Abstract
Tumor growth and metastasis are responsible for most cancer patients' deaths. Here, we report that eupolyphaga sinensis walker has an essential role in resisting hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. Compared with proliferation, colony formation, transwell assay and transplantable tumor in nude mouse in vitro and vivo, eupolyphaga sinensis walker extract (ESWE) showed good inhibition on the SMMC-7721 cell growth and metastasis. Using genome-wide microarray analysis, we found the down-regulated growth and metastasis factors, and selected down-regulated genes were confirmed by real-time PCR. Knockdown of a checkpoint PKCβ by siRNA significantly attenuated tumor inhibition and metastasis effects of ESWE. Moreover, our results indicate ESWE inhibits HCC growth by not only downregulating the signaling of PKCβ, Akt, m-TOR, Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1, but also increasing cyclin D1 protein levels and decreasing amount of cyclin E, cyclin B1 and cdc2 of the cycle proteins. At the same time, ESWE reduced MMP2, MMP9 and CXCR4, PLG, NFκB and P53 activities. Overall, our studies demonstrate that ESWE is a key factor in growth and metastasis signaling inhibitor targeting the PKC, AKT, MAPK signaling and related metastasis signaling, having potential in cancer therapy.
Tumor cell proliferation is closely related to the cell cycle and tumor cell metastasis, and therefore induction of cell cycle arrest and inhibition on metastasis are an effective method of controlling tumor cell growth1. Tumor metastasis is a complex process involving several key steps, during the process, tumor cell migration and invasion are the two critical steps and responsible for the entry of tumor cells into blood vessels and lymph nodes2. These include cell adhesion, invasion, proliferation and vessel formation3. There are various molecular players and signaling cascades involved in the proliferation and metastasis pathway, such as the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phospholipase-Cγ/protein kinase C (PLCγ/PKC) pathway, cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and endogenous CXC chemokine receptor-4(CXCR4), etc. These signaling pathways regulate important cellular functions including cellular proliferation, migration, cell cycle and apoptosis4,5.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common solid tumor in the world and the third most common cause of cancer mortality6. Despite significant advances in early detection and therapy, HCC is still one of the leading causes for cancer-related death worldwide7. Tumor recurrence in HCC can occur as metastases, whereas more than 90% of HCC-related deaths are the result of secondary local or distant diseases. Systemic pharmacotherapy is the main treatment for those patients. Recently, drugs targeting key pathways have generated new perspectives in the field of the treatment of HCC6.
However, efficacious or curative drug therapy for HCC and its metastases remains elusive7. There is an urgent need for more effective agents for the clinical management of HCC. Many traditional Chinese herbs are promising drugs for cancer therapy because of both their potential as chemopreventive agents and their chemotherapeutic activities against HCC in experimental studies8. Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker (ESW) is one of numerous insects commonly used as a food and has been used in Chinese traditional medicine for a long time9. As a spice in southeast Asia, including China, Thailand, India and Malaysia10, it has been used to treat many different diseases such as ecchymoma, post-traumatic wounds, hepatic fibrosis and tumors in clinical practice11. Previous studies have demonstrated that ESW has potential in curing leukemia by removing blood stasis and promoting blood circulation from the perspective of Chinese medicine12. But, there have been few reports about its inhibition on HCC. The present study aimed to extend the previous study of ESW and to evaluate its inhibition on HCC growth through arrest cell cycle and metastasis inhibition using proliferation, colony formation, transwell assay, siRNA assay and transplantable tumor in nude mouse in vitro and in vivo. All the results suggest that ESW could inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma activity by regulating PKC, AKT, MAPK signaling and related metastasis signaling, and be a useful therapeutic candidate for HCC intervention.
Results
ESWE suppressed liver cancer cell proliferation and colony formation
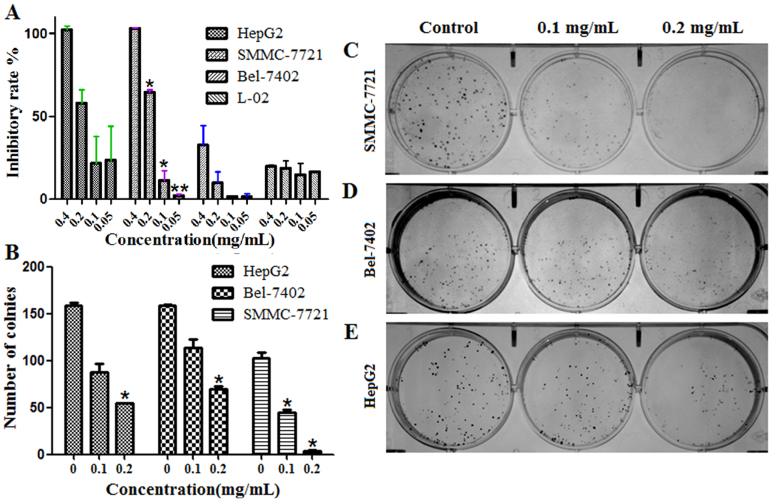
To evaluate the effect of ESWE on liver cancer cells, we observed its action on cell proliferation and colony formation. The results showed that ESWE significantly inhibited cell proliferation in SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cells. The IC50 was 0.13 mg/mL, 0.14 mg/mL and 0.67 mg/mL, respectively, and the IC50 of L-02 cell was 45.42 mg/mL (Figure 1A). In colony formation assay, upon 10 ~ 15 days continuous culture, ESWE suppressed colony formation of SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cells, and ESWE showed good inhibition on the colony formation of SMMC-7721 cells related to cells of BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cells (Figure 1B–E). These findings indicate that ESWE has potential anti-tumor properties in hepatocarcinogenesis but no obvious inhibition on normal cells.
