Abstract
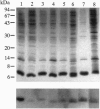
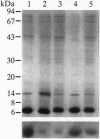
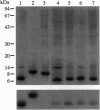
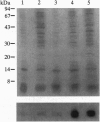
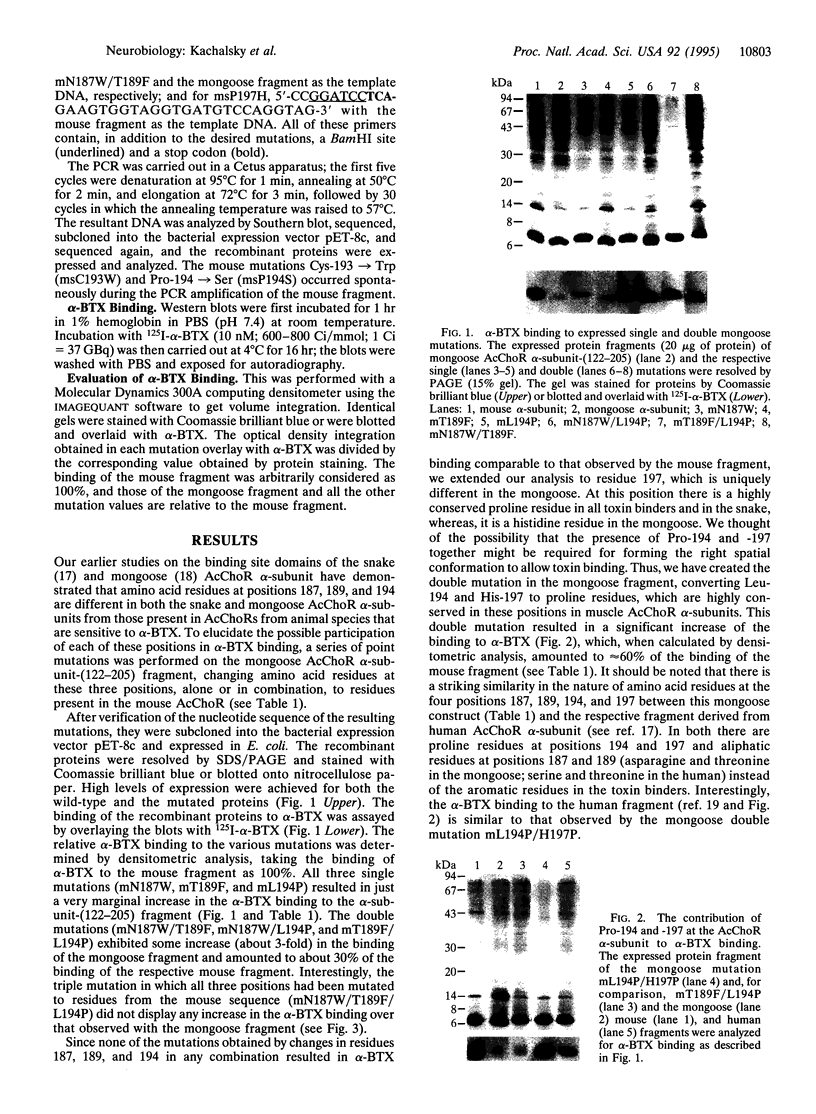
The ligand binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AcChoR) is localized in the alpha-subunit within a domain containing the tandem Cys-192 and -193. By analyzing the binding-site region of AcChoR from animal species that are resistant to alpha-neurotoxins, we have previously shown that four residues in this region, at positions 187, 189, 194, and 197, differ between animals sensitive (e.g., mouse) and resistant (e.g., mongoose and snake) to alpha-bungarotoxin (alpha-BTX). In the present study, we performed site-directed mutagenesis on a fragment of the mongoose AcChoR alpha-subunit (residues 122-205) and exchanged residues 187, 189, 194, and 197, either alone or in combination, with those present in the mouse alpha-subunit sequence. Only the mongoose fragment in which all four residues were mutated to the mouse ones exhibited alpha-BTX binding similar to that of the mouse fragment. The mongoose double mutation in which Leu-194 and His-197 were replaced with proline residues, which are present at these positions in the mouse AcChoR and in all other toxin binders, bound alpha-BTX to approximately 60% of the level of binding exhibited by the mouse fragment. In addition, replacement of either Pro-194 or -197 in the mouse fragment with serine and histidine, respectively, markedly decreased alpha-BTX binding. All other mutations resulted in no or just a small increase in alpha-BTX binding. These results have led us to propose two subsites in the binding domain for alpha-BTX: the proline subsite, which includes Pro-194 and -197 and is critical for alpha-BTX binding, and the aromatic subsite, which includes amino acid residues 187 and 189 and determines the extent of alpha-BTX binding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barchan D., Kachalsky S., Neumann D., Vogel Z., Ovadia M., Kochva E., Fuchs S. How the mongoose can fight the snake: the binding site of the mongoose acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7717–7721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchan D., Ovadia M., Kochva E., Fuchs S. The binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in animal species resistant to alpha-bungarotoxin. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 18;34(28):9172–9176. doi: 10.1021/bi00028a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Mauron A., Roth B., Alliod C., Tzartos S. J., Ballivet M. Mapping the main immunogenic region and toxin-binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.2432658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. Molecular basis of the two nonequivalent ligand binding sites of the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Luyten W., Evans K., Mason P., Ballivet M., Goldman D., Stengelin S., Martin G., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a clone coding for the alpha-subunit of a mouse acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2545–2552. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi V., Donnelly-Roberts D. L., Lentz T. L. Substitution of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor alpha 1-subunit residues with snake alpha 1- and rat nerve alpha 3-subunit residues in recombinant fusion proteins: effect on alpha-bungarotoxin binding. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 11;31(5):1370–1375. doi: 10.1021/bi00120a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier S., Bertrand D., Matter J. M., Hernandez M. C., Bertrand S., Millar N., Valera S., Barkas T., Ballivet M. A neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit (alpha 7) is developmentally regulated and forms a homo-oligomeric channel blocked by alpha-BTX. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):847–856. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90344-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski C., Karlin A. Agonist binding site of Torpedo electric tissue nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A negatively charged region of the delta subunit within 0.9 nm of the alpha subunit binding site disulfide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22603–22612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Revah F., Bessis A., Changeux J. P. Functional architecture of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: from electric organ to brain. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:37–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M. Expression of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by Escherichia coli transformants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4318–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Hawrot E., Lentz T. L. Binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to isolated alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica: quantitative analysis with protein blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4973–4977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Froehner S. C. Restoration of 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity to the alpha subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor isolated by gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8294–8297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Dwork A. J., Kaldany R. R., Silver M. L., Wideman J., Stein S., Karlin A. Identification of the alpha subunit half-cystine specifically labeled by an affinity reagent for the acetylcholine receptor binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11662–11665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Tobimatsu T., Imoto K., Tanaka K., Fujita Y., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Morimoto Y., Hirose T. Location of functional regions of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit by site-directed mutagenesis. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):364–369. doi: 10.1038/313364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Oneyser C., Alliod C., Couturier S., Ballivet M. Genes expressed in the brain define three distinct neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):595–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Fridkin M., Fuchs S. Analysis of ligand binding to the synthetic dodecapeptide 185-196 of the acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9250–9253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Horowitz M., Kochva E., Fuchs S. Snake acetylcholine receptor: cloning of the domain containing the four extracellular cysteines of the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7255–7259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Safran A., Gershoni J. M., Fuchs S. Mapping of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site within the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3008–3011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Gershoni J. M., Fridkin M., Fuchs S. Antibodies to synthetic peptides as probes for the binding site on the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3490–3493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohana B., Fraenkel Y., Navon G., Gershoni J. M. Molecular dissection of cholinergic binding sites: how do snakes escape the effect of their own toxins? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):648–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Cohen J. B. d-Tubocurarine binding sites are located at alpha-gamma and alpha-delta subunit interfaces of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. T., Lentz T. L., Hawrot E. Determination of the primary amino acid sequence specifying the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site on the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8790–8794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]