Abstract
Aim—To obtain further data on the structure and conformation of calprotectin, a prominent leucocyte protein found in many species.
Methods—The binding of Ca2+ to calprotectin was studied by means of equilibrium dialysis using 45Ca as tracer. The thermal stability and denaturation kinetics of calprotectin were studied by means of differential scanning calorimetry. Con-comitant alterations in optical activity resulting from different conditions were measured. A computer program calculated the parameters to fit different models of protein structure. Ultraviolet spectroscopy gave absorbtion spectra. Sedimentation velocity studies and molecular weight determinations by the low speed (sedimentation) equilibrium technique were performed.
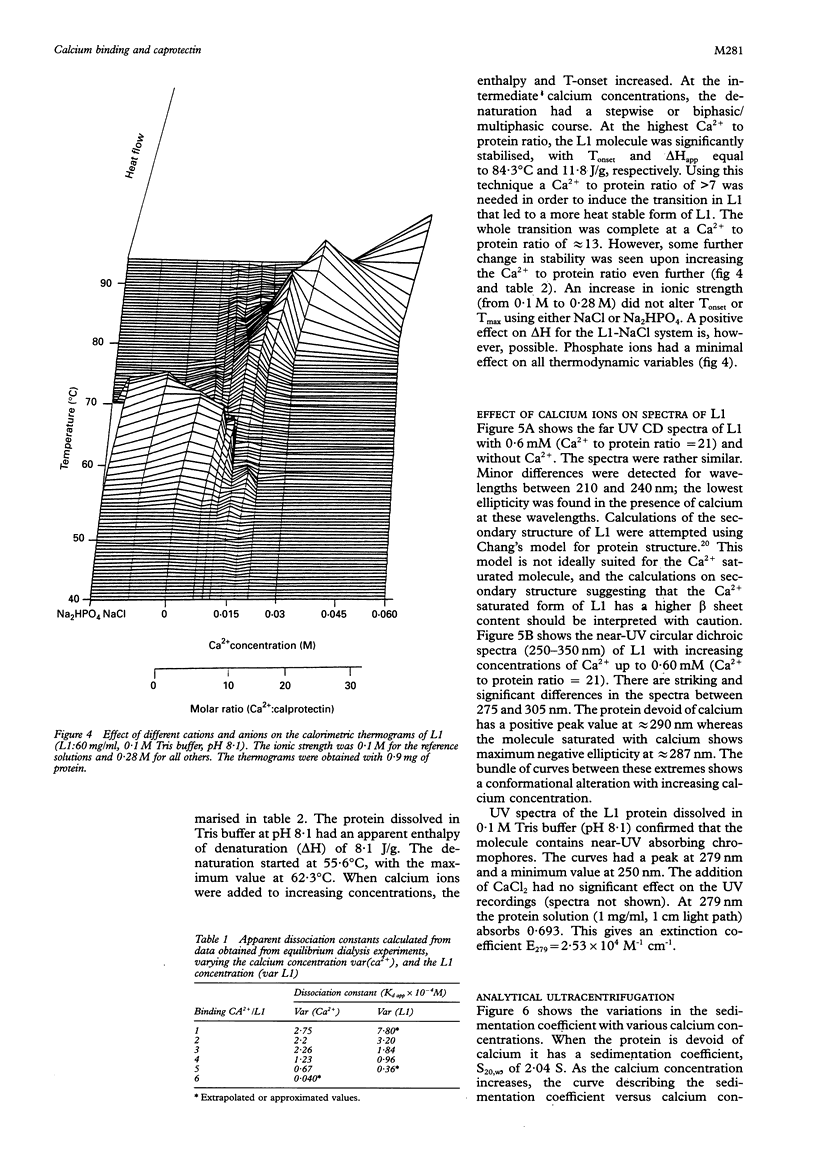
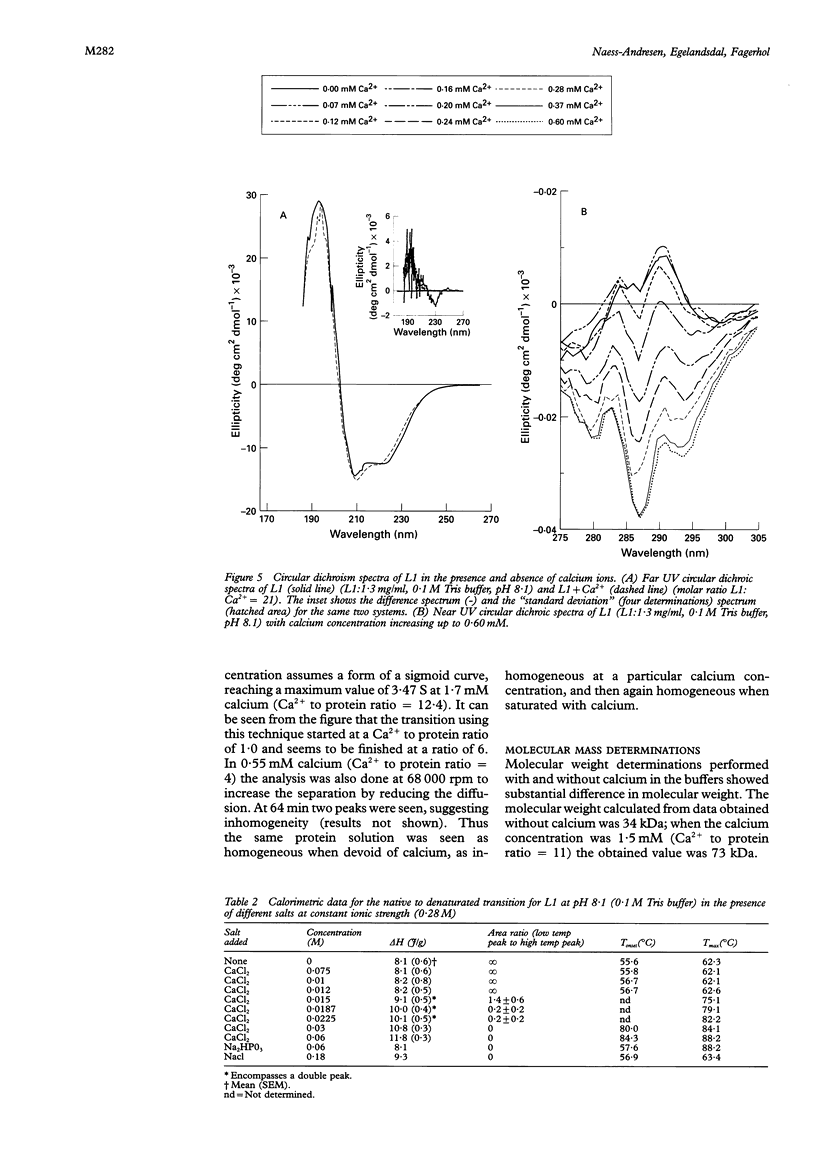
Results—A maximum of six calcium ions were bound per calprotectin molecule at 0·7 mM calcium chloride. The apparent dissociation constants were calculated. Ca2+ ions increased the denaturation temperature by 26°K. The enthalpy of denaturation was also increased by Ca2+. Addition of Ca2+ to the buffers caused a gradual change in the near UV circular dichroism spectrum, while only minor changes were seen at wavelengths of 210-240 nm. A gradual increase in the sedimentation coefficient was observed on addition of calcium chloride. The extinction coefficient at 279nm was determined: E279= 2·53·104 M−1 cm−1.
Conclusions—Calprotectin can bind six calcium ions. Upon binding, the protein shows distinct conformational changes and increased thermal stability. The former may be of importance for its function, while the biological significance of the latter is unknown.
Keywords: Calcium binding
Keywords: calprotectin
Keywords: heat stability
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson K. B., Sletten K., Berntzen H. B., Dale I., Brandtzaeg P., Jellum E., Fagerhol M. K. The leucocyte L1 protein: identity with the cystic fibrosis antigen and the calcium-binding MRP-8 and MRP-14 macrophage components. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Aug;28(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anteneodo C., Rodahl A. M., Meiering E., Heynen M. L., Sennisterra G. A., Lepock J. R. Interaction of dibucaine with the transmembrane domain of the Ca(2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 11;33(40):12283–12290. doi: 10.1021/bi00206a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. The binding of calcium to a salivary phosphoprotein, protein A, common to human parotid and submandibular secretions. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1550163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berner Berntzen H., Endresen G. K., Fagerhol M. K., Spiechowicz J., Mowinckel P. Calprotectin (the L1 protein) during surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;51(7):643–650. doi: 10.3109/00365519109104575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berntzen H. B., Fagerhol M. K. L1, a major granulocyte protein; isolation of high quantities of its subunits. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1990 Nov;50(7):769–774. doi: 10.1080/00365519009091071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Dale I., Fagerhol M. K. Distribution of a formalin-resistant myelomonocytic antigen (L1) in human tissues. II. Normal and aberrant occurrence in various epithelia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jun;87(6):700–707. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.6.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachia P. J., Van Eyk J., Ingraham R. H., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Hodges R. S. Calmodulin and troponin C: a comparative study of the interaction of mastoparan and troponin I inhibitory peptide [104-115]. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3553–3562. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Wu C. S., Yang J. T. Circular dichroic analysis of protein conformation: inclusion of the beta-turns. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90812-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch T. H., Klee C. B. Positive cooperative binding of calcium to bovine brain calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3692–3698. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
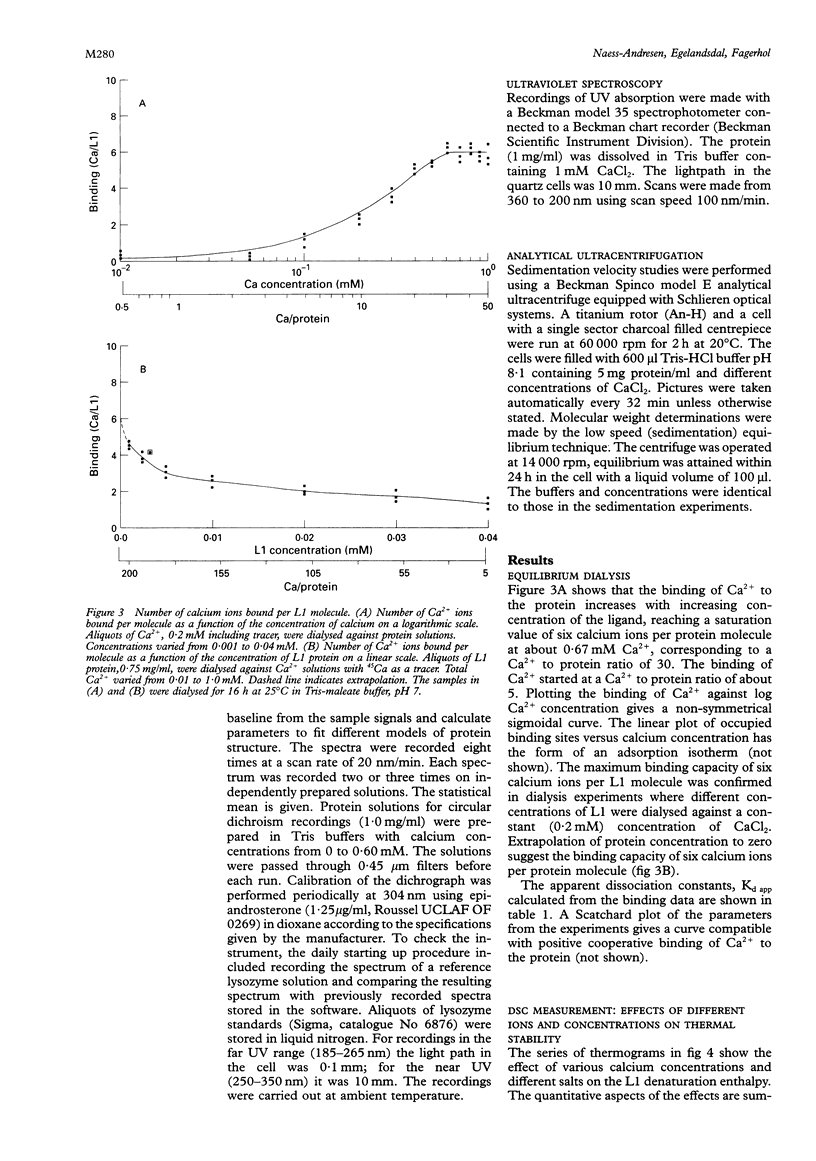
- Dale I., Fagerhol M. K., Naesgaard I. Purification and partial characterization of a highly immunogenic human leukocyte protein, the L1 antigen. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen T. O., Dale I., Brandtzaeg P., Hoel P. S., Fagerhol M. K., Larsen T. E., Thune P. O. Epidermal and dermal distribution of a myelomonocytic antigen (L1) shared by epithelial cells in various inflammatory skin diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986 Aug;15(2 Pt 1):173–179. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagasse E., Clerc R. G. Cloning and expression of two human genes encoding calcium-binding proteins that are regulated during myeloid differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2402–2410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odink K., Cerletti N., Brüggen J., Clerc R. G., Tarcsay L., Zwadlo G., Gerhards G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):80–82. doi: 10.1038/330080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Stability of proteins: small globular proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:167–241. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Røseth A. G., Kristinsson J., Fagerhol M. K., Schjønsby H., Aadland E., Nygaard K., Roald B. Faecal calprotectin: a novel test for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer? Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Dec;28(12):1073–1076. doi: 10.3109/00365529309098312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander J., Fagerhol M. K., Bakken J. S., Dale I. Plasma levels of the leucocyte L1 protein in febrile conditions: relation to aetiology, number of leucocytes in blood, blood sedimentation reaction and C-reactive protein. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;44(4):357–362. doi: 10.3109/00365518409083820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbakk M., Naess-Andresen C. F., Lingaas E., Dale I., Brandtzaeg P., Fagerhol M. K. Antimicrobial actions of calcium binding leucocyte L1 protein, calprotectin. Lancet. 1990 Sep 29;336(8718):763–765. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93237-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigelkamp S., Bhardwaj R. S., Roth J., Meinardus-Hager G., Karas M., Sorg C. Calcium-dependent complex assembly of the myeloic differentiation proteins MRP-8 and MRP-14. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13462–13467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsalkova T. N., Privalov P. L. Thermodynamic study of domain organization in troponin C and calmodulin. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 20;181(4):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dael H., Haezebrouck P., Morozova L., Arico-Muendel C., Dobson C. M. Partially folded states of equine lysozyme. Structural characterization and significance for protein folding. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 9;32(44):11886–11894. doi: 10.1021/bi00095a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venyaminov S. Y., Gogia Z. V. Optical characteristics of all individual proteins from the small subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):299–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]