Abstract
Aims—To directly visualise immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy (H) and light chain genes (κ and λ) in metaphase chromosomes and interphase nuclei of normal and malignant lymphocytes using small genomic probes targeted to intragenic sequences.
Methods—Cytogenetic preparations from phytohaemagglutinin stimulated lymphocytes, B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL) cells, and a B-prolymphocytic leukaemia (B-PLL) cell line, containing a t(11;14), were hybridised in situ using biotin or digoxigenin labelled plasmid probes. The κ genes were visualised with a combination of probes for the Cκ, Jκ, Vκ1, and Vκ2 segments, the λ genes with a probe containing the Jλ2-Cλ2, Jλ3-Cλ3 segments and the H genes with a probe for Cλ2. Hybridisation sites were visualised using appropriate fluorochrome conjugates and images were analysed by digital microscopy.
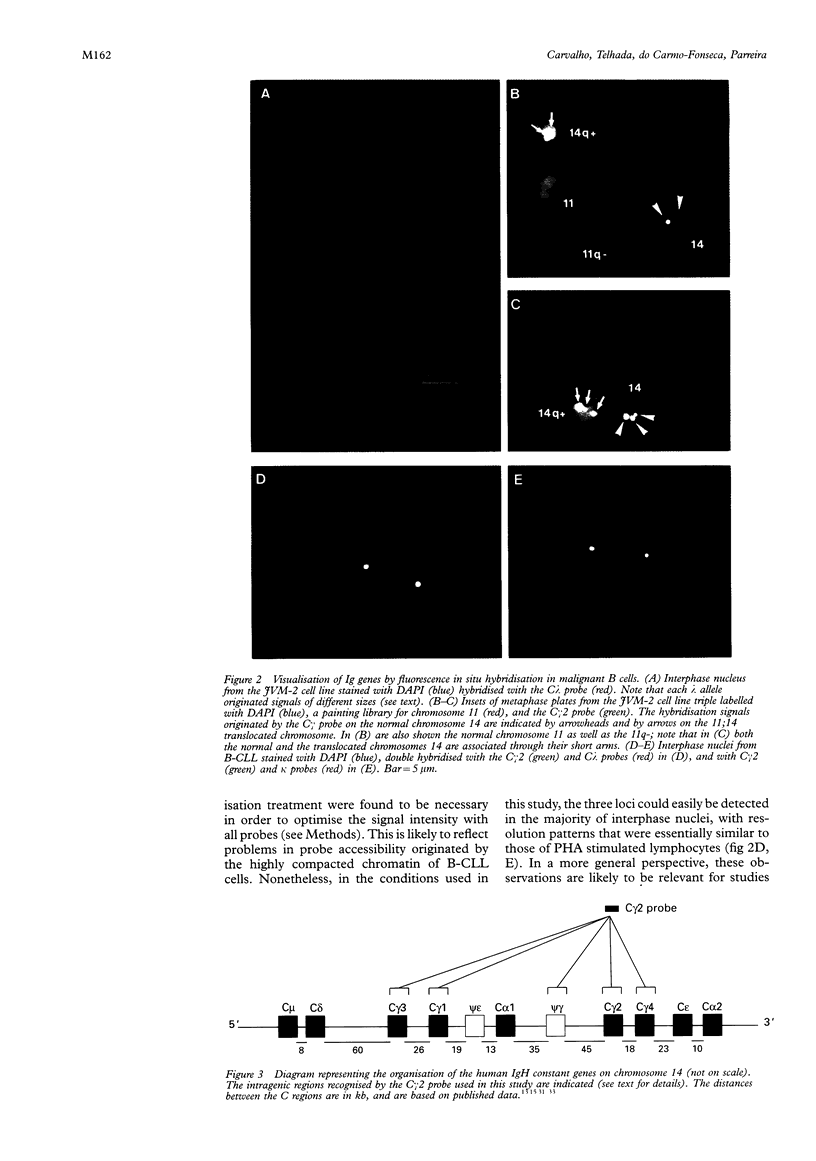
Results—In both normal and malignant lymphoid cells, the κ and λ genes were visualised as a single dot signal, whereas the H λ genes were resolved as either two or three separate signals per chromatid in metaphase chromosomes or per allele in interphase nuclei. In the malignant PLL cells, double hybridisation experiments with a painting library specific for the chromosome 11 showed that the λ region was retained in the translocated chromosome, with an in situ resolution pattern similar to that of the normal allele.
