Abstract
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is well known as a highly toxic environmental chemical threat. Prolonged exposure to H2S can lead to the formation of pulmonary edema. However, the mechanisms of how H2S facilitates edema formation are poorly understood. Since edema formation can be enhanced by an impaired clearance of electrolytes and, consequently, fluid across the alveolar epithelium, it was questioned whether H2S may interfere with transepithelial electrolyte absorption. Electrolyte absorption was electrophysiologically measured across native distal lung preparations (Xenopus laevis) in Ussing chambers. The exposure of lung epithelia to H2S decreased net transepithelial electrolyte absorption. This was due to an impairment of amiloride-sensitive sodium transport. H2S inhibited the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase as well as lidocaine-sensitive potassium channels located in the basolateral membrane of the epithelium. Inhibition of these transport molecules diminishes the electrochemical gradient which is necessary for transepithelial sodium absorption. Since sodium absorption osmotically facilitates alveolar fluid clearance, interference of H2S with the epithelial transport machinery provides a mechanism which enhances edema formation in H2S-exposed lungs.
Introduction
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gas with the typical smell of rotten eggs, is well known as a highly toxic environmental chemical threat. The high toxicity of H2S is, amongst other things, related to the fact that it is inhaled and can easily cross the alveolo-capillary barrier and is rapidly distributed within the human body [1]. The pulmonary epithelium is the first cell layer which is exposed to H2S. Although epithelial cells have been recently shown to have a high capacity to metabolize H2S [2], exposure to high concentrations of H2S (>500 ppm) can lead to severe lung irritation [3]. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to H2S (250–500 ppm) can impair the barrier function of the alveolar epithelium and lead to the formation of pulmonary edema in humans [3]. Similarly, pulmonary edema occurs in mice after exposure to H2S concentration >50 ppm [4].
However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms of how prolonged H2S exposure promotes edema formation are not completely understood.
The formation of pulmonary edema occurs due to infiltration of fluid into alveoli [5]. Furthermore, edema is enhanced due to an impaired resolution of fluid across the alveolar epithelium (alveolar fluid clearance) [5].
Alveolar fluid clearance is driven by an osmotic gradient across the alveolar epithelium. This osmotic gradient is created by active absorption of ions – particularly Na+ ions – across the epithelial cells [6]. The molecular nature of Na+ transport has been discovered in pioneer studies by Ussing and colleagues using frog skin preparations [7]: Na+ ions enter epithelial cells at the apical membrane via Na+-selective ion channels, such as the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC). These Na+ ions are actively pumped out of the cells, in exchange for K+, due to the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase at the basolateral membrane of the epithelium. This vectorial net movement of Na+ ions osmotically drives alveolar fluid clearance and thus prevents pulmonary edema.
On the other hand, impaired transepithelial Na+ transport is associated with the formation of pulmonary edema [5], [8], [9]. Transgenic mice which have a constitutively decreased pulmonary Na+ transport (due to reduced ENaC expression) are predisposed to edema formation [10]. Furthermore, the development of pulmonary edema in patients with acute lung injury (ALI) or its more severe form acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is tightly connected to impaired transepithelial Na+ absorption and patients with a functional Na+ transport have a better clinical outcome [11].
Given the association between edema formation and impaired absorption of Na+ ions across the alveolar epithelium, we hypothesized that H2S may affect the Na+ transporting machinery in pulmonary epithelial cells. We have recently shown that exogenously applied H2S decreases Na+ transport across a monolayer of a pulmonary epithelial cell line (H441) [12]. However, these data need to be confirmed in more physiologically relevant models. Unfortunately, the complex anatomy of a mammalian lung does not allow the preparation of native distal (i.e. alveolar) lung epithelia for transepithelial transport studies in Ussing chambers. The use of primary isolated alveolar epithelial cells and cell lines can also be problematic since the expression of ion channels which are required for vectorial Na+ transport is highly dependent on cell culture conditions [13], [14]. For those reasons we performed transepithelial transport studies on freshly isolated amphibian lungs from Xenopus laevis. These lungs have a simple sac-like anatomy and can easily be dissected into flat sheets which are suitable for Ussing chamber recordings. Xenopus lungs have only one epithelial cell type (pneumocyte) which is homologous to mammalian alveolar epithelial cells and has features of both alveolar type I and type II cells [15]. These pneumocytes express functional ENaCs as well as the Na+/K+-ATPase and have an ion channel and transporter repertoire which is similar to those of mammals [16], [17], [18], [19], [20].
Using this model, we demonstrate that exposure of these native lung epithelia to H2S decreases the rate of Na+ absorption due to an impairment of the Na+/K+-ATPase as well as K+ channels in the basolateral membrane of pulmonary epithelial cells.
Materials and Methods
Administration of H2S
H2S was administrated by the donor molecule NaHS (Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany). NaHS dissociates in aqueous solution into Na+, H2S/HS− and OH−. To avoid unspecific side effects due to alterations in pH, buffer solutions were adjusted to keep the pH values stable over the time course of experiments (data not shown). Initially, a concentration-response experiment was performed (Figure 1 E) and the IC50 value for transport inhibition by NaHS was determined as 1.18 mM. This corresponds to ∼50 ppm and is in a concentration range which is associated with lung irritation and pulmonary edema [4], [21]. Therefore, 1 mM was employed as the standard concentration for NaHS.
