Abstract
Objectives
To review the extent of health disparities in gynecologic cancer care and outcomes and to propose recommendations to help counteract the disparities.
Methods
We searched the electronic databases PubMed and the Cochrane Library. We included studies demonstrating quantifiable differences by race and ethnicity in the incidence, treatment, and survival of gynecologic cancers in the United States (US). Most studies relied on retrospective data. We focused on differences between Black and White women, because of the limited number of studies on non-Black women.
Results
White women have a higher incidence of ovarian cancer compared to Black women. However, the all-cause ovarian cancer mortality in Black women is 1.3 times higher than that of White women. Endometrial and cervical cancer mortality in Black women is twice that of White women. The etiology of these disparities is multifaceted. However, much of the evidence suggests that equal care leads to equal outcomes for Black women diagnosed with gynecologic cancers. Underlying molecular factors may play an additional role in aggressive tumor biology and endometrial cancer disparities.
Conclusion
Gynecologic cancer disparities exist between Black and White women. The literature is limited by the lack of large prospective trials and adequate numbers of non-Black racial and ethnic groups. We conclude with recommendations for continued research and a multifaceted approach to eliminate gynecologic cancer disparities.
Keywords: racial; ethnic; disparities; gynecologic cancer; cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers
Introduction
According to the National Cancer Institute, healthcare disparities are defined as differences in the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of a disease and the related adverse health conditions that exist among specific population groups [1]. Ten years since the publication of Unequal Treatment, in which the Institute of Medicine (IOM) documented root causes for health disparities in the United States (US) [2], disparities persist. An example from internal medicine, documents the disparate burden of stroke incidence, mortality, prevention, and treatment in Blacks compared to Whites [3]. From the surgical literature, Blacks are more likely to undergo leg amputations and be placed on dialysis, but less likely to undergo renal transplant than Whites [4-6]. In the field of surgical oncology, Blacks are less likely than Whites to undergo cancer surgery for the treatment of most solid tumors [7]. Finally, Blacks have a higher risk of death from cancer than Whites, despite an overall declining cancer mortality rate in the US [8].
The underlying causes of health disparities are multifactorial and include systemic, provider, and patient factors according to the IOM [2]. Systemic factors include differences in health care delivery, including differences in hospital systems (e.g. large cancer center versus small county hospital). Provider factors involve expectations and beliefs that impact clinical decisions and the persistent lack of ethnic and racial diversity among providers [9]. Patient factors take into account cultural, educational, socioeconomic, and geographic barriers to care. These factors often overlap, but the relative influence of each remains poorly understood in gynecologic cancer disparities.
In this report, we document gynecologic cancer disparities in endometrial cancer, the most common; ovarian cancer, the most lethal; and cervical cancer, the most preventable. We focus our report on disparities in gynecologic cancer care and outcomes between Black and White women, based on available data. We conclude our report with recommendations for a multi-pronged strategy to eliminate disparities in gynecologic cancer care.
Methods
The Health Disparities Taskforce convened in 2010 under the auspices of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) to review and provide recommendations for addressing health disparities in gynecologic cancer. We performed a literature search of primary research articles from January 1985 to December 2012, from the PubMed and the Cochrane Library electronic databases. The search criteria included the following MeSH terms: health care disparities AND racial and ethnic health disparities AND gynecologic cancers AND treatment AND outcome. In addition, we used individual MeSH terms for ovarian, endometrial, and cervical cancers. Ninety-four peer-reviewed articles were identified. The majority of articles were based on Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) data so the populations were similar. Due to the limited number of studies for non-Black women, we concentrated our review on disparities between Black and White women in the US. We developed recommendations based on a summary of the evidence.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is the deadliest gynecologic cancer in the US, with an estimated 22,240 new cases and 14,030 deaths for 2013 [8]. The incidence is 12.7/100,000 women and mortality is 8.1/100,000 [10]. The survival rate has improved from 36% (1975-77) to 44% (2001-2007), p<0.05 [10] and parallels the rate for White women (36% to 43%). Over time, however, survival rates have worsened for Black women, from 42% to 36% [10], and the hazard ratio (HR) for all-cause mortality for Black women compared to White women is 1.31 (95% CI, 1.26-1.37) [11].
A major theme which emerges from the literature suggests that lack of access to standard care is a major contributing factor to ovarian cancer disparities. In 1997, Parham et al. first documented that Black women were less likely to receive combined surgery and chemotherapy treatment and had poorer survival rates [12]. More recent studies evaluating large clinical databases demonstrated disparities in ovarian cancer care and survival, between Black and White women [11, 13-27] (Table 1). Interestingly, once adjustments are made for stage, treatment, and socioeconomic status, disparities are reduced and/or eliminated in many of the studies.
Table 1.
Summary of disparities between Blacks and Whites in ovarian cancer treatment and outcome (2007-2012),ranked by type of trial.
| Author | Study Source Number of patients (n) Black (%) | Adjusted for SES | Adjusted for Comorbidities | Disease Stage (FIGO) | Survival Outcomes | Disparities (reference, White women 1.0, 95% confidence interval, where applicable) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Winter, 2007 | Clinical Trial (6 GOG trials) n = 1,895 Black (5.9%) | No | Yes | Stages III- IV | No difference for Black women PFS (HR: 1.12, 0.91-1.38) OS (HR: 1.11, 0.88-1.3) | No differences within a clinical trial with similar treatment |
| 2 | Farley, 2009 | Clinical Trial (7 GOG trials) n = 1,489 Black (6.5%) | No | Yes | Stages III- IV | No difference for Black women PFS (HR: 1.12, 0.90-1.40) OS (HR: 1.19, 0.95-1.49) | No differences within a clinical trial w ith s im ilar treatment |
| 3 | Albain, 2009 | Clinical Trial (5 SWOG trials) n = 1429 Black (3.9%) | Yes | No | Stages III- IV | Cause specific OS (HR: 1.48,1.03-2.11) | Black women with worse outcomes even when adjusted for income and education |
| 4 | Terplan, 2009 | Meta-analysis of 24 studies (Literature review 1950-2008) | Variable | Variable | All Stages | No difference for Black women OS (RR: 1.07, 0.97-1.18) | Black women less likely to receive surgical treatment; No difference in outcome from pooled studies; significant heterogeneity in studies; after 1985, survival for Black women was worse |
| 5 | Bristow, 2013 | Population (NCDB) n= 47,160 Black (6.7%) | Yes | No | All Stages | OS (HR: 1.28, 1.22-1.36) | Black women less likely to receive NCCN guideline-adherent care |
| 6 | Terplan, 2012 | Clinical Database (SEER 1973-2007) n = 47,752 Black (6.7%) | No | No | All Stages | All cause mortality for Black women (HR: 1.10, 1.06 1.15) | Trend of worsening outcomes for Black women over time (p<0.01); Black less likely to receive cancer directed surgery (p<0.01); Disparity remained when surgical treatment added (HR: 1.27, 1.21-1.34) |
