Abstract
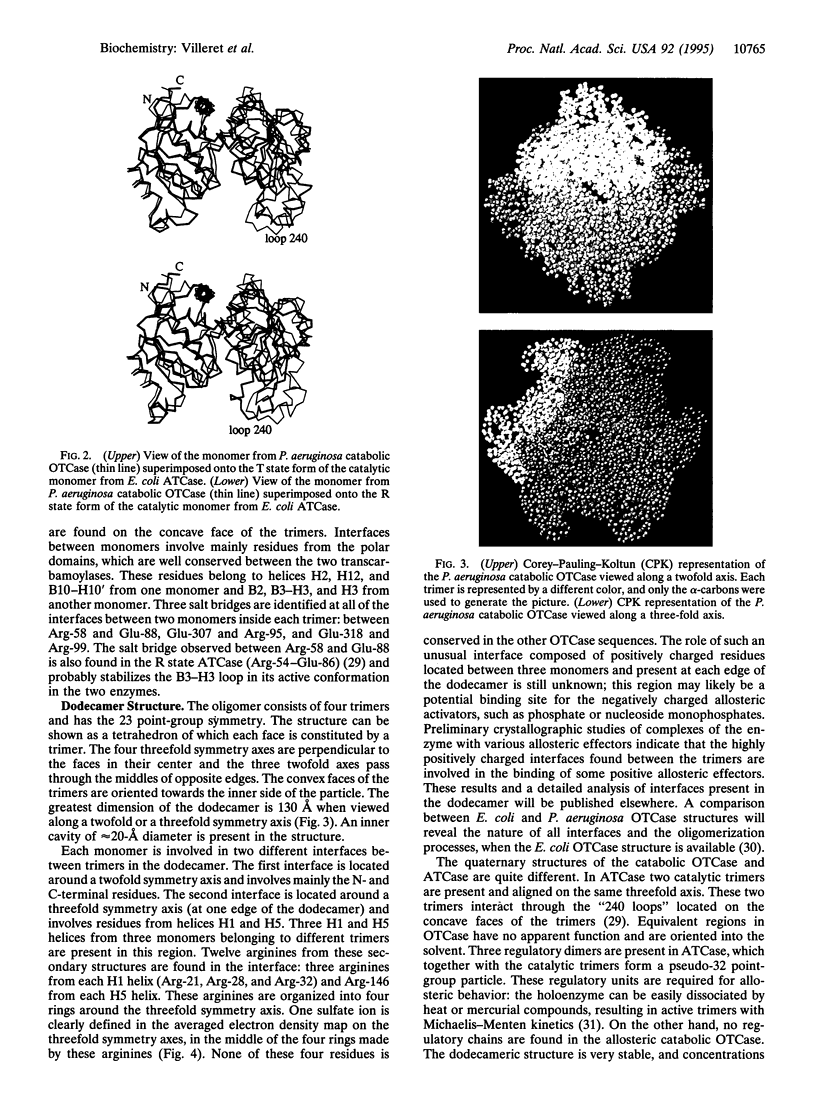
The crystal structure of the Glu-105-->Gly mutant of catabolic ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTCase; carbamoyl phosphate + L-ornithine = orthophosphate + L-citrulline, EC 2.1.3.3) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been determined at 3.0-A resolution. This mutant is blocked in the active R (relaxed) state. The structure was solved by the molecular replacement method, starting from a crude molecular model built from a trimer of the catalytic subunit of another transcarbamoylase, the extensively studied aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) from Escherichia coli. This model was used to generate initial low-resolution phases at 8-A resolution, which were extended to 3-A by noncrystallographic symmetry averaging. Four phase extensions were required to obtain an electron density map of very high quality from which the final model was built. The structure, including 4020 residues, has been refined to 3-A, and the current crystallographic R value is 0.216. No solvent molecules have been added to the model. The catabolic OTCase is a dodecamer composed of four trimers organized in a tetrahedral manner. Each monomer is composed of two domains. The carbamoyl phosphate binding domain shows a strong structural homology with the equivalent ATCase part. In contrast, the other domain, mainly implicated in the binding of the second substrate (ornithine for OTCase and aspartate for ATCase) is poorly conserved. The quaternary structures of these two allosteric transcarbamoylases are quite divergent: the E. coli ATCase has pseudo-32 point-group symmetry, with six catalytic and six regulatory chains; the catabolic OTCase has 23 point-group symmetry and only catalytic chains. However, both enzymes display homotropic and heterotropic cooperativity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur H., Tricot C., Stalon V., Haas D. Converting catabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase to an anabolic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14728–14731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass D., Evans R., Mercenier A., Simon J. P., Stalon V. Genetic and physiological characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants affected in the catabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):713–720. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.713-720.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. B., Neece S. H., Schachman H. K., Ginsburg A. Mercurial-promoted Zn2+ release from Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14793–14803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke H. M., Lipscomb W. N., Cho Y. J., Honzatko R. B. Complex of N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate with aspartate carbamoyltransferase. X-ray refinement, analysis of conformational changes and catalytic and allosteric mechanisms. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):725–747. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90365-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. L., Volz K. W., Lipscomb W. N. 2.5 A structure of aspartate carbamoyltransferase complexed with the bisubstrate analog N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):527–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. L., Volz K. W., Lipscomb W. N. Structure at 2.9-A resolution of aspartate carbamoyltransferase complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1643–1647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo L. C., Seaton B. A. X-ray diffraction analysis on single crystals of recombinant Escherichia coli ornithine transcarbamoylase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16246–16248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo L. C., Zambidis I., Caron C. Triggering of allostery in an enzyme by a point mutation: ornithine transcarbamoylase. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2667139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb W. N. Aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli: activity and regulation. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1994;68:67–151. doi: 10.1002/9780470123140.