Abstract
Aims—To investigate the immunohistochemical expression of bcl-2 and p53 proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinomas in relation to the expression of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encoded EBER messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1).
Methods—Formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded tissue from 44 nasopharyngeal carcinomas (NPCs) was stained by immunohistochemistry for p53, bcl-2 and LMP-1 proteins and by RNA in situ hybridisation for EBER mRNAs.
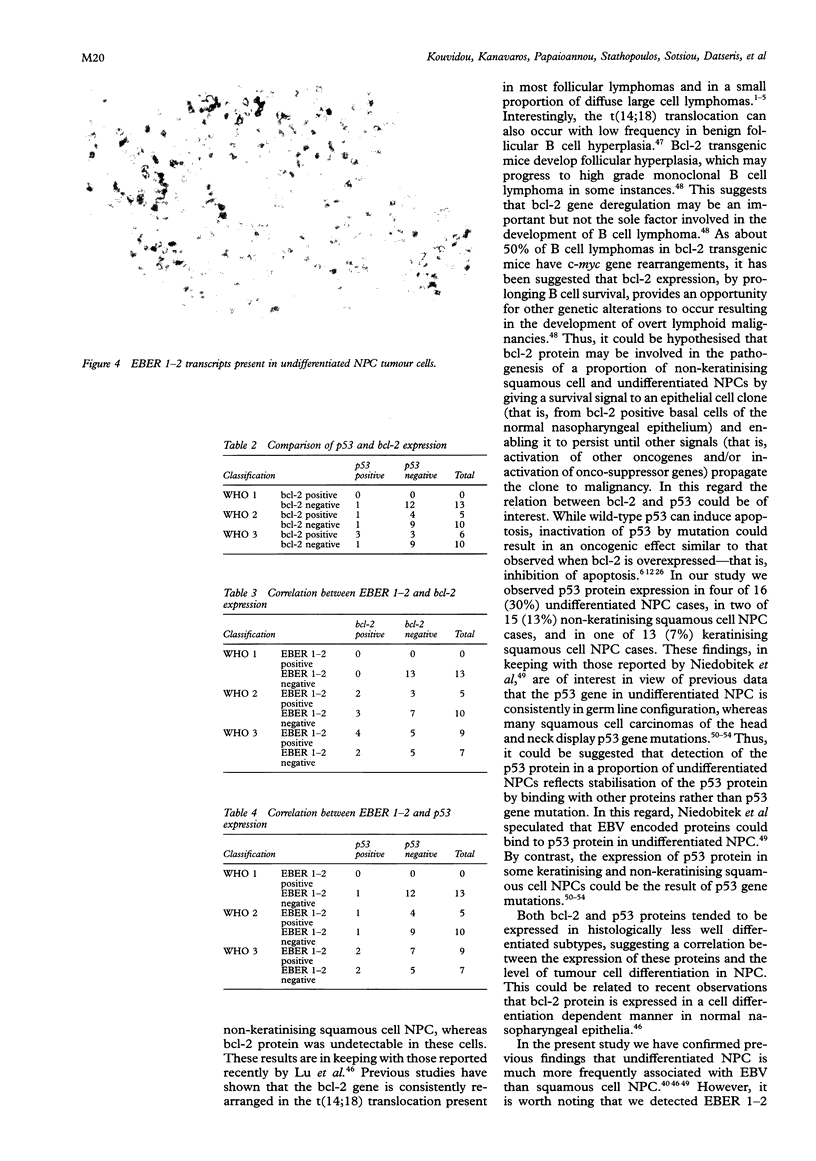
Results—The tumours were divided histologically into 13 cases of keratinising squamous cell NPC (KNPC), 15 cases of non-keratinising squamous cell NPC (NKNPC) and 16 cases of undifferentiated NPC (UNPC). Bcl-2 expression was observed in five of 15 NKNPC cases and in six of 16 UNPC cases; p53 expression was observed in one of 13 KNPC, two of 15 NKNPC and four of 16 UNPC cases. EBER 1-2 transcripts were detected in five of 15 NKNPC and nine of 16 UNPC cases, while LMP-1 expression was observed in one of 16 UNPC cases. All 13 KNPCs were EBV and bcl-2 negative. No correlation was found between the presence of EBER 1-2 transcripts and the detection of bcl-2 or p53 proteins, or both, in NPC cells.