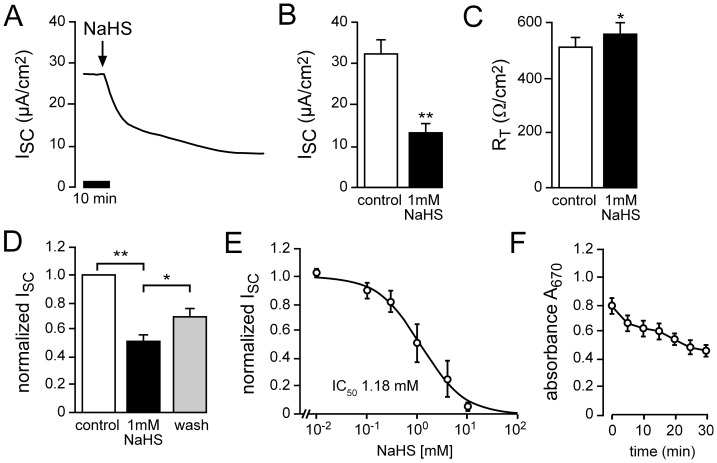
Figure 1. Exogenous H2S inhibits net ion transport of Xenopus lung epithelia.
A) Representative current trace of an Ussing chamber recording. The application of NaHS (1 mM) to the apical compartment of the chamber led to a strong decrease in transepithelial ion current (ISC). B) Statistical analysis of experiments as shown in panel A. NaHS significantly reduced ISC by approx. 60% (n = 19, N = 13, p≤0.01). C) Following application of NaHS, transepithelial resistance (RT) increased significantly (n = 19, N = 13, p≤0.05). D) The effect of NaHS was partially reversible. Depicted are values of ISC which were normalized to baseline values before application of NaHS. After wash-out of NaHS, there was a significant increase in current (n = 8, N = 5, p≤0.05). E) NaHS dose-dependently decreased ISC (n = 2–3, N = 3). Data were obtained from Ussing chamber recordings in which cumulative doses of NaHS were applied. Total values of ISC were fitted according to the Hill equation. F) Evaporative loss of H2S during experiments. NaHS (1 mM) was applied to NRS and aliquots were taken every 5 min. H2S was indirectly measured by the formation of methylene blue and its absorption at 670 nm (n = 3).
Determination of H2S in buffer solutions
In order to monitor the evaporative loss of H2S from the employed buffer solutions (see below), H2S concentrations where measured indirectly by the formation of methylene blue as previously described [22]. Aliquots (300 µl) were taken every 5 min after preparation of a solution containing 1 mM NaHS over a time period of 30 min. Aliquots were immediately mixed with ice-cold 4% zinc acetate and incubated for 30 min on ice. Afterwards, 200 µl of 0.1% dimethylphenylendiamine sulfate (DMPPDA; in 5 M HCl) and 100 µl of 50 mM FeCl3 (in 1.2 M HCl) were added to the samples. Samples were centrifuged at 5000×g at room temperature for 10 min and incubated for another 5 min at room temperature. The amount of formed methylene blue corresponds to the concentration of H2S in the buffers. Samples were eventually diluted 1∶10 and methylene blue was measured as absorbance at 670 nm with a spectrophotometer (Krüss Optronic, Germany).
Animal treatment and tissue preparation
Due to the complex anatomy of the mammalian lung it is not possible to perform electrophysiological measurements of ion transport across a native distal (alveolar) lung epithelium in rats or mice. Therefore, South-African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) were used as a well-established vertebrate model for pulmonary ion transport physiology [16], [17], [18], [19], [20]. Adult clawed frogs were purchased from Xenopus Express France (Vernassal, France) and kept in tanks with continuous freshwater supply. For experiments, frogs were tranquilized in ice water and subsequently killed by decapitation and sounding of the spinal cord. Lungs were dissected and longitudinally opened to flat sheets by incision from the bronchi along the pulmonary artery. Lung sheets were subsequently mounted between Lucite rings and transferred to perfusion Ussing chambers. The treatment of animals conformed to the German law of animal care and was authorized by the regional board of Giessen (“400_M Xenopus laevis”).
Ussing chamber studies
The excised lung sheets which were fixed between Lucite rings were mounted into custom-made perfusion Ussing chambers. The sheets separated the chamber halves into an apical and a basolateral compartment, which thereby allowed the specific application of drugs to either side of the epithelium. The chamber halves were perfused separately by a gravity-driven perfusion system. The chambers were perfused with neutral Ringer's solution (NRS), which contained (in mM): 100 NaCl, 3 KCl, 1 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, 10 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) and 10 glucose (pH 7.4, Tris-base).
The chambers were connected to a voltage-clamp amplifier by Ag/AgCl electrodes which were mounted into the chambers via 200 µl pipette tips which were filled with 3% 1 M KCl-agar (Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany). Only those electrodes were employed, which had a spontaneous electrical potential of less than 1 mV in perfusion solution. After complete mounting of the tissue and electrodes, the perfusion was started and the transepithelial potential (VT) was monitored. After equilibration of VT, the tissues were clamped to 0 mV and short-circuit currents (ISC) were recorded on a PC via an analog/digital interface and the software LabScribe (National Instruments, Munich, Germany). ISC values were additionally recorded on a strip-chart recorder (Kipp&Zonen, Delft, The Netherlands). In order to determine the transepithelial resistance (RT), 5 mV voltage pulses were applied to the epithelia and the resulting current deflections were recorded. RT was then calculated following Ohm's law. All experiments were performed at room temperature.
