Abstract
In this work, we utilise a combination of theory, computation and experiments to understand the early events related to the nucleation of Ag filaments on α-Ag2WO4 crystals, which is driven by an accelerated electron beam from an electron microscope under high vacuum. The growth process and the chemical composition and elemental distribution in these filaments were analysed in depth at the nanoscale level using TEM, HAADF, EDS and XPS; the structural and electronic aspects were systematically studied in using first-principles electronic structure theory within QTAIM framework. The Ag nucleation and formation on α-Ag2WO4 is a result of the order/disorder effects generated in the crystal by the electron-beam irradiation. Both experimental and theoretical results show that this behavior is associated with structural and electronic changes of the [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters and, to a minor extent, to the [WO6] cluster; these clusters collectively represent the constituent building blocks of α-Ag2WO4.
Tungstates of transition metals are ternary oxide semiconductors that contain a combination of covalent, ionic and metallic bonding. They have attracted considerable attention due to their unique symmetry-dependent and spontaneous polarization properties, which are technologically important in numerous applications, such as ferroelasticity, ionic conductivity and photoluminescence1,2,3,4. They show, in the range of a few nanometers, a surprising tendency to evolve into ordered structures of highly sophisticated architectures. Understanding the structural and electronic properties of the materials in these systems is critical to determining their physical/chemical properties and performance.
Ag2WO4 is a member of the tungstate family that crystallizes in an orthorhombic structure (α-Ag2WO4) with a space group of Pn2n. α-Ag2WO4 has been the focus of investigations by our group; we have synthesised this material using different methods (coprecipitation, sonochemistry and hydrothermal synthesis) and have studied its photoluminescence (PL) properties5. More recently, the formation of Ag filaments on α-Ag2WO4 crystal, via irradiation of electrons by an accelerated electron beam from an electron microscope under high vacuum, was reported6, and the corresponding potential applications7 were investigated. Our current investigation is motivated by our incomplete understanding of the underlying fundamental phenomena and mechanisms driving the nucleation and growth of Ag filaments.
While the concept of a crystalline solid as a perfect, periodic structure is at the core of our understanding of a wide range of material properties, in reality, disorder is ubiquitous and is capable of drastically influencing various properties8. α-Ag2WO4 is expected to exhibit interesting forms of structural and electronic disorder that play a central role in driving function. α-Ag2WO4 represents a class of inorganic compounds that exhibit unmatched structural versatility and unique intrinsic properties due to the fundamental characteristics of the interactions between its octahedral WO6 and [AgOx] (x = 2, 4, 6, and 7) clusters, which are its basic building blocks. These clusters are excellent candidates to study to explore the nature of the chemical bond and the influence of the so-called finite-size effects on the physical and electronic structures of such compounds.
Our emphasis is on highlighting how the structural and electronic disorder lead to interesting and unusual physical/chemical properties in this long-established class of materials. First, because this structure exhibits different types of coordination [AgOx] and because its synergistic coordination mode facilitates the formation of several types of clusters with low and high coordination numbers, the nature of the [WO6] and [AgOx] clusters and the interactions between them are inherently predisposed to the formation of flexible materials with open structures. Second, the O-Ag-O and O-W-O bonds in the clusters, which have a weak interaction between the basic units, may also be chemically modified using electron irradiation, as will be shown. Consequently, the stability of the lattice is dependent on the local bonding, and the enthalpic difference between the crystalline and amorphous forms may be very small because the local bonding arrangements are similar in both. This behavior is well established in the study of conventional glass-forming materials, and the network topology and connectivity play a critical role in stabilizing disordered states5. Thus, not only might these systems be somewhat predisposed to disorder, but this disorder might readily be tuned by exploiting the versatile structural chemistry of this broad family.
The goal of this work is to understand the basis of the early-nucleation and -growth of Ag filaments after the irradiation process. To investigate the in situ growth of Ag filaments in the α-AgWO4 crystal, information on the structural and electronic evolution, as defined by the changes in the electron density, was obtained by density functional theory (DFT) calculations using the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM). Experimental techniques such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with a high-angle annular dark field (HAADF), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were also employed. The results provide a valuable probe into the relationship between atomic-scale structural and electronic perturbations and their macroscopic consequences.
We focus primarily on the structural and electronic properties to answer three central questions: (i) What happens with the excess electron density, simulating the electron beam of TEM, as it approaches the surface and bulk of α–Ag2WO4? (ii) How are the electrons distributed in this material, and how does this distribution relate to the structural and electronic evolution? (iii) Can QTAIM properties provide insight into the strength of the bonds after electron irradiation of α–Ag2WO4? We studied the geometric and electronic structure of α-Ag2WO4 and derived a mechanism for the early events in the formation and growth of Ag filaments in the scenario of electron irradiation of [AgOx] (x = 2, 4, 6, and 7) and [WO6] clusters, which are the constituent polyhedra of α-Ag2WO4. We shall discuss how the analysis, provided by both the experimental and theoretical results, of the physical and electronic structure of α-Ag2WO4 allows us to explain the Ag-nucleation process. The discussion will address the details of image acquisition and analysis and will provide a guide to interpret the experimental results. All technical details are provided in the Supplementary Information (SI).
Results
A graphical representation of α-Ag2WO4 using polyhedra is presented in Fig. S1 (SI) to show [WO6] and [AgOx] (x = 2, 4, 6 and 7) as the building blocks of this material. The crystallographic structural characteristics of the as-prepared products investigated by XRD analysis are also presented in the Supplementary Information (Fig. S2). All of the diffraction peaks of the samples reflect an orthorhombic structure without any deleterious phases and with a space group of Pn2n and a point-group symmetry of C2v9,10; these results are in agreement with the standard values listed in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database (ICSD) no. 416510 and with those reported in the literature5,11. Optimised lattice parameters and atomic positions are listed in Table S1 (SI).