Conclusions—The expression of bcl-2 and p53 proteins may be associated with the level of the tumour cell differentiation in NPC. In addition, in view of the important role of the bcl-2 protein in the inhibition of apoptosis, the expression of bcl-2 protein may contribute to tumour cell survival in a proportion of NPCs. Furthermore, in the light of previous findings that the p53 gene in most UNPCs is in the wild-type configuration, mechanisms other than mutation may be responsible for stabilisation of the p53 protein in UNPCs.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus
Keywords: bcl-2
Keywords: p53
Keywords: nasopharyngeal cancer
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Wright J. J., McBride O. W., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisch-Chappuis B., Nezelof C., Müller H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Different Epstein-Barr virus expression in lymphomas from immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):751–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressac B., Kew M., Wands J., Ozturk M. Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma from southern Africa. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):429–431. doi: 10.1038/350429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Sklar J. Nucleotide sequence of a t(14;18) chromosomal breakpoint in follicular lymphoma and demonstration of a breakpoint-cluster region near a transcriptionally active locus on chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7439–7443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. W., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein inhibits human epithelial cell differentiation. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):777–780. doi: 10.1038/344777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doussis I. A., Pezzella F., Lane D. P., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. An immunocytochemical study of p53 and bcl-2 protein expression in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993 Jun;99(6):663–667. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/99.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Effert P., McCoy R., Abdel-Hamid M., Flynn K., Zhang Q., Busson P., Tursz T., Liu E., Raab-Traub N. Alterations of the p53 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3768–3775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3768-3775.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzera G. The clinico-pathological expressions of Epstein-Barr virus infection in lymphoid tissues. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1987;53(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF02890218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Rymo L., Rhim J. S., Klein G. Morphological transformation of human keratinocytes expressing the LMP gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):447–449. doi: 10.1038/345447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaidano G., Ballerini P., Gong J. Z., Inghirami G., Neri A., Newcomb E. W., Magrath I. T., Knowles D. M., Dalla-Favera R. p53 mutations in human lymphoid malignancies: association with Burkitt lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Dive C., Henderson S., Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Gordon J., Rickinson A. B. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes protects human B cells from death by apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):612–614. doi: 10.1038/349612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Norton A. J., Thompson I. W., Lister T. A., Bodmer J. G. p53 expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Br J Cancer. 1992 Oct;66(4):649–652. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Pallesen G., Franzmann M. B., Karkov J., Black F., Skinhøj P., Pedersen C. AIDS-related lymphoma. Histopathology, immunophenotype, and association with Epstein-Barr virus as demonstrated by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):149–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L. Mutant p53--the commonest genetic abnormality in human cancer? J Pathol. 1990 Sep;162(1):5–6. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Epstein-Barr virus and infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):263–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Oltvai Z. N., Yin X. M., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80066-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Kanavaros P., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Horstman A., Vos W., Mullink H., Meijer C. J. Expression of c-myc and bcl-2 oncogene products in Reed-Sternberg cells independent of presence of Epstein-Barr virus. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Mar;46(3):211–217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanavaros P., Ioannidou D., Tzardi M., Datseris G., Katsantonis J., Delidis G., Tosca A. Mycosis fungoides: expression of C-myc p62 p53, bcl-2 and PCNA proteins and absence of association with Epstein-Barr virus. Pathol Res Pract. 1994 Sep;190(8):767–774. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80423-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanavaros P., Lescs M. C., Brière J., Divine M., Galateau F., Joab I., Bosq J., Farcet J. P., Reyes F., Gaulard P. Nasal T-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic entity associated with peculiar phenotype and with Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2688–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leek R. D., Kaklamanis L., Pezzella F., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L. bcl-2 in normal human breast and carcinoma, association with oestrogen receptor-positive, epidermal growth factor receptor-negative tumours and in situ cancer. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jan;69(1):135–139. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limpens J., de Jong D., van Krieken J. H., Price C. G., Young B. D., van Ommen G. J., Kluin P. M. Bcl-2/JH rearrangements in benign lymphoid tissues with follicular hyperplasia. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2271–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q. L., Elia G., Lucas S., Thomas J. A. Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in Epstein-Barr-virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jan 2;53(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestro R., Dolcetti R., Gasparotto D., Doglioni C., Pelucchi S., Barzan L., Grandi E., Boiocchi M. High frequency of p53 gene alterations associated with protein overexpression in human squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1159–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Troncoso P., Brisbay S. M., Logothetis C., Chung L. W., Hsieh J. T., Tu S. M., Campbell M. L. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6940–6944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Agathanggelou A., Barber P., Smallman L. A., Jones E. L., Young L. S. P53 overexpression and Epstein-Barr virus infection in undifferentiated and squamous cell nasopharyngeal carcinomas. J Pathol. 1993 Aug;170(4):457–461. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Rowlands D. C., Young L. S., Herbst H., Williams A., Hall P., Padfield J., Rooney N., Jones E. L. Overexpression of p53 in Hodgkin's disease: lack of correlation with Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Pathol. 1993 Feb;169(2):207–212. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus persistence and virus-associated tumours. Lancet. 1994 Feb 5;343(8893):333–335. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedobitek G., Young L. S., Sam C. K., Brooks L., Prasad U., Rickinson A. B. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus genes and of lymphocyte activation molecules in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1992 Apr;140(4):879–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Morrison H., Jones M., Gatter K. C., Lane D., Harris A. L., Mason D. Y. Immunohistochemical detection of p53 and bcl-2 proteins in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology. 1993 Jan;22(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Turley H., Kuzu I., Tungekar M. F., Dunnill M. S., Pierce C. B., Harris A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 2;329(10):690–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309023291003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdie C. A., O'Grady J., Piris J., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. p53 expression in colorectal tumors. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):807–813. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai E., Tsuchida N. Most human squamous cell carcinomas in the oral cavity contain mutated p53 tumor-suppressor genes. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):927–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruck C. H., 3rd, Tsai Y. C., Huang D. P., Yang A. S., Rideout W. M., 3rd, Gonzalez-Zulueta M., Choi P., Lo K. W., Yu M. C., Jones P. A. Absence of p53 gene mutations in primary nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4787–4790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretch J. R., Gatter K. C., Ralfkiaer E., Lane D. P., Harris A. L. Expression of mutant p53 in melanoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 1;51(21):5976–5979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L. Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoproliferative disorders. Semin Hematol. 1988 Jul;25(3):269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Hegamyer G., Cheng Y. J., Hildesheim A., Chen J. Y., Chen I. H., Cao Y., Yao K. T., Colburn N. H. An infrequent point mutation of the p53 gene in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6516–6520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely L., Selivanova G., Magnusson K. P., Klein G., Wiman K. G. EBNA-5, an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen, binds to the retinoblastoma and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. M., Steel C. M., Chetty U., Hawkins R. A., Miller W. R., Carter D. C., Forrest A. P., Evans H. J. p53 gene mRNA expression and chromosome 17p allele loss in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1990 Jan;61(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1440–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.3874430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Movahed L. A. In situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr viral genomes in viral-associated B cell lymphoproliferations. Am J Pathol. 1989 Mar;134(3):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]