Abstract
Phosphoethanolamine (PEA) decoration of lipid A produced by Neisseria gonorrhoeae has been linked to bacterial resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides/proteins (CAMPs) and in vivo fitness during experimental infection. We now report that the lptA gene, which encodes the PEA transferase responsible for this decoration, is in an operon and that high-frequency mutation in a polynucleotide repeat within lptA can influence gonococcal resistance to CAMPs.
TEXT
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a strict human pathogen that has caused the sexually transmitted infection termed gonorrhea for thousands of years. Over the millennia, N. gonorrhoeae has developed multiple mechanisms to resist innate host defenses, including cationic antimicrobial peptides/proteins (CAMPs) produced by phagocytes and epithelial cells (1). Phosphoethanolamine (PEA) decoration of the lipid A possessed by N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis has been shown to contribute to their resistance to CAMPs by a mechanism that likely involves a reduction in ionic interactions of CAMPs with the bacterial surface (1–6), resistance of N. gonorrhoeae to complement-mediated killing by normal human serum (3, 4), N. gonorrhoeae fitness during experimental infection in mice and humans (5, 7), and the proinflammatory potential of N. gonorrhoeae (7, 8). Most commensal Neisseria do not encode lptA (8), but N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis (2, 3, 8) typically contain lptA and produce multiple isoforms of lipid A that differ in PEA decoration at the 4′ and/or 1 position, though the basis of these isoforms has not been fully defined. We now provide evidence that gonococcal lptA is within an operon and that N. gonorrhoeae resistance to a model CAMP (polymyxin B; PMB) is modulated by high-frequency mutation due to a phase-variable (PV) polynucleotide stretch in the lptA coding sequence.
Organization and expression of the lptA locus in N. gonorrhoeae.
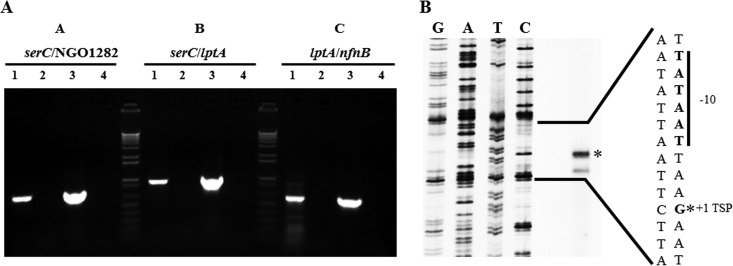
Bioinformatic analysis of the DNA sequence of the N. gonorrhoeae FA 1090 chromosome (http://www.genome.ou.edu/gono.html) suggested that lptA is transcriptionally linked to two upstream genes (serC and a hypothetical gene annotated as NGO1282) and a downstream gene (nfnB) (Fig. 1). This hypothesis was confirmed by results from reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) experiments (Fig. 2A) that demonstrated transcriptional linkage of lptA with the serC, hypothetical, and nfnB genes; details of the experimental procedures and a list of oligonucleotide primers are provided in the legends of Fig. 1 and 2 and in Table 1, respectively. However, primer extension analysis of total N. gonorrhoeae RNA performed as described previously (9) identified a transcriptional start point (TSP) positioned 61 nucleotides (nt) upstream of the lptA translational start codon and four nt downstream of near-consensus −10 and −35 elements (Fig. 1 and 2B). Thus, we tentatively conclude that lptA expression in N. gonorrhoeae can be initiated by two promoters upstream of serC and lptA, respectively. The mechanisms that control use of these promoters are now under investigation.
FIG 1.