Conclusions—This study shows that a high resolution in situ analysis of the three Ig loci can be efficiently performed with small size genomic probes on both normal and malignant lymphoid cells. Such an approach offers a flexible tool for the molecular characterisations of these loci on chromosomes and individual neoplastic cells.
Keywords: Gene visualisation
Keywords: lymphocytes
Keywords: leukaemia cells
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Evolution of immunoglobulin V genes: evidence indicating that recently duplicated human V kappa sequences have diverged by gene conversion. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzillo G. V., Cooper M. D., Kubagawa H., Landay A., Burrows P. D. Isotype switching in human B lymphocyte malignancies occurs by DNA deletion: evidence for nonspecific switch recombination. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1326–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro A., de Marchi M., Migone N., Carbonara A. O. Pulsed-field gel analysis of human immunoglobulin heavy-chain constant region gene deletions reveals the extent of unmapped regions within the locus. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):505–508. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H., Dmitrovsky E., Hieter P. A., Mitchell K., Leder P., Turoczi L., Kirsch I. R., Hollis G. F. Identification of three new Ig lambda-like genes in man. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):425–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Shander M., Martinis J., Cicurel L., D'Ancona G. G., Dolby T. W., Koprowski H. Chromosomal location of the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3416–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dariavach P., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. Human immunoglobulin C lambda 6 gene encodes the Kern+Oz-lambda chain and C lambda 4 and C lambda 5 are pseudogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9074–9078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Hood L. Linkage and sequence homology of two human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain constant region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin kappa light-chain genes are deleted or rearranged in lambda-producing B cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):368–372. doi: 10.1038/290368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. Cloned human and mouse kappa immunoglobulin constant and J region genes conserve homology in functional segments. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Walter M. A., Cox D. W. Complete physical map of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region gene complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. V., Singer R. H., Lawrence J. B. Fluorescent detection of nuclear RNA and DNA: implications for genome organization. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;35:73–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos S., Falk M. H., Lichter P., Haluska F. G., Henglein B., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Variable breakpoints in Burkitt lymphoma cells with chromosomal t(8;14) translocation separate c-myc and the IgH locus up to several hundred kb. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Nov;1(8):625–632. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.8.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Antigen receptor genes as molecular markers of lymphoid neoplasms. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1291–1295. doi: 10.1172/JCI112951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Rabbitts T. H. Comparison of the hinge-coding segments in human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain genes and the linkage of the gamma 2 and gamma 4 subclass genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):403–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., McNeil J. A. Interphase and metaphase resolution of different distances within the human dystrophin gene. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):928–932. doi: 10.1126/science.2203143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Boyle A. L., Cremer T., Ward D. C. Analysis of genes and chromosomes by nonisotopic in situ hybridization. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1991 Feb;8(1):24–35. doi: 10.1016/1050-3862(91)90005-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Borden J., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01790090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Swan D., Otey M. C., Leder P. Chromosomal location of human kappa and lambda immunoglobulin light chain constant region genes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1480–1490. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindl A., Klobeck H. G., Ohnheiser R., Zachau H. G. The V kappa gene repertoire in the human germ line. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1855–1863. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo J. V., Brito-Babapulle V., Foroni L., Robinson D. S., Luzzatto L., Catovsky D. Two new cell lines from B-prolymphocytic leukaemia: characterization by morphology, immunological markers, karyotype and Ig gene rearrangement. Int J Cancer. 1986 Oct 15;38(4):531–538. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo J. V., Foroni L., Brito-Babapulle V., Luzzatto L., Catovsky D. The establishment of cell lines from chronic B cell leukaemias: evidence of leukaemic origin by karyotypic abnormalities and Ig gene rearrangement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):23–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., Denny C. T., Witte O. N. Leukemia and the disruption of normal hematopoiesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90643-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):801–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R. A., Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Variable amplification of immunoglobulin lambda light-chain genes in human populations. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):172–174. doi: 10.1038/304172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B. J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization: applications in cytogenetics and gene mapping. Trends Genet. 1991 May;7(5):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udey J. A., Blomberg B. Human lambda light chain locus: organization and DNA sequences of three genomic J regions. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00768834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dekken H., van Rotterdam A., Jonker R., van der Voort H. T., Brakenhoff G. J., Bauman J. G. Confocal microscopy as a tool for the study of the intranuclear topography of chromosomes. J Microsc. 1990 May;158(Pt 2):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1990.tb02994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]