Measurement of basolateral membrane conductance
In order to measure the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase, apical membranes were permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM, Sigma). The use of nystatin for the specific permeabilisation of apical or basolateral membranes is a well-established method in epithelial physiology [23]. Nystatin generates pores which are selective for Na+, K+ and Cl− [24]. It does not cross the cell and permeabilise the opposite (basolateral) membrane [23]. Amiloride, an inhibitor of ENaC, was also present in the apical solution (10 µM). Under these conditions, ISC values reflect currents across the basolateral membrane, which are mainly due to Na+/K+-ATPase activity.
In order to measure basolaterally located K+ channels, the apical side of the epithelium was perfused with a high K+ NRS which contained (in mM): 3 NaCl, 100 KCl, 1 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, 10 HEPES and 10 glucose (pH 7.4, Tris-base). This resulted in an apical to basolateral K+ gradient (100∶3). After equilibration of the ISC, ouabain (1 mM) was applied to the basolateral compartment in order to block the Na+/K+-ATPase and the apical membrane was subsequently permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM). The resulting ISC represented current fluxes via basolateral K+ channels.
Chemicals
Amiloride (Sigma) was used as an inhibitor for ENaC and ouabain (Sigma) in order to block the Na+/K+-ATPase. Lidocaine (Sigma) was used as an unselective inhibitor of K+ channels. Where necessary, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as a solvent and was present in according control experiments.
Data analysis and statistics
Data are presented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The number of experiments is indicated with “n”, the number of donor frogs is indicated with “N”. For statistical analysis of dependent experiments (e.g. current values before and after drug application), paired Student's t-Test was employed. For independent experiments (e.g. comparing different lung preparations) unpaired Student's t-test was used. In general, a value of p≤0.05 was regarded to be statistically significant and marked with asterisks (* p≤0.05; ** p≤0.01).
Results
H2S inhibits net ion transport across Xenopus lung epithelia
The administration of the H2S donating molecule NaHS (1 mM, apical side) decreased transepithelial ion current (ISC) across Xenopus lung epithelia by approx. 60% (Figure 1 A, B). There was no decrease in transepithelial resistance (RT; Figure 1 C) which indicates that the NaHS-mediated decrease in ISC was not the result of damage to the epithelium. Furthermore, the effect of NaHS was partially reversible, since normalized values of ISC increased after wash-out of NaHS (Figure 1 D). The inhibition of ion transport by NaHS was also dose-dependent, with an IC50 of 1.18 mM (Figure 1 E). Importantly, in the employed perfusion Ussing chamber system there will be diffusion of H2S into the air. The amount of H2S was measured over time in the employed Ussing chamber solution by a colorimetric assay and the formation of methylene blue (Figure 1 F). There was a slow but constant decline of buffer H2S concentrations within the time frame of experiments which indicates that the effective H2S concentration is likely lower than reflected in the determined IC50 value for NaHS.
Taken together, these data indicate that exogenously applied H2S decreases net ion transport across Xenopus lung epithelia in toxicologically relevant concentrations (1 mM NaHS corresponds to ∼50 ppm).
H2S inhibits amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption
Under basal conditions, the main ion transport process in Xenopus lung epithelia is the absorption of Na+ ions from the apical to the basolateral side via the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) and the Na+/K+-ATPase [17], [18], [19], [20]. Therefore it was investigated if Na+ absorption was affected by NaHS. In order to address this question, amiloride was employed as an inhibitor of ENaC (Figure 2). Pre-treatment of the lungs with 1 mM NaHS significantly decreased amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption (Figure 2 B, C) compared to control experiments without NaHS (Figure 2 A).
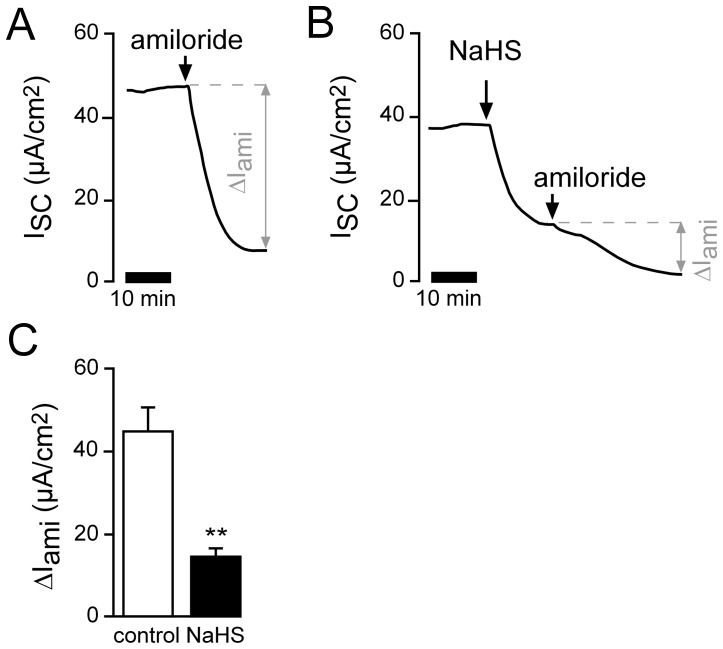
Figure 2. H2S inhibits amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption.
