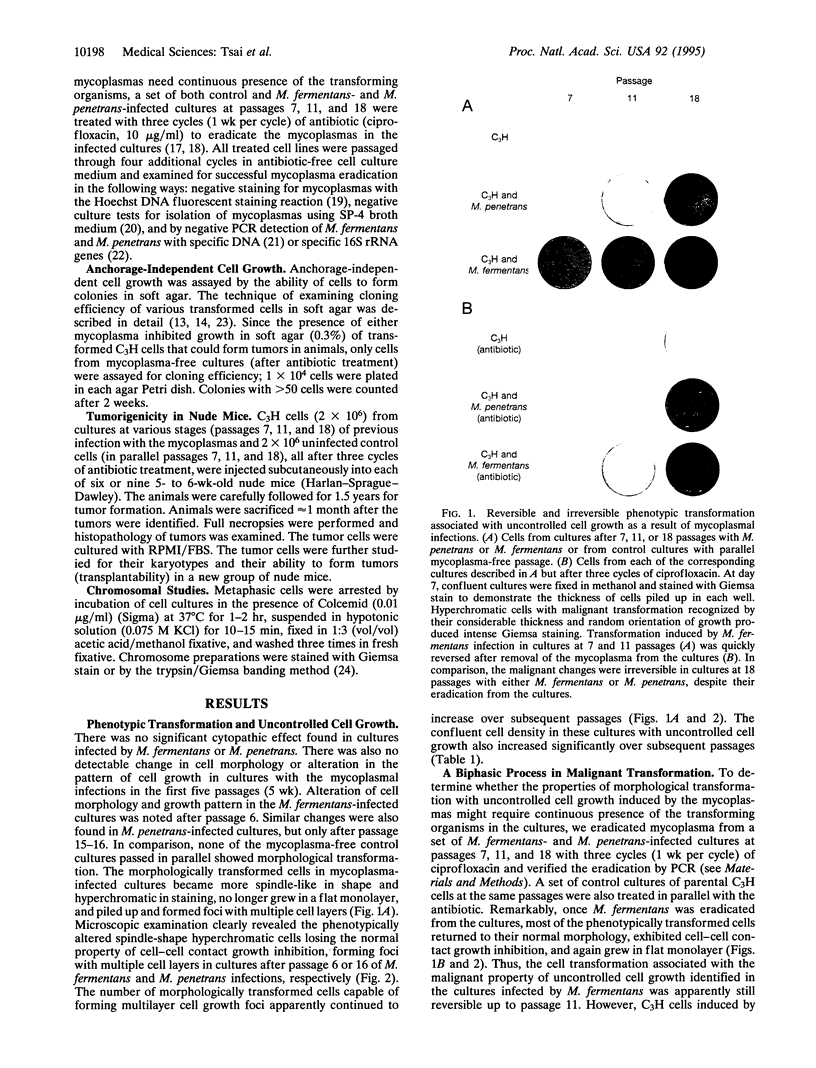
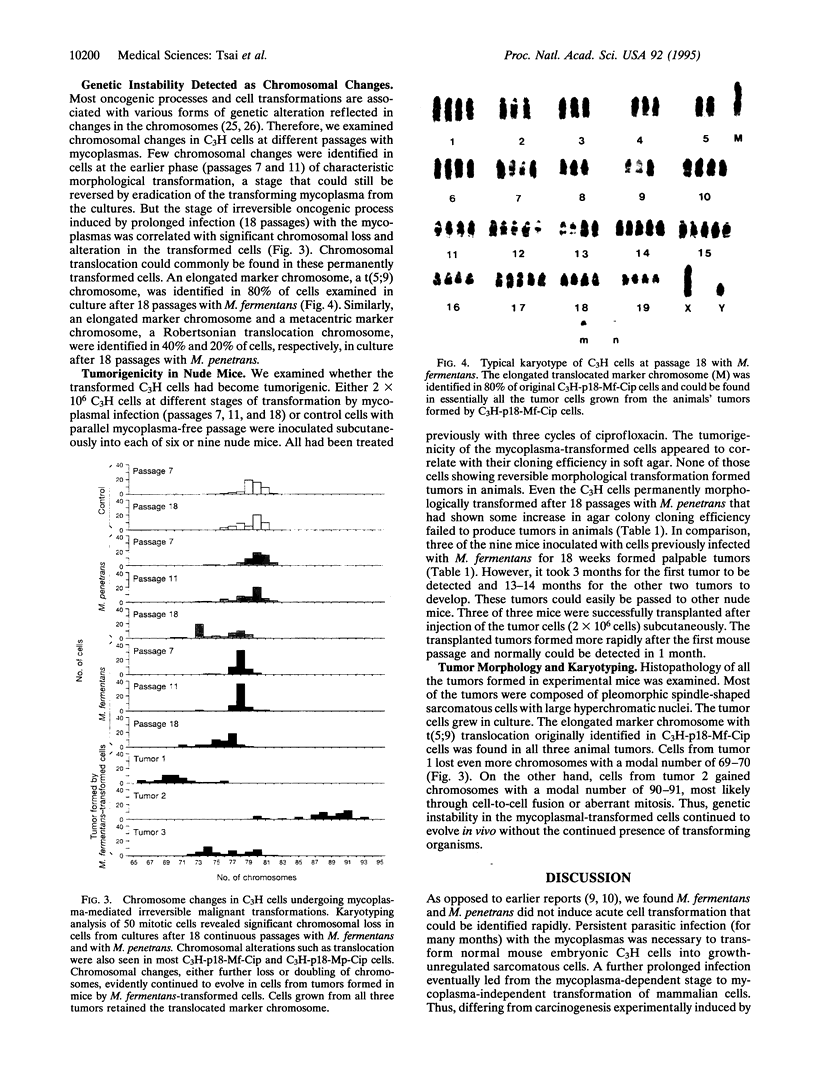
Abstract
Oncogenic potential of human mycoplasmas was studied using cultured mouse embryo cells, C3H/10T1/2 (C3H). Mycoplasma fermentans and Mycoplasma penetrans, mycoplasmas found in unusually high frequencies among patients with AIDS, were examined. Instead of acute transformation, a multistage process in promotion and progression of malignant cell transformation with long latency was noted; after 6 passages (1 wk per passage) of persistent infection with M. fermentans, C3H cells exhibited phenotypic changes with malignant characteristics that became progressively more prominent with further prolonged infection. Up to at least the 11th passage, all malignant changes were reversible if mycoplasmas were eradicated by antibiotic treatment. Further persistent infection with the mycoplasmas until 18 passages resulted in an irreversible form of transformation that included the ability to form tumors in animals and high soft agar cloning efficiency. Whereas chromosomal loss and translocational changes in C3H cells infected by either mycoplasma during the reversible stage were not prominent, the onset of the irreversible phase of transformation coincided with such karyotypic alteration. Genetic instability--i.e., prominent chromosomal alteration of permanently transformed cells--was most likely caused by mutation of a gene(s) responsible for fidelity of DNA replication or repair. Once induced, chromosomal alterations continued to accumulate both in cultured cells and in animals without the continued presence of the transforming microbes. Mycoplasma-mediated multistage oncogenesis exhibited here shares many characteristics found in the development of human cancer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Parsonnet J. Parasitism by the "slow" bacterium Helicobacter pylori leads to altered gastric homeostasis and neoplasia. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):4–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI117336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. E., Riches A. C. Oncogenic transformation of murine C3H 10T1/2 cells resulting from DNA double-strand breaks induced by a restriction endonuclease. Br J Cancer. 1989 Dec;60(6):852–854. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Scrable H. J., James C. D. Molecular genetics of human cancer predisposition and progression. Mutat Res. 1991 Apr;247(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. S., Hayes M. M., Wang R. Y., Armstrong D., Kundsin R. B., Lo S. C. Detection and isolation of Mycoplasma fermentans from urine of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993 May;117(5):511–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGH J., FOGH H. CHROMOSOME CHANGES IN PPLO-INFECTED FL HUMAN AMNION CELLS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:233–238. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau O., Kovacic R., Griffais R., Montagnier L. Development of a selective and sensitive polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Mycoplasma pirum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Feb 1;106(3):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han A., Elkind M. M. Transformation of mouse C3H/10T1/2 cells by single and fractionated doses of X-rays and fission-spectrum neutrons. Cancer Res. 1979 Jan;39(1):123–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. M., Foo H. H., Kotani H., Wear D. J., Lo S. C. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility testing of different strains of Mycoplasma fermentans isolated from a variety of sources. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2500–2503. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. M., Foo H. H., Timenetsky J., Lo S. C. In vitro antibiotic susceptibility testing of clinical isolates of Mycoplasma penetrans from patients with AIDS. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Jun;39(6):1386–1387. doi: 10.1128/aac.39.6.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A. R., Fox M., Murphy G., Little J. B. Relationship between x-ray exposure and malignant transformation in C3H 10T1/2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7262–7266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani H., Phillips D., McGarrity G. J. Malignant transformation of NIH-3T3 and CV-1 cells by a helical mycoplasma, Spiroplasma mirum, strain SMCA. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Dec;22(12):756–762. doi: 10.1007/BF02621093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Baker H. J., Overcash R. G., Cassell G. H., Hunt C. E. Murine chronic respiratory disease. Significance as a research complication and experimental production with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):675–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Shih J. W., Newton P. B., 3rd, Wong D. M., Hayes M. M., Benish J. R., Wear D. J., Wang R. Y. Virus-like infectious agent (VLIA) is a novel pathogenic mycoplasma: Mycoplasma incognitus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Nov;41(5):586–600. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothe R. A., Peltomäki P., Meling G. I., Aaltonen L. A., Nyström-Lahti M., Pylkkänen L., Heimdal K., Andersen T. I., Møller P., Rognum T. O. Genomic instability in colorectal cancer: relationship to clinicopathological variables and family history. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 15;53(24):5849–5852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson I., Russell W. Transformations in hamster cells mediated by mycoplasmas. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1343–1345. doi: 10.1038/2101343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarrity G. J., Vanaman V., Sarama J. Cytogenetic effects of mycoplasmal infection of cell cultures: a review. In Vitro. 1984 Jan;20(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02633326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Hansen S., Rodriguez L., Gelb A. B., Warnke R. A., Jellum E., Orentreich N., Vogelman J. H., Friedman G. D. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 5;330(18):1267–1271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405053301803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton G. R., Jacobs J. P., Perkins F. T. Chromosome changes in human diploid-cell cultures infected with Mycoplasma. Nature. 1965 Jul 3;207(992):43–45. doi: 10.1038/207043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Human tumor suppressor genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:615–657. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Shih J. W., Grandinetti T., Pierce P. F., Hayes M. M., Wear D. J., Alter H. J., Lo S. C. High frequency of antibodies to Mycoplasma penetrans in HIV-infected patients. Lancet. 1992 Nov 28;340(8831):1312–1316. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92493-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Shih J. W., Weiss S. H., Grandinetti T., Pierce P. F., Lange M., Alter H. J., Wear D. J., Davies C. L., Mayur R. K. Mycoplasma penetrans infection in male homosexuals with AIDS: high seroprevalence and association with Kaposi's sarcoma. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;17(4):724–729. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.4.724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1138–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1659741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K. Mycoplasmas in the AIDS spotlight. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):682–683. doi: 10.1126/science.2333519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster D. H. Mouse chromosomes identified by trypsin-Giemsa (T-G) banding. Cytogenetics. 1972;11(5):379–387. doi: 10.1159/000130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]