Figure 1. ESWE suppressed liver cancer cell proliferation and colony formation.
(A) Cells were treated by ESWE for 48 h at 0.05, 0.10, 020 mg/mL. ESWE inhibited SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cells growth in vitro, and had no obvious inhibition on L-02 cell. (B–E) Effect on colony formation of SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and Hep G2 by ESWE. (B) Quantitation data of (C–E). (C–E) The representative colony formation picture of SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cell. ESWE showed better inhibition on the colony formation of SMMC-7721 than BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cells. Data were expressed as means ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the untreated control group.
ESWE inhibits tumor growth in vivo
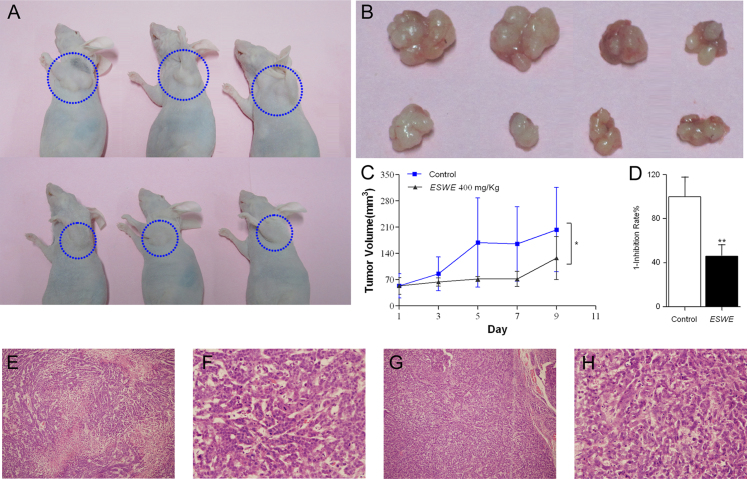
To further assess the effect of ESWE on tumor growth in vivo, human tumor models xenografted in athymic mice were used (Figure 2A). The anticancer effects of ESWE against SMMC-7721 transplantation tumor are shown in Figure 2B–D. Compared with the untreated group, the results showed that treatment with ESWE resulted in significant reduction of tumor weight (the mean tumor weight were 0.54 g in the untreated group and 0.2475 g in the treated group, respectively), inhibiting tumor growth at a rate of 54.16% at 400.0 mg/kg. Furthermore, there was no change in athymic mice body weight during the experiment. The H/E staining (Figure 2E–H) showed that the tumor cells in the tissue of the control group grew fast and caused necrosis, and more mitosis in the control group indicated cell proliferation was faster than that in the ESWE treated group. So, the HE staining proves that ESWE could inhibit cell proliferation.
Figure 2. Regression of live cancer xenograft by ESWE.
SMMC-7721 cells were subcutaneously injected on the right hinge region of athymic nude mice. Mice were regularly observed for appearance of tumor. (A) The representative xenografts of SMMC-7721 human liver cancer in control and ESWE-treated mice. (B) The transplantable tumor, upper row is control group tumor and lower row is ESWE-treated group tumor. (C) Effect of ESWE on the tumor volume growth curve. (D) ESWE inhibited tumor growth by tumor weight. The caused necrosis in the control group (E) and ESWE-treated group (F) mice tissue by the HE staining. Effect of ESWE on the mitosis in the control group (G) and ESWE-treated group (H) mice tissue by the HE staining (400× magnification). Data were expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the control group.
Differentially expressed genes in control and ESWE-treated cells
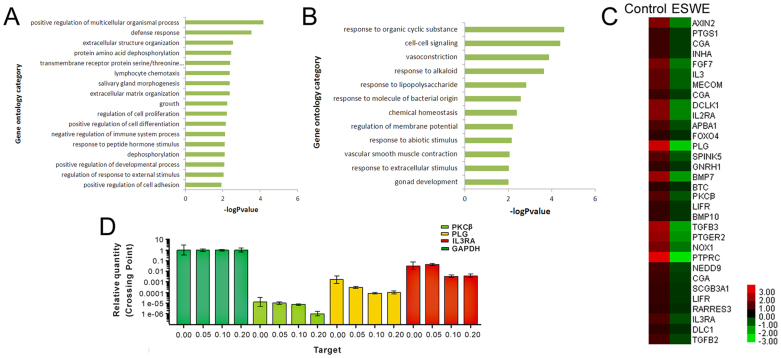
To gain insights into the mechanisms of ESWE on inhibition to HCC, SMMC-7721 cells were cultivated in the absence or presence of 0.1 mg/mL ESWE for 48 h, followed by the Agilent Whole Human Genome Oligo Microarray. A group of differentially expressed genes obtained from the primary analysis were analyzed by GO enrichment and decrease pathway analysis, respectively. Among the down-regulated genes in ESWE-treated cells, regulation of multicellular organismal process, defense response, extracellular structure organization, protein amino acid dephosphorylation, transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway, salivary gland morphogenesis, lymphocyte chemotaxis, extracellular matrix organization, growth, regulation of cell proliferation, positive regulation of cell differentiation, negative regulation of immune system process, dephosphorylation, response to peptide hormone stimulus, positive regulation of developmental process, regulation of response to external stimulus, positive regulation of cell adhesion are shown in Figure 3A. The GO enrichment analysis revealed that the main GO categories for the up-regulated genes in ESWE-treated cells included response to organic cyclic substance, cell-cell signaling, vasoconstriction, response to alkaloid, response to lipopolysaccharide, response to molecule of bacterial origin, chemical homeostasis, regulation of membrane potential, response to abiotic stimulus, vascular smooth muscle contraction, response to extracellular stimulus, gonad development and so on, as summarized in Figure 3B.