A) Representative current trace of a control experiment. In order to estimate the amount of Na+ absorption, the ENaC inhibitor amiloride (10 µM) was applied apically. B) Similar experiment showing the effects of amiloride after apical pre-treatment of the lung epithelium with apical NaHS (1 mM). C) Statistical evaluation of experiments as shown in panels A and B. Depicted are amiloride-sensitive (ΔIami) current fractions. NaHS significantly reduced ΔIami from 45.04±5.55 µA/cm2 to 14.84±1.77 µA/cm2 (n = 5; N = 3; p≤0.001).
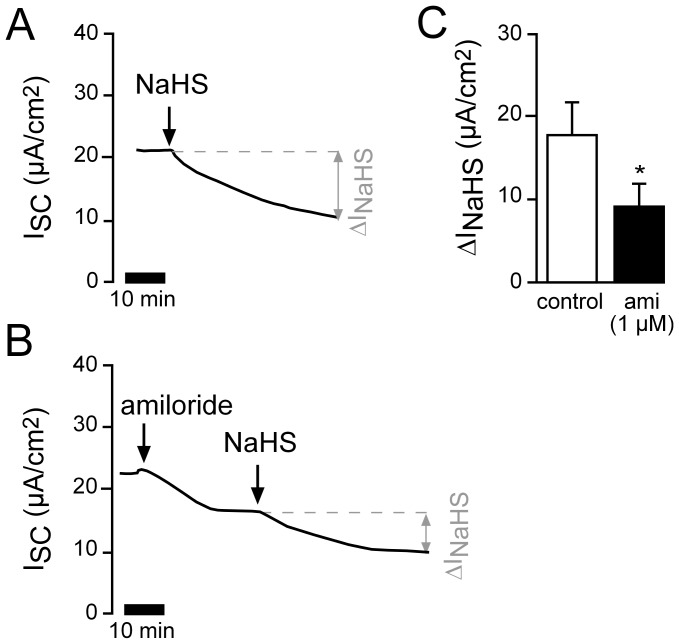
In order to confirm this finding, experiments were performed with even more specific concentrations of amiloride (1 µM in the reverse order of drug application (Figure 3)). Following application of 1 µM amiloride, the NaHS-mediated current decrease (ΔINaHS) was significantly smaller than under control conditions. These data indicate that exogenously applied H2S impairs amiloride-sensitive, ENaC-mediated Na+ transport in Xenopus lung epithelial cells.
Figure 3. Amiloride attenuates the H2S induced current decrease.
A) Representative current trace of a control experiment showing the effect of apical treatment with NaHS (1 mM). B) Lungs were treated with 1 µM amiloride apically and NaHS (1 mM) was subsequently applied for the same duration as the parallel conducted control experiment as depicted in panel A. C) Statistical evaluation. Amiloride significantly reduced the NaHS-mediated current decrease (ΔINaHS; n = 6, N = 6, p≤0.05).
Effects of exogenous H2S on Na+/K+-ATPase and basolateral K+ channels
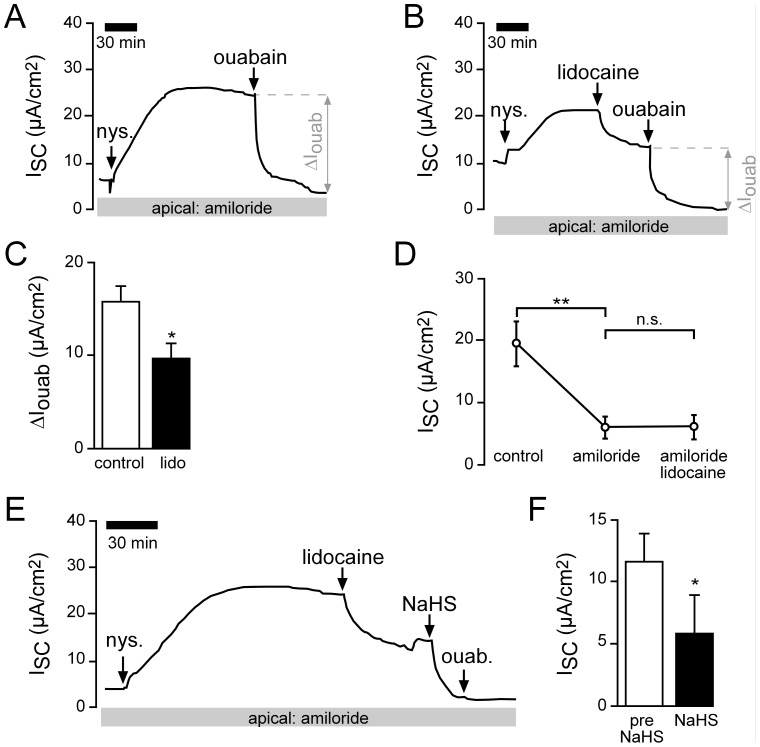
A significant contribution to total amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport comes from transporting molecules located in the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells. The Na+/K+-ATPase actively transports Na+ out of the cells and thus establishes the chemical gradient for Na+ influx via ion channels at the apical membrane. In addition, basolateral K+ channels largely determine electrochemical gradients since they contribute to the membrane potential (also of the apical membrane) as well as recycle K+ ions which are taken up by the Na+/K+-ATPase. An inhibition of both, the Na+/K+-ATPase as well as basolateral K+ channels, will eventually decrease total amiloride-sensitive ISC indirectly.
