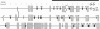Abstract
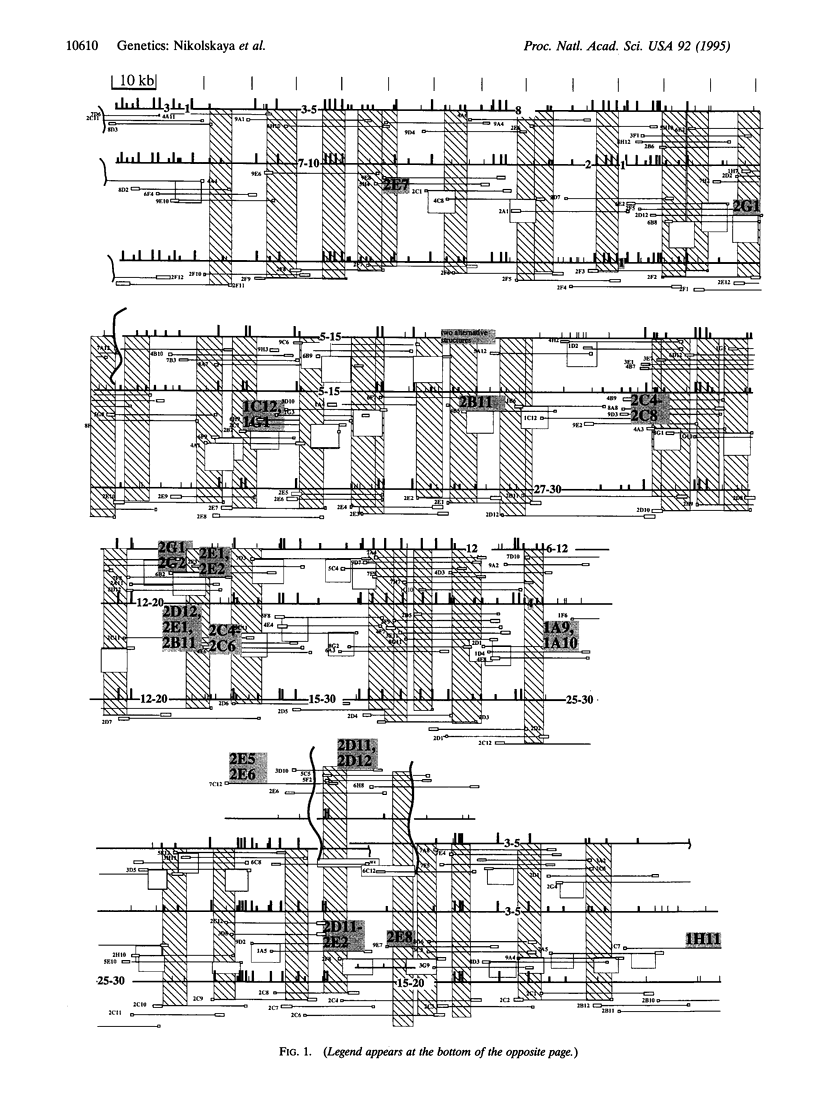
High-resolution physical maps of the genomes of three Rhodobacter capsulatus strains, derived from ordered cosmid libraries, were aligned. The 1.2-Mb segment of the SB1003 genome studied here is adjacent to a 1-Mb region analyzed previously [Fonstein, M., Nikolskaya, T. & Haselkorn, H. (1995) J. Bacteriol. 177, 2368-2372]. Probes derived from the ordered cosmid set of R. capsulatus SB1003 were used to link cosmids from the St. Louis and 2.3.1 strain libraries. Cosmids selected this way did not merge into a single contig but formed several unlinked groups. EcoRV restriction maps of the ordered cosmids were then constructed using lambda terminase and fused to derive fragments of the chromosomal map. In order to link these fragments, their ends were transcribed to produce secondary probes for hybridization to gridded cosmid libraries of the same strains. This linking reduced the number of subcontigs to three for the St. Louis strain and one for the 2.3.1 strain. Hybridization of the same probes back to the ordered cosmid set of SB1003 positioned the subcontigs on the high-resolution physical map of SB1003. The final alignment of the restriction maps shows numerous large and small translocations in this 1.2-Mb chromosomal region of the three Rhodobacter strains. In addition, the chromosomes of the three strains, whose fine-structure maps can now be compared over 2.2 Mb, are seen to contain regions of 15-80 kb in which restriction sites are highly polymorphic, interspersed among regions in which the positions of restriction sites are highly conserved.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlson C. R., Grønstad A., Kolstø A. B. Physical maps of the genomes of three Bacillus cereus strains. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3750–3756. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3750-3756.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. R., Kolstø A. B. A complete physical map of a Bacillus thuringiensis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):1053–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.1053-1060.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Haselkorn R. Chromosomal structure of Rhodobacter capsulatus strain SB1003: cosmid encyclopedia and high-resolution physical and genetic map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2522–2526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Haselkorn R. Physical mapping of bacterial genomes. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jun;177(12):3361–3369. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.12.3361-3369.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Nikolskaya T., Haselkorn R. High-resolution alignment of a 1-megabase-long genome region of three strains of Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1995 May;177(9):2368–2372. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.9.2368-2372.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Nikolskaya T., Zaporojets D., Nikolsky Y., Kulakauskas S., Mironov A. Tn10-mediated inversions fuse uridine phosphorylase (udp) and rRNA genes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(8):2265–2271. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.8.2265-2271.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Zheng S., Haselkorn R. Physical map of the genome of Rhodobacter capsulatus SB 1003. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4070–4077. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4070-4077.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Rosenthal A., Waterston R. H. Lorist6, a cosmid vector with BamHI, NotI, ScaI and HindIII cloning sites and altered neomycin phosphotransferase gene expression. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman D. S., Dykhuizen D. E. Clonal divergence in Escherichia coli as a result of recombination, not mutation. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1380–1383. doi: 10.1126/science.7973728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Gray J. A. Effects of chromosomal inversion on cell fitness in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1988 Aug;119(4):771–778. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. Rearrangements in the genome of the bacterium Salmonella typhi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazodier P., Davies J. Gene transfer between distantly related bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:147–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R., Bridges M. M. Molecular evolution of the Escherichia coli chromosome. IV. Sequence comparisons. Genetics. 1993 Mar;133(3):455–468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. G., Simons R. W. Chromosomal supercoiling in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(3):675–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Selander R. K. Evolutionary genetics of the proline permease gene (putP) and the control region of the proline utilization operon in populations of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6886–6895. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6886-6895.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Murialdo H., Delius H., Chai J. H., Poustka A., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. Analysis of cosmids using linearization by phage lambda terminase. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]