Figure 3. The genetically different populations by ESWE for SMMC-7721 cells.
(A) The GO category for the down-regulated genes in ESWE group compared with control group. (B) The GO category for the up-regulated genes in the ESWE group compared with the control group. –logPvalue ≥ 2 was used as a cut-off threshold to select significant GO categories. The higher the enrichment, the more significant the biological processes. (C) Hierarchical cluster analysis of 32 differentially down-regulated expressed genes for cell growth and metastasis in samples. Each column represents one sample, and each gene was depicted by one row, where red denotes an increase in gene expression and green denotes a decrease in gene expression as compared with the other group. The brighter the color, the higher the gene expression level. (D) Comparison of PKCβ, PLG and IL3RA gene expression levels between control and ESWE group by real-time PCR, which confirmed the microarray analysis. Data were expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the control group.
A heat map with two-dimensional hierarchical clustering revealed 32 genes differentially expressed between the two groups, which were down-regulated and related to growth, proliferation and metastasis, as illustrated in Figure 3C. The total genes were found to be differentially expressed between control and ESWE-treated cells at p < 0.05, and fold-change ≥ 2. In this experiment, the genes responsible for growth, proliferation and metastasis were most important to match our research goal. The analysis of our microarray data showed that PLG, PKCβ and IL3RA genes, associated with growth, proliferation and metastasis, were down-regulated in ESWE-treated cells as compared with the control cells. The PLG, PKCβ and IL3RA genes confirmation of microarray analysis was determined by real-time PCR (Figure 3D).
ESWE arrested cell cycle and regulated related cycle proteins
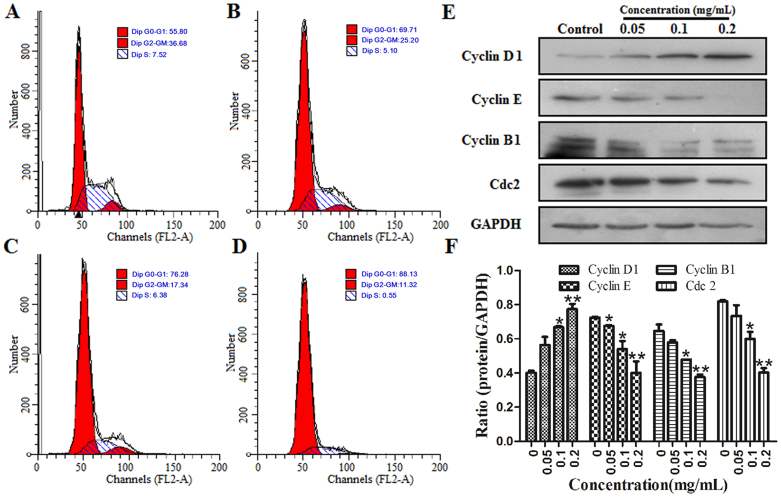
The effect of ESWE on cell cycle profile was analyzed using PI staining and flow cytometry analysis. Cells were treated without ESWE or with ESWE at 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 mg/mL for 48 h and stained with propidium iodide. As shown in Figure 4A–D, treatment of ESWE induced an accumulation of SMMC-7721 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. The population of untreated cells in phase G1 was 55.8%, whereas the population of cells in phase G1 treated with ESWE at 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 mg/mL was 69.71%, 76.28% and 88.13% respectively, showing a dose-dependent increase. A decrease in the population in the G2-GM and S phases was also observed.
Figure 4. ESWE arrested SMMC-7721 cell cycle at the G1 phase.
Cells were treated with ESWE for 48 h and stained with PI. The cells were then analyzed by FACS. (A) Control. (B) 0.05 mg/mL. (C) 0.1 mg/mL. (D) 0.2 mg/mL. Data were expressed as percentage of cell population in G0-G1, S and G2-M phases of the cell cycle (n = 3). (E) Effect of ESWE on cycle proteins expression of Cyclin D1, Cyclin E, Cyclin B and Cdc2 by western blot analysis. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 4E. (F) Quantitation data of (E). ESWE decreased the protein expressions of Cyclin E, Cyclin B and Cdc2 expressions, and increased Cyclin D1 expression in a dose-dependent manner compared to the untreated control. Data were expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the control group.
To elucidate the specific cell cycle regulatory proteins responsible for the cell cycle arrest, we explored the effect of ESWE on regulatory protein molecules including cyclin D1, cyclin E, and cyclin B1, which are cyclins required for advance from G1 to S, S to G2, G2 to G1 respectively. Meanwhile, we investigated the effect of ESWE on cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2. As shown in Figure 4E–F, the levels of cyclin D1 protein gradually increased with ESWE at the concentrations of 0.05–0.2 mg/mL. In contrast, the amount of cyclin E, cyclin B1 and cdc2 was significantly down-regulated in ESWE-treated cells. These data suggest that these cell cycle regulatory molecules are involved in ESWE-induced changes in cell cycle progression.