| 7 | Fairfield, 2012 | Clinical Database (SEER 2001-2005) Black (7.1%) | Yes | Yes | All Stages | NR | Black women less likely to receive hospice care (p<0.0001) |
| 8 | Fairfield, 2010 | Clinical Database (SEER 1998-2005) n = 3,286 Black (5.9%) | No | Yes | All Stages | No difference after adjusting for receipt of cancer-directed surgery | White women more likely to undergo cancer-directed surgery (OR: 1.41, 1.10-1.82); Higher mortality in nonwhites, older women, women with more comorbities, advanced stage and geographic hospital referral region (if did not receive cancer-directed surgery). |
| 9 | Chan, 2008 | Clinical Database (SEER1988-2001) n = 24,038 Black (6.8%) | No | No | All Stages | Poorer survival for Black women (HR: 1.18, 1.10-1.27) | Poorer survival in Black women persisted even after adjusting for stage |
| 10 | Chan, 2007 | Clinical Database (SEER1988-2001) n = 6, 686 Black (5.8%) | No | No | Stage I | No difference in survival | Black women less likely to undergo lymph node dissection (, p<0.001); however, race left out of hazard model |
| 11 | Chase, 2012 | Clinical Database (NCDB 2003-2006) n = 25, 916 Black (11%) | Yes | Yes | Stages III- IV | NR | Black women less likely to receive standard of care (RR: 0.87, 0.83 0.92) |
| 12 | Bristow, 2011 | Clinical Database (MHSCRC 2001 2009) n = 2487 Black (16.1%) | No | No | All Stages | NR | Black women less likely to undergo initial ovarian cancer surgery hysterectomy (OR: 0.53, 0.42-0.66, p<0.0001) or receive care from a high-volume surgeon (OR: 0.55, 0.44-0.69, p < 0.0001) |
| 13 | Du, 2008 | Clinical Database (SEER 1992-1999) n = 5,414 Black (5.9%) | Yes | Yes | All Stages | No difference for Black women (HR: 1.00, 0.88-1.13) | No s ignificant difference in survival after adjusting for tumor characteristics, treatment and socio- demographic factors |
| 14 | Morris, 2010 | Clinical Database (CCR 1996-2006) n = 16, 228 Black (6.8%) | Yes | No | Stages, I, III-IV Stage II excluded) | NR | Black women less likely to be diagnosed with early stage disease (OR: 0.78, 0.55-.92) |
| 15 | Aranda, 2008 | Clinical Database (CCR 1991-2002) n = 19,796 Black (4%) | Yes | Yes | All Stages | NR | Black (RR: 0.70, p<0.05) women less likely to receive care from a high-volume surgeon |
| 16 | Goff, 2007 | Hospital Care Cost and Utilization Discharge Data -9 states (1999 2002) n = 10,432 Black (6.4%) | Yes | Yes | All Stages | NR | Black (OR (0.52-0.83) less likely to undergo comprehensive surgical care; racial disparity significant event after adjusting for income |
SES=social economic status, FIGO=International Federation Gynecology Obstetrics, GOG=Gynecologic Oncology Group, PFS=progression-free survival, HR=hazard ratio, OS=overall survival, SWOG=Southwest Oncology Group, RR=response rate, NCDB=National Cancer Data Base, NCCN= National Comprehensive Cancer Network, SEER= Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results, NR=not reported, OR=overall response, MHSCRC=Maryland Health Cost Review Commission, CCR=California Cancer Registry Guidelines: Society of Gynecologic Oncology, American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Society of Clinical Oncology, National Comprehensive Cancer Network
Standard of care for the treatment of early stage ovarian cancer impacts survival. Women diagnosed with tumors that are completely confined to the ovary have a greater than 90% survival rate [10]. However, more than 25% of women who have not undergone proper staging are reclassified with higher stage disease [28]. While 97% of gynecologic oncologists perform all of the surgical procedures necessary to adequately stage women with ovarian cancer, this procedure is only accomplished by 52% of general obstetrician gynecologists and 35% of general surgeons [29]. In a study of factors associated with the diagnosis of early stage ovarian cancer Black women were less likely to be diagnosed with early ovarian cancer than White women (overall response (OR) = 0.78, 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.55-0.92) [25]. Ethnic and racial minorities and poor women are less likely to receive surgical treatment or care by a high-volume surgeon specializing in gynecologic oncology [16,23,26,30]. Thus, lack of access to a qualified surgeon for proper surgical staging may impact outcome and contribute to disparities in early stage ovarian cancer.
Approximately 70% of women with ovarian cancer are diagnosed with advanced stage disease, which is associated with a poorer prognosis[10]. Standard of care for advanced stage ovarian cancer entails aggressive surgical removal of tumors (cytoreductive surgery), followed by platinum/taxane-based chemotherapy regimen. Optimal cytoreductive surgery correlates directly with ovarian cancer outcomes and cancer-directed surgery by a gynecologic oncologist is associated with an increase in median survival [31-34]. Furthermore, in women diagnosed with advanced stage disease who complete optimal cytoreductive surgery adjuvant treatment with intraperitoneal chemotherapy provides a significant survival advantage [31]. Similar to the findings for early stage disease, Black women diagnosed with advanced stage disease were less likely to receive standard of care, cancer-directed surgery, and care from a high volume surgeon [11,16,17,19,22,23,26,30].
Underlying comorbidities could contribute to patient and provider factors for not receiving standard of care. A recent report showed that women with significant comorbidities were less likely to undergo standard of care therapy [22]. A high comorbidity score of 2+ was associated with a decreased chance of undergoing standard treatment (response rate (RR) = 0.74, 95% CI, 0.68-0.80)[22]. Black women have a higher incidence of medical comorbidities such as diabetes than White women [35]. However, direct correlations between the morbidity score, race, and overall ovarian cancer treatment and outcomes were not shown.
Disparities in outcome appear to dissipate between Black and White women who receive similar care. There were no disparities in outcome between Black and White women with advanced stage ovarian cancer in the Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) clinical trials in which patients received similar treatments [13,14]. Similarly, several small retrospective studies from major referral/tertiary care centers found no apparent disparity in treatment and outcomes between Black and White women [36,37]. Although these retrospective reports are limited by the type of study and small number of patients, the results suggest that equal treatment is associated with equal outcomes. In a more recent analysis, lack of adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines independently predicted poorer overall survival (OS) (HR: 1.43, 95% CI, 1. 38–1.47) [17]. Therefore, adherence to evidence-based guidelines could enhance quality care for all women and as a consequence contribute to reducing ovarian cancer disparities in outcome.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy diagnosed among women in the US. An estimated 49,560 new cases of uterine cancer and 8,190 deaths expected in 2013 [8]. When diagnosed at a local or regional stage, the 5-year survival rate is 96% and 67% respectively, while distant stage survival decreases to 16%. White women have the highest age-adjusted incidence (24.8/100,000) of endometrial cancer compared to any other ethnic group. Since 2004, incidence rates for endometrial cancer have been stable in most ethnic groups but increasing in Black women by 1.9% per year [38]. The age-adjusted incidence for Black women is 21.8/100,000, but the mortality rate is twice as high (7.3/100,000) compared to White women (3.9/100,000)[10]. The relative survival rate for endometrial cancer in Whites exceeds that for Blacks by greater than 7% at every stage of diagnosis [30].
