Abstract
Objective: The present study is based on an ethnobotanical research project conducted in Hormozgan province that is located in south of Iran, bordering waters of the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea. This survey was carried out in order to recover the ethnobotanical and ethnomedicinal knowledge of the residents of this province. They are using medicinal and functional plants for treating or preventing several diseases.
Materials and Methods: Ethnobotanical data sheets were run with the native inhabitants and people of the province by arranging frequent field trips to different parts of the province and direct interviews with them especially those who were more familiar with the plants and their usage.
Results: A total of 150 plant species belonging to 53 families were recorded for their ethnobotanical and ethnomedicinal uses among the people of province. The records were developed by scientific names, family names, local names, medicinal parts used, different ways of their application, and traditional uses of the plants. There was high compliance in the use of plants in painful disorders, gastrointestinal, and dermatological diseases.
Conclusion: This study revealed that the people of Hormozgan province have a rich knowledge of natural resources. The use and consumption of medicinal plants are still important parts of their life. Rational use of native medicinal plants may benefit and improve their living standards and quality of life. The results of this study can be used as a basis for selecting herbs for further pharmacological, phytochemical, and pharmacognostical studies.
Key Words: Ethnobotany, Hormozgan, Iran, Medicinal Plants, Persian Gulf
Introduction
Ethnobotany, understanding of knowledge systems through using anthropological methods, and ethnomedicine, as its branch are as old as man himself. Ethnobotany and ethnomedicine consider the collection of useful medicinal plants by a group of people and describing different uses of them. Utilizing plants for medicinal purposes has been done since the dawn of man (Namsa et al., 2011 ▶; Oliveira et al., 2011 ▶). Little by little people observed special interesting effects from each plant. Some of these people became experts in treating several ailments and illnesses using efficient plants and then they passed their knowledge to others verbally or by personal experiences (Kunwar et al., 2010 ▶; Zolfaghari et al., 2012 ▶). During this processes some information may be lost, vanished, or forgotten due to the society modernization so in this study we decided to collect these valuable documents and traditional knowledge in one of the southern provinces of Iran, Hormozgan. As a result, we can improve the quality of life and living standards of the native people by rational and standard using of medicinal plants along with effective synthetic drugs (Namsa et al., 2011 ▶; Oliveira et al., 2011 ▶).
Nowadays, almost 80% of world population uses medicinal plants for their primary healthcare needs because they are effective, cheap, and available (WHO, 2007 ▶). About 70,000 plant species are used in traditional medicine and nearly a tenth part of them are used in Asia. Iran which is located in southwest Asia, in the northern hemisphere, contains rich ecosystems and biodiversity due to the various climatic conditions and geographical characteristics (Bhattarai et al., 2010 ▶; Mirdeilami et al., 2011 ▶; Naghibi et al., 2005 ▶). Iran is surrounded by three seas and a passage toward the oceans. The flora of the country contains more than 8000 species and several of them are used in traditional Iranian medicine (Ghahreman, 1973 ▶; Namsa et al., 2011 ▶; Sabzian, 2008 ▶). A few ethnobotanical researches have been done in Iran and there is no previous published records on ethnobotanical knowledge from the Hormozgan province (Amin, 1991 ▶; Ghassemi Dehkordi et al., 2012 ▶; Gholassi Mood, 2008 ▶; Ghorbani, 2005 ▶; Ghorbani et al., 2006 ▶; Mazandarani, 2006 ▶; Miraldi et al., 2001 ▶; Mirdeilami et al., 2011 ▶; Mosaddegh et al., 2012 ▶; Naghibi et al., 2005 ▶; Shams Ardekani et al., 2011 ▶; Sharififar et al., 2010 ▶; Shokri and Safaian, 1993 ▶; Soltanipoor, 2005 ▶; Zolfaghari et al., 2012 ▶).
Geographical and historical overviews
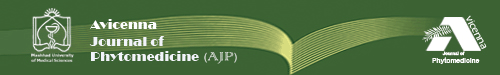
Hormozgan province district is situated in the southeast of Iran (Figure 1). More than 70% of the province is covered by mountains and hills thus it is a mountainous region (IGA, 1983 ▶; Zaeifi, 2001 ▶). The district is bounded by Kerman province in the north and northeast, Fars and Bushehr provinces in the west and northwest and Sistan and Baluchestan province in the east. The southern parts of this province which is surrounded by warm waters of the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea is approximately 900 km. This province is located between northern latitude 25⁰ 24' to 28⁰ 57' and eastern longitude 53⁰ 41' to 59⁰ 15'. It occupies an area of 70697 km2 (IGA, 1983 ▶; Sabzian, 2008 ▶; Mozaffarian, 1991 ▶; Soltanipoor, 2005 ▶; Zaeifi, 2001 ▶).
Figure 1.
Map of the study area (Hormozgan provice, south of Iran, bordering waters of the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea) (Zaeifi, 2001; Sabzian, 2008).
The history of Hormozgan province is mixed with the history and geography of the Persian Gulf. Hormoz straight, one of the today’s most sensitive and vital waterways, is situated in political territory of this province. Bandar-Abbas, Bandar Lengeh, Minab, Bandar Charak, Bandar Jask, Roudan, Khamir, Parsian, Sirik, Hadji-Abad, Kish, Hormoz, Abu-Moosa, and Gheshm islands constitute the famous townships and areas of the province. Bandar Abbas is the capital of Hormozgan province and Gheshm is the largest island of the Persian Gulf (Soltanipoor, 2006 ▶; Sabzian, 2008 ▶; Attar et al., 2004 ▶; Shahi et al., 2011 ▶).
Climate and vegetation types
Three types of climate exist in this province. The natural vegetation is forest, rangeland, and desert. Relatively high humidity, irregular, and little rainfalls with hot weather result in growing some special and native plants. Several of these plants are being used for medical purposes by indigenous people (IGA, 1983 ▶; Soltanipoor, 2005 ▶; Zaeifi, 2001 ▶). The average temperature affected by humidity is moderate and rarely gets higher than 45 ⁰C in summers. In the deserts, the temperature is about 0 ⁰C but there is no frigid weather in winters. The annual rainfall is less than 250 mm and relative humidity is more than 80% (IGA, 1983 ▶; Morid et al., 2001 ▶; Sabzian, 2008 ▶; Zaeifi, 2001 ▶).