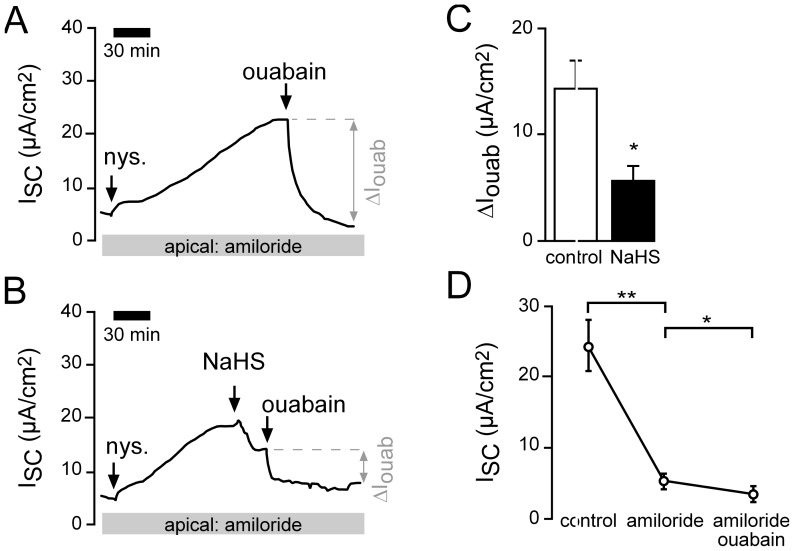
In order to measure currents across the basolateral membrane, amiloride was added to the apical side of lung epithelia and the apical membrane was subsequently permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM). This resulted in an increase of the ISC (Figure 4). This current is mainly mediated by the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase, since the perfusion solutions do not generate ion gradients across the permabilized epithelium, which would allow ion fluxes through basolateral ion channels. Furthermore, the nystatin-induced current was fully sensitive to the Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor ouabain (Figure 4 A), whereas without nystatin permeabilisation and in the presence of amiloride, ouabain had only a minor effect on ISC (Figure 4 D). When NaHS was applied to the apical bath after permeabilisation with nystatin, ISC decreased significantly (Figure 4B). The ouabain-sensitive fractions of the current (ΔIouab) also decreased significantly (Figure 4C), which indicates that the Na+/K+-ATPase is inhibited by NaHS.
Figure 4. H2S decreases Na+/K+-ATPase currents of Xenopus lung epithelia.
A) Representative current trace of a control recording. The apical membrane of the lung epithelium was permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM, apical) in the presence of amiloride (10 µM). This resulted in a current increase. When the current was stable, the Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor ouabain (1 mM) was applied to the basolateral side. The ouabain-sensitive current fraction (ΔIouab) represents the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase. B) After permeabilisation with nystatin, NaHS (1 mM) was applied to the apical bath. ISC decreased significantly from 20.83±3.99 µA/cm2 to 16.17±5.23 µA/cm2 (n = 6, N = 6, p≤0.05). Subsequently, ouabain-sensitive current fractions were determined. C) Statistical evaluation of experiments as shown in panels A and B. NaHS significantly inhibited Na+/K+-ATPase activity (ΔIouab; n = 6, N = 6, p≤0.05). D) Without permeabilisation with nystatin, ouabain had only a minor effect on transepithelial ion current in the presence of amiloride. Depicted are mean values of non-permeabilized lung epithelia which have been treated with amiloride (10 µM, apical) followed by ouabain (1 mM, basolateral).
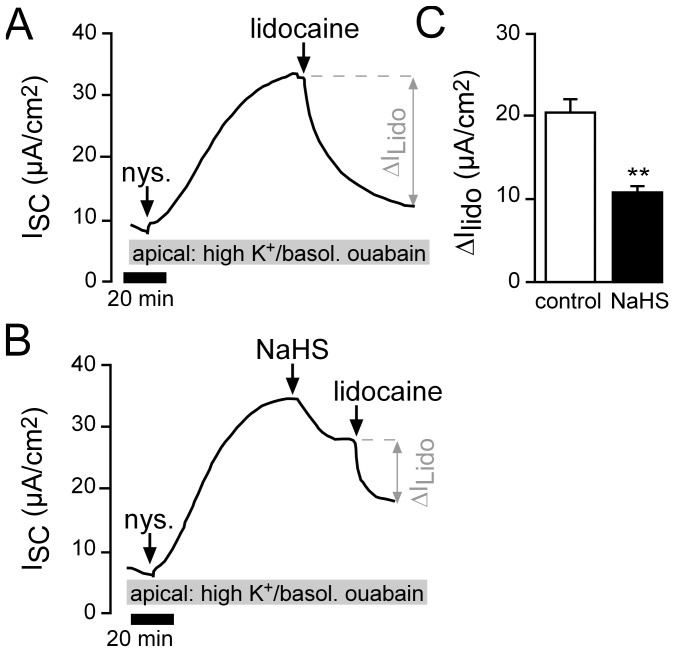
In order to measure a putative impact of NaHS on basolateral K+ channels, apical membranes of lung epithelia were permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM) in the presence of ouabain (1 mM, basolateral) and an apical to basolateral K+ gradient (Figure 5). Under these conditions, the nystatin-induced current was sensitive to the unselective K+ channel inhibitor lidocaine (1 mM; Figure 5 A). When NaHS was applied upon nystatin-permeabilisation, ISC decreased significantly (Figure 5 B). Furthermore, NaHS reduced the effect of lidocaine: Lidocaine-sensitive currents (ΔILido) were significantly smaller compared to those under control conditions (Figure 5 C). These data indicate that NaHS inhibits lidocaine-sensitive K+ channels at the basolateral membrane of Xenopus lung epithelia.