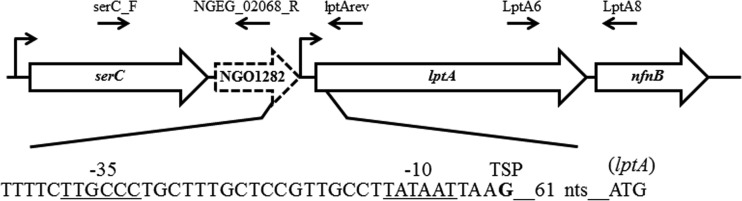
Genetic context of lptA in N. gonorrhoeae FA19. The 3.8-kb region of the FA19 genome shown corresponds to nucleotides 1236150 to 1232381 in N. gonorrhoeae FA 1090 (http://www.genome.ou.edu/gono.html and GenBank accession number AE004969.1). serC encodes a putative phosphoserine aminotransferase, NGO1282 encodes a hypothetical gene, lptA encodes a lipid A phosphoethanolamine transferase, and nfnB encodes a putative nitroreductase. The locations of the serC (undefined) and lptA (defined in the Fig. 2B legend) promoters are depicted with bent arrows. The lptA transcriptional start point, −10, and −35 promoter elements are shown below the illustration. The approximate sites of annealing for oligonucleotides used in RT-PCR experiments (Table 1) are shown with arrows.
FIG 2.
Transcription of the lptA coding sequence. (A) Transcriptional linkage between serC, NGO1282, lptA, and nfnB. All RT-PCRs were performed on purified RNA harvested (RNeasy minikit; Qiagen) from a log-phase culture of strain FA19 grown as described previously (9). First-strand cDNA was generated using SuperScript II reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen) and a gene-specific reverse primer (LptA8) that binds in the nfnB gene and primes elongation of a single-stranded cDNA toward serC. PCR was then performed to confirm transcriptional linkage between pairs of genes. Sections A, B, and C of the gel are grouped by forward- and reverse-primer locations and separated by 1-kb PLUS DNA ladders (Invitrogen). Lane 1, FA19 cDNA; lane 2, −RT negative control (RT omitted); lane 3, FA19 genomic DNA positive control; lane 4, no-template negative control. Section A, “serC” = serC_F; “NGO1282” = NGEG_02068_R. Section B, “serC” = serC_F; “lptA” = lptArev. Section C, “lptA” = LptA6; “nfnB” = LptA8. (B) Primer extension of the lptA transcript. Primer extension analysis was performed as described previously (9) using 20 μg of FA19 total RNA as the template and a radioactively ([γ-32P]ATP) labeled reverse primer (LptA7_R) that anneals 67 bp downstream of the lptA start codon. RNA was purified and cDNA generated as described for panel A. Radioactive single-stranded cDNA products were separated on a polyacrylamide gel alongside sequencing reactions that used the same reverse primer (LptA11 was the forward primer used for generation of the sequenced lptA promoter template). The TSP corresponds to the band labeled with an asterisk and is 4 bp downstream of a consensus σ70-type −10 element. A second band appeared running approximately 4 to 5 nucleotides shorter than the proposed +1 TSP band and could be due to a degraded mRNA transcript.
TABLE 1.