There are 900 plant species in the province that too many of them are medicinal. Different climate conditions result in growing of specific plants such as special marine plants and mangrove (Avicennia marina) forests which are very rare (Mozaffarian, 1991 ▶; Soltanipoor, 2005 ▶; Zaeifi, 2001 ▶). Iranian Mangrove forests as unique and highly productive ecosystems of the world were recorded in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea by Eratosthenes, who was a great geographer about 2300 years ago. Iran has the highest acreage of natural mangrove forest (Ghasemi et al., 2010 ▶; Sabzian, 2008 ▶).
Materials and Methods
Data collection and field trips were arranged in order to collect information about traditional and folk knowledge of medicinal plants by the local inhabitants, native practitioners, and old people for the treatment or prevention of several ailments. Direct interviews with local people especially those who were more familiar with the herbs and their usage, were the main method. Ethnobotanical data sheets were used to document the medicinal knowledge by holding the direct interviews with people and gathered information was checked again with the people of other neighboring areas (Bhattarai et al., 2010 ▶; Mosaddegh et al., 2012 ▶; Sharififar et al., 2010 ▶; Zolfaghari et al., 2012 ▶).
All collected plant specimens were dried, pressed and authenticated with the help of available literature and flora (Ghahreman, 1973 ▶; Rechinger, 1982 ▶). After the scientific name identification of the plants, the specimens were deposited in the herbarium of Hormozgan Agricultural and Natural Resource Research Center, Bandar Abbas. The popular names of plants as well as their pronunciations were recorded.
Results
In this paper information of 150 medicinal plant species were collected. This information contains scientific names, family names, local names, medicinal parts used, ways of their application, and traditional uses of them. A part of therapeutic properties of the mentioned plants were found in scientific resources and literature. This could be valuable since people use these plants because of their local useful effects. The information was sorted in Table 1 alphabetically.
| No. | Scientific name | Family name | Local or official name | Part(s) used | Ways of application | Uses/ Ailments treated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Abutilon fruticosum Guill. & Perr. | Malvaceae | Garshem | Flower, leaves, seed | Decoction fresh organ | Wound, acne, pustule, cold, emollient, bronchitis |
| 2. | Abutilon hirtum (Lam.) Sweet | Malvaceae | Sherbejan | Flower, leaves, seed | Decoction fresh organ | Cold, bronchitis, emollient, acne, wound, pustule, wound healing |
| 3. | Abutilon muticum (Delile ex DC.) Sweet | Malvaceae | Kharmalchook | Seed, flower, leaves | Decoction fresh organ | Wound healing, acne, pustule, cold, bronchitis, emollient |
| 4. | Acanthophyllum bracteatum Boiss. | Caryophyllaceae | Chubake bargdar | Root | Brew poultice powder |
Decongestant, diuretic, wound healing, joint pain, sciatica, emmenagogue |
| 5. | Acanthophyllum squarrosum Boiss. | Caryophyllaceae | Chubakeriz | Root | Brew poultice powder |
Cold, joint pain, sciatica, gluteus pain, wound healing, diuretic, kidney stones |
| 6. | Achillea eriophora DC. | Compositae | Benjerashk, berenjasf, sarzatdu | Flower, leaves | Poultice powder | Antipyretic, insects bite, bee bite, snake bite, scorpions bite, wound healing, bleeding |
| 7. | Achillea wilhelmsii C. Koch | Compositae | Gol sarbarze, Sarbarze, sarbarde, sarzard | Aerial parts esp. flower | Decoction powder | Diarrhea, stomachache, fever, bile, anti-parasite, snake bite, scorpions bite, muscle tonic, fatigue in newly delivered ladies, headache, cold |
| 8. | Aerva persica Merr. | Amaranthaceae | Porzu, ethag, gormenaku | Leaves | Powder | Wound |
| 9. | Alyssum homalocarpum Boiss. | Cruciferae | Ghodume | Seed | decoction | Intestine emollient |
| 10. | Ammi majus L. | Umbelliferea | - | Seed | Brew powder |
Flatulency, diuretic, carminative, tonic, digestant, dyspepsia |
| 11. | Amygdalus lycoides Spach | Rosaceae | Kutur, kulem | Aerial parts | Decoction fresh organ | Headache, burning wounds |
| 12. | Amygdalus scoparia Spach | Rosaceae | Badam talkh | Twigs, resin | Decoction fresh organ | Pain of different parts, back pain, foot pain, pertussis |
| 13. | Anagalis arvensis L. | Primulaceae | Gol nili, naem, golbadami, mash koshu, chehm kagu | Aerial parts | Brew poultice decoction |
Nephritis, insect bites, jaundices, diuretic, painful wounds, bile wound healing, expectorant, chest & urination disease |
| 14. | Anchusa italica Retz. | Boraginaceae | Gavzaban, gavzabane koohi | Leaves | Decoction | Cold, sore throat, chest pain |
| 15. | Andrachne aspera Spreng. | Euphorbiaceae | Darmamaron | Stem | Fresh organ | Pterygium |
| 16. | Artemisia Aucheri Boiss. | Compositae | Deraym koohi | Leaves | Fresh organ powder | Stomachache |
| 17. | Artemisia scoparia Waldst. & Kit | Compositae | Salbaku, muleng, omeabid | Leaves | Decoction fresh organ |
Flatulency in children, joint pain & rheumatism, hydrocele |
| 18. | Arundo Donax L. | Gramineae | Ghamish | Root rhisome |
Decoction | Alopecia , diuretic |
| 19. | Astragalus fasciculifolius | Papilionaceae | Gonza, chetat, genjar | Resin | Powder | Cold, fatigue, tightening bone fractures |
