhesion and autoaggregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Infect Immun. 1994 Oct;62(10):4107–4111. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.10.4107-4111.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. M., Marcus S., Tallock J., Miller D., Krainer E., Khare R. K., Naider F. Use of the chitin-synthesis inhibitor nikkomycin to treat disseminated candidiasis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):212–214. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E. CSD2, CSD3, and CSD4, genes required for chitin synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the CSD2 gene product is related to chitin synthases and to developmentally regulated proteins in Rhizobium species and Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1764–1776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E. Genetics and molecular biology of chitin synthesis in fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:505–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Mol P. C., Shaw J. A., Choi W. J. Biosynthesis of cell wall and septum during yeast growth. Arch Med Res. 1993 Autumn;24(3):301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Braun P. C. Adherence and receptor relationships of Candida albicans. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):1–20. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.1-20.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A. Cell wall of Candida albicans: its functions and its impact on the host. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1989;3:248–314. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3624-5_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman T., Kinsman O., Houston J. Chitin biosynthesis in Candida albicans grown in vitro and in vivo and its inhibition by nikkomycin Z. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):1909–1914. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Wu J. L., Zwicker J., Bowen A. R., Robbins P. W. Expression of chitin synthase genes during yeast and hyphal growth phases of Candida albicans. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi W. J., Sburlati A., Cabib E. Chitin synthase 3 from yeast has zymogenic properties that depend on both the CAL1 and the CAL3 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4727–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon D. M., Polak A., Szaniszlo P. J. Pathogenicity and virulence of wild-type and melanin-deficient Wangiella dermatitidis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1987 Apr;25(2):97–106. doi: 10.1080/02681218780000141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E. Candida cell wall mannan: a polysaccharide with diverse immunologic properties. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(1):33–51. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Rico H., Sentandreu R. Calcofluor white alters the assembly of chitin fibrils in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1577–1582. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel P. L., Jr, Sobel J. D. The role of cell-mediated immunity in candidiasis. Trends Microbiol. 1994 Jun;2(6):202–206. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(94)90112-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonzi W. A., Irwin M. Y. Isogenic strain construction and gene mapping in Candida albicans. Genetics. 1993 Jul;134(3):717–728. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Tsay E. Y., Kirsch D. R. Isolation of the Candida albicans gene for orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase by complementation of S. cerevisiae ura3 and E. coli pyrF mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00328721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S., Altboum Z., Savage D. C., Segal E. Adhesion of Candida albicans to epithelial cells effect of polyoxin D. Mycopathologia. 1991 Sep;115(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00462227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow N. A., Robbins P. W., Lester J. W., Brown A. J., Fonzi W. A., Chapman T., Kinsman O. S. A hyphal-specific chitin synthase gene (CHS2) is not essential for growth, dimorphism, or virulence of Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6216–6220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan L. H., Klein B. S. Altered expression of surface alpha-1,3-glucan in genetically related strains of Blastomyces dermatitidis that differ in virulence. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3543–3546. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3543-3546.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Miller S. M., Kurtz M. B., Kirsch D. R. Directed mutagenesis in Candida albicans: one-step gene disruption to isolate ura3 mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):199–208. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch D. R., Whitney R. R. Pathogenicity of Candida albicans auxotrophic mutants in experimental infections. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3297–3300. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3297-3300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel K. R., Goldman W. E. Cell walls from avirulent variants of Histoplasma capsulatum lack alpha-(1,3)-glucan. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2997–3000. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2997-3000.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Hein R. C., Smith R. L., Rouse J. B. The fibronectin adhesin of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1994 Oct;62(10):4679–4681. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.10.4679-4681.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollár R., Petráková E., Ashwell G., Robbins P. W., Cabib E. Architecture of the yeast cell wall. The linkage between chitin and beta(1-->3)-glucan. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):1170–1178. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer N., Segal E., Cihlar R. L., Calderone R. A. Pathogenesis of vaginal candidiasis: studies with a mutant which has reduced ability to adhere in vitro. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Apr;24(2):127–131. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcilla A., Elorza M. V., Mormeneo S., Rico H., Sentandreu R. Candida albicans mycelial wall structure: supramolecular complexes released by zymolyase, chitinase and beta-mercaptoethanol. Arch Microbiol. 1991;155(4):312–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00243448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Carruba G., Angiolella L., Cassone A. Induction of germ tube formation by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in Candida albicans: uptake of inducer and germinative response. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):555–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.555-562.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Shibata N., Podzorski R. P., Herron M. J. Candida mannan: chemistry, suppression of cell-mediated immunity, and possible mechanisms of action. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):1–19. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Preston R. A., Adams A. E., Stearns T., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K., Jones E. W. Fluorescence microscopy methods for yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:357–435. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncero C., Durán A. Effect of Calcofluor white and Congo red on fungal cell wall morphogenesis: in vivo activation of chitin polymerization. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1180-1185.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San-Blas G., San-Blas F. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: cell wall structure and virulence. A review. Mycopathologia. 1977 Dec 16;62(2):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01259396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Hammer C. F., Cihlar R. L. Analysis of mannans of two relatively avirulent mutant strains of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):413–419. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.413-419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsma J. H., Wessels J. G. Solubility of (1 leads to 3)-beta-D/(1 leads to 6)-beta-D-glucan in fungal walls: importance of presumed linkage between glucan and chitin. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):209–212. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh M., Nagahashi S., Doi M., Ohta A., Takagi M., Arisawa M. Cloning of the chitin synthase 3 gene from Candida albicans and its expression during yeast-hyphal transition. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Nov;241(3-4):351–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00284688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surarit R., Gopal P. K., Shepherd M. G. Evidence for a glycosidic linkage between chitin and glucan in the cell wall of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1723–1730. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troke P. F., Andrews R. J., Pye G. W., Richardson K. Fluconazole and other azoles: translation of in vitro activity to in vivo and clinical efficacy. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12 (Suppl 3):S276–S280. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_3.s276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]