The first step is the growth of metallic Ag on the α-Ag2WO4 crystal; this part of the process is accompanied by in situ TEM. A detailed characterisation of the chemical reactions and physical interactions involving nanomaterials requires simultaneous measurement of atomic structure and chemical composition at the nanoscale level. However, the ability to observe the formation and growth of a crystal in real time is reshaping our understanding of these molecular processes, revealing subtleties previously hidden in ensemble averages. In situ TEM is an elegant method for uncovering the dynamic processes in the growth of nanocrystals12. These recent technological advancements in conjunction with high-resolution imaging provide a new opportunity to view nanoscale processes and nanocrystal growth by aggregation and coalescence has been directly observed in real time by in situ TEM studies12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21. The injection of electrons can also be used to modify the properties of different materials16,22,23,24,25; for example, the localised electron probes used in TEM can be used to foster electron-induced processes on a nanometre or subnanometre scale26,27,28,29,30,31,32.
TEM provides a foundation for such atomic resolution studies and is an appropriate tool for monitoring nanoparticle growth in real time12,18,33,34,35,36. This in situ imaging allows the study of materials processes and biological, multistage reactions12,14,37,38,39,40. However, the studies to date have typically been performed on samples in solution, and the environment around nanoparticles is known to change their physical and chemical properties. The formation and growth conditions of nanoparticles in solution differ markedly from those of nanoparticles in a high-vacuum environment because the surface of nanoparticles adapts to its environment. This difference has been demonstrated using in situ spectroscopy and microscopy techniques12,39,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53.
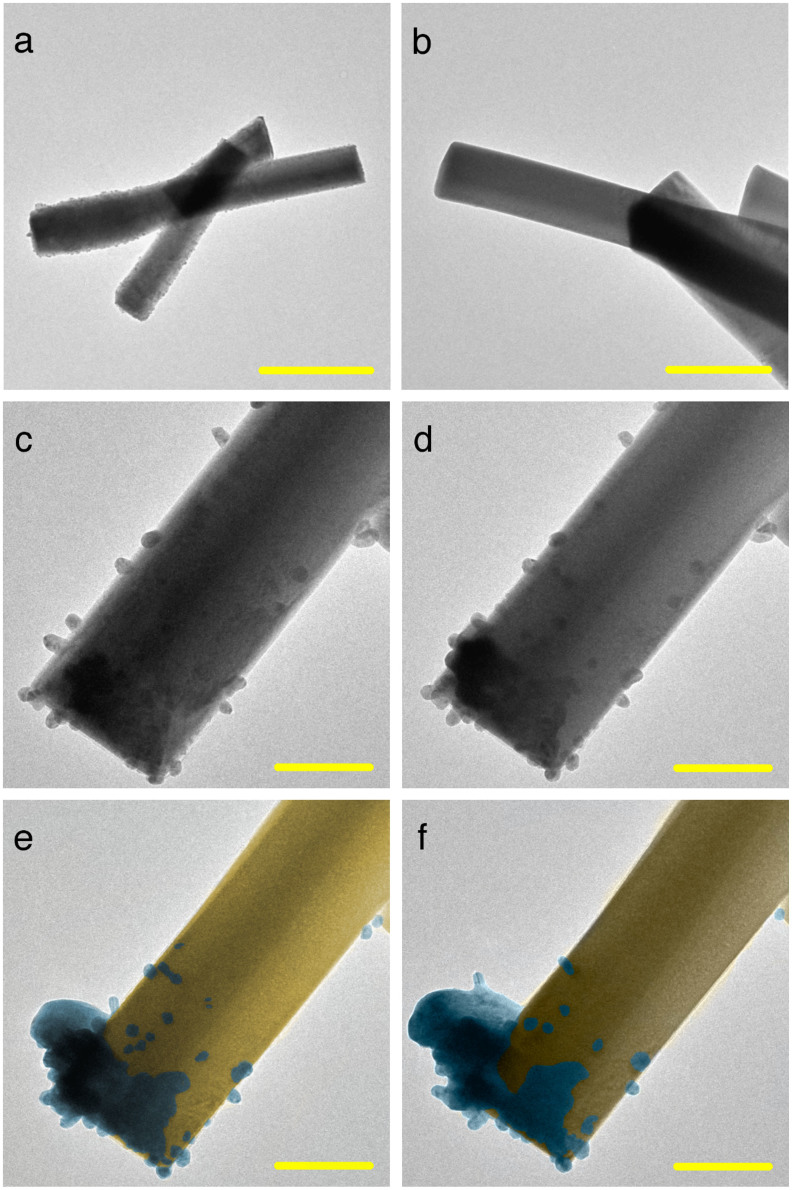
In a recent study6, we observed the growth of Ag on the α-Ag2WO4 structure. In the early steps of the process, the structure of α-Ag2WO4 was clean and smooth (Fig. 1a); a broader view of the same sample is shown in Fig. 1b. With a longer exposure (on the order of a fraction of a second) of electron irradiation, the nucleation process of several Ag nanoparticles occurred throughout the bulk structure (Fig. 1c). A greater density of Ag was observed at the end of the matrix structure, which resulted in the nucleation and growth of a thicker filament (Fig. 1d) that grew further, as shown in Figs. 1e and 1f.
Figure 1. TEM images of the formation of Ag filaments from the a-Ag2WO4 bulk.
(a) and (b) TEM images obtained at different magnifications indicate a smooth and clear surface. (c)–(f) Thick Ag filaments grow at the edge of the sample, whereas other Ag nanoparticles are absorbed by the matrix. (Scale bar = 500 nm in a, 200 nm in b and, 100 nm in (c–f).