Effect of ESWE on cell growth signaling pathway
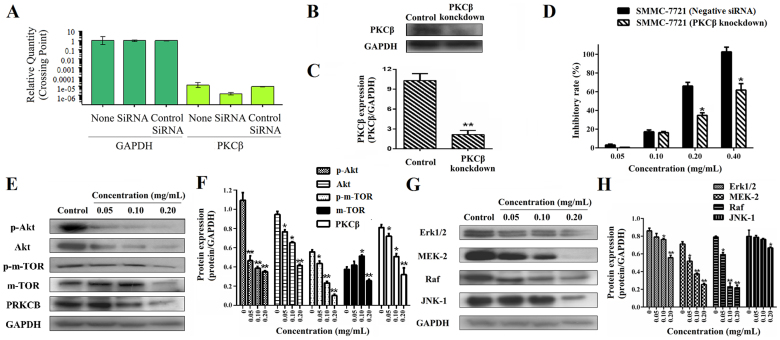
In order to clarify the inhibition and mechanism on the HCC growth by ESWE, we investigated the effect on PKCβ, Akt, P-Akt, m-TOR, P- m-TOR, Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1 expression of growth signaling pathway, and carried out the siRNA assay on the PKCβ gene in SMMC-7721 cells (Figure 5A–C). We also compared the proliferation between normal cells and knockdown of PKCβ in SMMC-7721 cells, and found that there was an obvious difference in the two groups, knockdown of PKCβ significantly reduced the inhibition of ESWE on the growth of SMMC-7721 cells, as compared with the control groups transfected by a negative control shRNA (shRNA-NC) and control (P < 0.05, Figure 5D). It indicates PKCβ is a key target and could affect cell growth by ESWE. Besides, ESWE inhibited the expressions of PKCβ, Akt, P-Akt, m-TOR and P-m-TOR in the PI3K/AKT pathway (Figure 5E and F) and Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1 in the Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway (Figure 5G and H) in a dose-dependent manner.
Figure 5. ESWE inhibited cell growth and decreased protein expressions of Akt, P-Akt, m-TOR, P-m-TOR, PKCβ, and Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1 involved in cell growth.
PKCβ knockdown affects the ESWE's anti-proliferation on SMMC-7721 cells. PKCβ mRNA expression (A) and protein expression (B and C) in SMMC-7721 cells transfection with 80 nM PKCβ siRNA using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent and SMMC-7721 cells (wild type) were determined by RT-PCR analysis and western blot assay. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 5B. Transfection with a control siRNA construct served as a negative control. Data represents the means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus the PKCβ expression in SMMC-7721 cells. (D) Effect of ESWE on cell proliferation in SMMC-7721 cells (wild type) and knockdown cells by MTT assay. After treated with PKCβ siRNA for 24 h, cells were treated with ESWE for 48 h. Data represents the means ± SD from three repeated experiments. Five wells were treated in each experiment. (E) Bands were corresponding to Akt, P-Akt, m-TOR, P-m-TOR, PKCβ and GAPDH in SMMC-7721 cells. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 5E. (F) Results were quantified by densitometry analysis of the bands form (E) and then normalization to GAPDH protein. (G) Bands were corresponding to Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf, JNK-1 and GAPDH in SMMC-7721 cells. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 5G. (H) Results were quantified by densitometry analysis of the bands form (G) and then normalization to GAPDH protein. Quantitation data showed ESWE decreased the proteins levels involved in cell growth in a dose-dependent manner compared to the untreated control. Values were expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, vs. control.
Effect of ESWE on cell migration signaling pathway
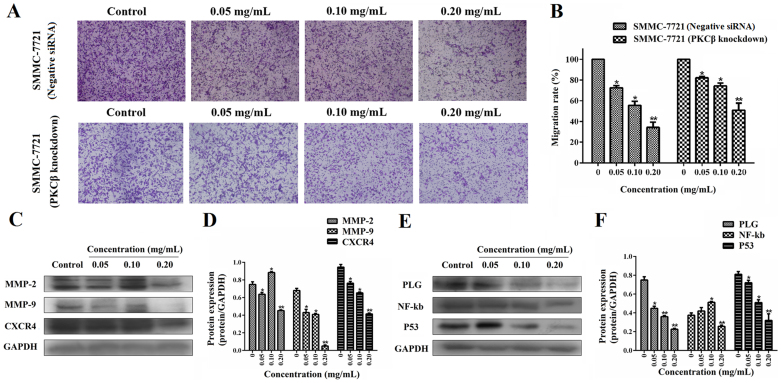
To evaluate the effect on cell migration between normal SMMC-7721 cells and PKCβ knockdown cells, we observed the inhibition on cell mobility by transwell system. The results showed that treatment of ESWE significantly decreased the migration ability at the concentrations of 0.05–0.20 mg/mL, respectively, and the knockdown of PKCβ significantly reduced the inhibition on the migration of SMMC-7721 cells, as compared with the control groups (P < 0.05, Figure 6A and B). It indicates PKCβ is also a key factor in the cell migration by ESWE. Figure 6C–D showed that MMP2, MMP9 and CXCR4 protein expressions were strongly decreased in SMMC-7721 cells compared to that of control cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, the related protein PLG, NFκB and P53 of growth and metastasis were down-regulated by treatment of ESWE (P < 0.05, Figure 6E and F).
Figure 6. Dose-response study of ESWE on the migration of cells transfected with siRNA of PKCβ and normal SMMC-7721 cell in vitro.
(A) Photographs of the knockdown cell and wide type cell migration through the polycarbonate membrane stained by 0.2% crystal violet. (B) Quantification of the number of cells (transfected with siRNAs of PKCβ and wide type cells) migrating through the polycarbonate membrane. Data represents the means ± SD from three repeated experiments. Five wells were treated in each experiment. (C) Bands were corresponding to MMP-2, MMP-9, CXCR4 and GAPDH in SMMC-7721 cells. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 6C. (D) Results were quantified by densitometry analysis of the bands form (C) and then normalization to GAPDH protein. (E) Bands were corresponding to PLG, NF-kb, P53 and GAPDH in SMMC-7721 cells. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 6E. (F) Results were quantified by densitometry analysis of the bands form (E) and then normalization to GAPDH protein. Quantitation data showed ESWE decreased the proteins levels involved in cell migration in a dose-dependent manner compared to the untreated control. Values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, vs. control.