Figure 5. H2S inhibits basolateral K+ channels.
A) Representative current trace of a control recording. In order to measure basolateral K+ channels, lungs were apically perfused with a high K+ solution. Ouabain (1 mM) was present in the basolateral perfusate in order to exclude a contribution of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Under these conditions, the apical membrane was permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM). This resulted in a current increase which was sensitive to the nonselective K+ channel inhibitor lidocaine (1 mM). B) The application of NaHS (1 mM) after nystatin permeabilisation resulted in a current decrease (from 47.2±5.12 µA/cm2 to 36.4±2.93 µA/cm2; n = 5, N = 5, p≤0.05). Subsequently applied lidocaine had a smaller effect compared to control recordings as shown in panel A. C) Statistical evaluation of experiments as shown in panels A and B. NaHS significantly reduced lidocaine-sensitive currents (ΔILido) of the basolateral membrane (n = 5, N = 5, p≤0.01).
Interplay of basolateral K+ channels and the Na+/K+-ATPase
Since NaHS inhibited basolateral K+ channels, it is important to investigate if this effect might also be apparent when determining Na+/K+-ATPase activity on apically permeabilized epithelia. When lidocaine (1 mM, basolateral) was applied to apically permeabilized lung epithelia (Figure 6), a decrease of ISC (Figure 6 B) was observed. Furthermore, ΔIouab decreased significantly (Figure 6). Without permeabilisation, basolateral lidocaine had no significant effect on ISC (Figure 6 D), which demonstrates that the observed current inhibition is not related to K+ channel activity of incompletely permeabilized cells. Together, those data demonstrate that under apically permeabilized conditions, there is still a direct or indirect contribution of a K+ conductance to ouabain-sensitive Na+/K+-ATPase currents. However, when this conductance was blocked with lidocaine (1 mM, basolateral), NaHS still decreased the remaining ISC (ΔIouab) (Figure 6 E, F), which represents an inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase currents.
Figure 6. Interplay of basolateral K+ channels and the Na+/K+-ATPase.
A) Representative current trace of a control recording. The apical membrane of the lung epithelium was permeabilized with nystatin (100 µM, apical) in the presence of amiloride (10 µM). This resulted in a current increase. When the current was stable, the Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor ouabain (1 mM) was applied to the basolateral side. The ouabain-sensitive current fraction (ΔIouab) represents the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase. B) After permeabilisation with nystatin, lidocaine (1 mM) was applied to the basolateral bath. This resulted in a decrease of the ISC from 17.20±2.58 µA/cm2 to 12.00±1.67 µA/cm2 (n = 5, N = 5, p≤0.05). Subsequently, ouabain-sensitive current fractions were determined. C) Statistical evaluation of experiments as shown in panels A and B. Lidocaine (lido.) significantly inhibited Na+/K+-ATPase activity (ΔIouab; n = 5, N = 5, p≤0.05). D) Without permeabilisation with nystatin, lidocaine had only a minor effect on transepithelial ion current. Depicted are mean values of non-permeabilized lung epithelia which have been treated with amiloride (10 µM, apical) followed by lidocaine (1 mM, basolateral). E) The application of NaHS (1 mM) to nystatin-permeabilized lungs which have been pre-treated with lidocaine (1 mM) additionally decreased ion current. Note that the subsequent application of ouabain was without any further effect. F) NaHS significantly decreased ISC under conditions as shown in panel E (n = 6, N = 6, p≤0.05).
In sum, these data demonstrate that exogenously applied H2S inhibits Na+ transport across Xenopus lung epithelia by inhibiting both the activity of the Na+/K+-ATPase as well as basolateral, lidocaine-sensitive K+ channels.
Discussion
The formation of pulmonary edema is a hallmark of patients who were exposed to H2S – particularly after prolonged exposure [3]. However, the molecular mechanisms leading to edema formation are poorly understood. In the present study we hypothesized that H2S may interfere with the clearance of Na+ and, consequently, liquid across the pulmonary epithelium. In native Xenopus lung preparations, the apical administration of the H2S liberating molecule NaHS led to a partially reversible and dose-dependent decrease in net ion transport (Figure 1). The employed concentrations of NaHS as well as the determined IC50 value for transport inhibition are within a concentration range (1 mM NaHS corresponds to ∼50 ppm) in which irritation of the respiratory tract [21]as well as pulmonary edema [4] occur. However, it has to be mentioned that due to the employed perfusion Ussing chambers and diffusion of H2S into the air, there is a decrease in the absolute H2S concentrations over time (Figure 1 F). This indicates that the effective H2S concentrations are probably even lower than reflected in the determined IC50 value for NaHS.