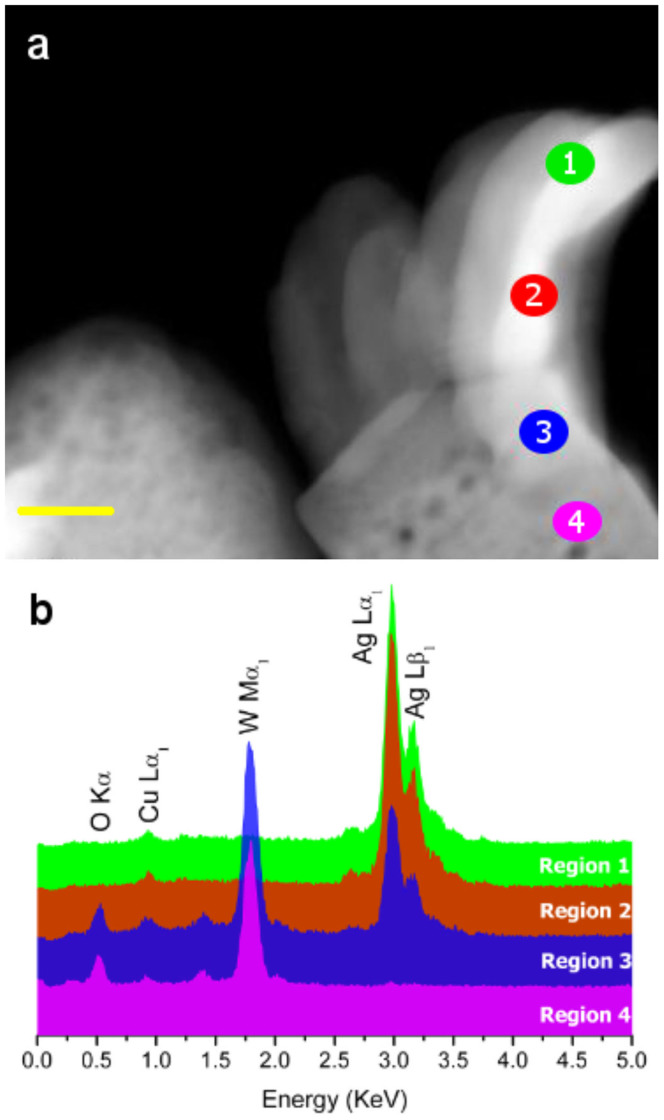
A detailed EDS analysis was performed to elucidate the composition of the nanostructures. Fig. 2a presents a HAADF image of a single nanostructure on which elemental EDS analysis was performed. This structure contains nanofilaments whose growth was stimulated by the electron-beam irradiation on the α-Ag2WO4 surface6. The EDS analyses performed on regions 1 to 4 confirmed that the filaments were mainly composed of Ag (Fig. 2b). However, in the nanostructure, mainly Ag, W, and O and mainly W and O were clearly identified in regions 3 and 4, respectively. A small amount of Cu atoms was also observed, which is related to the grid.
Figure 2.
(a) HAADF image of an isolated nanostructure. (b) EDS performed in different regions, which are illustrated in Fig. 2a. (Scale bar = 50 nm in a).
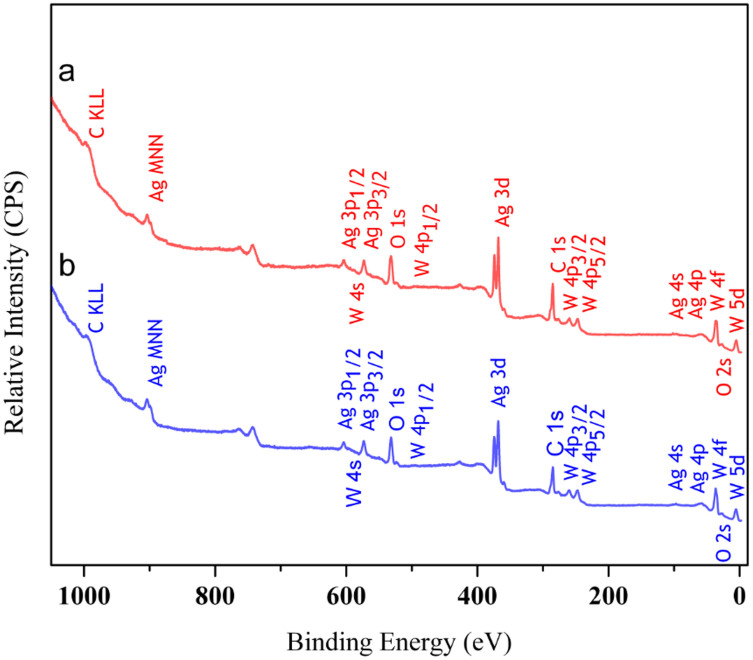
XPS measurements were performed on the irradiated and non-irradiated α-Ag2WO4 materials to compare the purity of the surface and the degree of oxidation, to gain insight into the shape evolution, and to unravel the formation mechanism of the samples. The wide-range spectrum is shown in Fig. 3. The results show the presence of a large amount of carbon, and the peaks of Ag, W, and O are clearly visible, indicating that the samples were highly pure. The core-level binding energies (BEs) of O 1 s, Ag 3 d, and W 4f, which have been corrected for the surface charging effect, were determined from the respective XPS spectra and are presented in Table S2 (SI). These results are consistent with the BE values reported in the literature54,55.
Figure 3. XPS survey spectrum of the irradiated in (a), and non-irradiated a-Ag2WO4 material in (b).