Oligonucleotide primers used in this study
| Primer name | Primer sequence | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| LptA6 | 5′-CGGTTTTGTATGTGGATCAGTT-3′ | Transcriptional linkage |
| LptA7 | 5′-GCCTTTCTTTCCCTGTATTCTT-3′ | Sequencing of the poly-T tract |
| LptA7_R | 5′-AAGAATACAGGGAAAGAAAGGC-3′ | Primer extension |
| LptA8 | 5′-ACGTTGCAATCCTACCTCGC-3′ | Transcriptional linkage |
| LptA11 | 5′-CCGGTTCGAATTTTGCTTACG-3′ | Primer extension |
| LptAdelL | 5′-TGCAGGTACATCATGAAATTAGAC-3′ | Sequencing of the poly-T tract |
| lptAJK4 | 5′-TAAGAATCTTTTTCAATAATCCGGAT-3′ | Sequencing of the poly-T tract |
| lptArev | 5′-GCCTCAGGTTCGGTTTTATC-3′ | Transcriptional linkage |
| LptAstart | 5′-TCTAGAAAGCTTCATCGACTTGT-3′ | Sequencing of the poly-T tract |
| NGEG_02068_R | 5′-GCGGGCAAAGCATTTCATAT-3′ | Transcriptional linkage |
| serC_F | 5′-CGACTACGGACTGATTTACG-3′ | Transcriptional linkage |
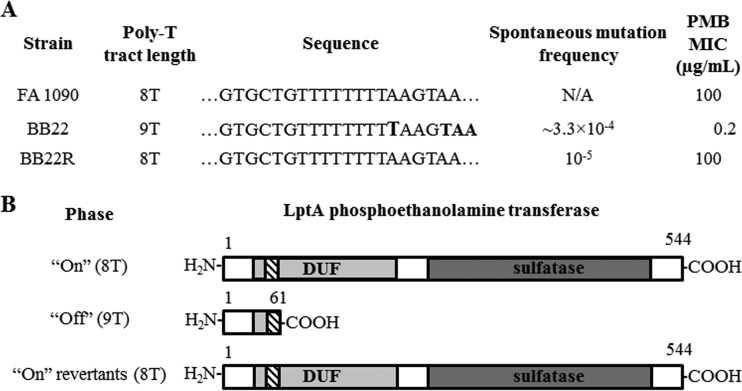
Analysis of the online FA 1090 genome sequence indicated that the lptA coding sequence contains a polynucleotide tract consisting of seven Ts (T-7), which would result in production of a truncated LptA enzyme due to a new translational stop codon (Fig. 3). However, our independent sequencing of a PCR product containing the lptA gene from FA 1090 as well from strain FA19 showed the presence of a T-8 tract (data not presented and Fig. 3A), which would result in production of a full-length LptA enzyme (Fig. 3B). Moreover, analysis of the online (http://www.broadinstitute.org/annotation/genome/neisseria_gonorrhoeae/GenomesIndex.html) whole-genome sequences of 13 other gonococcal strains indicated that their lptA gene contains the T-8 tract (data not presented). In addition, the genome sequence for 73 N. gonorrhoeae clinical isolates from patients with symptomatic gonorrhea was determined using Illumina technology; the details of this genome shotgun sequencing effort will be published separately. The nucleotide sequence of the FA19 lptA gene was searched against a BLAST database of all the whole-genome de novo-assembled contigs of these clinical isolates using BLASTN in WUBLAST, in order to identify the genome location of the gene within each of the strains. We used the default blastn parameters and specified hspsepSmax (maximum separation allowed between HSPs [high-scoring segment pair] along subject) to be 100 bp. Sequences of lptA genes were then extracted and screened for the presence of a T-8 tract on both the forward and reverse strands of the gene using pattern matching. The results showed that all strains contained a T-8 tract and a full-length lptA sequence with 100% nucleotide identity to FA 1090 (data not presented). Accordingly, we propose that possession of an in-frame lptA gene is a common feature of N. gonorrhoeae isolates.
FIG 3.
The lptA PV poly-T tract impacts LptA protein length and function. (A) Summary of the lptA PV poly-T tract. The PV poly-T tract comprises nucleotides 172 to 179 of the phase-on lptA open reading frame. Analysis of phase-on and phase-off lptA coding sequences using the ExPASy Translate tool (http://web.expasy.org/translate/) revealed that insertion of a ninth T nucleotide (bolded) in the poly-T tract of strain BB22 results in a frameshift mutation, which would generate a “UAA” stop codon shortly after this PV tract in the lptA mRNA transcript. (B) Impact of the PV poly-T tract on LptA protein length. When in the phase-on state, the lptA poly-T tract (hatched boxes) has 8 nucleotides and lptA encodes a protein 544 amino acids long. Frameshift of the lptA open reading frame (ORF) due to an insertion of a single T nucleotide within this poly-T tract would result in a premature stop codon and subsequent truncation of the LptA nascent polypeptide at just 61 amino acids. Phase-off variants are not predicted to translate the C-terminal sulfatase domain of the LptA protein (13). DUF, domain of unknown function.
lptA behaves as a PV gene in N. gonorrhoeae, and phase-off variants are hypersusceptible to PMB.