| 20. | Astragalus mucronifolius Boiss. | Papilionaceae | Genjarekhari | Root | Decoction | Back pain, bone fracture |
| 21. | Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. | Avicenniaceae | Harra | Fruit Root resin |
Poultice fresh organ |
Snakebite, contraception, sexual stimulant, sexual enhancing, abscess, blotch & wound |
| 22. | Bienteria cycloptera Bunge | Chenopodiaceae | Andere, samsil, samsul | Leaves | Decoction | Hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia |
| 23. | Blepharis persica (Burm.) O. Kuntze | Acanthaceae | Joojadoo, kisedokhtan | Leaves, seed, root | Fresh organ | Appetizing, astringent, energizer, tonic, mental discomforts, diuretic, styptic, anti-inflammatory, antitussive, hepatic and splenic discomforts |
| 24. | Boerhavia diffusa L. | Nyctaginaceae | Shabrangieafshan | Leaves, root |
Fresh organ | Joint pain, appetizing, tonic, expectorant, carminative, diuretic, jaundice, internal inflammation, edema |
| 25. | Brassica Tournefortii Gouan | Cruciferacea | Kalam | Aerial parts | Fresh organ | Food additive, appetizing |
| 26. | Bunium persicum (Boiss.) | Umbelliferae | Zireh | Seed | Decoction powder |
Toxicity, antitussive, decongestant, children earache, newly delivered ladies recovery |
| 27. | Capparis cartilaginea Decne | Capparidaceae | Kavarzeh barg pahn, naloostak | Leaves, fruit | Fresh organ | Rheumatism, joint pain, wounds |
| 28. | Capparis deciduas (Forssk.) Edgew. | Capparidaceae | Kalir | Leaves, twig | Powder | Antipyretic |
| 29. | Capparis spinosa L. | Capparidaceae | Konar eshkal, karaveng, kavarzah | Leaves, fruit | Fresh organ | Joint pain, rheumatism, abdominal pain |
| 30. | Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) | Cruciferae | Looseroo, loosiroo | Leaves, stem, latex | Poultice fresh organ |
Bleeding, superficial inflammations, wound healing |
| 31. | Caralluma edulis Benth. | Asclepiadaceae | Doghabis, howraghu | Stem, succulent stem | Fresh organ | Parasitic diseases, used as vegetable |
| 32. | Caralluma oxyacantha | Compositae | Karajusk, hesk, karala, kharkala | Leaves | Decoction | Kidney pain |
| 33. | Caralluma tuberculata | Asclepiadaceae | Moghmaar, maarangoosh | Succulent stem | Fresh organ | Parasite repellent |
| 34. | Cassia italica (Miller) F.W. Andrews | Caesalpinaceae | Setaap,hashi, kowsen,kowchen, gush ahu , setaag, | Leaves | Powder | Laxative, cathartic |
| 35. | Centaurea Bruguierana (DC.) | Compositae | Balehbord, badavard, badavardeh, kharkharangoo | Leaves, flower | Decoction | Headache, antipyretic, anti-scorpions bite |
| 36. | Centaurium tenuifolium (Hoffm. & Link) Fritsch | Gentianaceae | Ghontorion | Flower, leaves | Brew fresh organ |
Wound healing, hepatic and nephritic distress, jaundice, young girls anemia, diabetes, eczema |
| 37. | Cleome brachycarpa Vahl. ex DC. | Capparidaceae | Glepar, ruzgardesh | Aerial parts esp. leaves & stems | Decoction powder |
Toxicity of snake bite & scorpions bite |
| 38. | Cocculus pendulus (J.R. & G. Forst.) Diels | Menispermaceae | Zamoor, zamer | Root | Decoction | Antipyretic |
| 39. | Convolvulus glomeratus Choisy | Convolvulaceae | Pichak | All parts | Fresh organ | Cathartic |
| 40. | Convolvulus leptocladus Boiss. | Convolvulaceae | Rontazg | Root | Powder | Cathartic |
| 41. | Convolvulus spinosus Burm. | Convolvulaceae | Pichak khari | Flower | Fresh organ | Cathartic, antiparasite |
| 42. | Conyza Canadensis (L.) Cronq. | Compositae | Pirbaharakebagh | Whole plant esp. leaves | Brew | Wound healing, kidney stones, bleeding during menstruation, elimination of female secretions |
| 43. | Corchorus tricularis | Tiliaceae | Katan | All aerial parts | Decoction fresh organ | Emollient |
| 44. | Cornulaca monocantha | Chenopodiaceae | Javen, sekhar, kharune | Leaves | Fresh organ | Snake bite, scorpion bite, bee bite, wound healing |
| 45. | Cotoneaster kotschyi Klotz | Rosaceae | Shirkhesht | Fruit | Decoction | Jaundice, cooling |
| 46. | Cymbopogon Olivieri (Boiss.) Bor | Gramineae | Paashaam, nagerd, zeghbar, maade | Green leaves | Decoction | Cooling, stomachache, bone pain, fever lowering, measles, cold |
| 47. | Cyperus rotundus L. | Cyperaceae | Pizg | Rhizome, root | Decoction fresh organ | Dysentery, diuretic, gastric ailments, diarrhea, menstruation inducer, sweating inducer, parasite repellent, wound healing, pruritus, appetizing |
| 48. | Dalbergia sisso Roxb. | Papilionaceae | Jak | Stem bark | Decoction | Tonic, appetizing, abortion, emollient, indigestion, dysentery, antiparasite |
| 49. | Daphne oleoides Schreb. | Thymelaeaceae | Terbid, terbit | Peel, stem, leaf | Decoction fresh organ | Antipyretic, elimination of the pruritus & pain of a kind of insect bite called sisko |
| 50. | Datura innoxia Miller | Solanaceae | Megena, permengenas, kopakemengenas | Leaves, flower, seed | Decoction brew | Demulcent in asthmatic patients, cutaneous disease, washing swelling feet, antitussive |
| 51. | Demostachia bippinata L. | Graminae | Kertaki, kertah | Root | Fresh organ | Jaundice, peptic discomforts, emesis, nephritic disease, rash, kidney stones |
| 52. | Dionysia revolutea Boiss. | Primulaceae | Esfande mohammadi, gazir, gurzi | Aerial parts | Decoction Fresh organ powder |
Antiseptic, wound healing, gastric distress, stomachache, joint pain, insect bite, emollient in cold, ecchymosis, fatigue |