The observed net decrease in ion transport was due to an impaired amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport (Figures 2 and 3). Experiments on functionally isolated basolateral membranes of Xenopus lung epithelia demonstrate that the Na+/K+-ATPase as well as basolateral K+ channels are general targets for exogenous H2S (Figures 4–6). These findings confirm previous observations using a human airway epithelial cell line (H441; [12]). Both targets are crucial for the maintenance of epithelial Na+ transport: the Na+/K+-ATPase creates the chemical gradients for Na+ influx into the epithelial cells via Na+ channels located at the apical membrane, whereas basolateral K+ channels determine the epithelial membrane potential as well as recycle the K+ ions which are taken up by the Na+/K+-ATPase in exchange for Na+ [7].
Impairment of both components, as observed due to H2S administration, will eventually decrease the net absorption of Na+ ions. Nevertheless, H2S might also interact with Na+ channels located in the apical membrane. Due to the complex anatomy of the basolateral compartment of the Xenopus lung we were never able to get a sufficient permeabilisation of the basolateral epithelial membrane, which would allow the measurement of apically located Na+ channels. However, H2S has no effect on Na+ channels in H441 cells and on heterologously expressed human ENaCs [12]. Nevertheless, a possible effect of H2S on Na+ channels in the Xenopus lung cannot be completely excluded. Irrespective of whether or not Na+ channels are affected, the Na+/K+-ATPase is the major regulator of Na+ gradients and its impairment by H2S will eventually decrease overall Na+ absorption [9]. Consequently, the molecular driving force for liquid clearance is impaired and H2S-exposed lungs are predisposed to the formation of pulmonary edema.
An interesting question arises related to the chemical basis for the observed effects of H2S on K+ channels as well as the Na+/K+-ATPase. Given a pH value of the employed buffer solution of 7.4, a pK value for H2S of ∼7.0 and the assumption that all of the 1 mM NaHS stays in solution (which due to evaporation is not the case; Figure 1 F), the solution would contain ∼286 µM of H2S and ∼714 µM HS−. This would indicate that HS− represents the main species. In fact, it has recently been demonstrated that the chemical basis for H2S-mediated effects on proteins may include the generation of persulfides due to addition of HS- to thiolate or a sulfenic-group; or the interaction of HS− with reactive nitrogen species [25]. Interestingly, in the Xenopus lung preparation, NaHS had effects at the basolateral membrane although it was solely applied to the apical compartment. If HS− was not transported into the pulmonary epithelial cells by yet unidentified mechanisms, this would suggest a membrane-permeation of H2S which may subsequently act again as HS− in the cytoplasm and be transferred in a post-translational modification to ion channels/transporters or related signaling molecules.
Aside from being a chemical environmental threat, H2S has recently been recognized as a gaseous signaling molecule which affects various physiological processes [26]. Due to its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and vasoactive properties, H2S is currently evaluated as a potential therapeutic strategy in various models of lung diseases [27], [28], [29] including ALI/ARDS [4], [30], [31], [32], [33]. ALI/ARDS patients develop pulmonary edema and this correlates with the capacity of functional transepithelial Na+ absorption [11]. Both, beneficial and detrimental effects of H2S on edema formation have been reported in ALI models – depending on the employed concentration as well as whether H2S was inhaled or applied systemically [4]. The herein reported inhibition of Na+ absorption by H2S may account for the detrimental effects (including pulmonary edema) which have been observed upon exposure to higher concentrations of H2S (>50 ppm) in mice [4].
Taken together, inhibition of transepithelial Na+ transport provides a mechanism which may enhance edema formation in H2S exposed lungs. This finding expands the basic understanding of the pulmonary toxicology of H2S. Furthermore, the interference of H2S with ion transport processes in pulmonary epithelia needs to be carefully taken into consideration when exploring the therapeutic potential of H2S in the diseased lung.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mirjam Buss and Anja Schnecko for excellent technical assistance and Denis Revskij for the help with some experiments. Katrin Richter is acknowledged for expert advice in Xenopus preparations and animal handling.
Data Availability
The authors confirm that all data underlying the findings are fully available without restriction. All relevant data are included within the paper.
