Abstract
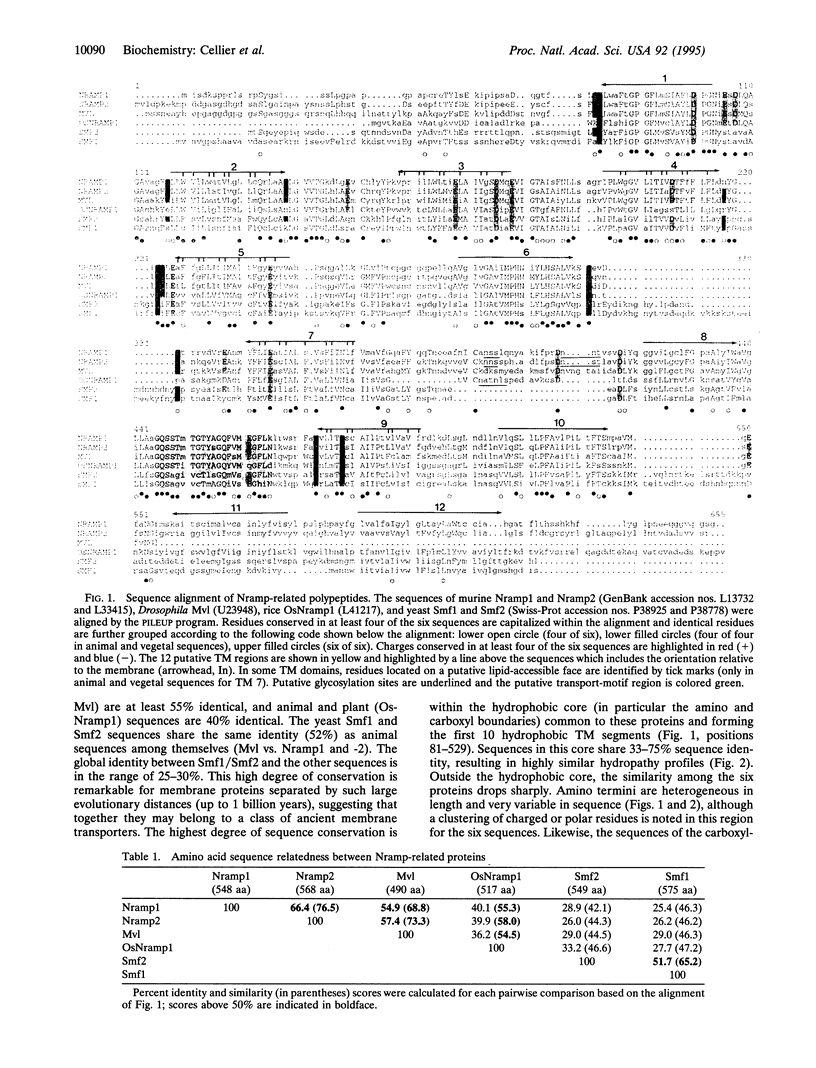
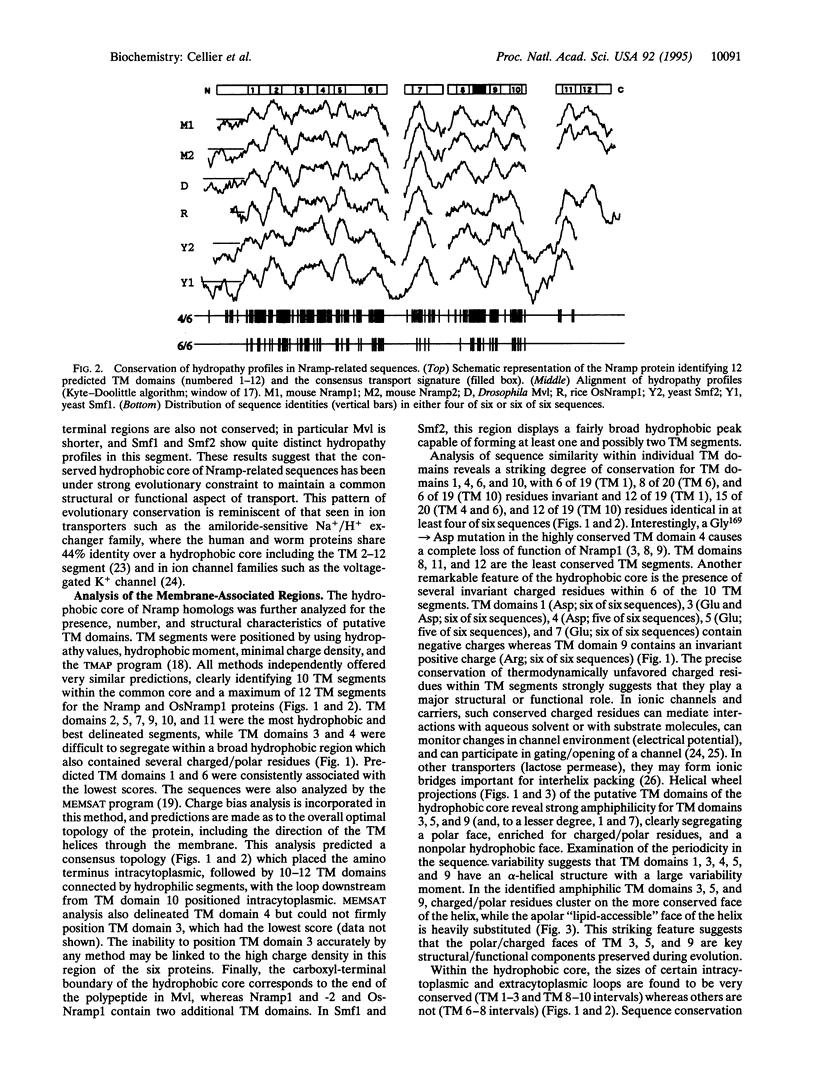
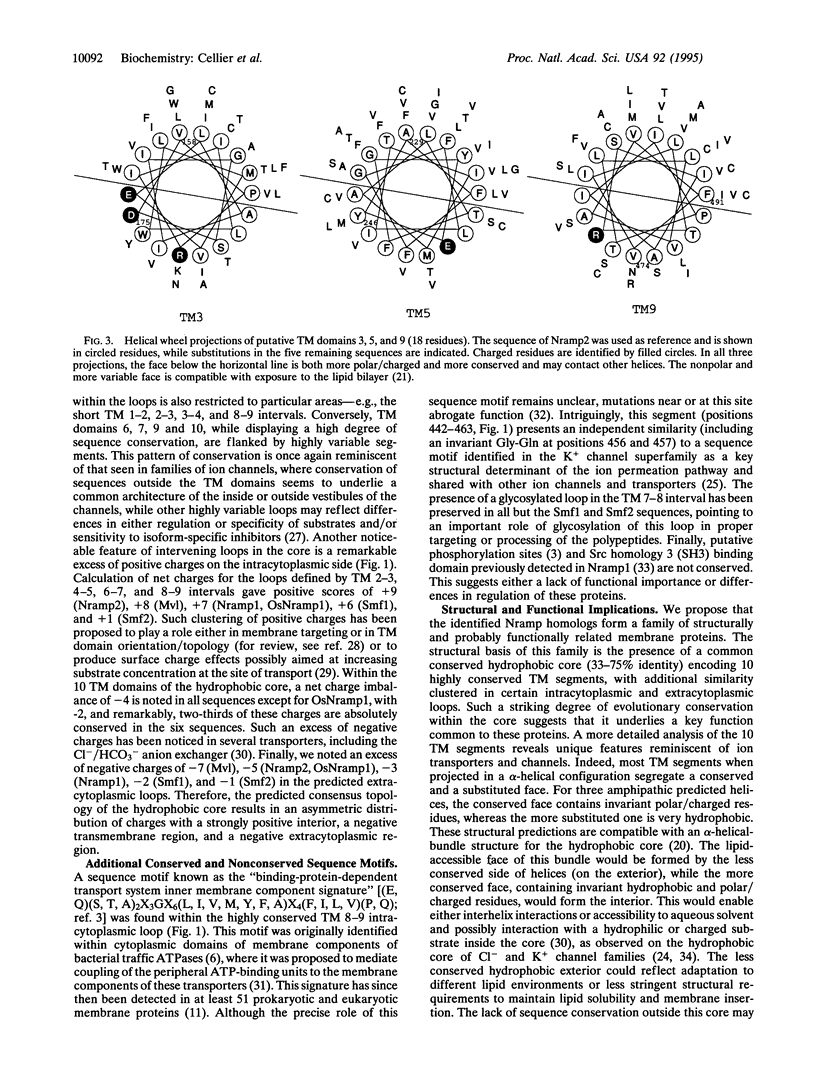
Nramp (natural resistance-associated macrophage protein) is a newly identified family of integral membrane proteins whose biochemical function is unknown. We report on the identification of Nramp homologs from the fly Drosophila melanogaster, the plant Oryza sativa, and the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Optimal alignment of protein sequences required insertion of very few gaps and revealed remarkable sequence identity of 28% (yeast), 40% (plant), and 55% (fly) with the mammalian proteins (46%, 58%, and 73% similarity), as well as a common predicted transmembrane topology. This family is defined by a highly conserved hydrophobic core encoding 10 transmembrane segments. Other features of this hydrophobic core include several invariant charged residues, helical periodicity of sequence conservation suggesting conserved and nonconserved faces for several transmembrane helices, a consensus transport signature on the intracytoplasmic face of the membrane, and structural determinants previously described in ion channels. These characteristics suggest that the Nramp polypeptides form part of a group of transporters or channels that act on as yet unidentified substrates.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bairoch A. The PROSITE dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins, its current status. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3097–3103. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C. H., White J. K., Roach T. I., Blackwell J. M. NH2-terminal sequence of macrophage-expressed natural resistance-associated macrophage protein (Nramp) encodes a proline/serine-rich putative Src homology 3-binding domain. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1683–1687. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley E. M., Wachter C., Schatz G. Putting energy into mitochondrial protein import. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):646–651. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90084-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cellier M., Govoni G., Vidal S., Kwan T., Groulx N., Liu J., Sanchez F., Skamene E., Schurr E., Gros P. Human natural resistance-associated macrophage protein: cDNA cloning, chromosomal mapping, genomic organization, and tissue-specific expression. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1741–1752. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly D., Overington J. P., Ruffle S. V., Nugent J. H., Blundell T. L. Modeling alpha-helical transmembrane domains: the calculation and use of substitution tables for lipid-facing residues. Protein Sci. 1993 Jan;2(1):55–70. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosik J. K., Barton C. H., Holiday D. L., Krall M. M., Blackwell J. M., Mock B. A. An Nramp-related sequence maps to mouse chromosome 17. Mamm Genome. 