Abstract
AIM: To evaluate the attitude of primary care physicians in the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) infection.
METHODS: Primary care physicians in the Seoul metropolitan area answered self-administered questionnaire from January to March 2003.
RESULTS: One hundred and eight doctors responded to the questionnaire. The most frequent reasons for testing H pylori infection were gastric and duodenal ulcers (93.5% and 88.9%, respectively). For patients with H pylori positive dyspepsia, 28.7% of doctors always tried to eradicate the worm and 34.4% treated selectively. A large proportion (28.7%) of primary care physicians treated H pylori on a patient’s request basis. Only 9.3% of primary care physicians always conducted follow-up testing after treating H pylori infection. When H pylori was not cleared by the first treatment, 40.7% of doctors reused the same regimen, 16.7% changed to another triple regimen and 25% to a quadruple regimen.
CONCLUSION: It has been well documented that the issuance of guidelines alone has little impact on practice. Communication between primary care physicians and gastroenterologists in the form of continuous medical education is required.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori, Guidelines, Primary care
INTRODUCTION
It is now accepted that infection of the gastric mucosa with Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) causes chronic gastritis. More than 90% of peptic ulcer patients are infected with H pylori and it has been shown that successful treatment prevents ulcer relapse[1-3]. National and international guidelines have been published on the management of H pylori, and it is tacitly assumed that these guidelines are adhered to in clinical practice[4-7]. But, there seems to be a discrepancy between current testing and treatment guidelines and clinical practice[8,9]. In particular, the approaches used in primary practice may differ markedly from those used in referral hospitals[10-13]. Patients commonly visit both primary care physicians and gastroenterologists because of upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Variable H pylori detection methods, including serologic assays and the urea breath test, are currently used. Although most physicians do not believe that H pylori causes non-ulcer dyspepsia, the majority often prescribe antibiotics for H pylori eradication. The extent to which research findings regarding H pylori have modified physicians’ practice in general has not been well studied. We conducted the present study to determine whether current guidelines regarding H pylori infection have influenced diagnostic and therapeutic primary care practice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January to March 2003, we conducted an observatio-nal, transverse study by using a self-administered questionnaire. Primary care physicians in the metropoli-tan area of Seoul were random-ly select-ed from the membership database of the Seoul Medical Association. Questionnaires were distributed by post, and non-respondents were sent reminders and then contacted by telephone. One hundred and thirty-five doctors participated in the study.
RESULTS
One hundred and eight doctors (80%) responded to the survey. We itemized below the physicians’ responses to the questions given in the questionnaire.
When do you test for H pylori
Primary care physicians widely used the H pylori test in cases of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer (88.9% and 93.5%, respectively, Figure 1). But they conducted tests for H pylori only in 26.9% and 13% of patients, after surgery for early gastric cancer or Maltoma (Figure 1). Frequently physicians tested for H pylori in cases of gastritis and due to a patient’s request (25.0% and 58.3%, respectively, Figure 1).
Figure 1.
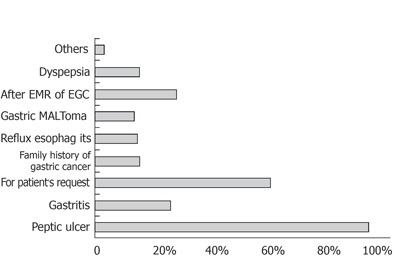
When do you test for H pylori
Which test do you prefer
More than half of the primary care physicians stated that they used the rapid urease test and biopsy, (55.6% and 54.6%, respectively, Figure 2), and a minority used the urea breath test and serology (8.3% and 22.2%, respectively, Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Which test do you prefer
How do you eradicate H pylori infection
An 88% of physicians responded that they prescribed a proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-based triple regimen according to Korean guidelines (Table 1, Figure 3), and only small numbers were found to prescribed dual and quadruple regimens (2.8% and 2.8%, respectively, Figure 3).
Table 1.
Korean guidelines for H pylori treatment (Korean H pylori Study Group, 1998)
| Indication for H pylori eradication | Peptic ulcer |
| Regardless of the stage of ulcer | |
| Low-grade MALT associated lymphoma | |
| Stage IE1 | |
| After endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of early gastric cancer (EGC) | |
| Recommended first line therapy | PPI-based triple therapy for 1-2 wk |
| - PPI (omeprazole 20 mg or lansoprazole 30 mg or pantoprazole 40 mg) b.i.d. | |
| - Amoxicillin (not ampicillin) 1 000 mg b.i.d. | |
| - Clarithromycin (or metronidazole) 500 mg b.i.d. | |
| Follow-up after eradication therapy | Urea breath test: test of choice, if available |
| Or both biopsy urease test and histology | |
| At least 4 wk after completion of therapy | |
| Serology: not useful to confirm the eradication | |
| Recommended second-line therapy | Quadruple therapy for 1 wk |
| (PPI+conventional bismuth-based triple therapy) | |
| - PPI (omeprazole 20 mg or lansoprazole 30 mg or pantoprazole 40 mg) b.i.d. | |
| - Denol 120 mg b.i.d. | |
| - Metronidazole 400-500 mg t.i.d. | |
| - Tetracycline 500 mg q.i.d |
Figure 3.