High-resolution C 1 s, O 1 s, Ag 3 d, and W 4f XPS spectra of the as-synthesised and irradiated samples are included for comparison purposes (see Figs. S3 (a–d) (SI) and Table S3 (SI)). An analysis of the XPS results shows a strong effect on both the Ag and W atoms. The irradiated sample has a larger amount of W(V), which indicates greater disorder of the structure, in accordance with previous HRTEM results. The Ag 3d5/2 peak is identified at 368.10 and 367.80 eV in the spectra of the as-synthesised and irradiated samples, respectively, which suggests the presence of metallic Ag56,57. To confirm the presence of metallic Ag from the XPS data, the asymmetric peaks observed in the Ag 3d5/2 core-level region and the Auger M4N45N45 peaks of α-Ag2WO4 and of irradiated α-Ag2WO4 were analysed (see Fig. S4 (SI)).
Our findings confirm the presence of metallic Ag, and the corresponding results agree with the results reported in the Handbook of Monochromatic XPS Spectra58. a The XPS spectra are also very similar to the spectrum of Ag M4N45N45 of α-Ag2WO4 published by Ho et al55. These results represent a valuable contribution to the XPS analysis of the in situ atomic-scale nucleation of Ag filaments on α-Ag2WO4.
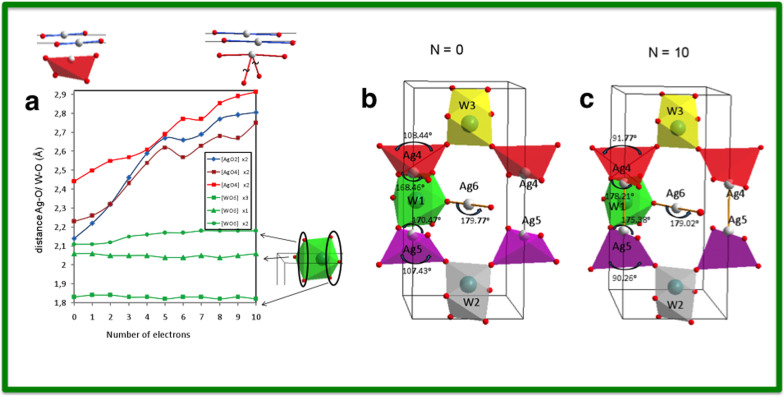
Because the formation of metallic Ag after the electron irradiation of α-Ag2WO4 is a quantum phenomenon, we performed quantum mechanical calculations to understand the structural and electronic modifications of α-Ag2WO4 that were observed experimentally. In the calculations, electrons were introduced one by one up to ten in the orthorhombic unit cell of α-Ag2WO4, and a redistribution of these extra electrons takes place by means of a simultaneously geometry optimization on both the lattice parameters and the atomic positions. The change of lattice constants (a, b, and c) as a function of the number of added electrons are presented in Fig. S5 (SI). In Fig. 4a, the values of the bond distances of Ag-O and W-O in [AgO2], [AgO4], and [WO6] clusters are shown as a function of electrons added. An analysis and a comparison of the geometries for a neutral (N = 0) and charged (N = 10) structures show a pronounced increase in the corresponding Ag-O distances with the addition of electrons. In the [AgO2] cluster, the Ag-O distance increases from 2.15 to 2.75 Å (in blue). In the [AgO4] cluster, two different distances are observed: one pair (in red) exhibits behaviour similar to that of the bonds in the [AgO2] cluster and has an O-Ag-O angle of approximately 170°; the other pair (in garnet) has an O-Ag-O angle of approximately 108° and a longer Ag-O distance, which indicates that the atoms detach as the electrons are added. In fact, when N = 10, the first pair of O atoms forms an O-Ag-O angle of approximately 178°, whereas the angle of the second pair is reduced to approximately 90°, as shown in Fig. 4b. In the two types of [WO6] clusters, we find that the W-O distances corresponding to the W2 and W3 atoms remain almost unaltered, whereas the distance of the W-O bond corresponding to W1 decreases smoothly with the addition of electrons. These results show that during electron irradiation, electronic and structural disorder was introduced into the materiaļ thus illustrating the fundamental role of cluster concepts in the formation and growth of Ag filaments.
Figure 4.
(a) Values of Ag-O and W-O bond distances in the [AgO2], [AgO4], and [WO6] clusters as a function of the number of electrons added. (b) Geometry of neutral (N = 0) and charged (N = 10) structures.
QTAIM, which was developed by Bader and collaborators59,60,61, allows the analysis of the experimental and theoretical electron density distributions, ρ(r), in a molecule or solid as well as the study of the properties of ρ(r); these analyses reveal the bonding interactions in a molecular or crystal system and the nature of these interactions. The electronic charge of each atom is evaluated using Bader charge analysis within the QTAIM framework, which is a way of dividing molecules or solids into atoms on the basis of electronic charge density. Finding zero flux surfaces between two atoms allows the charge of each atom to be calculated. In Fig. 5, the charge density of the Ag and W centres of the [AgO2], [AgO4], and [WO6] clusters is depicted as a function of the number of electrons added. Atomic charges were calculated using integrations of the charge density within the atomic basins, Ω, and subtracting the nuclear charge, Z, of the corresponding atom.
