Abstract
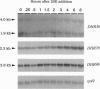
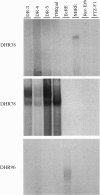
We have designed a rapid cloning and screening strategy to identify new members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that are expressed during the onset of Drosophila metamorphosis. Using this approach, we isolated three Drosophila genes, designated DHR38, DHR78, and DHR96. All three genes are expressed throughout third-instar larval and prepupal development. DHR38 is the Drosophila homolog of NGFI-B and binds specifically to an NGFI-B response element. DHR78 and DHR96 are orphan receptor genes. DHR78 is induced by 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) in cultured larval organs, and its encoded protein binds to two AGGTCA half-sites arranged as either direct or palindromic repeats. DHR96 is also 20E-inducible, and its encoded protein binds selectively to the hsp27 20E response element. The 20E receptor can bind to each of the sequences recognized by DHR78 and DHR96, indicating that these proteins may compete with the receptor for binding to a common set of target sequences.
Full text
PDF

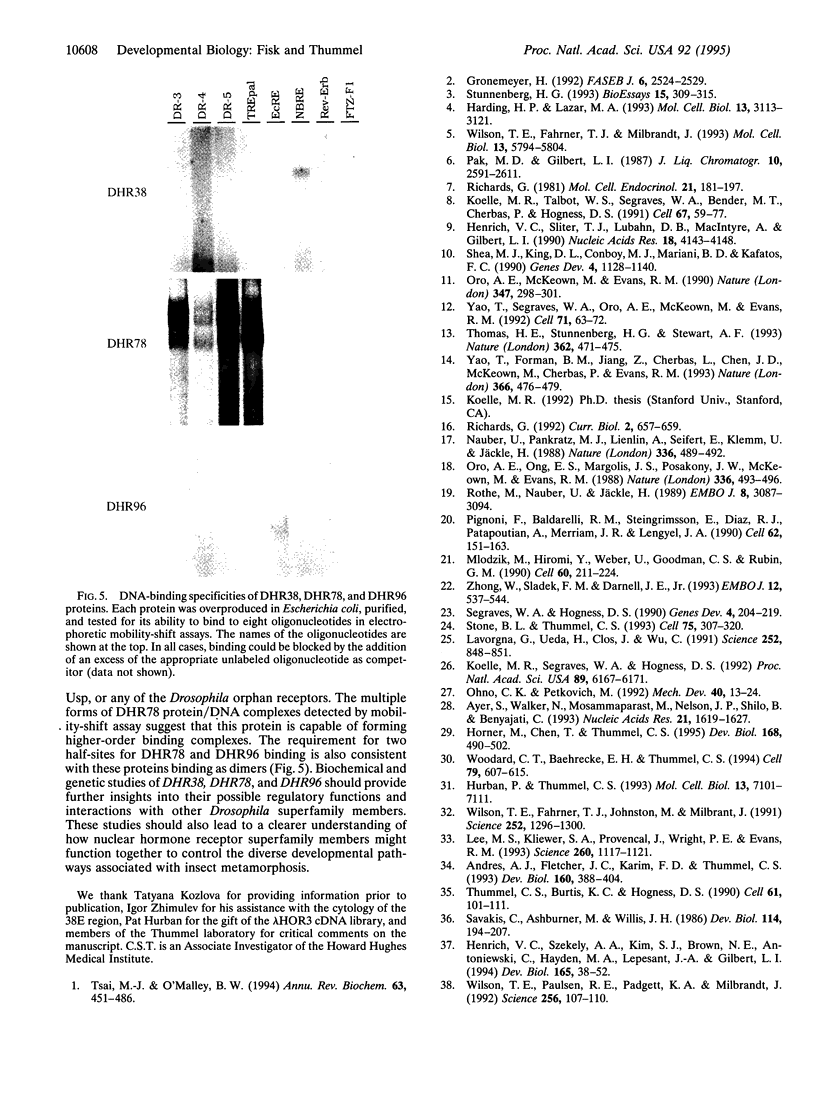
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. J., Fletcher J. C., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: a comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):388–404. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer S., Walker N., Mosammaparast M., Nelson J. P., Shilo B. Z., Benyajati C. Activation and repression of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase distal transcription by two steroid hormone receptor superfamily members binding to a common response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1619–1627. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H. Control of transcription activation by steroid hormone receptors. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2524–2529. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1592204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding H. P., Lazar M. A. The orphan receptor Rev-ErbA alpha activates transcription via a novel response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3113–3121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich V. C., Sliter T. J., Lubahn D. B., MacIntyre A., Gilbert L. I. A steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily member in Drosophila melanogaster that shares extensive sequence similarity with a mammalian homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4143–4148. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich V. C., Szekely A. A., Kim S. J., Brown N. E., Antoniewski C., Hayden M. A., Lepesant J. A., Gilbert L. I. Expression and function of the ultraspiracle (usp) gene during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1994 Sep;165(1):38–52. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner M. A., Chen T., Thummel C. S. Ecdysteroid regulation and DNA binding properties of Drosophila nuclear hormone receptor superfamily members. Dev Biol. 1995 Apr;168(2):490–502. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurban P., Thummel C. S. Isolation and characterization of fifteen ecdysone-inducible Drosophila genes reveal unexpected complexities in ecdysone regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7101–7111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. DHR3: a Drosophila steroid receptor homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Talbot W. S., Segraves W. A., Bender M. T., Cherbas P., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90572-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna G., Ueda H., Clos J., Wu C. FTZ-F1, a steroid hormone receptor-like protein implicated in the activation of fushi tarazu. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):848–851. doi: 10.1126/science.1709303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Kliewer S. A., Provencal J., Wright P. E., Evans R. M. Structure of the retinoid X receptor alpha DNA binding domain: a helix required for homodimeric DNA binding. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1117–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.8388124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Hiromi Y., Weber U., Goodman C. S., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila seven-up gene, a member of the steroid receptor gene superfamily, controls photoreceptor cell fates. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90737-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauber U., Pankratz M. J., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Klemm U., Jäckle H. Abdominal segmentation of the Drosophila embryo requires a hormone receptor-like protein encoded by the gap gene knirps. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):489–492. doi: 10.1038/336489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno C. K., Petkovich M. FTZ-F1 beta, a novel member of the Drosophila nuclear receptor family. Mech Dev. 1993 Jan;40(1-2):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90084-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Relationship between the product of the Drosophila ultraspiracle locus and the vertebrate retinoid X receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):298–301. doi: 10.1038/347298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., Ong E. S., Margolis J. S., Posakony J. W., McKeown M., Evans R. M. The Drosophila gene knirps-related is a member of the steroid-receptor gene superfamily. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):493–496. doi: 10.1038/336493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignoni F., Baldarelli R. M., Steingrímsson E., Diaz R. J., Patapoutian A., Merriam J. R., Lengyel J. A. The Drosophila gene tailless is expressed at the embryonic termini and is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90249-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. Switching partners? Curr Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):657–659. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90123-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. The radioimmune assay of ecdysteroid titres in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Mar;21(3):181–197. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Nauber U., Jäckle H. Three hormone receptor-like Drosophila genes encode an identical DNA-binding finger. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3087–3094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea M. J., King D. L., Conboy M. J., Mariani B. D., Kafatos F. C. Proteins that bind to Drosophila chorion cis-regulatory elements: a new C2H2 zinc finger protein and a C2C2 steroid receptor-like component. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1128–1140. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone B. L., Thummel C. S. The Drosophila 78C early late puff contains E78, an ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes a novel member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80072-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G. Mechanisms of transactivation by retinoic acid receptors. Bioessays. 1993 May;15(5):309–315. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. E., Stunnenberg H. G., Stewart A. F. Heterodimerization of the Drosophila ecdysone receptor with retinoid X receptor and ultraspiracle. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):471–475. doi: 10.1038/362471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Fahrner T. J., Johnston M., Milbrandt J. Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection in yeast. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1296–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.1925541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Fahrner T. J., Milbrandt J. The orphan receptors NGFI-B and steroidogenic factor 1 establish monomer binding as a third paradigm of nuclear receptor-DNA interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5794–5804. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Paulsen R. E., Padgett K. A., Milbrandt J. Participation of non-zinc finger residues in DNA binding by two nuclear orphan receptors. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):107–110. doi: 10.1126/science.1314418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodard C. T., Baehrecke E. H., Thummel C. S. A molecular mechanism for the stage specificity of the Drosophila prepupal genetic response to ecdysone. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Forman B. M., Jiang Z., Cherbas L., Chen J. D., McKeown M., Cherbas P., Evans R. M. Functional ecdysone receptor is the product of EcR and Ultraspiracle genes. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):476–479. doi: 10.1038/366476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Segraves W. A., Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90266-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr The expression pattern of a Drosophila homolog to the mouse transcription factor HNF-4 suggests a determinative role in gut formation. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):537–544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]