Multiple studies cite cultural barriers, socioeconomic status, lack of access to care, comorbidities, inequity in treatment, and tumor biological factors as reasons for endometrial cancer disparities [39,40]. A multivariate analysis showed that Black women with lower socioeconomic status were more likely to present with advanced stage disease at the time of diagnosis, even when controlling for poor histology [41]. Once in the medical system, studies show Black women are less likely to be treated for advanced disease [41-42]. Comorbities such as diabetes and hypertension may impact this treatment disparity. In the Black/White Cancer Survival study, Black women were more than twice as likely as White women to be obese, diabetic, and hypertensive and these risk factors associated with the development of endometrial cancer [43]. However, the effects of comorbidities on disease-specific and OS have been mixed. Some studies revealed poorer OS in women with diabetes, while others showed no association [42, 44-46].
Similar to the findings in ovarian cancer, variations in access to care and unequal treatment across races have been cited as major contributors to disparity in endometrial cancer survival. The National Cancer Data Base (NCDB) endometrial cancer outcome data of over 50,000 subjects found that 9% of Black patients did not receive any cancer-directed treatment compared to 4% of White women. Among the women who did receive treatment, Black women were more likely to receive primary radiotherapy and less likely to undergo surgery [41-42]. Randall et al. also found Black women were less likely to undergo hysterectomy after controlling for tumor grade and histology at all stages of disease [47]. Some studies have cited cultural barriers that prevent Black women from seeking medical care even when symptomatic, which contributes to late presentation with advanced disease [40-41]. In contrast, other studies demonstrate similar intervals from onset of symptoms to hysterectomy among Black and White women diagnosed with endometrial cancer [40,48].
More recent studies reveal that Black women are more likely to be treated in high volume, large urban teaching hospitals by a specialist, but still have a higher mortality rate than White women (4.7 yr OS Black vs. 6.4 yr OS White) [49]. In fact, when surgery was performed, the rate of staging with lymphadenectomy in Black women appears similar to their White counterparts [49-51]. However, even when treated within the same medical system, Black women had a higher incidence of unfavorable histologies, higher grade lesions, and decreased OS compared to Whites (OS; 72%, 77%, 91% respectively) [51].
Aggressive histology types, such as serous or clear cell adenocarcinoma, carcinosarcoma, and uterine sarcomas, have been shown to account for a disproportionate percentage of tumors seen among Black women [42,43,46,52,53]. The histopathologic features evaluated in these large population based studies typically represent the usual types of endometrial cancers, (serous, clear cell, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas) and may account for more advanced stage at presentation seen among Black women [42,43,47,53,54](Table 2A). Although poor histology surely effects outcome, in an analysis of the SEER database, survival remained worse for Black women for all histopathological categories, regardless of stage, and worsened with age [46,52,54,55]. Furthermore, Black women had an overall RR of only 34.9% compared to 43.2% for White women among participants in a GOG randomized clinical trial for advanced stage and recurrent endometrial cancer [55]. In that study, Black women had a 26% greater chance of dying when compared with White patients, despite receiving similar surgical and chemotherapy treatments and controlling for prognostic factors. Even in early-stage endometrial cancer, recurrence-free survival was shorter for Black women under the same clinical trial settings [56]. Thus, unlike ovarian cancer where similar treatment appears to be associated with similar outcomes, disparities in endometrial cancer outcomes persist after adjusting for socioeconomic factors and treatment environment. Taken together, these studies suggest a role for a molecular basis for the aggressive tumor biology and response to treatment observed among Black women.
Table 2A.
Summary of disparities between Blacks and Whites in endometrial cancer outcomes: The Role of Histology
| Author | Study Source Number of patients (n) Black (%) | Adjusted for SES | Adjusted for Comorbidities | Disease Stage / Histology * | Survival Outcomes | Disparities (reference, White women 1.0, 95% confidence interval, where applicable) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hill 1996 | Population (Black/White Cancer Survival Study 1985-1987) n=459 Black (28.3%) | Yes | Yes | All Stages * | Poorer survival for Black women (HR: 4.0 2.8-5.6) | Black women more likely to present with advanced stage, aggressive + histologies, & poorly differentiated tumors (p<.001) Black women less likely to have surgical treatment in early Stage disease (OR 6.2, 2.5, 15.6 p<.001) |
| 2 | Hicks 1998 | Population (NCDB 1998-1994) n=55,533 Black (5.8%) | Yes | Yes | All Stages * | Poorer survival for Black women at every Stage | Black women more likely to present with aggressive histologies, advanced stage, poorly differentiated tumors. Black women less likely to have surgery (79% vs 91%) Income level not associated with receiving cancer-directed treatment |
| 3 | Sherman 2003 | Clinical Database (SEER 1992-1998) n=20,192 Black (9.1%) | No | No | All Stages* Includes carcinosarcoma & other uterine sarcomas | Poorer survival for Black women for every Stage, Age (>75yo) & Histopathology category | Black women have higher incidence of serous/clear cell RR 1.85 1.61 2.12 More aggressive tumors (Category II-III) reflect highest mortality rate for blacks (53% vs 36%) |
| 4 | Randall 2003 | Clinical Database (SEER 1992-1998) n=21,561 Black (5.7%) | No | No | All Stages * | All cause mortality worse for Black women (HR: 2.57 2.31 2.86) | Black women more likely to present with advanced stage & poor histology (P<.0005) Black women less likely to undergo surgery after adjusting for tumor & sociodemographic characteristics (OR .28: 0.19-0.41 for Stage I-III) (OR .54: .34-.85 for Stage IV) |
| 4 | Madison 2004 | Clincal Database (SEER 1990-1998) n=3168 Black (15.4%) | Yes | No | All Stages* | Blacks with higher mortality rate at every stage (47% vs 26.3% p<.001) | Black women more likely to have aggressive histology, higher grade & advanced stage (p=.001) Black women less likely to have a hysterectomy (OR= 39 .30-.50) Higher income inversely related with advanced stage, independent of race (OR: 0.83 .69-.99) |
| 5 | Setiawan 2007 | Population (Multiethnic cohort study 1993-1996) n= 46,933 Black (16.5%) | No | Yes | All Stages* Includes transitional cell carcinosarcoma | NR | Black women more likely to have aggressive histologies, high grade tumors even at same stage (p<.001) Black women more likely to have advanced cancer (RR 1.80; RR↓1.57 after adjustment for risk factors) Prevalence of risk factors by race 28 did not account for disparities. |
| 6 | Wright 2008 | Clinical Database (SEER 1988-2004) n=80,915 Black (7%) | No | No | All Stages* Includes carcinosarcoma & pure sarcoma | Blacks with higher mortality (HR:1.60 1.51 1.69) | Black women more likely to have aggressive histology, advanced stage (p<.001) No difference in staging lymphadenectomy, or use of radiation |
| 7 | Oliver 2011 | Tumor Registry Database (Department of Defense 1990-2003) n = 2582 Black (7.1%) | No | No | All Stages* | NR | Older Black women (>50yo) are more likely to present with non endometrioid histology; poorly differentiated tumors (p<.01) & non- localized tumors (p =.02) in equal access environment. |
| 8 | Smotkin 2012 | Single Institution Review (1999-2009) n=984 Black (31.3%) | No | Yes | All Stages* Included carcinosarcoma & other uterine sarcomas sarcoma | Black women with higher mortality (HR:1.94 p<.001) | Black women more likely to have non endometrioid histologies p< .001 When controlled for histology, no difference in survival seen. (HR 1.12 .84-1.48) |
SES=social economic status, HR=hazard ratio, OR=overall response, NCDB=National Cancer Data Base, SEER= Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results, RR=response rate, NR=not reported
includes usual histology types endometrioid adenocarcinoma, clear cell, papillary serous, squamous cell carcinoma, undifferentiated carcinoma
aggressive histologies refer to papillary serous, clear cell, carcinosarcomas; "other sarcomas": Leiomyosarcoma, adenosarcoma when included with the study
Initial studies to evaluate molecular alterations focused on individual genes such as p53, HER2/neu, and PTEN (Table 2B). Overexpression of mutant tumor suppressor p53 has been associated with poor histologic grade, non-endometrioid histology, advanced stage, and poor survival rates [57,58]. Clifford et al. found worse survival and higher recurrence rates among Black women diagnosed with Stage I tumors which were three times more likely to have overexpression of mutant p53[57]. HER2/neu is a proto-oncogene whose overexpression has been associated with resistance to treatment and poor outcomes in breast, ovary, and endometrial cancer[59,60]. HER2/neu expression was three-fold higher in Black patients with uterine papillary serous cancer than in Whites with the same histology [59]. PTEN mutations occur in one-third of endometrial cancers and are typically associated with more favorable tumor characteristics and prognosis. Maxwell et al. [60] performed PTEN mutation analysis on tumors of 140 women with advanced endometrial cancer. Those with PTEN mutations were more likely to be White women and to have endometrioid histology and improved OS when compared to Black women.