Discussion
Although the extract eupolyphaga sinensis walker has been used for treating various human diseases, few are related to the effect on HCC, and its anti-tumor mechanism is largely unknown. The current study focuses on the evaluation of its inhibition on HCC growth through arrest cell cycle and metastasis inhibition. In this study, we showed that ESWE had a good inhibitory effect on liver cancer growth in vivo and in vitro. The molecular mechanism, in which ESWE affects cell cycle and metastasis, involves the regulation of cycle proteins, proliferation and cell migration signaling pathway.
Through in vivo and in vitro assays (Figure 1 and Figure 2), ESWE displayed good inhibition on cell proliferation, colony formation and transplantation tumor growth. To gain insights into the mechanisms of ESWE on inhibition to HCC, microarray analysis of Agilent microarray-based gene expression profiling was used to screen the potential targets and signaling pathways (Figure 3). The major findings in microarray analysis were that the differentially expressed genes associated with growth and migration were obtained, such as PLG, PKCβ and IL3RA, the selected down-regulated genes were confirmed by real-time PCR. The genes responsible for growth, proliferation and metastasis were most important to match our research goal. So we carried out potential signaling pathways analysis by ESWE.
Cancer cell growth is complicated progression which is regulated and controlled by multiple factors including cell cycle and metastasis. Cell cycle progression is tightly related to various cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), such as cyclin B1, cyclin D1, cyclin E and cdk2, as well as cell proliferation13. Induction of cell cycle arrest is an effective method of controlling tumor cell proliferation. Cyclins are positive regulators of cell cycle progression, and cyclin gene expression is regulated in a phase-specific manner1, such as cyclin D1 in phase G0-G1and cyclin E in phase S. Both Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E are activators of the G1/S transition14. Cyclin B1 accumulates in the S phase, reaches a maximum at mitosis, and is then rapidly degraded at the metaphase/anaphase transition. It has been established that cdc2, when associated with cyclin B, is responsible for M-phase-inductive activities15,16. Flow cytometry revealed treatment of ESWE induced an accumulation of SMMC-7721 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle and a decrease in the population of cells in the G2-GM and S phase. WB assay showed the levels of cyclin D1 protein gradually increased with ESWE at the concentrations of 0.05–0.2 mg/mL. In contrast, the amount of cyclin E, cyclin B1 and cdc2 was significantly down-regulated in ESWE-treated cells. These data suggest that these cell cycle regulatory molecules are involved in ESWE-induced changes in cell cycle progression. It indicates ESWE could inhibit cell growth by arresting cell cycle caused by regulating cyclin D1, cyclin E, cyclin B1 and cdc2 expressions.
There are various molecular players and signaling cascades involved in the cellular growth pathway, such as the PKCβ, Akt and m-TOR of the PLCγ/PKC, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and the Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1 of MAPK signaling pathway17,18,19,20. Aberrant proliferation is likely driven by up-regulated expressions of PLCγ/PKC, PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathway. Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine- and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by calcium and the second messenger diacylglycerol. PKC family members phosphorylate a wide variety of protein targets and are known to be involved in diverse cellular signaling pathways21,22. The Akt/PKB kinase has been implicated in the genesis and/or progression of numerous human tumors, because AKT has a wide range of downstream targets that regulate endothelial cell functions such as migration, growth, proliferation, and apoptosis17. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a key kinase acting downstream of the activation of PI3K, and mTOR that acts as a master switch of cellular catabolism and anabolism determining tumor cell growth and proliferation19. At the same time, Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1 are key checkpoints in MAPK signaling pathway. The major MAPKs including ERK and JNK are regulated by distinct signal transduction pathways that control many aspects of mammalian cellular physiology, including cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis23. In addition, in the MAPK/ERK pathway, Raf1 becomes activated when it binds to Ras, and several MAPK kinases have been suggested to be important for phosphorylation of Raf1 as well as positive feedback phosphorylation by MAPK. This represents a conformation in which Raf1 can phosphorylate the downstream target MEK, and this allows Raf1 to function as part of a kinase cascade, which can have profound effects on cellular proliferation and tumorigenesis24,25. Our results showed ESWE exhibited broad spectrum inhibitory activity on the expressions of PKCβ, Akt, m-TOR, Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1, and targeted the PLCγ/PKC, PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathway involved in tumor progression. At the same time, P-Akt and P-m-TOR were also downregulated. It provides an anti-proliferative advantage for ESWE to HCC associated with these signaling pathways for survival. In addition, knockdown of a checkpoint PKCβ by siRNA significantly attenuated tumor inhibitory effects of ESWE (Figure 5), which confirmed the role of PKCβ, which contributes to cell proliferation in the HCC growth, and verified the above correlated analysis.
Migration is responsible for most cancer deaths, and tumor metastasis consists of a series of sequential steps, all of which must be successfully completed. These include cell adhesion, invasion, proliferation and vessel formation8,26. Hence, interruption of one or more of these steps is one approach for anti-metastatic therapy. In this study, we have found ESWE displayed a relation with inhibition metastasis by the down-regulated metastasis genes. Although several enzymes involved degradation of basement membrane, MMP-2 (gelatinase A) and MMP-9 (gelatinase B) play a key role in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Therefore, inhibition of the function of MMPs, especially MMP-2 and MMP-9, is being most actively pursued for anticancer therapy27,28. And also, CXCR4 plays critically important roles in cell metastasis in that decreased CXCR4 expression results in significant inhibition of cancer cell migration29. We observed the inhibition on cell mobility by transwell system, and the knockdown of PKCβ significantly reduced the inhibition on the migration of SMMC-7721 cells by ESWE, as compared with the control groups (Figure 6A and B). WB assay showed that MMP2, MMP9 and CXCR4 activity was strongly decreased, which dissected the alterations and function of MMPs and CXCR4 in ESWE-inhibited cell metastasis activities.