| 53. | Dodonaea viscose (L.) Jacq. | Sapindaceae | Shahaf, mordang, nader, naterak | Leaves | Fecoction fresh organ |
Headache, bone pain, foot pain, papule & blotch healer |
| 54. | Echinops Aucheri Boiss. | Compositae | Shekar kooh | Resin | Decoction | Emollient in cold & pectoralgia, laxative |
| 55. | Eclipta prostrate (L.) L. | Compositae | Masture khabideh | Aerial parts | Decoction fresh organ | blood purifier |
| 56. | Ephedra major Host | Ephedraceae | Houm | Stem, root, fruit | Decoction | Rheumatism, syphilis, respiratory ailments |
| 57. | Erodium cicutarium (L.) L’Her. | Geraniaceae | Sikh shabgard | Root | Decoction | Toothache |
| 58. | Euphorbia larica Boiss. | Euphorbaceae | Paah, paragh | Latex | Fresh organ | Wound healing |
| 59. | Euphorbia osyridea Boiss. | Euphorbiaceae | Rutazgh | Root | Fresh organ | Constipation |
| 60. | Euphorbia turcomanica Boiss. | Euphorbiaceae | - | Leaves | Fresh organ | Cold |
| 61. | Ferula assa-feotida L. | Umbelliferae | Heng, anghuzeh, angosht gande,engez | Resin or latex, root | Powder | Insect repellent, wound healing, ear ache, antiseptic, parasite repellent |
| 62. | Fortuynia bungei Boiss. | Cruciferae | - | Seed, twig | Fresh organ | Bone pain, joint aches, flatuosity |
| 63. | Francoeuria undulate (L.) Lack | Compositae | Porz, tahre | Leaves | Fresh organ | Children complaints |
| 64. | Fumaria parviflora Lam. | Fumariaceae | Shahtareh, shatareh | Leaves, stem | Decoction | Pain relief, back cramps, infected wound, skin disease, stomachache |
| 65. | Gailonia Aucheri Jaub. Spach | Rubiaceae | Toosoo, boogandoo, titisko, khargol, kartos | Leaves, twig, flower | Fresh organ brew |
Toothache, rheumatism, flatuosity, diarrhea, gonalgia, gnathitis |
| 66. | Geranium rotundifolium L. | Geraniaceae | Suzanuk | Root | Fresh organ | Diarrhea, diuretic, astringent |
| 67. | Gisekia pharnaceoides L. | Molluginaceae | - | All parts | Fresh organ Powder |
Digestant, anti-parasite, wound healing, appetizing, bronchitis, cutaneous discomforts, edema of nose mucous, anti parasite |
| 68. | Glaucium flavum Crantz | Papaveraceae | Shaghayegh shakhdarezard | seed | Powder | Laxative |
| 69. | Glossonema variance Decne | Asclepiadaceae | - | Fruit | Fresh organ | Cooling, digestant |
| 70. | Glycyrrhiza glabra L. | Papilioceae | Shirinbayan, choobshirin, mahak, marah | Leaves, stem, root | Fresh organ decoction | Joint pain, measles, gastric ulcer, duodenum ulcer, cold |
| 71. | Grantia Aucheri Boiss. | Compositae | Halamook, halamoogh, kalmir, talpik nar,kalmuru | Leaves | Fresh organ | Pain |
| 72. | Grewia tenax (Forssk.) Fiori | Tiliaceae | Pootooroo, pootroo | Stem | Decoction | Cough, flank pain |
| 73. | Hammada saliocornica (Moq.) Lijin. | Chenopodiaceae | Zaaz, jar, terat, peshker, rems, jaru | Leaves | Fresh organ decoction | Antipyretic, sensitivity of bees bite, wound healing |
| 74. | Heliotropium bacciferum Forssk. | Boraginaceae | Aftabparast, ramram,defrak, rafetork, debrak, mispara | Aerial parts | Fresh organ | Wound bleeding, wound healing |
| 75. | Heliotropium europaeum L. | Boraginaceae | Kolohmu, balghandu | Leaves, flower, seed, twigs | Brew fresh organ |
Gout, cardiac tonic, headache, kidney stone, worm repellent |
| 76. | Herniaria hirsuta L. | Paranychiaceae | Alafe fatgh kork alud | Aerial parts | Decoction brew | Washing wound & eye, kidney stone, almost all of kidney & bladder diseases, jaundice, female secretion |
| 77. | Hippocrepis unisilliquosa L. | Papilionaceae | Naal asbi | Aerial parts | Fresh organ | Wound healing |
| 78. | Hymenocarpus circinnatus (L.) Savi | Papilionaceae | - | Aerial parts | Fresh organ | Abscess |
| 79. | Hyoscyamus muticus Bornm. | Solanaceae | Bazrolbanj | Seed | Smokes fumes | Toothache |
| 80. | Juniperus excelsa M.B. | Cupressaceae | Ouras, abras, aras, hooras, gazkooh | Leaves, fruit | Decoction fresh organ | Rheumatism, dermal allergies, joint pain, back pain, foot pain, earache, diarrhea |
| 81. | Lagoecia cuminoides L. | Umbelliferae | - | Aerial parts | Fresh organ | Bile stone repellent |
| 82. | Lallemantia royleana Benth. | Lamiaceae | Balangu | Seed | Powder | Gum bleeding, psychotic disease, tonic |
| 83. | Launaea nudicaulis (L.) Hook. f. | Compositae | Kahusa | Leaves | Fresh organ | Fever in children |
| 84. | Launaea procumbens (Roxb.) | Compositae | Bonmoghi , nonak | Leaves | Fresh organ | Urination difficulty in children |
| 85. | Lavandula stricta Del. | Lamiaceae | Ostokhodoos, ghadaar | Aerial parts | Fresh organ decoction |
Rheumatism, cold, bone pain, carminative, abdominal cramps |
| 86. | Leptadenia pyrotechnica (Forssk.) | Asclepiadaceae | Shahm nar, shahm oshtori, garishahk | Aerial parts | Powder | Carminative, wart, cutaneous fungal disease |
| 87. | Lycium Shawii Roemer & Schult | Solanaceae | Dehir, zirok, dish | Twigs, leaves, fruit | Decoction | Gastric ailments, wound healing |
| 88. | Malva parviflora L. | Malvaceae | Zazagh, sholaki | Seed | Decoction | Cold |
| 89. | Mentha longifolia (L.) Hudson | Lamiaceae | Poden, pishe | Leaves, root | Decoction fresh organ brew | Carminative, diarrhea, cold, gastric ailments, stomachache, headache, antipyretic |
| 90. | Mentha mozaffariani Jamzad | Lamiaceae | Poden kuhi | Leaves, twigs | Brew fresh organ |
Cooling, diarrhea, stomachache, headache, carminative |