Table 2B.
Biologic factors associated with endometrial cancer disparities between Black and White women.
| Author | Genetic Alterations | Gene Type | Histologic Association | Cases | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clifford, 1997 | p53 overexpression | Tumor Suppressor Gene | Non endometrioid, papillary serous, metastatic, advanced stage tumors | n=164 Stage I 28 mutations found | 34% Blackvs 11% White had overexpression; 14% Black vs 8%White had recurrent disease |
| Maxwell, 2000 | PTEN mutation | Tumor Suppressor Gene | Endometrioid, early stage | n=140 Stage III/IV 20 mutations found | 5% Blackvs 22% White had overexpression |
| Santin, 2005 | HER2/neu expression | Proto-oncogene | Papillary serous | n=27 Stage I-IV 17 mutations found | 90% Black vs 48%White had overexpression; Overall survival at 4 yr 23% Black vs 63% White |
Exploratory analyses have been extended to look for multiple genomic factors. Despite finding higher proportion of non-endometrioid type tumors among Black women no differences in profiles of VEGF, HIF-1alpha, or ki67 were associated with outcome [61]. Array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) from DNA derived from 80 tumor specimens revealed a gain of chromosome 1q23 as a frequent event in Black patients irrespective of stage. The overall frequency of this event in high grade or advanced stage endometrial cancer was 15-20% [62]. Although the numbers are small, these molecular studies provide evidence for impact on outcome based on molecular alterations despite equivalent stage and grade of tumor. Larger genome-wide analyses of endometrial cancer through the Cancer Genome Atlas will provide additional insight into whether the molecular alterations are surrogate markers or contributors to disparities in endometrial cancer.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is the second-most common cancer in women worldwide with nearly 530,000 new cases and 275,000 deaths attributed to the disease annually [63]. The widespread implementation of effective cervical cancer screening programs in the US had led to a steady decline in the incidence and mortality from the disease among US women since the 1970s. These decreases, however, have begun to level off in recent years. Between 2005 and 2009 cervical cancer mortality has been stable for all women and the incidence has been stable for women less than 50 years of age [38]. Despite the past improvements, an estimated 12,340 American women will be diagnosed with cervical cancer in 2013, and 4,030 women will die of the disease [8, 38]. While cervical cancer rates have declined over time for all US women, significant disparities persist.
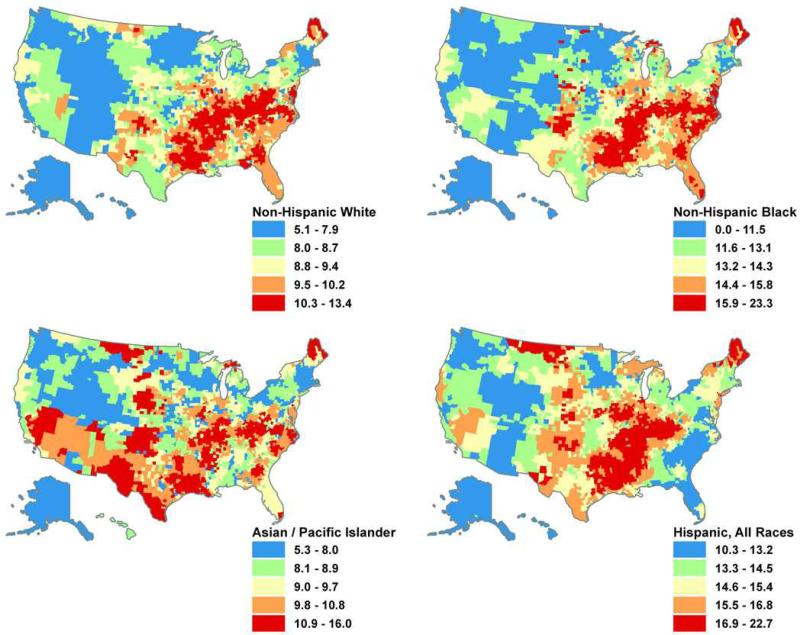
Between 2005 and 2009, the age-adjusted incidence of cervical cancer calculated by the SEER database was 8.0/100,000 for White women compared to 9.8/100,000 for Black women. The corresponding mortality rates (per 100,000 women) are 2.2 for White women and 4.3 for Black women [10]. There are also significant variations in the geographic distribution of cervical cancer within the US. Figure 1 shows the estimated US cervical cancer incidence rates among racial and ethnic groups by county between 1995 and 2004. The distribution of counties with elevated cervical cancer incidence rates among non-Hispanic White women and Black women was similar and included the lower Mississippi valley and the South Atlantic [64].
Figure 1.
Estimated United States cervical cancer incidence rates among racial and ethnic groups by county
Despite decreasing mortality rates for all US women the risk of death from cervical cancer for Black women remains twice that of White women. Between 2003 and 2007, the SEER database estimated a mortality rate of 4.4/100,000 for Black women and 2.2/100,000 for White women [65]. The overall 5-year survival for all stages of cervical cancer is 61% for Black women compared with 72% for White women [10].