Knockdown of PKCβ significantly reduced the inhibition on the proliferation and migration of SMMC-7721 cells by ESWE. So, the PLG, NF-kB and P53 that are related to proteins cell proliferation and metastasis are also analyzed. PLG (Plasminogen) plays an essential role in the proteolytical degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) and the basement membrane surrounding the primary tumor, which is a major determinant for cancer invasion and metastasis. Recent studies indicate that PLG affects adhesion, angiogenesis, differentiation and proliferation30. NF-κB is important and complicated in regulating cellular responses, and promotes cell proliferation and transformation, migration and initiation, promotion and progression of cancer31,32. P53 gene is the most commonly mutated gene in human cancer, the normal gene product exerts the antiproliferative and antitransforming activity and in some cases promotes cell death via apoptosis33. The above molecules are essential for migration, fusion, proliferation, and so on. Figure 6E showed PLG, NFκB and P53 related to growth and metastasis were down-regulated by ESWE. In fact, there is an interrelation in the Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1of PLCγ/PKC, PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathway, and CXCR4, PLG, NFκB and P53 signaling pathway32,34,35,36. We, therefore, concluded that the inhibiting effect of ESWE on HCC was through synthetically regulating cell growth and metastasis signaling.
Taken together, results presented in this work demonstrate that ESWE inhibits HCC growth by downregulating the signaling of PKCβ, Akt, m-TOR, Erk1/2, MEK-2, Raf and JNK-1 as well as phosphorylation of Akt and m-TOR, simultaneously increasing cyclin D1 protein levels and decreasing amount of cyclin E, cyclin B1 and cdc2 of the cycle proteins. Furthermore, ESWE reduced MMP2, MMP9 and CXCR4, and PLG, NFκB and P53 activities. These results support the likelihood that ESWE affects HCC growth by blocking two cellular processes essential for tumor development: cell proliferation (including arrest cell cycle) and tumor metastasis. These data support the development of ESWE as a novel, multiple action growth and metastasis signaling inhibitor targeting the PKC, AKT, MAPK signaling and MMP2, MMP9 and CXCR4, and PLG, NFκB and P53.
Methods
Reagents
RNase and PI were obtained from Sigma (USA). Akt rabbit mAb, Raf-1 rabbit mAb, JNK-1 rabbit mAb, MMP-2 rabbit mAb and MMP-9 rabbit mAb were obtained from Epitomics (USA). P-Akt, P- m-TOR, MEK 1/2 rabbit mAb and p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) rabbit mAb were purchased from Cell Signaling (USA). PKCβ rabbit PolyAb, MTOR rabbit PolyAb, CXCR4 mouse mAb, NF-κb rabbit PolyAb, PLG rabbit PolyAb, Cyclin B1 rabbit polyAb, cyclin D1 mouse mAb, cyclin E rabbit polyAb and cdc2 rabbit polyAb, HRP-conjugated GAPDH mAb were from proteintech group (USA). Mutated P53 rabbit mAb was from Abcam (England). Goat anti-rabbit IgG were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (CA, USA). Protease inhibitor cocktail was from Roche (Roche Tech., Switzerland). Rabbit anti-mouse IgG, goat anti-rabbit IgG, BCA protein assay reagent kit and enhanced chemiluminescent (ECL) plus reagent kit were obtained from Pierce (Pierce Biotech, USA). Total RNA extracted kit was from Fastagen (Fastagen, China). Revert AIDTM. first strand cDNA synthesis kit was from Fermentas (Hanover, Lithuania). RNAi was from Fermentas (Hanover, Lithuania). Other reagents used were analytical grade.
Animals and cell culture
6-8 weeks ALB/C nude male mice (the Experimental Animal Center of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China) were used for all experiments. The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines of the regional authorities according to China animal-care regulations. SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and Hep G2 cancer cells from Shanghai Institute of Cell Biology in the Chinese Academy of Sciences were maintained in RPMI1640 and MEM with 10% FBS.
Preparation of eupolyphaga sinensis walker extract (ESWE)
The raw material used in the study was commercially available as dry matter. The raw material was crushed and soaked in 70% ethanol overnight and then refluxed gently in 10 volumes of 70% ethanol (v/w) for 1 h for two times. The merged extracting solutions were filtered, and supernatant was evaporated under reduced pressure and dried in vacuum conditions overnight. The dry powder was dissolved and stored at 4°C before use. In the next assays, ESWE was dissolved in serum free medium with DMSO as cosolvent, the equal DMSO in serum free medium was as control.
Cell proliferation assay
SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and HepG2 cells (1 × 104) or siRNA cells of SMMC-7721 were cultured in 96-well plates, and fresh medium with or without ESWE, was added for 48 h. Cell proliferation reagent MTT was added and incubated at 37°C and 5%CO2 for 4 h. Absorbance was then measured at 490 nm with a microplate reader (Bio-RAD instruments, USA). In addition, SMMC-7721 cells were cultured in 6-well plates in fresh medium with or without ESWE for 5 days. The cell numbers were analyzed for the dynamic proliferation rate of cells. The experiment was repeated three times independently.
Colony formation assay
SMMC-7721, BEL-7402 and HepG2 cells were cultured in 6-well plates and fresh medium with or without ESWE, was added for 10 ~ 15 days. Colonies with cell numbers of >50 cells per colony were counted after staining with crystal violet solution. All the experiments were performed in triplicate wells in three independent experiments37.
