Abstract
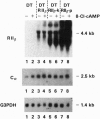
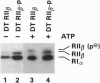
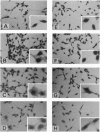
The RII beta regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) contains an autophosphorylation site and a nuclear location signal, KKRK. We approached the structure-function analysis of RII beta by using site-directed mutagenesis. Ser114 (the autophosphorylation site) of human RII beta was replaced with Ala (RII beta-P) or Arg264 of KKRK was replaced with Met (RII beta-K). ras-transformed NIH 3T3 (DT) cells were transfected with expression vectors for RII beta, RII beta-P, and RII beta-K, and the effects on PKA isozyme distribution and transformation properties were analyzed. DT cells contained PKA-I and PKA-II isozymes in a 1:2 ratio. Over-expression of wild-type or mutant RII beta resulted in an increase in PKA-II and the elimination of PKA-I. Only wild-type RII beta cells demonstrated inhibition of both anchorage-dependent and -independent growth and phenotypic change. The growth inhibitory effect of RII beta overexpression was not due to suppression of ras expression but was correlated with nuclear accumulation of RII beta. DT cells demonstrated growth inhibition and phenotypic change upon treatment with 8-Cl-cAMP. RII beta-P or RII beta-K cells failed to respond to 8-Cl-cAMP. These data suggest that autophosphorylation and nuclear location signal sequences are integral parts of the growth regulatory mechanism of RII beta.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ally S., Tortora G., Clair T., Grieco D., Merlo G., Katsaros D., Ogreid D., Døskeland S. O., Jahnsen T., Cho-Chung Y. S. Selective modulation of protein kinase isozymes by the site-selective analog 8-chloroadenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate provides a biological means for control of human colon cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6319–6322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe S. J., Oyen O., Sandberg M., Frøysa A., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning of a tissue-specific protein kinase (C gamma) from human testis--representing a third isoform for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):465–475. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S. Role of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in growth, differentiation, and suppression of malignancy: new approaches to therapy. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7093–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb C. E., Beth A. H., Corbin J. D. Purification and characterization of an inactive form of cAMP-dependent protein kinase containing bound cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16566–16574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durgerian S., Taylor S. S. The consequences of introducing an autophosphorylation site into the type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9807–9813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharrett A. J., Malkinson A. M., Sheppard J. R. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases from normal and SV40-transformed 3T3 cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 16;264(5587):673–675. doi: 10.1038/264673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Comparison of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rabbit skeletal and bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7795–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen T., Hedin L., Kidd V. J., Beattie W. G., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Durica J., Schulz T. Z., Schiltz E., Browner M. Molecular cloning, cDNA structure, and regulation of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from rat ovarian granulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12352–12361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Howard B. H. A rapid method for recombination and site-specific mutagenesis by placing homologous ends on DNA using polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):62–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsaros D., Tortora G., Tagliaferri P., Clair T., Ally S., Neckers L., Robins R. K., Cho-Chung Y. S. Site-selective cyclic AMP analogs provide a new approach in the control of cancer cell growth. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Johnson K. E., Nicolette C., Zoller M. J. Mutagenesis of the regulatory subunit of yeast cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Isolation of site-directed mutants with altered binding affinity for catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9149–9154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy F. O., Oyen O., Sandberg M., Taskén K., Eskild W., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning, complementary deoxyribonucleic acid structure and predicted full-length amino acid sequence of the hormone-inducible regulatory subunit of 3'-5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from human testis. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1364–1373. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U. Regulation of the cellular and subcellular concentrations and distribution of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:63–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado F., Hanks S. K. A cDNA clone encoding human cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit C alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8189–8190. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeady M. L., Kerby S., Shankar V., Ciardiello F., Salomon D., Seidman M. Infection with a TGF-alpha retroviral vector transforms normal mouse mammary epithelial cells but not normal rat fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1375–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Clegg C. H., Uhler M. D., Chrivia J. C., Cadd G. G., Correll L. A., Otten A. D. Analysis of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase system using molecular genetic approaches. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1988;44:307–335. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571144-9.50014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Reich E. Gene expression and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesterova M., Cho-Chung Y. S. A single-injection protein kinase A-directed antisense treatment to inhibit tumour growth. Nat Med. 1995 Jun;1(6):528–533. doi: 10.1038/nm0695-528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ko M., Ogura A., Liu D. G., Amano T., Takano T., Ikawa Y. Sarcoma viruses carrying ras oncogenes induce differentiation-associated properties in a neuronal cell line. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):73–75. doi: 10.1038/318073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Selinger Z., Scolnick E. M., Bassin R. H. Flat revertants isolated from Kirsten sarcoma virus-transformed cells are resistant to the action of specific oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5602–5606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten A. D., McKnight G. S. Overexpression of the type II regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase eliminates the type I holoenzyme in mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20255–20260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten A. D., Parenteau L. A., Døskeland S., McKnight G. S. Hormonal activation of gene transcription in ras-transformed NIH3T3 cells overexpressing RII alpha and RII beta subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23074–23082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-Aldao R., Rosen O. M. Dissociation and reassociation of the phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of adenosine 3':5' -monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3375–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohlff C., Clair T., Cho-Chung Y. S. 8-Cl-cAMP induces truncation and down-regulation of the RI alpha subunit and up-regulation of the RII beta subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase leading to type II holoenzyme-dependent growth inhibition and differentiation of HL-60 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5774–5782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J. Reversible autophosphorylation of a cyclic 3':5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7788–7794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Rubin C. S. Identification and differential expression of two forms of regulatory subunits (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Differentiation and 8-bromo-cAMP elicit a large and selective increase in the rate of biosynthesis of only one type of RII. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6296–6303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showers M. O., Maurer R. A. A cloned bovine cDNA encodes an alternate form of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16288–16291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skålhegg B. S., Landmark B., Foss K. B., Lohmann S. M., Hansson V., Lea T., Jahnsen T. Identification, purification, and characterization of subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in human testis. Reverse mobilities of human RII alpha and RII beta on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis compared with rat and bovine RIIs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5374–5379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliaferri P., Katsaros D., Clair T., Neckers L., Robins R. K., Cho-Chung Y. S. Reverse transformation of Harvey murine sarcoma virus-transformed NIH/3T3 cells by site-selective cyclic AMP analogs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):409–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the regulatory subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4200–4206. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Bubis J., Toner-Webb J., Saraswat L. D., First E. A., Buechler J. A., Knighton D. R., Sowadski J. CAMP-dependent protein kinase: prototype for a family of enzymes. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2677–2685. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.3294077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Sasagawa T., Ericsson L. H., Kumar S., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of the regulatory subunit of bovine type I adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4193–4199. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortora G., Budillon A., Yokozaki H., Clair T., Pepe S., Merlo G., Rohlff C., Cho-Chung Y. S. Retroviral vector-mediated overexpression of the RII beta subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces differentiation in human leukemia cells and reverts the transformed phenotype of mouse fibroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Jul;5(7):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortora G., Cho-Chung Y. S. Type II regulatory subunit of protein kinase restores cAMP-dependent transcription in a cAMP-unresponsive cell line. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18067–18070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortora G., Clair T., Cho-Chung Y. S. An antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeted against the type II beta regulatory subunit mRNA of protein kinase inhibits cAMP-induced differentiation in HL-60 leukemia cells without affecting phorbol ester effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):705–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortora G., Yokozaki H., Pepe S., Clair T., Cho-Chung Y. S. Differentiation of HL-60 leukemia by type I regulatory subunit antisense oligodeoxynucleotide of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):2011–2015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehner J. M., Malkinson A. M., Wiser M. F., Sheppard J. R. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases from Balb 3T3 cells and other 3T3 derived lines. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Aug;108(2):175–184. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]