| 91. | Mesembryanthemum nodiflorum L. | Aizoaceae | Hooshalang, ria, kheizaran, | Aerial parts | Decoction | Hives |
| 92. | Micromeria persica Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Ovshen estaku | Leaves | Decoction | Acute fever, cold, stomachache, bone pain, carminative, abdominal discomforts |
| 93. | Myriophyllum verticallatum L. | Haloragaceae | Partavoosi | Leaves | Fresh organ | Antipyretic, chronic dysentery, children cold |
| 94. | Nannorhops Ritchieana H. Wendl. | Palmae | Daaz | Young leaves | Fresh organ | Diarrhea |
| 95. | Nerium indicum Miller | Apocynaceae | Gish, kharzahreh | Leaves, latex | Fresh organ | Joint pain, gonalgia, foot pain, foot & hand edema remedy |
| 96. | Ochradenus Aucheri Boiss. | Resedaceae | Shahm | Twigs, fruits | Brew decoction fresh organ |
Stomachache, neck pain, pectoralgia |
| 97. | Otostegia Aucheri Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Mesvake joojeh tighi | Root | Brew decoction fresh organ | Hair tonic, strengthening gums, dental cleaning & brightness, prevention of hair loss |
| 98. | Otostegia persica (Burm.) Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Golgoder, gol khari, khoransh, golder | Leaves, flower, thistle | Brew decoction fresh organ |
Cardiac distress, reducing palpitation, regulating blood pressure, laxative, carminative, antipyretic, cough, headache, gastric discomfort, parasite repellent |
| 99. | Pentatropis spiralis (Forssk.) Decne. | Asclepiadaceae | Shahm | Roots | Decoction | Astringent, tonic, cooling, gonorrhea |
| 100. | Pergularia tomentosa L. | Asclepiadaceae | Keshtu,helayah, labashir | Leaves | Powder fresh organ |
Remedy for wounds in scorpions bite, wound healing |
| 101. | Perovskia artemisioides Boiss. | Lamiaceae | - | Seed | Fresh organ | Rash, bone pain |
| 102. | Phragmithes australis (Cav.) Trin. Ex Steud. | Gramineae | Ney, ghalam | Root | Brew | parasitic disease of stomach & intestine, flatulency |
| 103. | Physalis divaricata D. Don. | Solanaceae | Kank | Leaves | Fresh organ | Abdominal pain in children |
| 104. | Pistacia atlantica Desf. | Anacardiaceae | Sogand, bane, gan | Leaves, flower, resin | Decoction fresh organ powder | Acne, diarrhea, septic sore throat, back pain, old wounds, expectorant, infant GI tonic, children flatulency, anti rash, chest pain |
| 105. | Plantago amplexicaulis Cav. | Plantaginaceae | Sialdaneh, danich, lajane, spiosh | Aerial parts | Powder Decoction syrup |
Diarrhea, chest pain, strengthening children skeleton, stomachache, heatstroke, wounds, edema repellent |
| 106. | Platychaete glaucescense (Boiss.) Boiss. | Compositae | Khormakharoo,mangoru, mangolo, kaskekharu | Leaves | Powder decoction | Wound healing, stomachache |
| 107. | Prosopis cineraria (L.) Durce | Mimosaceae | Kahoor | Leaves, flower, resin | Fresh organ powder | Cutaneous fungal disease, wound healing, anemia in pregnant women, diarrhea |
| 108. | Pteropyrum Aucheri Jaub. & Spach | Polygonaceae | Parand, patant, ostaparang, sidaf | Leaves, flower, root, stem | Decoction fresh organ | Bone, hand, leg & Knee pain, toothache, headache, back pain, wound healing, washing wounds |
| 109. | Pycnocycla Aucherana Decne. Ex Boiss. | Umbelliferae | Sagdandan | Leaves, stem | Fresh organ | Back, leg & other part muscles pain |
| 110. | Ranunculus muricatus L. | Ranunculaceae | Alale | Aerial parts | Fresh organ | Antipyretic |
| 111. | Reseda Aucheri Boiss. | Resedaceae | Domroobahi, roogardesh, roozgardesh,gonavak, gararuz, dun eshtoru, gadukh | Leaves | Fresh organ | Remove the toxicity & sensitivity of snake bite, insect bite, scorpions bite |
| 112. | Rhazya stricta Decne. | Apocynaceae | Eshvarak, kheshbarg, isur | Leaves | Decoction fresh organ |
Bone pain, rheumatism, joint pain, toothache, eye pain |
| 113. | Rhizophora mucronata Poir. | Rhizophoraceae | Chandal, chantela | Stem bark | Powder | Wound healing |
| 114. | Rumex dentatus L. | Polygonaceae | Naazdolat | Seed | Decoction | Menstruation regulator, stops bleeding during menstruation |
| 115. | Salvadora persica L. | Salvadoraceae | Chooch, chooj, raak, derakhte mesvak | Leaves, root | Toothpick | Headache, joint pain, cleaning teeth, strengthening gum |
| 116. | Salvia macrosiphon Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Buing | Seed | Powder | Weakness, regulating cardiac action during pregnancy, lethargy after child birth |
| 117. | Salvia Mirzayanii Rech. F. & Esfand. | Lamiaceae | Moortalkh, marve tahl, shir ghanam, mor porzu | Leaves | Powder decoction | Heart burn, diarrhea, emesis, stomachache, abdominal pain, flatulency, cooling, hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, jaundice, joint pain, headache, wound healing, scorpions scurry |
| 118. | Salvia Sharifii Rech. F. & Esfand. | Lamiaceae | Borzoi, borooj, babriz, marmareshk | Seeds | Powder Decoction syrup |
Emollient, cooling, wounds, diarrhea |
| 119. | Samolus Valerandi L. | Primulaceae | Alaf juibari | All parts | Decoction | Astringent |
| 120. | Scorzonera paradoxa Fisch. & C.A. Mey. | Compositae | komboluh | Bulb | Fresh organ | Laxative |
| 121. | Solanum incanum L. | Solanaceae | Limoo aboojahl, limoo torgi, genj torgi, gelgelengak tourgi | Fruit, seed | Decoction | Wound, blotch, pustule treatment |
| 122. | Sonchus asper (L.) Hill | Compositae | Shirtighak | Leaves, root, stem, flower, fruit | Fresh organ | Earache, asthma, chest discomforts, organ inflammation |