A comprehensive review of the possible explanations for cervical cancer disparity should begin with an examination of cervical cancer prevention efforts among various groups. Primary prevention is now possible due to the introduction of prophylactic human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccines. Since 2005, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices has recommended the routine vaccination of adolescent girls with the HPV vaccine at 11 or 12 years of age as well as “catch-up” vaccination of women up to the age of 26 years [66]. An analysis of data from the 2008-2009 National Immunization Survey-Teen for girls aged 13-17 years who received at least one dose of HPV vaccine, however, demonstrated a significantly lower rate of completion of the vaccination schedule among Black and Hispanic adolescents compared with White adolescents. Poverty was also an independent predictor of compliance with adolescents living below the federal poverty line having a significantly lower vaccination completion rate than those with household incomes greater than $75,000 per year [67]. Widdice et al. showed that Black adolescents were 50% less likely to complete the vaccination schedule compared with their White counterparts and that adolescents with public insurance were 24% less likely to complete the vaccination compared with those with private insurance [65]. Despite the lower rates of completing the 3-dose schedule, Black adolescents are significantly more likely to initiate the HPV vaccination process compared to White adolescents [66]. The precise explanations for the disparities in HPV vaccination completion rates are unknown, but these findings suggest that the barriers to completion of vaccination are distinct from those for initiation. The HPV vaccines represent a paradigm shift from cancer screening and early detection to cervical cancer prevention and hold the potential to dramatically reduce the overall cervical cancer burden as well as eradicate cervical cancer disparities. Identifying and addressing barriers to vaccination are essential steps toward realizing this potential.
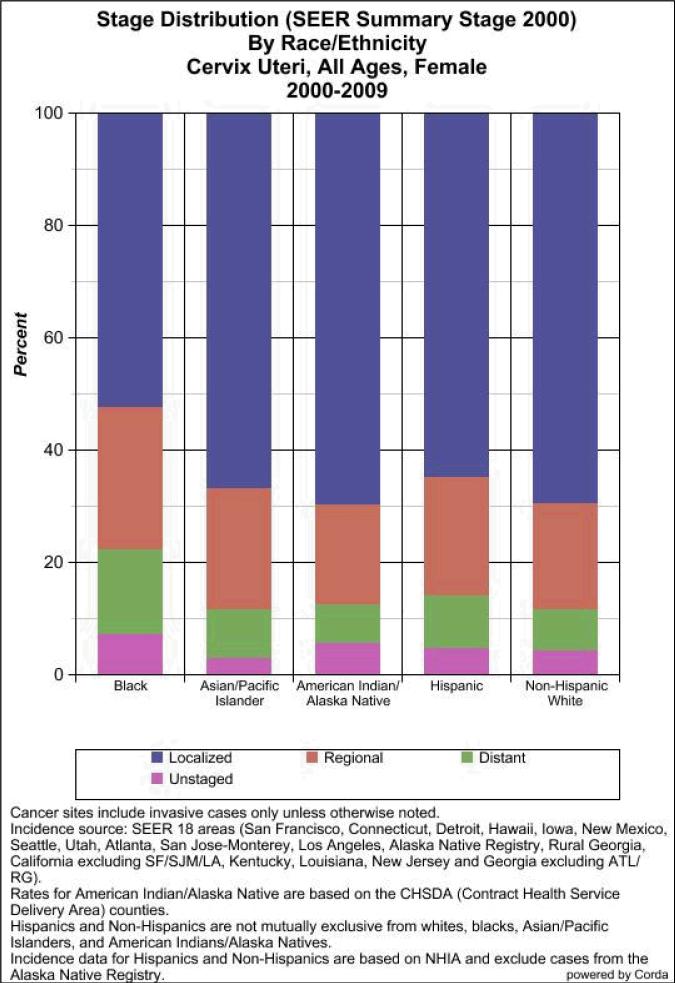
This variation in the rate of cervical cancer screening is another potential explanation for the observed disparity in cervical cancer incidence and mortality. Data collected from the National Health Interview Survey 2010 showed 83% of US women who had not undergone hysterectomy had a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear within the past three years. However, the disparity in cervical cancer incidence between Black and White women cannot be explained by differences in screening, as compliance rates were similar between the two groups (85% and 83.4%, respectively) [70]. Screening rates in all US women fell well below the goal of 97% compliance set by the Department of Health and Human Services through the Healthy People 2010 initiative. Nevertheless, even if parity in the frequency at which women obtain Pap smears is achieved, differences in the rate of follow-up for abnormal cervical cytology remains a potential cause of outcome disparity. A study of 10,004 women in the National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program found that only 44% of patients with two consecutive low-grade abnormal Pap smears were followed up appropriately with colposcopy. Black women were the most likely to receive no follow-up [71]. Thus, varying rates of cervical cancer screening and compliance with follow-up may partially explain the observed differences in disease stage at presentation. Figure 2 outlines the stage distribution of cervical cancer for the major ethnic/racial groups in the US according to the SEER database from 2000-2009. Black women were less likely to present with localized disease and more likely to present with distant metastases compared with White women.
Figure 2.
SEER stage distribution of cervical cancer
Treatment differences have been well-documented and likely play a major role in cervical cancer disparity. An analysis of 7,627 women diagnosed with cervical cancer between 1992 and 1996 demonstrated significant treatment and survival differences based on race/ethnicity. Of subjects who underwent cancer-directed surgery as part of their initial treatment, more Hispanics (51.7%) underwent radical hysterectomy, and considerably more Blacks (32.4%) had local surgery compared to the other racial/ethnic groups. The 5-year observed survival was similar for non-Hispanic White women (68%, 95% CI: 67–70%) and Hispanic women (71%, 95% CI: 68–73%). However, Black women had significantly decreased 5-year observed survival (56%, 95% CI: 53– 59%) compared to White women. After controlling for age, stage, histology, type of initial treatment, and SEER registry, Black women remained at 19% increased risk of death compared to White women. Other studies have shown Black women are less likely to receive radical hysterectomy (compared with pelvic irradiation) for early-stage cervical cancer compared to White women[72], and are less likely to receive intra-cavitary radiation for the treatment of locally-advanced disease[73].
In an attempt to control for many of the socioeconomic and demographic factors that biased prior studies, Farley et al. [74] examined the impact of race/ethnicity on cervical cancer treatment and survival within the US Armed Forces Health Care System. Given the universal access to healthcare provided within an ethnically diverse military, socioeconomic, and racial biases would likely be minimized, if not eliminated. The authors found no difference in the age of diagnosis, the stage distribution, or the percentage of patients receiving surgery or radiation as initial therapy between Black and White women. Five- and 10-year survival rates for Whites and Blacks were similar at 75% and 64%, respectively (P = 0.59). Similar to several ovarian cancer studies, this study suggests that when given equal access to care, there is no disparity in cervical cancer treatment or survival between Black and White women.