Subcutaneous xenografts in athymic mice and H/E staining
Tumors were induced in 4-week-old nude mice (male immune-deficient BALB/C nude mice) by subcutaneous flank inoculation of SMMC-7721 cells. Tumors were measured once every three days and tumor volumes (Vt) [(d2 × L)/2] were calculated from caliper measurements, where d and L are the shortest and the longest diameters, respectively. Mice were treated with ESWE at 400.0 mg/kg and vehicle alone by intragastric administration, the number of mice in each group was 4. After 10 days, mice weight and tumor volume were recorded. The tumors were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for immunohistochemical analysis. Tumor specimens were embedded into paraffin and the paraffin sections (4-mm thick) were used for H/E staining. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all of the procedures performed in this study.
Microarray analysis
The RNA for the microarray experiments was extracted from SMMC-7721 cells. Microarray experiments were performed in the whole human genome oligo microarray (Agilent Technologies, 4 × 44K, CA, USA), which represents more than 41000 human genes and transcripts. It was used in this study to further systematically screen the differentially expressed genes between control and ESWE-treated cells at the Shanghai Biotechnology Corporation. Single stranded and double stranded cDNA was synthesized from total RNA samples (2 μg) according to Agilent Gene-Chip Expression Analysis Technical Manual. The cRNA was purified and fluorochrome labeled with Cy3, and then fragmented and hybridized to the gene chip at 65°C with rotation for 17 h38,39. Data were normalized by the Quantile method. The 2-fold change between two groups was the threshold for significant regulation. All microarray datasets were submitted to the “Gene Expression Omnibus” with an accession number of GSE52554.
Analyses of the cell cycle
SMMC-7721 cells were cultured in six-well culture plates for 24 h and incubated for 24 h after the medium was changed to serum-free medium. Cells were incubated for another 48 h with ESWE (0, 0.05, 0.10 and 0.20 mg/mL). The cell cycle was assessed according to the percentage of cells with DNA using the PI staining technique as described previously40. Obtained data were analyzed with Modfit LT software.
siRNA analysis
Specific knockdown was achieved using siRNAs against PKCβ or a control siRNA. A smart pool of double-stranded siRNA against PKCβ as well as nonspecific siRNA was obtained from Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd. For transfection, siRNA was delivered at a final concentration of 50 nM using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions41. We incubated the cells for 24 h to allow knockdown of PKCβ. These cells were used for proliferation and transwell assays42.
RNA isolation and RT-PCR
Total RNA of SMMC-7721 cells treated with or without ESWE were isolated using total RNA extracted kit. The total RNA was reversely transcribed in 20 μl reaction solution using the Revert AID™. first strand cDNA synthesis kit. Its integrity and subsequent RT-PCR performed for PKCβ, PLG, IL3RA and GAPDH were described as previously. The sequence details of individual pairs of primers of PKCβ, PLG, IL3RA and GAPDH were in Supplementary Table 1. The PCR reactions were performed with the Thermal Cycler Dice Real Time System (Takara, Japan) in 96-well reaction plates. The relative amount of mRNA for each gene was normalized and represented as the ratio of the mRNA value of a target gene to that of the GAPDH gene.
Migration assay
A cell migration assay was performed using a transwell system, which allows cells to migrate throughout an 8-μm pore size polycarbonate membrane of millicell26. Briefly, SMMC-7721 cells were first serum-starved for 24 h and then plated (1 × 104 cells/well) in serum-free medium containing ESWE at concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 mg/mL in the upper chamber of a 12-well plate. The lower chamber was filled with 1.5 mL medium containing 10% FBS. After 48 h, cells remaining on the upper surface of the membrane were scraped using a cotton swab and the cells on the lower surface of the membrane were fixed with cold methanol for 15 min and stained with 0.2% crystal violet. Cells that had migrated to the bottom of the membrane were visualized and counted using an inverted microscope. For each repetition, cells in four randomly selected fields were counted and averaged. Data were expressed as a ratio to the untreated group.
Western blot analysis
The SMMC-7721 cells treated with or without ESWE for 48 h were prepared by extracting proteins with RIPA lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor cocktail and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail on ice. Cell lysates were analyzed for western blot analysis with primary antibodies, followed by enhanced chemiluminescence. Blots were reprobed with GADPH to compare protein load in each lane43.
Statistical analysis
Data were given as mean ± S.D. in quantitative experiments. Statistical analyses of differences between the groups were performed with ANOVA by Student's t tests. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Author Contributions
L.C.H. designed the conception and reviewed the manuscript. Y.M.Z. performed the research, and wrote the manuscript. B.L.D. and W.N.M. performed development of methodology. J.P.Q. and R.L. acquired data (provided animals, provided facilities, etc.). Y.Z.Z. and D.D.Z. performed analysis and interpretation of data (e.g., statistical analysis, biostatistics, computational analysis).
Supplementary Material
supplementary figures
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 81370088 and 81227802) the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of zhuizong, the project of shaanxi star of science and technology (2012KJXX-06), and supporting plan of education ministry's new century excellent talents (NCET-13-0467).