| 123. | Sophora mollis (Royle) Backer | Papilionaceae | Talkhak, kalkhak | Root, seed, leaves | Decoction poultice |
Cholera, irregular bile secretion, laxative, cathartic |
| 124. | Stachys inflata Benth | Lamiaceae | Mohrkhari | Leaves | Decoction powder | Stomachache |
| 125. | Suaeda fruticosa (L.) | Chenopodiaceae | Jar, kakol masilela | Leaves | Decoction | Jaundice |
| 126. | Tamarix dioica Roth. | Tamaricaceae | Gaz | Stem bark, gall leafy branches | Poultice | Astringent, diarrhea, dysentery, cough, wound |
| 127. | Tamarix masqatensis Bge. | Tamaricaceae | Gaz, gaze roodkhaneh, gazak | Leaves | Decoction | Joint pain, bone pain, softening muscle |
| 128. | Tanacetum fruticulosum Ledeb. | Compositae | Dermene shah | Leaves | Fresh organ | Stomachache, abdominal pain, flatulency |
| 129. | Taverniera spartea (Burm, f.) DC. | Papilionaceae | Laati, horosh nar | Stem | Decoction | Bone fractures |
| 130. | Tecomella undulate (Roxb.) G. Don. | Bignoniaceae | Anare sheytani, anare aboojahl | Whole plant | Fresh organ | liver and gastrointestinal diseases |
| 131. | Tephrosia persica Boiss. | Papilionaceae | Madkinak, bolbolengu | Leaves | Fresh organ | Scorpions bite, snake bite treatment |
| 132. | Teucrium orientale (L.) | Lamiaceae | Golmaash | Leaves, flower | Decoction | Hoarseness |
| 133. | Teucrium pollium L. | Lamiaceae | Kerishk, kalpuru | Flower, leaves, seed | Powder decoction Fresh organ |
Stomachache, abdominal pain, flatulency, diarrhea, regulating blood pressure, menstruation in newly born ladies, measles, eye pain, headache, scorpions bite, snake bite, wound healing |
| 134. | Teucrium stocksianum Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Kalpure kuhi, krishk daii | Leaves | Decoction Powder Fresh organ |
Stomachache, abdominal pain, flatulency, toxicity, emesis, stomach acidification, regulating blood pressure, lipid lowering, newly born ladies recovery |
| 135. | Trianthema portulacastrum L. | Aizoaceae | Vizakh, gooshe gorbeh | Whole plant | Powder | Cathartic, laxative, anemia, hemorrhoid, polydipsia, inflammation, pain relief, stomach tonic |
| 136. | Tribulus macropterus Boiss. | Zygophyllaceae | Naalook | Leaves, flower, fruit | Decoction | Kidney pain & discomfort |
| 137. | Tribulus terresteris L. | Zygophyllaceae | Kharkhasak, naalook, golezarde khaari | Leaves | Decoction | Kidney pain |
| 138. | Trichodesma africanum (L.) R. Br. | Boraginaceae | Chaarmaahang | Root, leaves | Brew decoction |
Cold, tightening bone fracture, abdominal pain, mouth ulcers, measles, scarlet fever, chickenpox, headache, emollient, chest congestion, children constipation |
| 139. | Vitex agnus-castus L. | Verbenaceae | Bangela | Leaves, fruit, flowering twigs | Brew decoction |
Cold, carminative, energizer, sedative, anticonvulsant, reducing libido |
| 140. | Vitex Negundo L. | Verbenaceae | Bangela | Leaves, root, stem bark | Fresh organ | Toothache, rheumatism, carminative, anti-worm |
| 141. | Vitex trifolia L. | Verbenaceae | Felfel khari, bamplusakh | Seed | Fresh organ | Ant repellent |
| 142. | Withania coagulans (Stocks) Dun. | Solanaceae | Kheshtbargekasergkani | Fruit, seed | Fresh organ | Sedative, diuretic, dyspepsia, flatulency, intestine disorders, emetic, antidote |
| 143. | Withania somnifera (L.) Dun. | Solanaceae | Mayepanir | Fruit | Fresh organ | Migraine, digestive disorders, hypnotic |
| 144. | Zataria multiflora Boiss. | Lamiaceae | Oshen, azgand | Leaves | Powder Brew Fresh organ |
Cold, diarrhea, stomachache, carminative, chest pain, headache, toothache, wound healing, fatigue, antipyretic, bone pain, earache, measles, reducing blood lipid & glucose |
| 145. | Zhumeria Majdae Rech. F. & Wendelbo | Lamiaceae | Moorkhash, marvkhash, moorkhosh | Leaves | Powder Decoction fresh organ | Stomachache |
| 146. | Ziziphora tenuir L. | Lamiaceae | Kakooti, golmoshkoo, ostokhodus, mongorush, hard angoshh | Aerial parts | Brew decoction |
Gastric discomfort, cold, fever, diarrhea |
| 147. | Ziziphus jujuba Mill. | Rhamnaceae | Annab | Fresh fruit, dried fruit | Decoction | Laxative, sedative, diuretic, emollient, chest disease |
| 148. | Ziziphus nummularia (Burm. F.) Wight & Arn. | Rhamnaceae | Ramalik | Leaves, fruit | Decoction Fresh organ |
Acne, sore throat, bleeding gums, joint pain, appetizing, gastric tonic |
| 149. | Zygophyllum qatarense Hadidi | Zygophyllaceae | Shirmerku | Leaves, twigs | Powder Fresh organ |
Wound healing, earache |
| 150. | Zygophyllum simplex L. | Zygophyllaceae | Ghich | Seed, leaves | Brew | Eye disorders, worm killing |
Discussion
There are good network and several phytopharmaceutical industries and a technical wealth of botanical and herbal medicine experts available in Iran, however there has been little effort to document the volume and impact of medicinal plants in this country. More successful efforts are in progress about these fields. The Traditional Medicine Chancellery in the Iranian Ministry of Health and Medical Education was established in 2012 and for the first time in Iranian medical history, offering the postgraduate PhD degrees in Persian traditional medicine and traditional pharmacy sciences in Iranian universities of medical sciences were started from six years ago. Hopes to find more achievements especially in the ethnobotany and ethnomedicine disciplines are flourishing.