The presence of the T-8 tract in the 5′ end of the lptA coding sequence suggested to us that it is a member of the PV gene family possessed by N. gonorrhoeae (10). If so, production of a full-length LptA, PEA decoration of lipid A, and CAMP resistance could differ within a population of gonococci. To test this possibility, we employed a PMB screen/selection procedure since loss of lptA expression renders N. gonorrhoeae hypersusceptible to this model CAMP (3, 5, 7). After replica plating approximately 3,000 colonies of strain FA 1090 (T-8 tract and PMB MIC of 100 μg/ml) onto gonococcal base (GCB) agar plates with or without PMB selection, we identified (approximate frequency of 3.3 × 10−4) a colony (strain BB22) that was unable to grow on GCB agar plates containing 10 μg/ml of PMB. The PMB MIC against BB22 was 0.2 μg/ml (Fig. 3A), which is similar to the PMB MIC against an lptA deletion mutant of FA 1090 described previously (5). DNA sequence analysis of the lptA sequence of BB22 revealed that it possessed a T-9 tract that would result in premature truncation of LptA (Fig. 3). We then selected for spontaneous variants of BB22 that would grow on GCB agar containing 10 μg/ml of PMB. In four separate experiments, spontaneous PMB-resistant variants arose at a frequency of approximately 10−5; in contrast, spontaneous erythromycin-resistant mutants (selected at 1 μg/ml) were recovered at a frequency of 10−8 (data not presented). The PMB MIC against PMB-resistant mutants of BB22 was, like that seen with parental strain FA 1090, 100 μg/ml (see strain BB22R data in Fig. 3A). DNA sequencing of the lptA PV tract from sixteen randomly picked PMB-resistant revertants of BB22 showed that all possessed a wild-type T-8 tract (see BB22R in Fig. 3A) and would produce a full-length LptA (Fig. 3B). Based on this reversion frequency, we estimate that the poly-T tract in lptA phase varies at an approximate frequency of 10−5. This frequency is 2 to 3 orders of magnitude lower than that seen with other PV genes of N. gonorrhoeae, which may be due to its shorter tract (8 nt) and A/T characteristics that reduce slipped-strand mispairing events compared to the results seen with longer, G/C-rich repeats (10–12).
Conclusions.
Production of PEA-decorated lipid A by N. gonorrhoeae has been linked with bacterial resistance to mediators of innate host defense, the capacity of N. gonorrhoeae to elicit a proinflammatory response, and in vivo fitness (3–5, 7, 8). The structurally variable lipooligosaccharide (LOS) chemotypes produced by gonococci have been linked to PV genes that encode enzymes responsible for adding carbohydrates within the branched-chain oligosaccharide region (11, 12). Our work now extends this PV expression property of LOS to the lipid A isoforms and emphasizes the complexity of LOS structures that can be presented by N. gonorrhoeae. Importantly, to our knowledge, this is the first direct evidence that gonococcal resistance to CAMPs can be modulated by a PV process.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Jo-Anne Dillon, Carlos del Rio, and Magnus Unemo for providing N. gonorrhoeae strains and DNA used in whole-genome sequencing (WGS).
This work was supported by NIH grants U19 AI031496 (to P. F. Sparling, University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill), R37 AI021150-29 (W.M.S.), R43 AI09768 (T.D.R.), and R01 AI42053 (A.E.J.) and a VA Merit Award from the Medical Research Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs to W.M.S. W.M.S. was supported by a Senior Research Career Scientist Award from the Medical Research Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs.