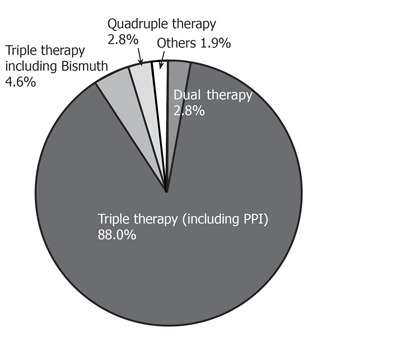
How do you eradicate H pylori infection
How long do you treat H pylori infection
The majority of physicians responded that they prescribe medication for 7,14 d (90.7%), according to Korean guidelines (Figure 4). A small number responded that they prescribed for less than 7, 21 or 28 d, accounting for 4.6%, 1.9%, 2.8%, respectively (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
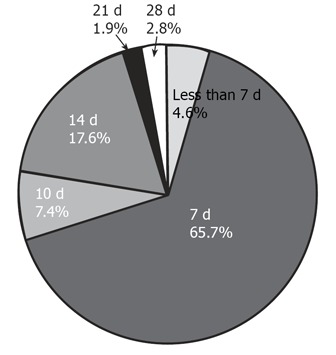
How long do you treat H pylori infection
Do you perform follow-up testing after treating H pylori infection
Only 9.3% replied that they always conducted follow-up testing after treating H pylori infection (Figure 5). The majority of primary care physicians stated that they selectively apply follow-up tests (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
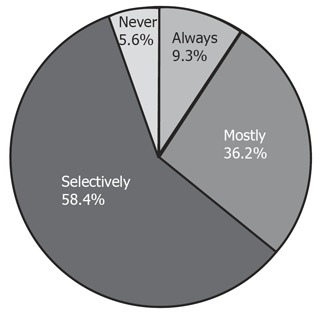
Do you perform follow-up testing after treating H pylori infection
What kind of method do you prefer as follow-up test
The majority percent of physicians stated that they used the rapid urease test or biopsy, accounting for 35.2% and 25.9%, respectively (Figure 6), while a minority favored urea breath testing or serology, accounting for 21.3% and 6.5%, respectively (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
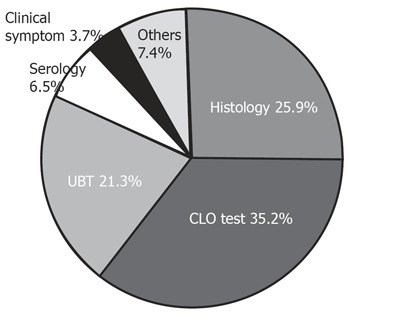
What kind of method do you prefer as follow-up test
Treatment plan after failure to eradicate H pylori
Surprisingly, a large proportion (40.7%) of primary care physicians prescribed the original regimen after failure to eradicate H pylori (Figure 7). Only 25.0% physicians prescribed regimens complying with Korean guidelines (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
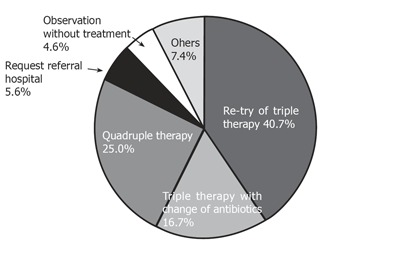
Treatment plan after failure to eradicate H pylori.
Do you treat H pylori infection in dyspepsia patients without peptic ulcer
Physicians (31.5%) responded that they always eradicate H pylori (Figure 8), while 10.2% treated H pylori on patient’s request without testing (Figure 8).
Figure 8.
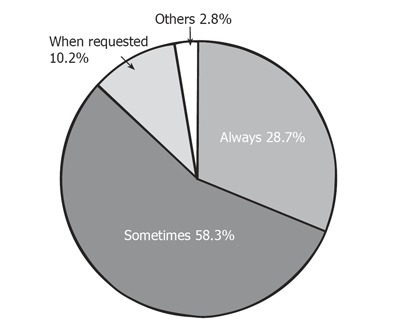
Do you treat H pylori infection in dyspepsia patients without peptic ulcer
Do you medicate for H pylori eradication by patient’s request
A large number (28.7%) of physicians responded positively (Figure 9).
Figure 9.