By doing this ethnobotanical research and after discussions with the people of Hormozgan province it was learnt that they are very close to the nature like other parts of Iran and the plants listed in the Table 1 are very much used by them for the variety of ailments. The recorded information revealed that the painful ailments, gastrointestinal, and dermatological disorders are in the top list of diseases that are treated by native plants. Plant specimens were belonging to 53 families and the most representative families were Lamiaceae and Compositae with 18 and 17 species, respectively, followed by Papilionaceae, Solanaceae, Asclepiadaceae and Umbelliferae, each with less than ten species.
The ethnobotanical usage of medicinal plants in this is interesting and monopolizing and leads researchers and other medical and pharmaceutical experts to investigate further ethnopharmacological and pharmacognostical investigations (Attar et al., 2004 ▶; Soltanipoor, 2005 ▶; Soltanipoor, 2006 ▶). In this way, some species may be used in herbal drug preparation after the confirmation of their therapeutic efficacy and extraction of their active natural ingredients. Although the indigenous knowledge about plants is very important and useful, clinical trials and pharmacological studies should be done to prove their definite phytotherapical effects (Kazemi et al., 2012 ▶; Kunwar et al., 2010 ▶; Ghassemi Dehkordi et al., 2012 ▶; Zolfaghari et al., 2012 ▶).
During this survey, we completed and compared traditional and folk medicines information using phytotherapeutical and medicinal plants books and literature (Amin, 1991 ▶; BHP, 1983; Boger et al., 2006 ▶; Emami et al., 2010 ▶; IHP, 2002 ▶; PDR, 2000 ▶; WHO, 2007 ▶). The uses of several of these plants are consistent with our latest pharmacognostical and pharmacological findings (Asadipour et al., 2003 ▶; Ghannadi et al., 2000 ▶; Ghannadi et al., 2010 ▶; Ghannadi and Davoodi, 2012a ▶; Ghannadi et al., 2012b ▶; Jaffary et al., 2000 ▶; Jaffary et al., 2004 ▶; Minaiyan et al., 2005 ▶; Mohagheghzadeh et al., 2000a ▶; Mohagheghzadeh et al., 2000b ▶; Mohagheghzadeh et al., 2004 ▶; Sadraei et al., 2003a ▶; Sadraei et al., 2003b ▶; Shams Ardekani et al., 2005 ▶; Soltanipoor et al., 2003 ▶).
There has been relatively little basic research on the plants of Hormozgan province, Iran. This paper indicates that indigenous herbal knowledge is still alive in Iran and local people of Hormozgan province tend to use medicinal herbs and natural health products of their ecosystems for primary healthcare needs.
The ethnobotanical survey of Hormozgan province allowed us to document the persistency of a number of traditional uses of medicinal plants, most of them are unique and original and potentially interesting as a basis for future research works.
Acknowledgment
This article was obtained from a research thesis and proposal from Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences (Reg. No.: 75/83/50). The authors would like to thank the moral and financial supports by this university and Hormozgan Agricultural and Natural Resource Research Center, Bandar Abbas. We are highly grateful to the warm local inhabitants and practitioners of Hormozgan province for their sincere contribution to this study and sharing their wisdom and great treasures of knowledge with the authors.
Conflict of interest
There is not any conflict of interest in this study.
References
- Amin Gh. Popular medicinal plants of Iran. Tehran: Publications of the Iranian Research Institute of Medicinal Plants; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Asadipour A, Rezaei Z, Saberi-Amoli S, Amanzadeh Y, Ghannadi A. Volatile constituents of the aerial parts of Cymbopogon olivieri (Boiss.) Bor. from Iran. J Essent Oil Bear Plant. 2003;6:51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Attar F, Hamzeh’ee B, Ghahreman A. A contribution to the flora of Qeshm island, Iran. Iran J Bot. 2004;10:199–218. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai Sh, Chaudhary RP, Quave CL, Taylor RSL. The use of medicinal plants in the trans-Himalayan arid zone of Mustang district, Nepal. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2010;6:1–11. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-6-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogers RJ, Craker LE, Lange D. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. Dordrecht: Springer; 2006. pp. 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- British Herbal Medicine Association. Bournemouth. British Herbal Pharmacopeia Publications; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Emami SA, Fassihi Sh, Mehregan I, Mohammadpour AH, Taleb AM, Khalili H. Medicinal plants, a complete source book. Vol. 1. Tehran: Andisheh Avar Publications; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahreman A. Flora of Iran in color. 1-24. Tehran: Publications of Forests and Rangelands Research Institute; 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannadi A, Ghassemi N, Sohrabi MJ. Isolation and structural elucidation of Iranian senna flavonoids. Res Med Sci. 2000;5:54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannadi A, Sajjadi SE, Khayat Kashani M, Khayat Kashani M. Vinegar processed Zireh- Evaluation of chemical changes before and after treating of “Bunium persicum”. J Islam Iran Trad Med. 2010;1:217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannadi A, Davoodi N. Miswak tree in Islamic medicine, traditional Iranian medicine and modern medicine. Quarterly J Med History. 2012a;3:123–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannadi A, Rabbani M, Ghaemmaghami L, Malekian N. Phytochemical screening and essential oil analysis of one of the Persian sedges- Cyperus rotundus L. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2012b;3:424–427. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi S, Zakaria M, Abdul-Hamid H, Yusof E, Danehkar A, Rajpar MN. A review of mangrove value and conservation strategy by local communities in Hormozgan province, Iran. J American Sci. 2010;6:329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemi Dehkordi N, Norouzi M, Safaei Aziz A. Collection and evaluation of the traditional applications of some plants of Jandagh. J Islam Trad Med. 2012;3:105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gholassi Mood Sh. A contribution to some ethnobotanical aspects of Birjand flora (Iran) Pak J Bot. 2008;40:1783–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani A. Studies on pharmaceutical ethnobotany in the region of Turkmen Sahra, north of Iran (Part 1)- general results. J Ethnopharm. 2005;102:58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani A, Naghibi F, Mosaddegh M. Ethnobotany, ethnopharmacology and drug discovery. Iran J Pharm Sci. 2006;2:109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Iranian Geographical Administration. Geographical culture of Bandar Abbas villages, Iran. Vol. 122. Tehran: Iranian Ministry of Defence Publications; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Iranian Herbal Pharmacopeia Scientific Committee. Iranian Herbal Pharmacopeia. 