Abstract
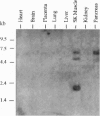
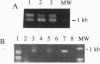
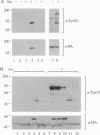
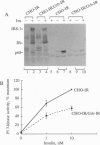
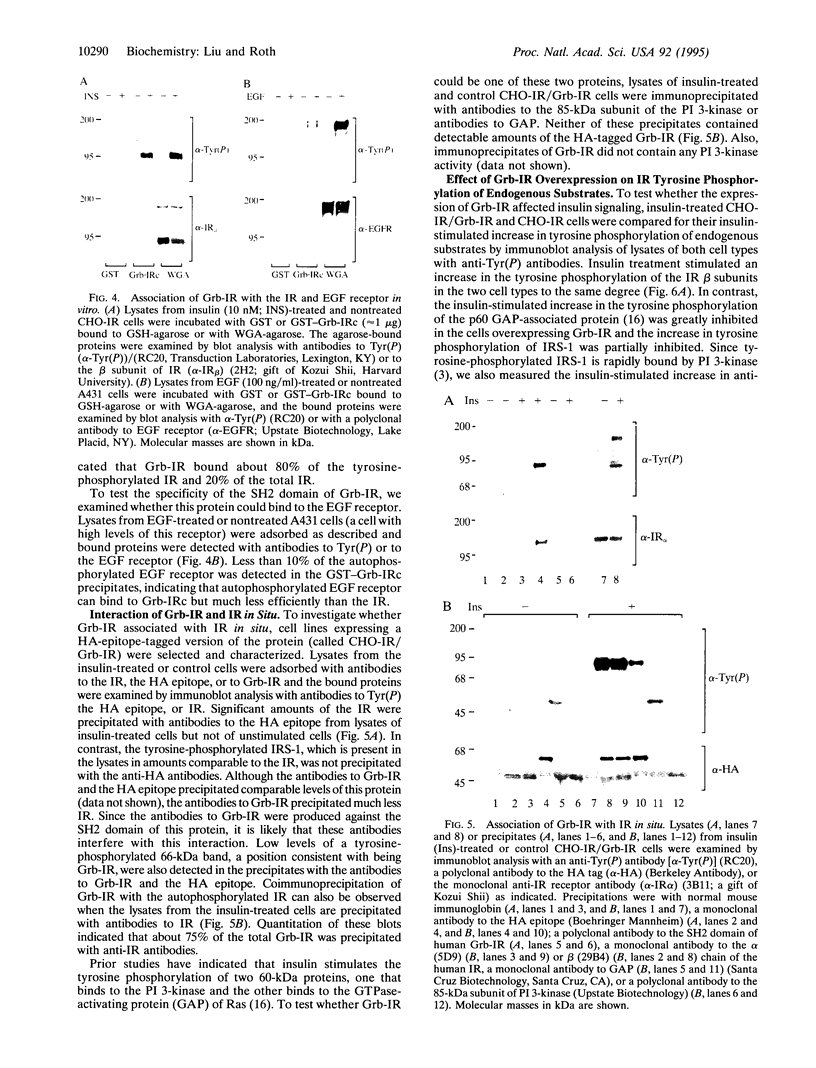
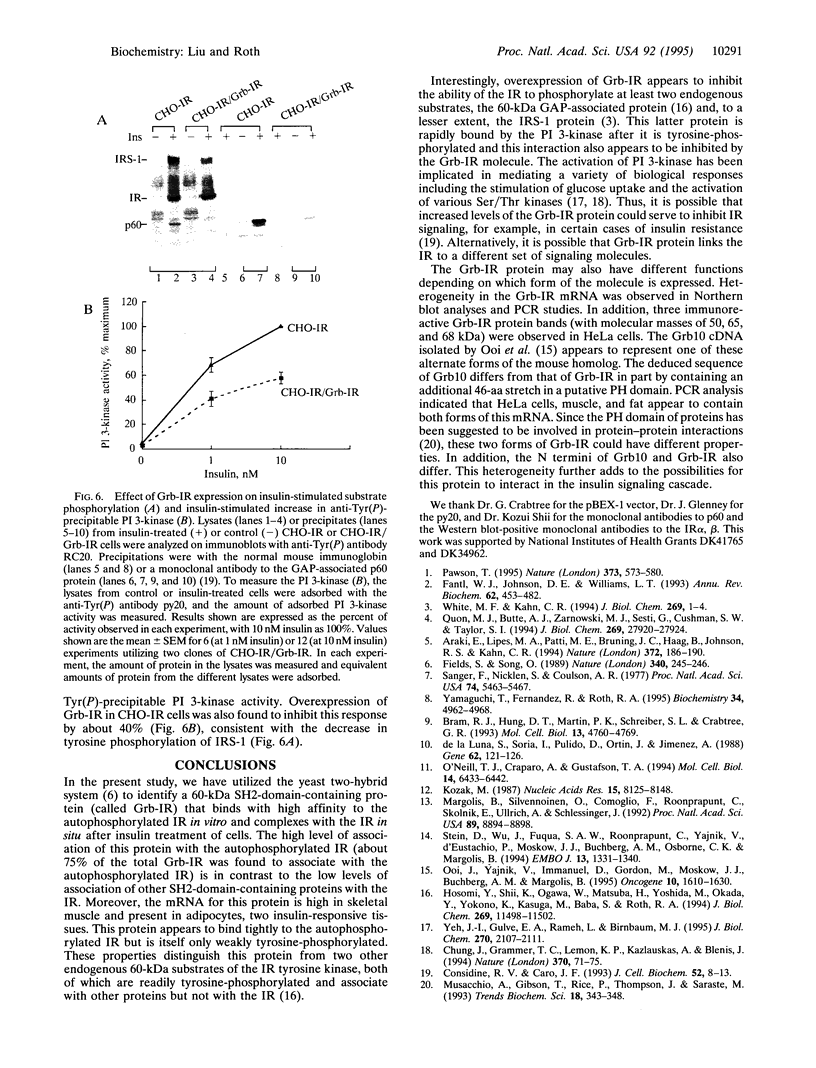
To identify potential signaling molecules involved in mediating insulin-induced biological responses, a yeast two-hybrid screen was performed with the cytoplasmic domain of the human insulin receptor (IR) as bait to trap high-affinity interacting proteins encoded by human liver or HeLa cDNA libraries. A SH2-domain-containing protein was identified that binds with high affinity in vitro to the autophosphorylated IR. The mRNA for this protein was found by Northern blot analyses to be highest in skeletal muscle and was also detected in fat by PCR. To study the role of this protein in insulin signaling, a full-length cDNA encoding this protein (called Grb-IR) was isolated and stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells overexpressing the human IR. Insulin treatment of these cells resulted in the in situ formation of a complex of the IR and the 60-kDa Grb-IR. Although almost 75% of the Grb-IR protein was bound to the IR, it was only weakly tyrosine-phosphorylated. The formation of this complex appeared to inhibit the insulin-induced increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of two endogenous substrates, a 60-kDa GTPase-activating-protein-associated protein and, to a lesser extent, IR substrate 1. The subsequent association of this latter protein with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase also appeared to be inhibited. These findings raise the possibility that Grb-IR is a SH2-domain-containing protein that directly complexes with the IR and serves to inhibit signaling or redirect the IR signaling pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki E., Lipes M. A., Patti M. E., Brüning J. C., Haag B., 3rd, Johnson R. S., Kahn C. R. Alternative pathway of insulin signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature. 1994 Nov 10;372(6502):186–190. doi: 10.1038/372186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Hung D. T., Martin P. K., Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. Identification of the immunophilins capable of mediating inhibition of signal transduction by cyclosporin A and FK506: roles of calcineurin binding and cellular location. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4760–4769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Considine R. V., Caro J. F. Protein kinase C: mediator or inhibitor of insulin action? J Cell Biochem. 1993 May;52(1):8–13. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240520103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi Y., Shii K., Ogawa W., Matsuba H., Yoshida M., Okada Y., Yokono K., Kasuga M., Baba S., Roth R. A. Characterization of a 60-kilodalton substrate of the insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11498–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Silvennoinen O., Comoglio F., Roonprapunt C., Skolnik E., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. High-efficiency expression/cloning of epidermal growth factor-receptor-binding proteins with Src homology 2 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8894–8898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Rice P., Thompson J., Saraste M. The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill T. J., Craparo A., Gustafson T. A. Characterization of an interaction between insulin receptor substrate 1 and the insulin receptor by using the two-hybrid system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6433–6442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi J., Yajnik V., Immanuel D., Gordon M., Moskow J. J., Buchberg A. M., Margolis B. The cloning of Grb10 reveals a new family of SH2 domain proteins. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 20;10(8):1621–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quon M. J., Butte A. J., Zarnowski M. J., Sesti G., Cushman S. W., Taylor S. I. Insulin receptor substrate 1 mediates the stimulatory effect of insulin on GLUT4 translocation in transfected rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):27920–27924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D., Wu J., Fuqua S. A., Roonprapunt C., Yajnik V., D'Eustachio P., Moskow J. J., Buchberg A. M., Osborne C. K., Margolis B. The SH2 domain protein GRB-7 is co-amplified, overexpressed and in a tight complex with HER2 in breast cancer. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1331–1340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Fernandez R., Roth R. A. Comparison of the signaling abilities of the Drosophila and human insulin receptors in mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 18;34(15):4962–4968. doi: 10.1021/bi00015a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. I., Gulve E. A., Rameh L., Birnbaum M. J. The effects of wortmannin on rat skeletal muscle. Dissociation of signaling pathways for insulin- and contraction-activated hexose transport. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 3;270(5):2107–2111. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Luna S., Soria I., Pulido D., Ortín J., Jiménez A. Efficient transformation of mammalian cells with constructs containing a puromycin-resistance marker. Gene. 1988;62(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90585-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]