Discussion
The reasons for health disparities in gynecologic cancer care and outcomes are multifactorial and still not completely understood. Since the publication of the IOM ten years ago [2], there appears to be increased awareness and understanding about ethnic and racial health disparities, including gynecologic cancer care and outcomes. However, most published studies have focused on disparities between Black and White women, while studies including non-Black women are sparse. Most studies relied heavily on large clinical databases with incomplete information about systemic factors (ex. large, tertiary cancer center, community hospital, and inner city public hospital); provider (ex. level of expertise, training, clinical expectations, and beliefs); and patients (ex. socioeconomic status, insurance, comorbidities, education, language, culture expectations, and beliefs). Despite more recent research examining systemic and provider factors, the number of studies remains comparatively small. The majority of the literature is concentrated on patient factors, particularly socioeconomic status and comorbidities. An additional intriguing patient factor that may contribute to endometrial cancer disparities relates to the molecular biology of tumors in Black women. A few reports suggest that cultural and educational barriers are associated with lack of uptake for genetic testing for breast and ovarian cancers among Black women [75,76]. As advances in the molecular underpinnings of gynecologic cancers increase, access to and acceptance of genetic testing is an understudied area of investigation. This could mitigate the difficulties of racial categorization (ex. self reporting versus physical reporting; mixed race persons) inherent in the studies of disparities based upon race.
Conclusion
As molecular genetic information becomes more readily accessible and the cost of new technologies such as whole genome sequencing decreases [77], the prospect of individualized therapy, with the promise of improving treatment and outcomes in cancer approaches a reality. At the same time, gaps in cancer disparities persist and are even widening in some instances. As a result of our review, we conclude that the lack of access to quality care remains a major burden for women diagnosed with gynecologic cancers and is a major point for intervention. From prevention and screening (cervical cancer) to cancer-directed surgery (ovarian, endometrial, and cervical cancers) receipt of standard of care positively impacts survival. To this end, one of the recommendations published in the IOM 2002 report is to “provide consistency and equity of care through the use of evidence-based guidelines” [2]. At a minimum, adherence to evidence-based guidelines should enhance quality care for more women and could reduce health disparities in ovarian and other gynecologic cancer outcomes. Through these initiatives, we can begin to improve survival for all populations with gynecologic cancers. We recommend a research priority for the development of specific interventions to increase access to quality gynecologic cancer care.
We acknowledge that addressing access to care will not be sufficient to account for the complex and multifactorial reasons for gynecologic care disparities (Table 3). Ongoing research and policy interventions are required in the context of larger efforts to eliminate health disparities in general. We believe that in line with the stated mission “to eradicate gynecologic cancers”, SGO is in a position to lead efforts to eliminate disparities in gynecologic cancer care. We believe that this can be achieved by partnering with other organizations with research and policies already in place to: 1) expand access to quality health care; 2) enhance educational efforts and awareness of racial and ethnic disparities; 3) train a more diverse oncology workforce; 4) include disparities in research priorities; 5) expand clinical trials to include more diverse patient populations, and 6) enhance individual patient participation in care[78] is a critical step to eliminating gynecologic cancer disparities.
Table 3.
Summary of the most commonly cited factors for gynecologic cancer disparities and potential strategies to alleviate the disparity.
| IOM Factor | Disparities | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| I. Systemic | ||
| Geographic/low capacity region (inner city urban/rural) | Partner with regional referral centers | |
| Low volume hospital/catchment area | Refer to specialized regional centers | |
| II. Provider | ||
| Low volume surgeon | Encourage referral to high volume surgeons | |
| Non-gynecologic oncology specialist | Encourage referral to gynecologic oncology specialists | |
| Clinical decision making | Investigate factors beyond patient comorbidities Increase awareness and incorporate health disparities/equity topics into national meetings Encourage participation in clinical trials | |
| III. Patient | ||
| Socioeconomic status (poverty, education levels and lack of insurance) | Encourage policies to expand access to prevention and screening, treatment and clinical trials | |
| Comorbidities | Increase awareness and interventions for healthy lifestyle/behavior | |
| Willingness to undergo care | Outreach, education and awareness about gynecologic cancers | |
We conclude with a quote from Franklin D. Roosevelt: “The test of our progress is not whether we add more to the abundance of those who have much; it is whether we provide enough for those who have too little.”[79].
Statement from Society of Gynecologic Oncology
This document was prepared through the auspices of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. However, the authors are solely responsible for the content.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Daniele A. Sumner, BA for her assistance in editing this manuscript. However, the authors are solely responsible for the content.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement:
Drs. Yvonne Collins and Kevin Holcomb disclose that they have received honoraria for the Merck speaker bureau. Additionally, Dr. Dineo Khabele discloses that she has received a research grant from the Celgene Corporation. Drs. Eloise Chapman-Davis and John H. Farley have no financial relationships and/or conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.National Cancer Institute . Cancer Health Disparities [Internet] National Institute of Health; Bethesda (MD): 1999. [cited 2012 May 30]. Available from: http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/disparities/cancer-health-disparities. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smedley BD, Stith AY, Nelson AR, editors. Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. Vol. 20. National Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cruz-Flores S, Rabinstein A, Biller J, Elkind MS, Griffith P, Gorelick PB, et al. Racial-ethnic disparities in stroke care: the American experience: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011 Jul;42(7):2091–116. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3182213e24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lefebvre K, Metraux S. Disparity in level of amputation among minorities: implications for improved preventative care. J Natl Med Assoc. 2009 Jul;101(7):649–55. doi: 10.1016/s0027-9684(15)30973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gunderman RB. Addressing racial and ethnic disparities in health care. Radiology. 2007 Jul;244(1):28–30. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2441060305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, Velopulos C, Bentley JM, Cornwell EE, 3rd, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013 Mar;216(3):482–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Morris AM, Rhoads KF, Stain SC, Birkmeyer JD. Understanding racial disparities in cancer treatment and outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2010 Jul;211(1):105–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.02.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013 Jan;63(1):11–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Association of American Medical Colleges . Diversity Policy and Programs. Association of American Medical Colleges; Diversity in Medical Education: Facts and Figures 2012. [Internet] Available from: http://www.aamc.org/factsandfigures. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Altekruse SF, et al., editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations) National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/, based on November 2011 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Terplan M, Schluterman N, McNamara EJ, Tracy JK, Temkin SM. Have racial disparities in ovarian cancer increased over time? An analysis of SEER data. Gynecol Oncol. 2012 Apr;125(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Parham G, Phillips JL, Hicks ML, Andrews N, Jones WB, Shingleton HM, et al. The National Cancer Data Base report on malignant epithelial ovarian carcinoma in African-American women. Cancer. 1997 Aug 15;80(4):816–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Winter WE, 3rd, Maxwell GL, Tian C, Carlson JW, Ozols RF, Rose PG, et al. Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Prognostic factors for stage III epithelial ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Aug 20;25(24):3621–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.10.2517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Farley JH, Tian C, Rose GS, Brown CL, Birrer M, Maxwell GL. Race does not impact outcome for advanced ovarian cancer patients treated with cisplatin/paclitaxel: an analysis of Gynecologic Oncology Group trials. Cancer. 