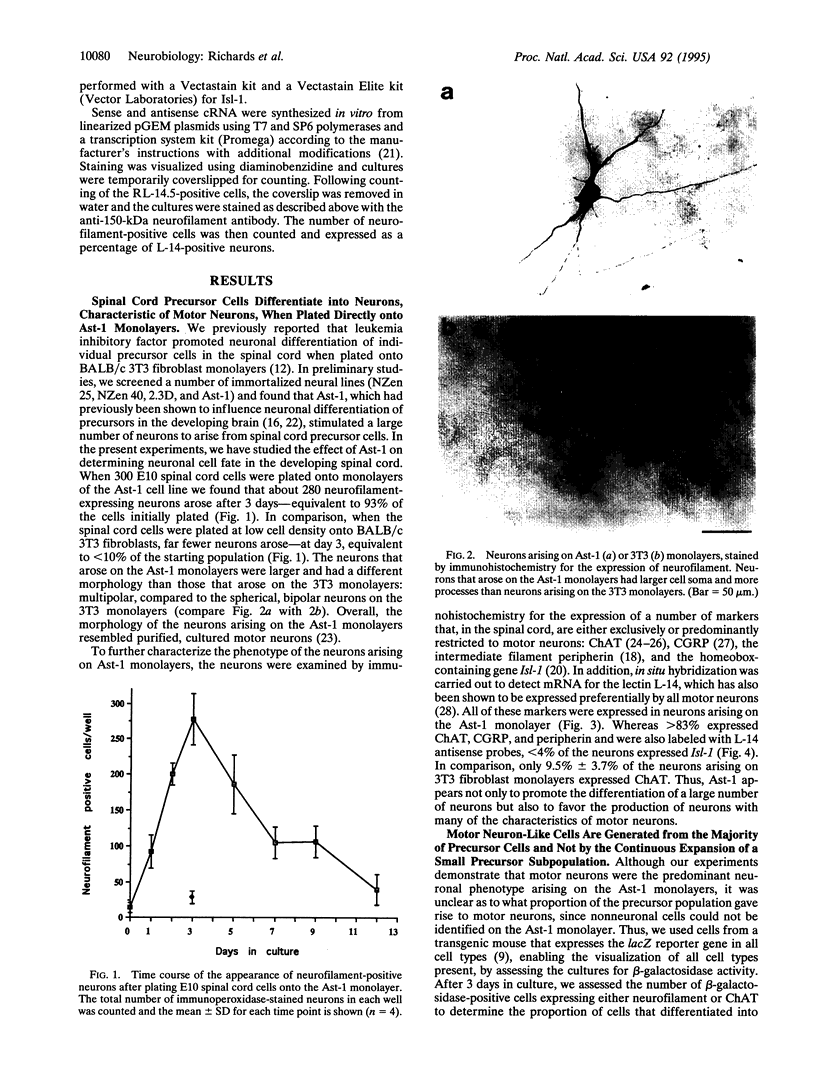
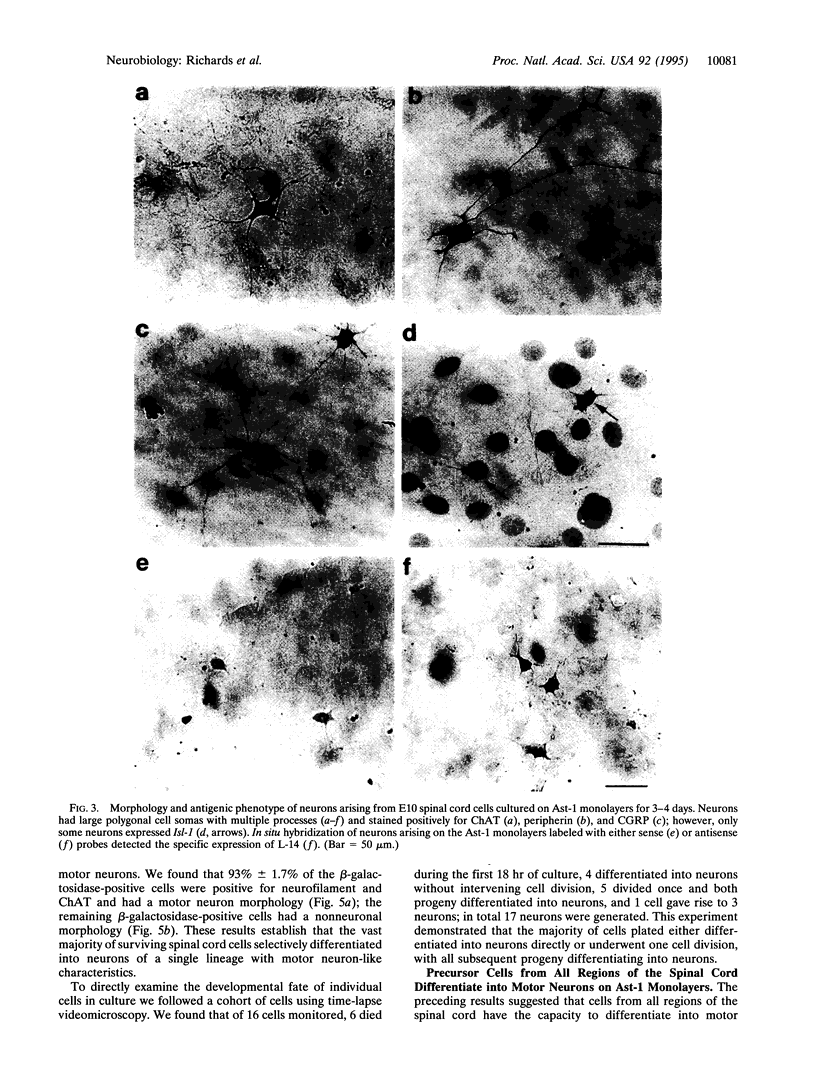
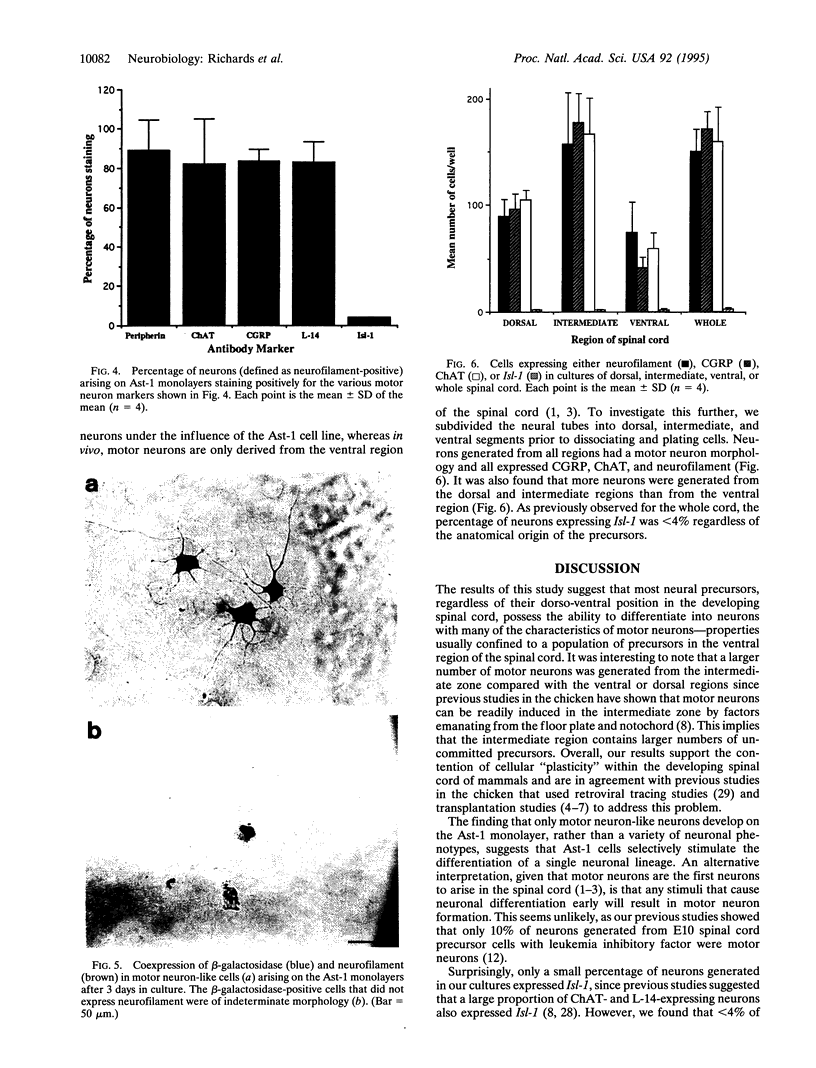
Abstract
We have investigated the differentiation potential of precursor cells within the developing spinal cord of mice and have shown that spinal cord cells from embryonic day 10 specifically give rise to neurons when plated onto an astrocytic monolayer, Ast-1. These neurons had the morphology of motor neurons and > 83% expressed the motor neuron markers choline acetyltransferase, peripherin, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and L-14. By comparison, < 10% of the neurons arising on monolayers of other neural cell lines or 3T3 fibroblasts had motor neuron characteristics. Cells derived from dorsal, intermediate, and ventral regions of the spinal cord all behaved similarly and gave rise to motor neuron-like cells when plated onto Ast-1. By using cells that expressed the lacZ reporter gene, it was shown that > 93% of cells present on the Ast-1 monolayers were motor neuron-like. Time-lapse analysis revealed that the precursors on the Ast-1 monolayers gave rise to neurons either directly or following a single cell division. Together, these results indicate that precursors in the murine spinal cord can be induced to differentiate into the motor neuron phenotype by factors produced by Ast-1 cells, suggesting that a similar factor(s) produced by cells akin to Ast-1 may regulate motor neuron differentiation in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber R. P., Phelps P. E., Houser C. R., Crawford G. D., Salvaterra P. M., Vaughn J. E. The morphology and distribution of neurons containing choline acetyltransferase in the adult rat spinal cord: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Nov 1;229(3):329–346. doi: 10.1002/cne.902290305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett P. F., Noble M. D., Pruss R. M., Raff M. C., Rattray S., Williams C. A. Rat neural antigen-2 (RAN-2): a cell surface antigen on astrocytes, ependymal cells, Müller cells and lepto-meninges defined by a monoclonal antibody. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 12;204(2):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90593-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett P. F., Reid H. H., Bailey K. A., Bernard O. Immortalization of mouse neural precursor cells by the c-myc oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3255–3259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Reid H. H., Bartlett P. F. Role of the c-myc and the N-myc proto-oncogenes in the immortalization of neural precursors. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Sep;24(1):9–20. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drago J., Murphy M., Bailey K. A., Bartlett P. F. A method for the isolation of purified murine neuroepithelial cells from the developing mouse brain. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 May;37(3):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90031-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenstein F., Thoenen H. Production of specific antisera and monoclonal antibodies to choline acetyltransferase: characterization and use for identification of cholinergic neurons. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):363–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01175.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson J., Thor S., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Yamada T. Early stages of motor neuron differentiation revealed by expression of homeobox gene Islet-1. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1555–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.1350865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escurat M., Djabali K., Gumpel M., Gros F., Portier M. M. Differential expression of two neuronal intermediate-filament proteins, peripherin and the low-molecular-mass neurofilament protein (NF-L), during the development of the rat. J Neurosci. 1990 Mar;10(3):764–784. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-03-00764.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Camu W., Mettling C., Gouin A., Poulsen K., Karihaloo M., Rullamas J., Evans T., McMahon S. B., Armanini M. P. Neurotrophins promote motor neuron survival and are present in embryonic limb bud. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):266–270. doi: 10.1038/363266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Fuse S., Sohal G. S. The effect of the floor plate on pattern and polarity in the developing central nervous system. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):310–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1987648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollyday M., Hamburger V. An autoradiographic study of the formation of the lateral motor column in the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 26;132(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90416-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ernfors P., Persson H. Developmental and regional expression of choline acetyltransferase mRNA in the rat central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Jun;29(2):163–171. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490290205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Epstein M. L. Monoclonal antibodies and polyvalent antiserum to chicken choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1986 Mar;46(3):968–976. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juurlink B. H., Munoz D. G., Devon R. M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide identifies spinal motoneurons in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Jun;26(2):238–241. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick T. J., Bartlett P. F. Cloning and growth of multipotential neural precursors: requirements for proliferation and differentiation. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90316-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick T. J., Cheema S. S., Koblar S. A., Tan S. S., Bartlett P. F. The engraftment of transplanted primary neuroepithelial cells within the postnatal mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Nov 7;181(1-2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90576-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick T. J., Talman P. S., Bartlett P. F. The differentiation and survival of murine neurons in vitro is promoted by soluble factors produced by an astrocytic cell line. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Jun 1;35(2):147–161. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman J., Haden C. C. Formation and migration of neuroblasts in the spinal cord of the chick embryo. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Apr;138(4):419–425. doi: 10.1002/cne.901380403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leber S. M., Breedlove S. M., Sanes J. R. Lineage, arrangement, and death of clonally related motoneurons in chick spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2451–2462. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02451.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou J. C., Bierer F., Le Van Thai A., Weber M. J. Influence of the culture substratum on the expression of choline acetyltransferase activity in purified motoneurons from rat embryos. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 Jun 1;47(2):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nornes H. O., Carry M. Neurogenesis in spinal cord of mouse: an autoradiographic analysis. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 22;159(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puche A. C., Key B. Identification of cells expressing galectin-1, a galactose-binding receptor, in the rat olfactory system. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Jul 10;357(4):513–523. doi: 10.1002/cne.903570403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards L. J., Kilpatrick T. J., Bartlett P. F. De novo generation of neuronal cells from the adult mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8591–8595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards L. J., Kilpatrick T. J., Bartlett P. F., Murphy M. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes the neuronal development of spinal cord precursors from the neural tube. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Nov;33(3):476–484. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490330314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Williams E. A., Tam P. P. X-chromosome inactivation occurs at different times in different tissues of the post-implantation mouse embryo. Nat Genet. 1993 Feb;3(2):170–174. doi: 10.1038/ng0293-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor S., Ericson J., Brännström T., Edlund T. The homeodomain LIM protein Isl-1 is expressed in subsets of neurons and endocrine cells in the adult rat. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):881–889. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90334-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida T., Ensini M., Morton S. B., Baldassare M., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Pfaff S. L. Topographic organization of embryonic motor neurons defined by expression of LIM homeobox genes. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):957–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Pfaff S. L., Edlund T., Jessell T. M. Control of cell pattern in the neural tube: motor neuron induction by diffusible factors from notochord and floor plate. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90248-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Placzek M., Tanaka H., Dodd J., Jessell T. M. Control of cell pattern in the developing nervous system: polarizing activity of the floor plate and notochord. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90247-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten H. W., Hekking J. W., Beursgens J. P., Terwindt-Rouwenhorst E., Drukker J. Effect of the notochord on proliferation and differentiation in the neural tube of the chick embryo. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):793–803. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten H. W., Thors F., Wiertz-Hoessels L., Hekking J., Drukker J. Effect of a notochordal implant on the early morphogenesis of the neural tube and neuroblasts: histometrical and histological results. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]