References
- Nerse P. A long twentieth century of the cell cycle and beyond. Cell 100, 71–78 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen C. et al. Gankyrin promotes breast cancer cell metastasis by regulating Rac1 activity. Oncogene 32, 3452–3460 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz M., Christofori G. & Lehembre F. Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol Med 13, 535–541 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang B. H. & Liu L. Z. AKT signaling in regulating angiogenesis. Currt Cancer Drug Tar 8, 19–26 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Chapuli R., Quesada A. R. & Angel Medina M. Angiogenesis and signal transduction in endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 61, 2224–2243 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. et al. Novel synergistic antitumor effects of rapamycin with bortezomib on hepatocellular carcinoma cells and orthotopic tumor model. BMC Cancer 12, 166 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. et al. PPARgamma inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastases in vitro and in mice. Brit J Cancer 106, 1486–1494 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou L. et al. Ardipusilloside inhibits survival, invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 19, 603–608 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C. X., Tang X. D. & Cheng J. A. The utilization and industrialization of insect resources in China. Entomol Res 38, S38–S47 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y., Zhao M., He Z., Chen Z. Y. & Sun L. Research and utilization of medicinal insects in China. Entomol Res 39, 313–316 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Ge G. F. et al. Antitumor effects and chemical compositions of Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker ethanol extract. J Ethnopharmacol 141, 178–182 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. et al. A bi-functional anti-thrombosis protein containing both direct-acting fibrin(ogen)olytic and plasminogen-activating activities. PloS one 6, e17519 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C. C. et al. Mediation of the inhibitory effect of thyroid hormone on proliferation of hepatoma cells by transforming growth factor-beta. J Mol Endocrinol 36, 9–21 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Gossen M., Bujard H. & Reed S. I. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol cell Biol 14, 1669–1679 (1994). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C. & Nurse P. Review animal cell cycles. Annu Rev Biochem 61, 441–470 (1992). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G. & Walker C. L. Cyclins and cell cycle checkpoints. Annu Review Pharmacol Toxicol 39, 295–312 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinda M. J. et al. AKT-1, -2, and -3 are expressed in both normal and tumor tissues of the lung, breast, prostate, and colon. Clin Cancer Res 7, 2475–2479 (2001). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berra E. M. J. et al. Signaling angiogenesis via p42p44 MAP kinase and hypoxiamain.pdf. Biochem Pharmacol 60, 1171–1178 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N. The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer cell 8, 179–183 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faivre S., Kroemer G. & Raymond E. Current development of mTOR inhibitors as anticancer agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5, 671–688 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippi A. et al. Haplotypes in the gene encoding protein kinase c-beta (PRKCB1) on chromosome 16 are associated with autism. Mol Psychiatr 10, 950–960 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lintas C. et al. Involvement of the PRKCB1 gene in autistic disorder: significant genetic association and reduced neocortical gene expression. Mol Psychiatr 14, 705–718 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang S. M., Wang L. C. & Yang J. L. Roles of JNK, p38 and ERK mitogen-activated protein kinases in the growth inhibition and apoptosis induced by cadmium. Carcinogenesis 21, 1423 (2000). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo W. et al. Brucine suppresses colon cancer cells growth via mediating KDR signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 17, 1316–1324 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balan V. et al. Identification of novel in vivo Raf-1 phosphorylation sites mediating positive feedback Raf-1 regulation by extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Mol Biol Cell 17,1141–1153 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams L. S. et al. Blueberry phytochemicals inhibit growth and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through modulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Cancer res 70, 3594–3605 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodkeeree S., Chaiwangyen W., Garbisa S. & Limtrakul P. Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin differentially inhibit cancer cell invasion through the down-regulation of MMPs and uPA. J Nutr Biochem 20, 87–95 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q. Y. et al. Curcumin inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion through Rac1-dependent signaling pathway. J Nutr Biochem 25, 177–85 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. C., Stamatoyannopoulos G. & Song C. Z. Down-Regulation of CXCR4 by Inducible Small Interfering RNA Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Invasion in Vitro. Cancer res 63, 4801–1804 (2003). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. et al. RNAi-mediated downregulation of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor inhibits proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion in oral cancer cells. Oral oncology 44, 1172–1180 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen H. M. & Tergaonkar V. NFkappaB signaling in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 14, 348–363 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. et al. Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB, vascular endothelial growth factor, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer res 66, 2778–2784 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick M. O. C. et al. Role of the p53 Tumor Suppressor Gene in Cell Cycle Arrest and Radiosensitivity of Burkitt's Lymphoma Cell Lines. Cancer Res 53, 4776–4780 (1993). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocic J. et al. Interleukin-17 modulates myoblast cell migration by inhibiting urokinase type plasminogen activator expression through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Int J Biochem Cell B 45, 464–475 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. H., Han S. B. & Lee J. K. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress CXCR4-mediated dendritic cell migration by regulation of maturation process. Cell Immunol 284, 139–145 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley B. R., Beaulieu L. M., Carter J. C. & Church F. C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt regulates the balance between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and urokinase to promote migration of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 104, 470–479 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W. et al. ADAMTS9 is a functional tumor suppressor through inhibiting AKT/mTOR pathway and associated with poor survival in gastric cancer. Oncogene 32, 3319–3328 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y., Zou Q., Ge R., Shen F. & Wang Y. The critical role of CD133(+)CD44(+/high) tumor cells in hematogenous metastasis of liver cancers. Cell res 22, 259–272 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. et al. NDRG1 as a biomarker for metastasis, recurrence and of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer lett 310, 35–45 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Zhang J., Dai B., Wang N. & He L. Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of the novel taspine derivative tas41 in the Caco-2 cell line. Environ Toxicol Pharm 31, 406–415 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortylewski M. et al. In vivo delivery of siRNA to immune cells by conjugation to a TLR9 agonist enhances antitumor immune responses. Nat biotechnol 27, 925–932 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiang L. et al. HIF-1alpha is critical for hypoxia-mediated maintenance of glioblastoma stem cells by activating Notch signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ 19, 284–294 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. M. et al. A novel angiogenesis inhibitor impairs lovo cell survival via targeting against human VEGFR and its signaling pathway of phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis 3, e406 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
supplementary figures