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Rossmann M. G. Structure determination of Mengo virus. Acta Crystallogr B. 1989 Feb 1;45(Pt 1):85–92. doi: 10.1107/s0108768188010894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcq S., Diaz-Ruano A., Charlier P., Dideberg O., Tricot C., Piérard A., Stalon V. Molecular size and symmetry of Pseudomonas aeruginosa catabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase. An X-ray crystallography analysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 5;220(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90375-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M., Cohen P. P. The essential sulfhydryl group of ornithine transcarbamylases. pH dependence of the spectra of its 2-mercuri-4-nitrophenol derivative. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7296–7300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall S., van Heeswijck R., Hoogenraad N. Site-directed mutagenesis of Arg60 and Cys271 in ornithine transcarbamylase from rat liver. Protein Eng. 1990 Oct;4(1):73–77. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercenier A., Simon J. P., Vander Wauven C., Haas D., Stalon V. Regulation of enzyme synthesis in the arginine deiminase pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):159–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.159-163.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco H. L., Crawford J. L., Lipscomb W. N. Three-dimensional structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli and of its complex with cytidine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5276–5280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navaza J. On the computation of the fast rotation function. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Nov 1;49(Pt 6):588–591. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993005141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalon V., Legrain C., Wiame J. M. Anabolic ornithine carbamolytransferase of Pseudomonas. The bases of its functional specialization. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):319–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalon V., Ramos F., Piérard A., Wiame J. M. The occurrence of a catabolic and an anabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase in Pseudomonas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbins J. W., Xu W., Kantrowitz E. R. Three residues involved in binding and catalysis in the carbamyl phosphate binding site of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2592–2600. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. C., Chook Y. M., Cho C. Y., Lipscomb W. N., Kantrowitz E. R. Escherichia coli aspartate carbamoyltransferase: the probing of crystal structure analysis via site-specific mutagenesis. Protein Eng. 1991 Apr;4(4):391–408. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L. A., Rossmann M. G. The locked rotation function. Acta Crystallogr A. 1990 Oct 1;46(Pt 10):783–792. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390005530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricot C., Nguyen V. T., Stalon V. Steady-state kinetics and analysis of pH dependence on wild-type and a modified allosteric Pseudomonas aeruginosa ornithine carbamoyltransferase containing the replacement of glutamate 105 by alanine. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):833–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet F., Cunin R., Jacobs A., Piette J., Gigot D., Lauwereys M., Piérard A., Glansdorff N. Evolutionary divergence of genes for ornithine and aspartate carbamoyl-transferases--complete sequence and mode of regulation of the Escherichia coli argF gene; comparison of argF with argI and pyrB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6277–6289. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Wauven C., Piérard A., Kley-Raymann M., Haas D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants affected in anaerobic growth on arginine: evidence for a four-gene cluster encoding the arginine deiminase pathway. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):928–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.928-934.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellieux F. M., Huitema F., Groendijk H., Kalk K. H., Jzn J. F., Jongejan J. A., Duine J. A., Petratos K., Drenth J., Hol W. G. Structure of quinoprotein methylamine dehydrogenase at 2.25 A resolution. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2171–2178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