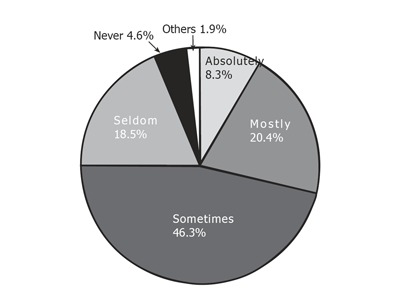
Do you medicate for H pylori eradication by patient’s request
DISCUSSION
The prevalence of H pylori among Korean adults is 60% - 80%[14], and gastric cancer remains the most common malignancy in Korea[15]. Most Korean primary care physicians are interested in H pylori, and more frequently prescribe medication for the treatment of H pylori than gastroenterologist. The indications for H pylori eradication in Korea (Korean H pylori Study Group, 1998) are peptic ulcer, low-grade MALT-associated lymphoma, and post-endoscopic mucosal resection of early gastric cancer (Table 1). The recommended first-line therapy in Korea is the PPI-based triple therapy for 1 to 2 weeks. PPI would be the omeprazole, lansoprazole, or pantoprazole (Table 1). The treatment of choice in terms of antibiotics is the amoxicillin+clarithromycin (Table 1). The recommended second-line therapy according to the Korean guidelines is quadruple therapy for a week (Table 1), based on PPI, Denol, metronidazole, and tetracycline (Table 1). The issued Korean guidelines are similar to those issued by the Asia Pacific Consensus Conference on the management of H pylori infection[6]. The survey conducted for the present study involved mailing a questionnaire to primary physicians in Seoul, Korea. The questions primarily addressed physician decisions concerning the evaluation and treatment of H pylori infection in patients with gastroenterologic disease. Alternative treatment regimens were also examined. The survey results indicate that primary care physicians widely adopt H pylori testing in cases of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer according to Korean guidelines. However, physicians only conduct H pylori testing in 26.9% and 13.0% of postoperative early gastric cancer and Maltoma patients. In addition, they frequently test for H pylori in cases of gastritis and due to a patient’s request, accounting for 25.0% and 58.3%, respectively, but many do not perform follow-up testing after H pylori treatment. Only 9.3% of primary care physicians always conduct follow-up testing after H pylori treatment. The majority of primary care physicians prefer the rapid urease test or biopsy, accounting for 35.2%, 25.9%, respectively, as follow-up tests, because generally in Korea primary care physicians have an endoscopic unit, but not urea breath test equipment; 6.5% physicians use a serology-based follow-up test. Only 25.0% prescribe a quadruple regimen as second line therapy, contrary to the Korean guidelines and a large number (40.7%) of physicians prescribe the same regimen after failing to eradicate H pylori. In addition, they frequently treat H pylori in cases of non-ulcer dyspepsia and patient’s request. This finding is at odds with the current guideline and primary care practice for the diagnosis and treatment of H pylori infetion in Korea. Moreover, the finding of the present study compare well with data published in other countries[10-13]. Thus, the issuance of guidelines has little impact on practice. Our findings suggest that communication programs, such as continuous medical education, between primary care physicians and gastroenterologists are needed. Moreover, schemes designed to ensure guideline implementation should be preceded by a detailed analysis of likely primary care physician response.
Footnotes
S- Editor Wang XL and Guo SY L- Editor Elsevier HK E- Editor Wu M and Li HY
References
- 1.Marshall BJ. Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89:S116–S128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rauws EA, Tytgat GN. Cure of duodenal ulcer associated with eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1990;335:1233–1235. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91301-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Graham DY, Lew GM, Klein PD, Evans DG, Evans DJ, Saeed ZA, Malaty HM. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. A randomized, controlled study. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116:705–708. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-9-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. The Maastricht Consensus Report. European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group. Gut. 1997;41:8–13. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: evaluation of dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:579–581. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70541-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lam SK, Talley NJ. Report of the 1997 Asia Pacific Consensus Conference on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1998.tb00537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Peterson WL, Fendrick AM, Cave DR, Peura DA, Garabedian-Ruffalo SM, Laine L. Helicobacter pylori-related disease: guidelines for testing and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:1285–1291. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.9.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sharma VK, Howden CW. A national survey of primary care physicians' perceptions and practices related to Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:326–331. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200404000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang J, Lam SK, Malfertheiner P, Hunt RH. Has education about Helicobacter pylori infection been effective Worldwide survey of primary care physicians. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18:512–520. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.03017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Provenzale D, Ofman J, Gralnek I, Rabeneck L, Koff R, McCrory D. Gastroenterologist specialist care and care provided by generalists--an evaluation of effectiveness and efficiency. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cardin F, Zorzi M, Furlanetto A, Guerra C, Bandini F, Polito D, Bano F, Grion AM, Toffanin R. Are dyspepsia management guidelines coherent with primary care practice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002;37:1269–1275. doi: 10.1080/003655202761020533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Martínez-Sánchez G, Saperas E, Benavent J, Mearin F, Piñol JL, Barenys M, Mascort JJ, Forné M, Bordas JM, Azagra R, et al. [The attitude of primary health care physicians in the metropolitan area of Barcelona about the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in gastroduodenal diseases] Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;21:473–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Breuer T, Goodman KJ, Malaty HM, Sudhop T, Graham DY. How do clinicians practicing in the U.S. manage Helicobacter pylori-related gastrointestinal diseases A comparison of primary care and specialist physicians. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:553–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.164_b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim JH, Kim HY, Kim NY, Kim SW, Kim JG, Kim JJ, Roe IH, Seo JK, Sim JG, Ahn H, et al. Seroepidemiological study of Helicobacter pylori infection in asymptomatic people in South Korea. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;16:969–975. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2001.02568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bae JM, Jung KW, Won YJ. Estimation of cancer deaths in Korea for the upcoming years. J Korean Med Sci. 2002;17:611–615. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2002.17.5.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