1st ed. Tehran: Iranian Ministry of Health and Medical Education Publications; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffary F, Ghannadi A, Siahpoush A. Anti- inflammatory effects of Zataria multiflora Boiss. Res Med Sci. 2000;5:6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffary F, Ghannadi A, Siahpoush A. Antinociceptive effects of hydroalcoholic extract and essential oil of Zataria multiflora. Fitoterapia. 2004;75:217–220. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2003.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi M, Eshraghi A, Yegdaneh A, Ghannadi A. Clinical pharmacognosy- a new interesting era of pharmacy in the third millenium. Daru J Pharm Sci. 2012;20:18. doi: 10.1186/2008-2231-20-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunwar RM, Shrestha KP, Bussmann RW. Traditional herbal medicine in far-west Nepal, a pharmacological appraisal. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2010;6:1–18. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-6-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazandarani M. Ethnobotany and folk pharmaceutical knowledge of the major trees and shrubs in north of Iran. J Plant Sci Res. 2006;1:1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Minaiyan M, Ghannadi A, Salehi E. Anti-ulcerogenic effect of Zataria multiflora Boiss. on cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcer in rats. Iran J Pharm Sci. 2005;1:223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Miraldi E, Ferri S, Mostaghimi V. Botanical drugs and preparations in the traditional medicine of West Azerbaijan (Iran) J Ethnopharmacol. 2001;75:77–87. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(00)00381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirdeilami SZ, Barani H, Mazandarani M, Heshmati GA. Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants in Maraveh Tappe region, north of Iran. Iran J Plant Physiol. 2011;2:327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghzadeh A, Shams Ardekani M, Ghannadi A. Linalool-rich essential oil of Zataria multiflora. Flavour Frag J. 2000a;15:119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghzadeh A, Shams Ardekani M, Ghannadi A. Volatile constituents of callus and flower-bearing tops of Zataria multiflora Boiss (Lamiaceae) Flavour Frag J. 2000b;15:373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghzadeh A, Shams Ardekani M, Ghannadi A, Minaiyan M. Rosmarinic acid from Zataria multiflora tops and in vitro cultures. Fitoterapia. 2004;75:315–321. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2004.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morid S, Ghaemi H, Mir Abolghasemi H, Abediny Evaluation of the HEC-1 model for flood forecasting and stimulation in the Hormozgan province, Iran. J Environ Hydrol. 2001;9:1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mosaddegh M, Naghibi F, Moazzeni H, Pirani A, Esmaeili S. Ethnobotanical survey of herbal remedies traditionally used in Kohgiluyeh va Boyer Ahmad province of Iran. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;141:80–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian V. A short survey of Hormozgan province vegetation (Iran) Mitteilungen der Botanischen Staatssammlung München. 1991;30:417–429. [Google Scholar]
- Nadjafi F, Koocheki A, Ghasemi Arian A. The status of exudate species in Iran and existing challenges in their sustainable utilization. Med Plant Conserv. 2006;12:22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Naghibi F, Mosaddegh S, Motamed M. Labiatae family in folk medicine in Iran- from ethnobotany to pharmacology. Iran J Pharm Res. 2005;2:63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Namsa ND, Mandal M, Tangjang S, Mandal SC. Ethnobotany of the Monpa ethnic group at Arunachal Pradesh, India. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2011;7:1–14. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-7-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira AKM, Oliveira NA, Resende UM, Martins PFRB. Ethnobotany and traditional medicine of the inhabitants of the Pantanal Negro sub-region and the raizeiros of Miranda and Aquidauna, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Brazil J Biol. 2011;71:283–289. doi: 10.1590/s1519-69842011000200007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PDR for Herbal Medicines. Montvale: Medical Economic Publications; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rechinger KH. Flora Iranica. 1-176. Graz: Akademische Druck-u. Verlagsanstalt; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sabzian M. Iran tourism, a complete source book. Tehran: Kamel Publications; 2008. pp. 560–581. [Google Scholar]
- Sadraei H, Ghannadi A, Malekshahi K. Composition of the essential oil of asa-foetida and its spasmolytic action. Saudi Pharm J. 2003a;11:136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sadraei H, Ghannadi A, Taki-bavani M. Effects of Zataria multiflora and Carum carvi essential oils and hydroalcoholic extracts of Passiflora incarnata, Berberis integerrima and Crocus sativus on rat isolated uterus contractions. Int J Aromather. 2003b;13:121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Shahi M, Hosseini A, Shemshad K, Rafinejad J. The Occurrence of Red-Black Spider Latrodectus hasselti (Araneae: Theridiidae) in Bandar Abbas, Southern Part of Iran. Iran J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2011;5:63–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shams Ardekani M, Ghannadi A, Badr P, Mohagheghzadeh A. Biotransformation of terpenes and related compounds by suspension culture of Glycyrrhiza glabra L.(Papilionaceae) Flavour Frag J. 2005;20:141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shams Ardekani M, Mohebbi A, Shajari E. A survey of Iranian ethnomedicine. Tehran: Sahbaye Danesh Publications; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharififar F, Koohpayeh A, Mehdi Motaghi M, Amirkhosravi A, Puormohseni Nasab E, Khodashenas M. Study the ethnobotany of medicinal plants in Sirjan, Kerman province, Iran. J Herbal Drug. 2010;1:19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shokri M, Safaian N. The study of medicinal plants in Mazandaran (northern Iran) Acta Horticulturae. 1993;333:165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanipoor MA, Moradshahi A, Rezaei M, Barazandeh MM. The comparison of constituents of essential oils of Zhumeria majdae at different stages. Pajouhesh and Sazandegi. 2003;60:88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanipoor MA. Medicinal plants of the Geno protected area. Pajouhesh and Sazandegi. 2005;68:27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanipoor MA. Introduction to the Flora, life form and chronology for Hormoz island plants, S. Iran. Rostaniha. 2006;7:19–32. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO monographs on selected medicinal plants. Geneva: WHO Publications; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zaeifi M. The flora of Hormozgan province. Vol. 1. Bandar Abbas: Research Center of Agriculture and Natural Resources Publications; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari B, Sadeghi M, Tiri I, Yousefali Tabar M. Collection, identification and evaluation of the traditional applications of some plants of Babol. J Islam Iran Trad Med. 2012;3:113–123. [Google Scholar]