Funding Statement
This work has been funded by a grant from the German Research Foundation (DFG) No. AL1453/1-1. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Guidotti TL (1996) Hydrogen sulphide. Occup Med (Lond) 46 5: 367–371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Mimoun S, Andriamihaja M, Chaumontet C, Atanasiu C, Benamouzig R, et al. (2012) Detoxification of H(2)S by differentiated colonic epithelial cells: implication of the sulfide oxidizing unit and of the cell respiratory capacity. Antioxid Redox Signal 17 1: 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Guidotti TL (2010) Hydrogen sulfide: advances in understanding human toxicity. Int J Toxicol 29 6: 569–581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Francis RC, Vaporidi K, Bloch KD, Ichinose F, Zapol WM (2011) Protective and Detrimental Effects of Sodium Sulfide and Hydrogen Sulfide in Murine Ventilator-induced Lung Injury. Anesthesiology 115 5: 1012–1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Fronius M (2013) Treatment of pulmonary edema by ENaC activators/stimulators. Curr Mol Pharmacol 6 1: 13–27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Olver RE, Ramsden CA, Strang LB, Walters DV (1986) The role of amiloride-blockable sodium transport in adrenaline-induced lung liquid reabsorption in the fetal lamb. J Physiol (Lond) 376: 321–340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Koefoed-Johnsen V, Ussing HH (1958) The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand 42 3–4: 298–308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Althaus M, Clauss WG, Fronius M (2011) Amiloride-sensitive sodium channels and pulmonary edema. Pulm Med 2011: 830320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Sznajder JI, Factor P, Ingbar DH (2002) Invited review: lung edema clearance: role of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. J Appl Physiol 93 5: 1860–1866 10.1152/japplphysiol.00022.2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Egli M, Duplain H, Lepori M, Cook S, Nicod P, et al. (2004) Defective respiratory amiloride-sensitive sodium transport predisposes to pulmonary oedema and delays its resolution in mice. J Physiol (Lond) 560 Pt 3: 857–865 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.066704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Ware LB, Matthay MA (2001) Alveolar fluid clearance is impaired in the majority of patients with acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163 6: 1376–1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Althaus M, Urness K, Clauss W, Baines D, Fronius M (2012) The gasotransmitter hydrogen sulphide decreases Na(+) transport across pulmonary epithelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 166 6: 1946–1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Althaus M, Pichl A, Clauss WG, Seeger W, Fronius M, et al. (2011) Nitric oxide inhibits highly selective sodium channels and the Na+/K+-ATPase in H441 cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44 1: 53–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Jain L, Chen XJ, Ramosevac S, Brown LA, Eaton DC (2001) Expression of highly selective sodium channels in alveolar type II cells is determined by culture conditions. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280 4: L646–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Meban C (1973) The pneumonocytes in the lung of Xenopus laevis. J Anat 114 Pt 2: 235–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Berger J, Richter K, Clauss WG, Fronius M (2011) Evidence for basolateral Cl- channels as modulators of apical Cl- secretion in pulmonary epithelia of Xenopus laevis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300 3: R616–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Fischer H, Clauss W (1990) Regulation of Na+ channels in frog lung epithelium: a target tissue for aldosterone action. Pflugers Arch 416 1–2: 62–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Fischer H, van Driessche W, Clauss W (1989) Evidence for apical sodium channels in frog lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 256 4 Pt 1: C764–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Fronius M, Clauss W, Schnizler M (2003) Stimulation of transepithelial Na(+) current by extracellular Gd(3+) in Xenopus laevis alveolar epithelium. J Membr Biol 195 1: 43–51 10.1007/s00232-003-2043-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Sommer D, Bogdan R, Berger J, Peters DM, Morty RE, et al. (2007) CFTR-dependent Cl- secretion in Xenopus laevis lung epithelium. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 158 1: 97–106 10.1016/j.resp.2007.03.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Reiffenstein RJ, Hulbert WC, Roth SH (1992) Toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 32: 109–134 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.000545 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Rashid S, Heer JK, Garle MJ, Alexander SPH, Roberts RE (2013) Hydrogen sulphide-induced relaxation of porcine peripheral bronchioles. Br J Pharmacol 168 8: 1902–1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lewis SA, Eaton DC, Clausen C, Diamond JM (1977) Nystatin as a probe for investigating the electrical properties of a tight epithelium. J Gen Physiol 70 4: 427–440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Russell JM, Eaton DC, Brodwick MS (1977) Effects of nystatin on membrane conductance and internal ion activities inAplysia neurons. J Membrain Biol 37 1: 137–156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Kolluru GK, Shen X, Kevil CG (2013) A tale of two gases: NO and H2S, foes or friends for life. Redox Biol 1 1: 313–318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Wang R (2012) Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide: a whiff exploration that blossomed. Physiol Rev 92 2: 791–896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Cao H, Zhou X, Zhang J, Huang X, Zhai Y, et al. (2014) Hydrogen sulfide protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats by inhibiting NF-κB expression and regulating Th1/Th2 balance. Toxicol Lett 224 3: 387–394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Madurga A, Mizikova I, Ruiz-Camp J, Vadász I, Herold S, et al. (2014) Systemic hydrogen sulfide administration partially restores normal alveolarization in an experimental animal model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Vadivel A, Alphonse RS, Ionescu L, Machado DS, O'Reilly M, et al. (2014) Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Protects Alveolar Growth in Experimental O2-Induced Neonatal Lung Injury. PLoS ONE 9 3: e90965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Esechie A, Enkhbaatar P, Traber DL, Jonkam C, Lange M, et al. (2009) Beneficial effect of a hydrogen sulphide donor (sodium sulphide) in an ovine model of burn- and smoke-induced acute lung injury. Br J Pharmacol 158 6: 1442–1453 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00411.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Faller S, Ryter SW, Choi AMK, Loop T, Schmidt R, et al. (2010) Inhaled hydrogen sulfide protects against ventilator-induced lung injury. Anesthesiology 113 1: 104–115 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181de7107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Faller S, Zimmermann KK, Strosing KM, Engelstaedter H, Buerkle H, et al. (2012) Inhaled hydrogen sulfide protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Med Gas Res 2 1: 26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Otulakowski G, Kavanagh BP (2010) Hydrogen sulfide in lung injury: therapeutic hope from a toxic gas. Anesthesiology 113 1: 4–6 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181dec00e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that all data underlying the findings are fully available without restriction. All relevant data are included within the paper.