2009 Sep 15;115(18):4210–7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Albain KS, Unger JM, Crowley JJ, Coltman CA, Jr, Hershman DL. Racial disparities in cancer survival among randomized clinical trials patients of the Southwest Oncology Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 Jul 15;101(14):984–92. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Terplan M, Smith EJ, Temkin SM. Race in ovarian cancer treatment and survival: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2009 Sep;20(7):1139–50. doi: 10.1007/s10552-009-9322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bristow RE, Powell MA, Al-Hammadi N, Chen L, Miller JP, Roland PY, et al. Disparities in Ovarian Cancer Care Quality and Survival According to Race and Socioeconomic Status. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Jun 5;105(11):823–32. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fairfield KM, Murray KM, Wierman HR, Han PK, Hallen S, Miesfeldt S, et al. Disparities in hospice care among older women dying with ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2012 Apr;125(1):14–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.11.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fairfield KM, Lucas FL, Earle CC, Small L, Trimble EL, Warren JL. Regional variation in cancer-directed surgery and mortality among women with epithelial ovarian cancer in the Medicare population. Cancer. 2010 Oct 15;116(20):4840–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chan JK, Zhang M, Hu JM, Shin JY, Osann K, Kapp DS. Racial disparities in surgical treatment and survival of epithelial ovarian cancer in United States. J Surg Oncol. 2008 Feb 1;97(2):103–7. doi: 10.1002/jso.20932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chan JK, Munro EG, Cheung MK, Husain A, Teng NN, Berek JS, et al. Association of lymphadenectomy and survival in stage I ovarian cancer patients. Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Jan;109(1):12–9. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000249610.95885.ef. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chase DM, Fedewa S, Chou TS, Chen A, Ward E, Brewster WR. Disparities in the allocation of treatment in advanced ovarian cancer: are there certain patient characteristics associated with nonstandard therapy? Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Jan;119(1):68–77. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823d4006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bristow RE, Zahurak ML, Ibeanu OA. Racial disparities in ovarian cancer surgical care: a population-based analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2011 May 1;121(2):364–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.12.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Du XL, Sun CC, Milam MR, Bodurka DC, Fang S. Ethnic differences in socioeconomic status, diagnosis, treatment, and survival among older women with epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2008 Jul-Aug;18(4):660–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2007.01081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Morris CR, Sands MT, Smith LH. Ovarian cancer: predictors of early-stage diagnosis. Cancer Causes Control. 2010 Aug;21(8):1203–11. doi: 10.1007/s10552-010-9547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aranda MA, McGory M, Sekeris E, Maggard M, Ko C, Zingmond DS. Do racial/ethnic disparities exist in the utilization of high-volume surgeons for women with ovarian cancer? Gynecol Oncol. 2008 Nov;111(2):166–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.08.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Goff BA, Matthews BJ, Larson EH, Andrilla CH, Wynn M, Lishner DM, et al. Predictors of comprehensive surgical treatment in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer. 2007 May 15;109(10):2031–42. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stier EA, Barakat RR, Curtin JP, Brown CL, Jones WB, Hoskins WJ. Laparotomy to complete staging of presumed early ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1996 May;87(5 Pt 1):737–40. doi: 10.1016/0029-7844(96)00021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McGowan L, Lesher LP, Norris HJ, Barnett M. Misstaging of ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Apr;65(4):568–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Boyd LR, Novetsky AP, Curtin JP. Ovarian cancer care for the underserved: are surgical patterns of care different in a public hospital setting? Cancer. 2011 Feb 15;117(4):777–83. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bristow RE, Tomacruz RS, Armstrong DK, Trimble EL, Montz FJ. Survival effect of maximal cytoreductive surgery for advanced ovarian carcinoma during the platinum era: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2002 Mar 1;20(5):1248–59. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.20.5.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fader AN, Rose PG. Role of surgery in ovarian carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Jul 10;25(20):2873–83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.0932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Armstrong DK, Bundy B, Wenzel L, Huang HQ, Baergen R, Lele S, et al. Gynecologic Oncology Group. Intraperitoneal cisplatin and paclitaxel in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006 Jan 5;354(1):34–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Muggia F. Platinum compounds 30 years after the introduction of cisplatin: implications for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2009 Jan;112(1):275–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.09.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Center for Disease Control and Prevention . Division of Diabetes Translation. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; Diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes in the United States, all ages, 2010. [Internet] (cited 2011 May 23) Available from : http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/estimates11.htm#4. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bristow RE, Ueda S, Gerardi MA, Ajiboye OB, Ibeanu OA. Analysis of racial disparities in stage IIIC epithelial ovarian cancer care and outcomes in a tertiary gynecologic oncology referral center. Gynecol Oncol. 2011 Aug;122(2):319–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.04.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Terplan M, Temkin S, Tergas A, Lengyel E. Does equal treatment yield equal outcomes? The impact of race on survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008 Nov;111(2):173–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.08.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts and Figures 2012 [Internet] American Cancer Society, Inc.; Atlanta (GA): 2012 [cited 2012 May 30]. Available from: http://www.cancer.org/Research/CancerFactsFigures/ [Google Scholar]
- 39.Allard JE, Maxwell GL. Race disparities between black and white women in the incidence, treatment, and prognosis of endometrial cancer. Cancer Control. 2009 Jan;16(1):53–6. doi: 10.1177/107327480901600108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yap S, Matthew RP. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Cancers of the Uterine Corpus. J Natl Med Accoc. 2006;98(12):1930–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Madison T, Schottenfeld D, James SA, Schwartz AG, Gruber SB. Endometrial cancer: socioeconomic status and racial/ethnic differences in stage at diagnosis, treatment, and survival. Am J Public Health. 2004 Dec;94(12):2104–11. doi: 10.2105/ajph.94.12.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hicks ML, Phillips JL, Parham G, Andrews N, Jones WB, Shingleton HM, et al. The National Cancer Data Base report on endometrial carcinoma in African-American women. Cancer. 1998 Dec 15;83(12):2629–37. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19981215)83:12<2629::AID-CNCR30>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hill HA, Eley JW, Harlan LC, Greenberg RS, Barrett RJ, 2nd, Chen VW. Racial differences in endometrial cancer survival: the black/white cancer survival study. Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Dec;88(6):919–26. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(96)00341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Olson SH, Atoria CL, Cote ML, Cook LS, Rastogi R, Soslow RA, et al. The impact of race and comorbidity on survival in endometrial cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012 May;21(5):753–60. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Folsom AR, Anderson KE, Sweeney C, Jacobs DR., Jr Diabetes as a risk factor for death following endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2004 Sep;94(3):740–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Setiawan VW, Pike MC, Kolonel LN, Nomura AM, Goodman MT, Henderson BE. Racial/ethnic differences in endometrial cancer risk: the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2007 Feb 1;165(3):262–70. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwk010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Randall TC, Armstrong K. Differences in treatment and outcome between African-American and white women with endometrial cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003 Nov 15;21(22):4200–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.01.