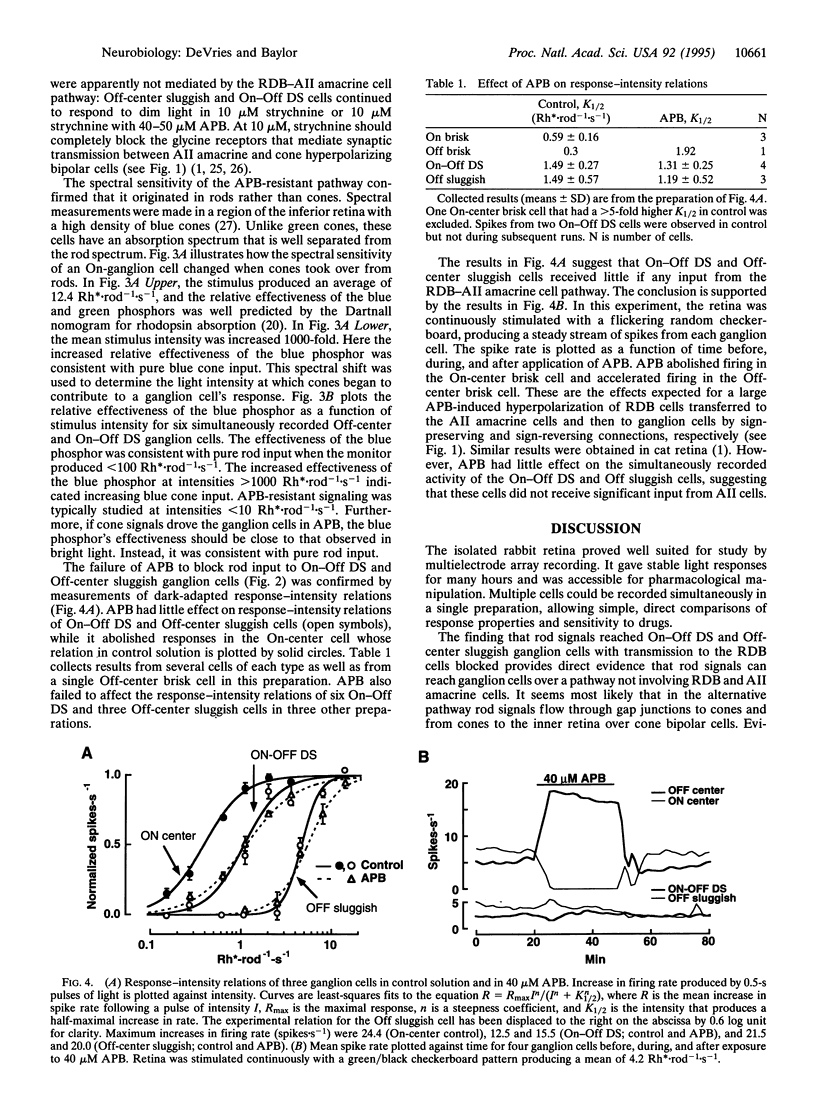
Abstract
Rod signals in the mammalian retina are thought to reach ganglion cells over the circuit rod-->rod depolarizing bipolar cell-->AII amacrine cell-->cone bipolar cells-->ganglion cells. A possible alternative pathway involves gap junctions linking the rods and cones, the circuit being rod-->cone-->cone bipolar cells-->ganglion cells. It is not clear whether this second pathway indeed relays rod signals to ganglion cells. We studied signal flow in the isolated rabbit retina with a multielectrode array, which allows the activity of many identified ganglion cells to be observed simultaneously while the preparation is stimulated with light and/or exposed to drugs. When transmission between rods and rod depolarizing bipolar cells was blocked by the glutamate agonist 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (APB), rod input to all On-center and briskly responding Off-center ganglion cells was dramatically reduced as expected. Off responses persisted, however, in Off-center sluggish and On-Off direction-selective ganglion cells. Presumably these responses were generated by the alternative pathway involving rod-cone junctions. This APB-resistant pathway may carry the major rod input to Off-center sluggish and On-Off direction-selective ganglion cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARLOW H. B., HILL R. M., LEVICK W. R. RETINAL GANGLION CELLS RESPONDING SELECTIVELY TO DIRECTION AND SPEED OF IMAGE MOTION IN THE RABBIT. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;173:377–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L. Detection and resolution of visual stimuli by turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(1):163–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nunn B. J., Schnapf J. L. Spectral sensitivity of cones of the monkey Macaca fascicularis. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:145–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. H., Daw N. W. New properties of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:257–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E., Sterling P. Demonstration of cell types among cone bipolar neurons of cat retina. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Dec 29;330(1258):305–321. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner J. D., MacLeod D. I. Rod photoreceptors detect rapid flicker. Science. 1977 Feb 18;195(4279):698–699. doi: 10.1126/science.841308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner J. D. The temporal properties of rod vision. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:139–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARTNALL H. J. A. The interpretation of spectral sensitivity curves. Br Med Bull. 1953;9(1):24–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a074302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacheux R. F., Raviola E. Horizontal cells in the retina of the rabbit. J Neurosci. 1982 Oct;2(10):1486–1493. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-10-01486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacheux R. F., Raviola E. The rod pathway in the rabbit retina: a depolarizing bipolar and amacrine cell. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):331–345. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00331.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daw N. W., Jensen R. J., Brunken W. J. Rod pathways in mammalian retinae. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Mar;13(3):110–115. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90187-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan R. P., Schiller P. H. Evidence for only depolarizing rod bipolar cells in the primate retina. Vis Neurosci. 1989;2(5):421–424. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800012311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Boycott B. B. Organization of the primate retina: electron microscopy. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Nov 15;166(1002):80–111. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famiglietti E. V., Jr Functional architecture of cone bipolar cells in mammalian retina. Vision Res. 1981;21(11):1559–1563. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(81)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliusson B., Bergström A., Röhlich P., Ehinger B., van Veen T., Szél A. Complementary cone fields of the rabbit retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 Mar;35(3):811–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karschin A., Wässle H. Voltage- and transmitter-gated currents in isolated rod bipolar cells of rat retina. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Apr;63(4):860–876. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Pine J., Baylor D. A. Multi-neuronal signals from the retina: acquisition and analysis. J Neurosci Methods. 1994 Jan;51(1):95–106. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Wong R. O., Baylor D. A., Shatz C. J. Synchronous bursts of action potentials in ganglion cells of the developing mammalian retina. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):939–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2035024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Wässle H., Voigt T. Pharmacological modulation of the rod pathway in the cat retina. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Jun;59(6):1657–1672. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.6.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawy S., Jahr C. E. cGMP-gated conductance in retinal bipolar cells is suppressed by the photoreceptor transmitter. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90380-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. Cat cones have rod input: a comparison of the response properties of cones and horizontal cell bodies in the retina of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Mar 1;172(1):109–135. doi: 10.1002/cne.901720106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R., Kolb H. Synaptic patterns and response properties of bipolar and ganglion cells in the cat retina. Vision Res. 1983;23(10):1183–1195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviola E., Gilula N. B. Gap junctions between photoreceptor cells in the vertebrate retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1677–1681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. C., Shapley R. M. Spatial structure of cone inputs to receptive fields in primate lateral geniculate nucleus. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):716–718. doi: 10.1038/356716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeweis D. M., Schnapf J. L. Photovoltage of rods and cones in the macaque retina. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1053–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.7754386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G., Naghshineh S. Action of glutamate and aspartate analogues on rod horizontal and bipolar cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):592–594. doi: 10.1038/294592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.6255566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Freed M. A., Sterling P. Microcircuitry of the dark-adapted cat retina: functional architecture of the rod-cone network. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3505–3517. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03505.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. H. Rod and cone contributions to S-potentials from the cat retina. Vision Res. 1969 Nov;9(11):1319–1329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strettoi E., Dacheux R. F., Raviola E. Synaptic connections of rod bipolar cells in the inner plexiform layer of the rabbit retina. J Comp Neurol. 1990 May 15;295(3):449–466. doi: 10.1002/cne.902950309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Tachibana M., Kaneko A. Effects of glycine and GABA on isolated bipolar cells of the mouse retina. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:645–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaney D. I., Young H. M., Gynther I. C. The rod circuit in the rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci. 1991 Jul-Aug;7(1-2):141–154. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800011019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]