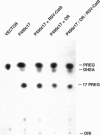
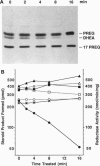
Abstract
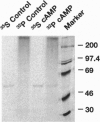
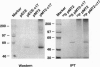
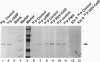
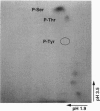
Microsomal cytochrome P450c17 catalyzes both steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase activity and scission of the C17-C20 steroid bond (17,20-lyase) on the same active site. Adrenal 17 alpha-hydroxylase activity is needed to produce cortisol throughout life, but 17,20-lyase activity appears to be controlled independently in a complex, age-dependent pattern. We show that human P450c17 is phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Phosphorylation of P450c17 increases 17,20-lyase activity, while dephosphorylation virtually eliminates this activity. Hormonally regulated serine phosphorylation of human P450c17 suggests a possible mechanism for human adrenarche and may be a unifying etiologic link between the hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance that characterize the polycystic ovary syndrome.
Full text
PDF

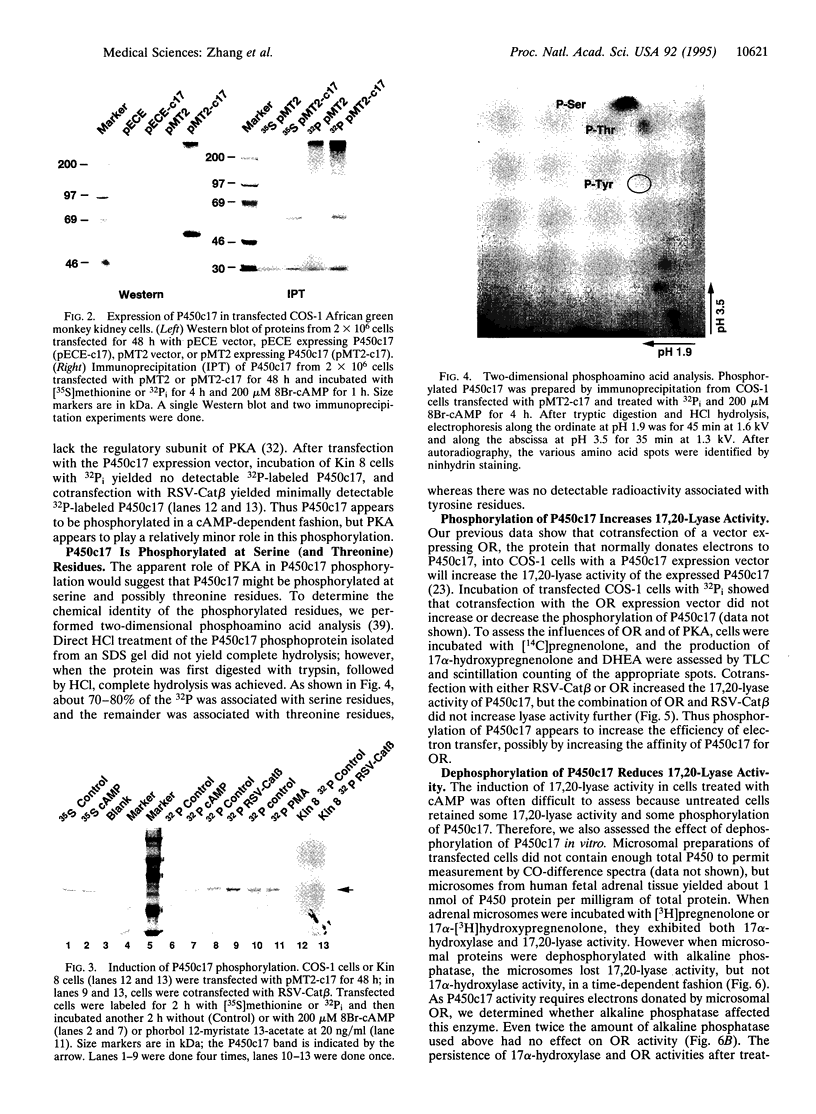
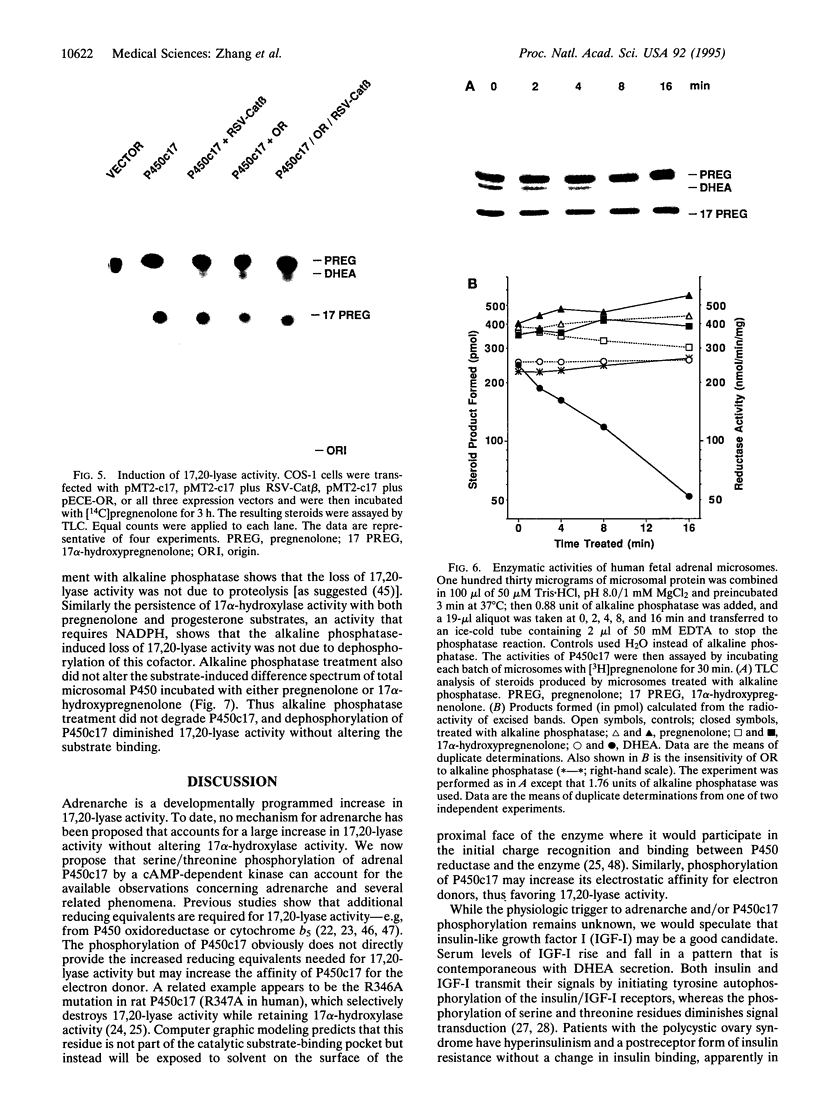
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama T., Nagata K., Yamazoe Y., Kato R., Matsunaga E., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Cytochrome b5 potentiation of cytochrome P-450 catalytic activity demonstrated by a vaccinia virus-mediated in situ reconstitution system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5425–5429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Lewis R. E., Woon C. W., Vissavajjhala P., Ross A. H., Czech M. P. Catalysis of serine and tyrosine autophosphorylation by the human insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellino F. L., Holben L. Placental estrogen synthetase (aromatase): evidence for phosphatase-dependent inactivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):498–504. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. M., Szklarz G. D., Harikrishna J. A., Lin D., Wolf C. R., Miller W. L. Regulation of proteins in the cholesterol side-chain cleavage system in JEG-3 and Y-1 cells. Endocrinology. 1993 Feb;132(2):539–545. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.2.8425475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. E., Dickens M., Tavare J. M., Roth R. A. Overexpression of protein kinase C isoenzymes alpha, beta I, gamma, and epsilon in cells overexpressing the insulin receptor. Effects on receptor phosphorylation and signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6338–6347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Picado-Leonard J., Haniu M., Bienkowski M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E., Miller W. L. Cytochrome P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): cloning of human adrenal and testis cDNAs indicates the same gene is expressed in both tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):407–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch R. M., Muller J., Winter J. S. Regulation of the activities of 17-hydroxylase and 17,20-desmolase in the human adrenal cortex: kinetic analysis and inhibition by endogenous steroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Sep;63(3):613–618. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-3-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler G. B., Jr, Glenn M., Bush M., Hodgen G. D., Graham C. E., Loriaux D. L. Adrenarche: a survey of rodents, domestic animals, and primates. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2112–2118. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaif A. Hyperandrogenic anovulation (PCOS): a unique disorder of insulin action associated with an increased risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1995 Jan 16;98(1A):33S–39S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)80057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fardella C. E., Hum D. W., Homoki J., Miller W. L. Point mutation of Arg440 to His in cytochrome P450c17 causes severe 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Jul;79(1):160–164. doi: 10.1210/jcem.79.1.8027220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fardella C. E., Zhang L. H., Mahachoklertwattana P., Lin D., Miller W. L. Deletion of amino acids Asp487-Ser488-Phe489 in human cytochrome P450c17 causes severe 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Aug;77(2):489–493. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.2.8345056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Oie H. K., Shackleton C. H., Chen T. R., Triche T. J., Myers C. E., Chrousos G. P., Brennan M. F., Stein C. A., La Rocca R. V. Establishment and characterization of a human adrenocortical carcinoma cell line that expresses multiple pathways of steroid biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5488–5496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasemann C. A., Kurumbail R. G., Boddupalli S. S., Peterson J. A., Deisenhofer J. Structure and function of cytochromes P450: a comparative analysis of three crystal structures. Structure. 1995 Jan 15;3(1):41–62. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson I., Eliasson E., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Hormone controlled phosphorylation and degradation of CYP2B1 and CYP2E1 in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90481-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura M., Buczko E., Dufau M. L. Dissociation of hydroxylase and lyase activities by site-directed mutagenesis of the rat P45017 alpha. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1373–1380. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh Y., Buczko E., Dufau M. L. Requirement of phenylalanine 343 for the preferential delta 4-lyase versus delta 5-lyase activity of rat CYP17. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18267–18271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Black S. M., Nagahama Y., Miller W. L. Steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase activities of P450c17: contributions of serine106 and P450 reductase. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2498–2506. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Harikrishna J. A., Moore C. C., Jones K. L., Miller W. L. Missense mutation serine106----proline causes 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15992–15998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Zhang L. H., Chiao E., Miller W. L. Modeling and mutagenesis of the active site of human P450c17. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Mar;8(3):392–402. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.3.8015556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and proteolytic peptide mapping of proteins immobilized to membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:149–152. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01014-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Both isoforms of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit can activate transcription of the prolactin gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6870–6873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Shively J. E., Miller W. L. Human proopiomelanocortin-(79-96), a proposed androgen stimulatory hormone, does not affect steroidogenesis in cultured human fetal adrenal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jan;72(1):19–22. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monno S., Ogawa H., Date T., Fujioka M., Miller W. L., Kobayashi M. Mutation of histidine 373 to leucine in cytochrome P450c17 causes 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25811–25817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. C., Brentano S. T., Miller W. L. Human P450scc gene transcription is induced by cyclic AMP and repressed by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and A23187 through independent cis elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6013–6023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Hall P. F. Microsomal cytochrome P-450 from neonatal pig testis. Purification and properties of A C21 steroid side-chain cleavage system (17 alpha-hydroxylase-C17,20 lyase). J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3871–3876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Hall P. F., Onoda M. Testicular microsomal cytochrome P-450 for C21 steroid side chain cleavage. Spectral and binding studies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6134–6139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Shinoda M., Haniu M., Shively J. E., Hall P. F. C21 steroid side chain cleavage enzyme from porcine adrenal microsomes. Purification and characterization of the 17 alpha-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3971–3976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajin S., Shively J. E., Yuan P. M., Hall P. F. Microsomal cytochrome P-450 from neonatal pig testis: two enzymatic activities (17 alpha-hydroxylase and c17,20-lyase) associated with one protein. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4037–4042. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch-Bartlomowicz B., Oesch F. Phosphorylation of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in intact hepatocytes and its importance for their function in metabolic processes. Arch Toxicol. 1990;64(4):257–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01972984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoda M., Hall P. F. Cytochrome b5 stimulates purified testicular microsomal cytochrome P-450 (C21 side-chain cleavage). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90850-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orentreich N., Brind J. L., Rizer R. L., Vogelman J. H. Age changes and sex differences in serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate concentrations throughout adulthood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Sep;59(3):551–555. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-3-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. N., Odell W. D. Control of adrenal androgen secretion. Endocr Rev. 1980 Fall;1(4):392–410. doi: 10.1210/edrv-1-4-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoat A., Sanchez P., Jaillard C., Langlois D., Bégeot M., Saez J. M. Human proopiomelanocortin-(79-96), a proposed cortical androgen-stimulating hormone, does not affect steroidogenesis in cultured human adult adrenal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jan;72(1):23–26. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picado-Leonard J., Miller W. L. Cloning and sequence of the human gene for P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): similarity with the gene for P450c21. DNA. 1987 Oct;6(5):439–448. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. A., Gutmann N. S., Tsao J., Schimmer B. P. Mutations in cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and corticotropin (ACTH)-sensitive adenylate cyclase affect adrenal steroidogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapuano M., Rosen O. M. Phosphorylation of the insulin receptor by a casein kinase I-like enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12902–12907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P., Bateman A., Mulay S., Spencer S. J., Jaffe R. B., Solomon S., Bennett H. P. Isolation and characterization of three forms of joining peptide from adult human pituitaries: lack of adrenal androgen-stimulating activity. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):859–867. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebinger R. J., Albertson B. D., Cassorla F. G., Bowyer D. W., Geelhoed G. W., Cutler G. B., Jr, Loriaux D. L. The developmental changes in plasma adrenal androgens during infancy and adrenarche are associated with changing activities of adrenal microsomal 17-hydroxylase and 17,20-desmolase. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1177–1182. doi: 10.1172/JCI110132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer B. P. Isolation of ACTH-resistant Y1 adrenal tumor cells. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:350–356. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar C. A., Kaplan S. L., Grumbach M. M. Evidence for dissociation between adrenarche and gonadarche: studies in patients with idiopathic precocious puberty, gonadal dysgenesis, isolated gonadotropin deficiency, and constitutionally delayed growth and adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):548–556. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes R. S., Klisak I., Miller W. L. Regional mapping of genes encoding human steroidogenic enzymes: P450scc to 15q23-q24, adrenodoxin to 11q22; adrenodoxin reductase to 17q24-q25; and P450c17 to 10q24-q25. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):359–365. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L., Rosen O. M. Increasing the cAMP content of IM-9 cells alters the phosphorylation state and protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3402–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staels B., Hum D. W., Miller W. L. Regulation of steroidogenesis in NCI-H295 cells: a cellular model of the human fetal adrenal. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Mar;7(3):423–433. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.3.8387159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Phorbol ester-induced serine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor decreases its tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3440–3447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilgrain I., Defaye G., Chambaz E. M. Adrenocortical cytochrome P-450 responsible for cholesterol side chain cleavage (P-450scc) is phosphorylated by the calcium-activated, phospholipid-sensitive protein kinase (protein kinase C). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):554–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90575-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Hall P. F. Role of electron transport in the regulation of the lyase activity of C21 side-chain cleavage P-450 from porcine adrenal and testicular microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8429–8433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase T., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency: from clinical investigation to molecular definition. Endocr Rev. 1991 Feb;12(1):91–108. doi: 10.1210/edrv-12-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Expression of bovine 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 cDNA in nonsteroidogenic (COS 1) cells. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1258–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.3535074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van GELDER B., SLATER E. C. The extinction coefficient of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:593–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]