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 12 May 2014
REFERENCES
- 1.Goytia M, Kandler JL, Shafer WM. 2013. Mechanisms and significance of bacterial resistance to human cationic antimicrobial peptides, chapter 9, p 219–254 In Hiemstra P, Zaat S. (ed), Antimicrobial peptides and innate immunity. Springer Press, Basel, Switzerland [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tzeng Y-L, Ambrose K, Zughaier S, Zhou X, Miller YK, Shafer WM, Stephens DS. 2005. Cationic antimicrobial peptide resistance in Neisseria meningitidis. J. Bacteriol. 187:5387–5396. 10.1128/JB.187.15.5387-5396.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lewis LA, Choudhury B, Balthazar JT, Martin LE, Ram S, Rice PA, Stephens DS, Carlson R, Shafer WM. 2009. Phosphoethanolamine substitution of lipid A and resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to cationic antimicrobial peptides and complement-mediated killing by normal human serum. Infect. Immun. 77:1112–1120. 10.1128/IAI.01280-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lewis LA, Shafer WM, Ray TD, Ram S, Rice P. 2013. Phosphoethanolamine residues on the lipid A moiety of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide modulate binding of complement inhibitors and resistance to complement killing. Infect. Immun. 81:33–42. 10.1128/IAI.00751-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hobbs MM, Anderson JE, Balthazar JT, Kandler JL, Carlson RW, Ganguly J, Begum AA, Duncan JA, Lin JT, Sparling PF, Jerse AE, Shafer WM. 2013. Lipid A's structure mediates Neisseria gonorrhoeae fitness during experimental infection of mice and men. mBio 4:e00892-13. 10.1128/mBio.00892-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lappann M, Danhof S, Guenther F, Olivares-Florez S, Mordhorst IL, Vogel U. 2013. In vitro resistance mechanisms of Neisseria meningitidis against neutrophil extracellular traps. Mol. Microbiol. 89:433–449. 10.1111/mmi.12288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Packiam M, Yedery R, Begum AA, Carlson RW, Ganguly J, Sempowski GD, Ventevogel MS, Shafer WM, Jerse AE. 31 March 2014. Phosphoethanolamine decoration of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipid A plays a dual immunostimulatory and protective role during experimental genital tract infection. Infect. Immun. 10.1128/IAI.01504-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.John CM, Liu M, Phillips NJ, Yang Z, Funk CR, Zimmerman LI, Griffiss JM, Stein DC, Jarvis GA. 2012. Lack of lipid A pyrophosphorylation and functional lptA reduces inflammation by Neisseria commensals. Infect. Immun. 80:4014–4026. 10.1128/IAI.00506-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ohneck EA, Zalucki YM, Johnson PJT, Dhulipala V, Golparian D, Unemo M, Jerse AE, Shafer WM. 2011. A novel mechanism of high-level, broad-spectrum antibiotic resistance caused by a single base pair change in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. mBio 2:e00187-11. 10.1128/mBio.00187-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Snyder LA, Butcher SA, Saunders NJ. 2001. Comparative whole genome analyses reveal over 100 putative phase-variable genes in the pathogenic Neisseria spp. Microbiology 147:2321–2332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yang QL, Gotschlich EC. 1996. Variation of gonococcal lipooligosaccharide structure is due to alterations in poly-G tracts in lgt genes encoding glycosyl transferases. J. Exp. Med. 183:323–327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Banerjee A, Wang R, Uljon SN, Rice PA, Gotschlich EC, Stein DC. 1998. Identification of the gene (lgtG) encoding the lipooligosaccharide beta chain synthesizing glucosyl transferase from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95:10872–10877. 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10872 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wanty C, Anandan A, Piek S, Walshe J, Ganguly J, Carlson RW, Stubbs KA, Kahler CM, Vrielink A. 2013. The structure of the neisserial lipooligosaccharide phosphoethanolamine transferase A (LptA) required for resistance to polymyxin. J. Mol. Biol. 425:3389–3402. 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.06.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]