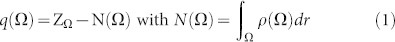 |
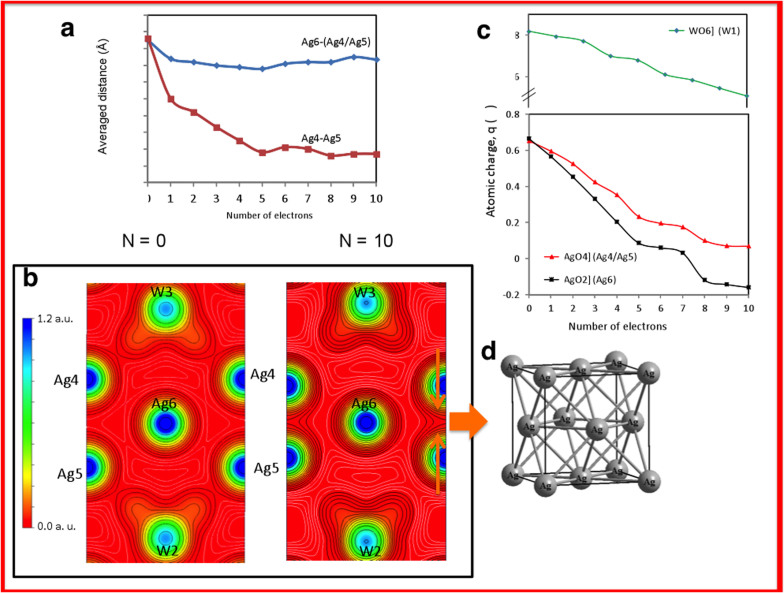
The average bond distances of Ag-Ag as a function of the number of electrons added are presented in Fig. 5a, and electron density contours on the (100) plane for the neutral (N = 0) structure and charged (N = 10) structures are depicted in Fig. 5b. Isodensity lines less than 0.02 a.u. are coloured white to highlight the differences between them. An analysis of the results presented in Fig. 5b reveals that the electron density distribution is enhanced between Ag4 and Ag5 at the same time that the Ag4–Ag5 contact distance is shortened when the number of added electrons is increased from N = 0 to N = 10. In addition, there is an electronic charge density enlargement in the vicinity of Ag6 atoms on going from N = 0 to N = 10.
Figure 5.
(a) Average Ag-Ag distances as a function of the number of electrons added. (b) Electron density contours on the (100) plane for a neutral (N = 0) structure and a charged (N = 10) structure. Isodensity lines less than 0.02 a.u. are coloured white. (c) Charge density of the Ag and W centres in [AgO2], [AgO4], and [WO6] clusters as a function of the number of electrons added. q(Ω) represents the number of valence electrons minus the calculated charge density. (d) Structure of metallic Ag.
An analysis of the results presented in Fig. 5c reveals that the Ag6 atoms of the [AgO2] clusters are the atoms most prone to reduction. At N = 7, the Ag6 atoms are practically reduced, whereas the Ag4/Ag5 centres require at least 10 electrons to reach the same state. This behaviour implies the existence of two different paths to obtaining metallic Ag, which are associated with the [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters. In the case of W atoms that form [WO6] clusters, W1 atoms behave differently than W2 and W3 atoms, and a minor decrease in electron density relative to that of Ag centres is observed (a decrease of 0.2 units at N = 10). Therefore, the extra electron density added to the material is transferred from one cluster to another through the lattice network, and the Ag-formation process involves both adjacent [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters and, to a minor extent, [WO6] clusters. During electron irradiation, electronic and structural disorder is introduced into the material, indicating the fundamental role that cluster concepts play in the formation and growth of Ag filaments.
The results of the calculations of the Laplacian, ∇2ρbcp, and the charge density, ρbcp, at the (3,−1) bond critical points (BCP) in Ag-O bonds in the [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters are shown in Table 1. The effect of adding electrons to the material produces striking differences in the values of the Laplacian and the charge density at the (3,−1) BCP. Notably, the Laplacian and charge density values of the Ag-O bonds decrease considerably as electrons are added, which indicates that these bonds become weaker in favour of the formation of metallic Ag from both the [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters.
Table 1. Laplacian and charge density at the (3,−1) BCPs in Ag-O bonds for [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters as a function of the number of electrons added, N.
| BCP [AgO2] | BCP [AgO4] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag-O | Ag-O1 | Ag-O2 | ||||
| N | ρbcp | ∇2ρbcp | ρbcp | ∇2ρbcp | ρbcp | ∇2ρbcp |
| 0 | 0.49 | 6.80 | 0.26 | 3.29 | 0.42 | 4.91 |
| 1 | 0.42 | 4.56 | 0.23 | 2.93 | 0.39 | 4.35 |
| 2 | 0.34 | 3.88 | 0.21 | 2.67 | 0.35 | 3.86 |
| 3 | 0.26 | 3.10 | 0.20 | 2.56 | 0.28 | 3.10 |
| 4 | 0.20 | 2.26 | 0.19 | 2.35 | 0.22 | 2.56 |
| 5 | 0.17 | 1.84 | 0.16 | 1.96 | 0.19 | 2.17 |
| 6 | 0.17 | 1.76 | 0.15 | 1.83 | 0.19 | 2.08 |
| 7 | 0.16 | 1.71 | 0.13 | 1.65 | 0.19 | 2.12 |
| 8 | 0.14 | 1.55 | 0.12 | 1.39 | 0.17 | 1.80 |
| 9 | 0.14 | 1.47 | 0.10 | 1.23 | 0.17 | 1.76 |
| 10 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 0.10 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 1.51 |
Finally, we have calculated the total and projected density of states (DOS) on atoms and orbitals in order to complement the Bader charge analysis. For neutral Ag2WO4 (N = 0), there is essentially no visible difference in orbital character between PBE and PBE + U, however up to U = 6, the band gap values are maintained nearly constant to 2.0 eV which conveys the most satisfactory picture for both the occupied and unoccupied states. The DOS plots depicted in Fig. S6 (SI) are focused on the upper part of the valence band (VB) and the lower part of the conduction band (CB) for different Ag atoms as the number of electrons is added, for N = 0, 2, 4 and 8. For the DOS evaluation, from a total of 16 Ag atoms in the unit cell, three different types of Ag atoms have been classified according to previous results of the electron density distribution: “Ag1/2/3” (10 atoms), “Ag4/5” (4 atoms) and “Ag6” (2 atoms). An analysis of the plots shows a 50% of reduction of the band gap energy for N = 2, with a high contribution of s orbitals in the lower part of CB from Ag4/5 and Ag6. When the number of electrons is increased to 3 and up to 8 the system becomes a conductor. For N = 4 and N = 8 the DOS images have been also depicted in Fig. S6, highlighting the same contribution around 0.0 eV for N = 4 and in the energy range −1.5–1.0 eV for N = 8. It is worth noting that the Fermi level is placed at energy of 0 eV. Therefore, a shift of the s band (and the d band as a minor contribution) of Ag4/5 and Ag6 atoms is possibly induced by the interaction of the sample with the electron beam, and predicted by XPS analysis. Consequently, a structural rearrangement is caused related to the shortening of the distance Ag4–Ag5 and the Ag-Ag metallic bond formation when the number of added electrons is increased in accordance with the dynamics results measured in situ using TEM.