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Liu JR, Conaway M, Rodriguez GC, Soper JT, Clarke-Pearson DL, Berchuck A. Relationship between race and interval to treatment in endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Oct;86(4 Pt 1):486–90. doi: 10.1016/0029-7844(95)00238-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Armstrong K, Randall TC, Polsky D, Moye E, Silber JH. Racial differences in surgeons and hospitals for endometrial cancer treatment. Med Care. 2011 Feb;49(2):207–14. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3182019123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wright JD, Fiorelli J, Schiff PB, Burke WM, Kansler AL, Cohen CJ, et al. Racial disparities for uterine corpus tumors: changes in clinical characteristics and treatment over time. Cancer. 2009 Mar 15;115(6):1276–85. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kost ER, Hall KL, Hines JF, Farley JH, Nycum LR, Rose GS, et al. Asian-Pacific Islander race independently predicts poor outcome in patients with endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2003 May;89(2):218–26. doi: 10.1016/s0090-8258(03)00050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sherman ME, Devesa SS. Analysis of racial differences in incidence, survival, and mortality for malignant tumors of the uterine corpus. Cancer. 2003 Jul 1;98(1):176–86. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Oliver KE, Enewold LR, Zhu K, Conrads TP, Rose GS, Maxwell GL, et al. Racial disparities in histopathologic characteristics of uterine cancer are present in older, not younger blacks in an equal-access environment. Gynecol Oncol. 2011 Oct;123(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Smotkin D, Nevadunsky NS, Harris K, Einstein MH, Yu Y, Goldburg GL. Histopathologic differences account for racial disparity in uterine cancer survival. Gynecol Oncol. 2012 Dec;127(3):616–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.08.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Maxwell GL, Tian C, Risinger J, Brown CL, Rose GS, Thigpen JT, et al. Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Racial disparity in survival among patients with advanced/recurrent endometrial adenocarcinoma: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Cancer. 2006 Nov 1;107(9):2197–205. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Maxwell GL, Tian C, Risinger JI, Hamilton CA, Barakat RR, Gynecologic Oncology Group Study Racial disparities in recurrence among patients with early-stage endometrial cancer: is recurrence increased in black patients who receive estrogen replacement therapy? Cancer. 2008 Sep 15;113(6):1431–7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kohler MF, Berchuck A, Davidoff AM, Humphrey PA, Dodge RK, Iglehart JD, et al. Overexpression and mutation of p53 in endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 15;52(6):1622–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Clifford SL, Kaminetsky CP, Cirisano FD, Dodge R, Soper JT, Clarke-Pearson DL, et al. Racial disparity in overexpression of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in stage I endometrial cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997 Jun;176(6):S229–32. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(97)70380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Santin AD, Bellone S, Siegel ER, Palmieri M, Thomas M, Cannon MJ, et al. Racial differences in the overexpression of epidermal growth factor type II receptor (HER2/neu): a major prognostic indicator in uterine serous papillary cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Mar;192(3):813–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.10.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Maxwell GL, Risinger JI, Hayes KA, Alvarez AA, Dodge RK, Barrett JC, et al. Racial disparity in the frequency of PTEN mutations, but not microsatellite instability, in advanced endometrial cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Aug;6(8):2999–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Schimp VL, Ali-Fehmi R, Solomon LA, Hammoud A, Pansare V, Morris RT, et al. The racial disparity in outcomes in endometrial cancer: could this be explained on a molecular level? Gynecol Oncol. 2006 Sep;102(3):440–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Morrison C, Miecznikowski J, Darcy KM, Dolce JM, Kandel E, Erwin DO, et al. A GOG 210 aCGH study of gain at 1q23 in endometrioid endometrial cancer in the context of racial disparity and outcome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010 Sep;49(9):791–802. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.WHO/ICO Information Centre . Human Papillomavirus and Related Cancers in World: Summary Report 2010 [Internet] WHO/ICO Information Centre on HPV and Cervical Cancer (HPV Information Centre); Barcelona, Spain: Feb 19, 2010. [cited 2012 May 31]. Available from: http://hpv2010.org/main/images/stories/docs/HPVInformationCentre_SummaryReportWorld_Feb2010.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Horner MJ, Altekruse SF, Zou Z, Wideroff L, Katki HA, Stinchcomb DG. U.S. geographic distribution of prevaccine era cervical cancer screening, incidence, stage, and mortality. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011 Apr;20(4):591–9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program, SEER*Stat Database: Mortality - All COD, Aggregated With State, Total U.S. (1969-2007) <Katrina/Rita Population Adjustment> [Internet] National Cancer Institute, DCCPS, Surveillance Research Program, Cancer Statistics Branch [cited June 2010] Available from: http://www.seer.cancer.gov and Underlying mortality data provided by NCHS (www.cdc.gov/nchs)
- 66.Center for Disease Control and Prevention Recommended immunization schedules for persons aged 0 through 18 years—United States, 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012 Feb 10;61(5):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Niccolai LM, Mehta NR, Hadler JL. Racial/Ethnic and poverty disparities in human papillomavirus vaccination completion. Am J Prev Med. 2011 Oct;41(4):428–33. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2011.06.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Widdice LE, Bernstein DL, Leonard AC, Marsolo KA, Kahn JA. Adherence to the HPV vaccine dosing intervals and factors associated with completion of 3 doses. Pediatrics. 2011 Jan;127(1):77–84. doi: 10.1542/peds.2010-0812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Center for Disease Control and Prevention National and state vaccination coverage among adolescents aged 13-17 years--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012 Aug 31;61(34):671–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Cancer Screening — United States, 2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012 Jan 27;61(3):41–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Benard VB, Lawson HW, Eheman CR, Anderson C, Helsel W. Adherence to guidelines for follow-up of low-grade cytologic abnormalities among medically underserved women. Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Jun;105(6):1323–8. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000159549.56601.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.del Carmen MG, Montz FJ, Bristow RE, Bovicelli A, Cornelison T, Trimble E. Ethnic differences in patterns of care of stage 1A(1) and stage 1A(2) cervical cancer: a SEER database study. Gynecol Oncol. 1999 Oct;75(1):113–7. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1999.5543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mundt AJ, Connell PP, Campbell T, Hwang JH, Rotmensch J, Waggoner S. Race and clinical outcome in patients with carcinoma of the uterine cervix treated with radiation therapy. Gynecol Oncol. 1998 Nov;71(2):151–8. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1998.5203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Farley JH, Hines JF, Taylor RR, Carlson JW, Parker MF, Kost ER, et al. Equal care ensures equal survival for African-American women with cervical carcinoma. Cancer. 2001 Feb 15;91(4):869–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.MacNew HG, Rudolph R, Brower ST, Beck AN, Meister EA. Assessing the knowledge and attitudes regarding genetic testing for breast cancer risk in our region of southeastern Georgia. Breast J. 2010 Mar-Apr;16(2):189–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2009.00880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Thompson HS, Valdimarsdottir HB, Duteau-Buck C, Guevarra J, Bovbjerg DH, Richmond-Avellaneda C, et al. Psychosocial predictors of BRCA counseling and testing decisions among urban African-American women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002 Dec;11(12):1579–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Macconaill LE, Garraway LA. Clinical implications of the cancer genome. J Clin Oncol. 2010 Dec 10;28(35):5219–28. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Goss E, Lopez AM, Brown CL, Wollins DS, Brawley OW, Raghavan D. American society of clinical oncology policy statement: disparities in cancer care. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jun 10;27(17):2881–5. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.1680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Franklin D. Roosevelt. Second Inaugural Address. 1937 Jan 20; Available from: http://www.bartleby.com/124/pres50.html.