1994 Jul;5(7):458–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00357010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor P. T., Zhang J. F., Horne W. A., Tsien R. W. Structural determinants of the blockade of N-type calcium channels by a peptide neurotoxin. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):272–275. doi: 10.1038/372272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Fröhlich O. The Na+/H+ exchanger: an update on structure, regulation and cardiac physiology. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):273–285. doi: 10.1042/bj2960273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. N., Andersen O. S. Surface charges and ion channel function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:341–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Cellular mechanisms of genetically controlled host resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1966–1972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenheid S., Cellier M., Vidal S., Gros P. Identification and characterization of a second mouse Nramp gene. Genomics. 1995 Jan 20;25(2):514–525. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80053-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hyde S. C., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Gill D. R., Gallagher M. P. Binding protein-dependent transport systems. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Aug;22(4):571–592. doi: 10.1007/BF00762962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. E., Chuat J. C., Galibert F. A voltage-gated chloride channel in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1994 Sep 30;242(4):595–598. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Potassium channels and their evolving gates. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):119–122. doi: 10.1038/371119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Taylor W. R., Thornton J. M. A model recognition approach to the prediction of all-helical membrane protein structure and topology. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 15;33(10):3038–3049. doi: 10.1021/bi00176a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola R. E., Ames G. F. Topology of the hydrophobic membrane-bound components of the histidine periplasmic permease. Comparison with other members of the family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2329–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo D., Vogan K., Vidal S., Hu J., Cellier M., Schurr E., Fuks A., Bumstead N., Morgan K., Gros P. Haplotype mapping and sequence analysis of the mouse Nramp gene predict susceptibility to infection with intracellular parasites. Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):51–61. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Argos P. Prediction of transmembrane segments in proteins utilising multiple sequence alignments. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 25;237(2):182–192. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigeon R. P., Silver R. P. Topological and mutational analysis of KpsM, the hydrophobic component of the ABC-transporter involved in the export of polysialic acid in Escherichia coli K1. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Dec;14(5):871–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C., Komiya H., Yeates T. O., Allen J. P., Feher G. The bacterial photosynthetic reaction center as a model for membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:607–633. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues V., Cheah P. Y., Ray K., Chia W. malvolio, the Drosophila homologue of mouse NRAMP-1 (Bcg), is expressed in macrophages and in the nervous system and is required for normal taste behaviour. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 3;14(13):3007–3020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Tóth M., Dunten R. L., Gonzalez A., Kaback H. R. Functional interactions between putative intramembrane charged residues in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10547–10551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. A workbench for multiple alignment construction and analysis. Proteins. 1991;9(3):180–190. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkles S. E., Hawker K. L., Grieve C., Campbell E. I., Montague P., Kinghorn J. R. crnA encodes a nitrate transporter in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):204–208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S. M., Malo D., Vogan K., Skamene E., Gros P. Natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90135-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S., Belouchi A. M., Cellier M., Beatty B., Gros P. Cloning and characterization of a second human NRAMP gene on chromosome 12q13. Mamm Genome. 1995 Apr;6(4):224–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00352405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S., Tremblay M. L., Govoni G., Gauthier S., Sebastiani G., Malo D., Skamene E., Olivier M., Jothy S., Gros P. The Ity/Lsh/Bcg locus: natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites is abrogated by disruption of the Nramp1 gene. J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):655–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N., Sarabia V. E., Reithmeier R. A., Kühlbrandt W. Three-dimensional map of the dimeric membrane domain of the human erythrocyte anion exchanger, Band 3. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3230–3235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West A. H., Clark D. J., Martin J., Neupert W., Hartl F. U., Horwich A. L. Two related genes encoding extremely hydrophobic proteins suppress a lethal mutation in the yeast mitochondrial processing enhancing protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24625–24633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane proteins: from sequence to structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:167–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]