Discussion
Understanding the in situ atomic-scale nucleation induced by the electron irradiation of Ag filaments on α-Ag2WO4 can be achieved through a combination of experimental and theoretical analyses. We used experimental techniques (TEM, EDS, and XPS) and first-principle calculations based on the QTAIM framework to study the geometric and electronic structure of α-Ag2WO4. We then derived a mechanism on the basis of the electron irradiation of [AgOx] (x = 2, 4, 6, and 7) and [WO6] clusters, which are the constituent polyhedra of α-Ag2WO4. The mechanism is relevant to the nucleation and growth of Ag filaments that occurs when α-Ag2WO4 is irradiated using an accelerated electron beam from an electron microscope under high vacuum. Our model allows us to better understand the atomic events in this process, and we are currently pursuing this relevant area of investigation. The results of the present work provide an atomic-scale picture of the formation of metallic Ag as well as an initial glimpse into how [WO6] and [AgOx] clusters behave in this material when it is irradiated with electrons from an external source. The strategy reported here for retrospective mapping of the growth of metallic Ag has the potential to yield valuable insights into the mechanistic aspects of the clusters, particularly when the experimental results are considered in conjunction with first-principles calculations.
Our main conclusions are as follows: During the electron irradiation process, electronic and structural disorder is introduced into the materiaļ showing the fundamental role of clusters in the nucleation and growth of Ag filaments. Extra electrons added to the material are transferred from one cluster to another through the lattice network, and Ag formation occurs via the reduction of both [AgO2] and [AgO4] clusters that are adjacent and, to a lesser extent, through the reduction of the [WO6] cluster. These findings provide a valuable probe into the relationship between atomic-scale structural and electronic perturbations and their macroscopic consequences. The broader significance of this work lies in the direct and visually impressive demonstration of the conversion of electron irradiation into structural and electronic order/disorder effects to cause the formation of Ag on α-Ag2WO4. Therefore, the Ag nucleation mechanisms observed here can provide deep insight into the physical and electronic structure of other silver-metal-oxide-based materials under electron irradiation conditions. The present work leads to a unified understanding of the complex behaviour of these materials and opens a new direction for the rational design of materials with exciting properties.
Methods
Experimental details
The α-Ag2WO4 samples were synthesised at 90°C in 1 min by the injection of precursor ions into hot aqueous solutions according to the method reported in our previous work6. TEM analysis was performed on a CM200-Philips and JEOL JEM 2100F TEM/STEM microscope operated at 200 kV. Specimens for TEM images were obtained by drying droplets of as-prepared samples from an acetone dispersion that had been sonicated for 10 min and deposited on 300-mesh Cu grids. The chemical analyses of the samples were performed by EDS using a Thermo-Noran EDS attached to the JEM 2100F and equipped with a Si detector.
XPS spectra were collected using a commercial spectrometer (UNI-SPECS-UHV). To analyse the near-surface composition and the chemical environment in the α-Ag2WO4 nanocrystals, the measurements were performed in a small area of each sample using the Mg Kα line (hν = 1253.6 eV); the analyser pass energy was set to 10 eV. In particular, the inelastic background of the C 1 s, O 1 s, W 4f, and Ag 3 d electron core-level spectra and the Auger Ag MNN peak were subtracted using Shirley's method62; the BEs were corrected using the hydrocarbon component of adventitious carbon fixed at 285.0 eV.
The X-ray diffraction measurements were performed on a D/Max-2500PC diffractometer (Rigaku, Japan) using Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) in the 2θ range from 10° to 70° in the normal routine with a scanning velocity of 2°/min and a step of 0.02°.
Calculation details
First-principles total-energy calculations were performed within the periodic DFT framework using the VASP program63,64. The Kohn-Sham equations were solved by means of the Perdew, Burke, and Ernzerhof exchange-correlation functional64, and the electron-ion interaction was described by the projector-augmented-wave pseudopotentials65,66. Because of the well-known limitations of standard DFT in describing the electronic structure of “strongly-correlated” compounds, a correction to the PBE wavefunctions was made (PBE + U) by including a repulsive on-site Coulomb interaction, U, according to the formula of Dudarev et al67. PBE + U scheme contains the same PBE approximate correlation, but takes into account orbital dependence (applied to the d states of silver) of the Coulomb and exchange interactions. The value of the Hubbard parameter was tested, and a value of U = 6 eV for the Ag element was used. The plane-wave expansion was truncated at a cut-off energy of 400 eV, and the Brillouin zones were sampled through Monkhorst-Pack special k-points grids (6 × 6 × 6) that ensure geometrical and energetic convergence for the Ag2WO4 structures considered in this work. The keyword NELECT was used to increase the number of electrons in the bulk structure, and all the crystal structures were optimised simultaneously on both the volume of the unit-cell and the atomic positions. Further information, as well as details of the ab initio quantum chemical calculations, is given in the Supplementary Information.
Author Contributions
L.G., P.G.-N. and V.M.L. have been carried the calculations and the theoretical part. M.F. and P.S.L. prepared the samples and performed the structural analysis; D.P.V. and W.A. performed the electron microscopy data collection. F.A.L.P. has been carried out the XPS analysis. J.A., A.C.H. and E.L. conceived the project. All of the authors participated in writting the manuscript and discussion of the results.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Info
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to FAPESP 2013/07296-2, CAPES, CNPq, Prometeo/2009/053 (Generalitat Valenciana), CTQ2012-36253-C03-02 (Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad, Spain), CTQ2012-36253-C03-02, and the Spanish Brazilian program (PHB2009-0065-PC). Special thanks are given to Dr. P. Hammer (LEFE-IQ/UNESP) for help with the XPS analyses. STEM analysis were performed in the Electron Microscopy Laboratory (LME) of the Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory (LNNano).
References
- Heyer O. et al. A new multiferroic material: MnWO4. J. Phys.-Condens. Matter 18, L471–L475 (2006). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Lu C., Wang Y. & Cheng Y. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of MnWO4 nanoplates and their ionic conductivity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 103, 433–436 (2007). [Google Scholar]
- Song X. C. et al. Hydrothermal preparation and photoluminescence of bundle-like structure of ZnWO4 nanorods. Appl. Phys. A 94, 185–188 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y. et al. Microemulsion-mediated solvothermal synthesis and photoluminescent property of 3D flowerlike MnWO4 micro/nanocomposite structure. Solid State Sci. 10, 1299–1304 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante L. S. et al. Cluster Coordination and Photoluminescence Properties of alpha-Ag2WO4 Microcrystals. Inorg. Chem. 51, 10675–10687 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo E. et al. Direct in situ observation of the electron-driven synthesis of Ag filaments on alpha-Ag2WO4 crystals. Sci. Rep. 3, 1676 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo E. et al. Toward an Understanding of the Growth of Ag Filaments on α-Ag2WO4 and their Photoluminescent Properties: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 10.1021/jp408167v (2014). [Google Scholar]
- Ziman J. M. Models of disorder: the theoretical physics of homogeneously disordered systems (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge Eng.; New York, 1979). [Google Scholar]
- Cui X. J. et al. Selective synthesis and characterization of single-crystal silver molybdate/tungstate nanowires by a hydrothermal process. Chem.-a Eur. J. 10, 218–223 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad P. M. & Geller S. (W4O16)8− Polyion in High-Temperature Modification of Silver Tungstate. Mater. Res. Bull. 10, 791–799 (1975). [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. et al. Layered atomic structures of double oxides for low shear strength at high temperatures. Scripta Mater. 62, 735–738 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H. M. et al. Observation of Single Colloidal Platinum Nanocrystal Growth Trajectories. Science 324, 1309–1312 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai J., Liao X., Giam L. R. & Mirkin C. A. Nanoreactors for Studying Single Nanoparticle Coarsening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 158–161 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. E., Jungjohann K. L., Browning N. D. & Arslan I. Controlled Growth of Nanoparticles from Solution with In Situ Liquid Transmission Electron Microscopy. Nano Lett. 11, 2809–2813 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H. G., Cui L. K., Whitelam S. & Zheng H. M. Real-Time Imaging of Pt3Fe Nanorod Growth in Solution. Science 336, 1011–1014 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou A. C., Pang C. L., Chen Q. & Thornton G. Low-dimensional, reduced phases of ultrathin TiO2. ACS Nano 1, 409–414 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin H. L. L. & Zheng H. M. In Situ Observation of Oscillatory Growth of Bismuth Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 12, 1470–1474 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuk J. M. et al. High-Resolution EM of Colloidal Nanocrystal Growth Using Graphene Liquid Cells. Science 336, 61–64 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus T. & de Jonge N. Dendritic Gold Nanowire Growth Observed in Liquid with Transmission Electron Microscopy. Langmuir 29, 8427–8432 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M., Liao H.-G., Niu K. & Zheng H. Structural and Morphological Evolution of Lead Dendrites during Electrochemical Migration. Sci. Rep. 3, 3227 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuk J. M. et al. In situ atomic imaging of coalescence of Au nanoparticles on graphene: rotation and grain boundary migration. Chem. Commun. 49, 11479–11481 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann T., Bohler E. & Swiderek P. Low-Energy-Electron-Induced Hydroamination of an Alkene. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 48, 4643–4645 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsier R. D. & Yates J. T. Electron-Stimulated Desorption - Principles and Applications. Surf. Sci. Rep. 12, 243–378 (1991). [Google Scholar]
- Turchanin A. et al. One Nanometer Thin Carbon Nanosheets with Tunable Conductivity and Stiffness. Adv. Mater. 21, 1233-+ (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Xu W. et al. In-situ atomic-scale observation of irradiation-induced void formation. Nat. Commun. 4, 2288 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph S. J., Fowlkes J. D. & Rack P. D. Focused, nanoscale electron-beam-induced deposition and etching. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mat. Sci. 31, 55–89 (2006). [Google Scholar]
- Utke I., Hoffmann P. & Melngailis J. Gas-assisted focused electron beam and ion beam processing and fabrication. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 26, 1197–1276 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- van Dorp W. F. & Hagen C. W. A critical literature review of focused electron beam induced deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 081301 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- van Dorp W. F., Hagen C. W., Crozier P. A. & Kruit P. Growth behavior near the ultimate resolution of nanometer-scale focused electron beam-induced deposition. Nanotechnology 19, 225305 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dorp W. F., van Someren B., Hagen C. W. & Kruit P. Approaching the resolution limit of nanometer-scale electron beam-induced deposition. Nano Lett. 5, 1303–1307 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kouwen L., Botman A. & Hagen C. W. Focused Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition of 3 nm Dots in a Scanning Electron Microscope. Nano Lett. 9, 2149–2152 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. M. et al. Electrons as “Invisible Ink”: Fabrication of Nanostructures by Local Electron Beam Induced Activation of SiOx. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 49, 4669–4673 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Takayanagi K., Kobayashi K. & Honjo G. Insitu Observations of Growth Processes of Multiply Twinned Particles. J. Cryst. Growth 28, 117–124 (1975). [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge N. & Ross F. M. Electron microscopy of specimens in liquid. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 695–704 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. U., Cha S. H., Shin K., Jho J. Y. & Lee J. C. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles from gold(I)-alkanethiolate complexes with supramolecular structures through electron beam irradiation in TEM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 9962–9963 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohn J. H. et al. Preparation of conducting silver paste with Ag nanoparticles prepared by e-beam irradiation. Rad. Phys. Chem. 79, 1149–1153 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge N., Peckys D. B., Kremers G. J. & Piston D. W. Electron microscopy of whole cells in liquid with nanometer resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 2159–2164 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein K. L., Anderson I. M. & De Jonge N. Transmission electron microscopy with a liquid flow cell. J. Microsc. 242, 117–123 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao F. & Salmeron M. In Situ Studies of Chemistry and Structure of Materials in Reactive Environments. Science 331, 171–174 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. J., Tromp R. M., Vereecken P. M., Hull R. & Ross F. M. Dynamic microscopy of nanoscale cluster growth at the solid-liquid interface. Nat. Mater. 2, 532–536 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman M. S. CO Prefers the Aisle Seat. Science 327, 789–790 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smit E. et al. Nanoscale chemical imaging of a working catalyst by scanning transmission X-ray microscopy. Nature 456, 222–U239 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friebel D., Miller D. J., Nordlund D., Ogasawara H. & Nilsson A. Degradation of Bimetallic Model Electrocatalysts: An In Situ X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 50, 10190–10192 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen P. L. et al. Atom-resolved imaging of dynamic shape changes in supported copper nanocrystals. Science 295, 2053–2055 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketteler G. et al. In situ spectroscopic study of the oxidation and reduction of Pd(111). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 18269–18273 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen L., Cheng F., Zhang S. R. & Tao F. Visualization of Surfaces of Pt and Ni Model Catalysts in Reactive Environments Using Ambient Pressure High Temperature Scanning Tunneling Microscopy and Understanding the Restructurings of Surfaces of Model Metal Catalysts under Reaction Conditions at Near Ambient Pressure. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 971–977 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Park J. et al. Direct Observation of Nanoparticle Superlattice Formation by Using Liquid Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy. ACS Nano 6, 2078–2085 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. A. et al. Activity of CeOx and TiOx nanoparticles grown on Au(111) in the water-gas shift reaction. Science 318, 1757–1760 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao F. et al. Break-Up of Stepped Platinum Catalyst Surfaces by High CO Coverage. Science 327, 850–853 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao F., Tang D., Salmeron M. & Somorjai G. A. A new scanning tunneling microscope reactor used for high-pressure and high-temperature catalysis studies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 084101 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thostrup P. et al. Adsorption-induced step formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 126102 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard E. K. et al. Adsorbate-induced alloy phase separation: A direct view by high-pressure scanning tunneling microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 126101 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachs I. E. & Roberts C. A. Monitoring surface metal oxide catalytic active sites with Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 5002–5017 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C. D. W. W., Riggs W. W., Davis L. E., Moulder J. F. & Muilenberg G. E. Handbook of X-ray Photoeclectron Spectroscopy (Physical Electronics Division, Perkin–Elmer Corporation, Wellesley, MA, 1979). [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. F., Contarini S. & Rabalais J. W. Ion-Beam-Induced Chemical-Changes in the Oxyanions (CrOYN-, MoOYN-, WOYN-, VOYN-, NbOYN-, and TaOYN-) and Oxides (CrOX, MoOX, WOX, VOX, NbOX, and TaOX). J. Phys. Chem. 91, 4779–4788 (1987). [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Xue G., Zhen Y., Fu F. & Li D. Monodispersed Ag nanoparticles loaded on the surface of spherical Bi2WO6 nanoarchitectures with enhanced photocatalytic activities. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 4751–4758 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L. S. et al. AgBr-Ag-Bi2WO6 nanojunction system: A novel and efficient photocatalyst with double visible-light active components. Appl. Catal. A 363, 221–229 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Crist V. Handbook of Monochromatic XPS spectra. The Elements and Native Oxides. (John Wiley & Sons Ltd., New York 2000). [Google Scholar]
- Bader R. F. W. Atoms in molecules: a quantum theory (Clarendon Press Oxford New York, 1990). [Google Scholar]
- Matta C. F. & Boyd R. J. The quantum theory of atoms in molecules (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2007). [Google Scholar]
- Popelier P. L. A. Atoms in molecules: an introduction (Prentice Hall, Harlow, 2000). [Google Scholar]
- Shirley D. A. High-Resolution X-Ray Photoemission Spectrum of Valence Bands of Gold. Phys. Rev. B 5, 4709–& (1972). [Google Scholar]
- Kresse G. & Hafner J. ab-initio Molecular-Dynamics Simulation Of The Liquid-Metal Amorphous-Semiconductor Transition In Germanium. Phys. Rev. B 49, 14251–14269 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse G. & Furthmuller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 6, 15–50 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew J. P., Burke K. & Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse G. & Joubert D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999). [Google Scholar]
- Dudarev S. L., Botton G. A., Savrasov S. Y., Humphreys C. J. & Sutton A. P. Electron-energy-loss spectra and the structural stability of nickel oxide: An LSDA + U study. Phys. Rev. B 57, 1505–1509 (1998). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Info