Abstract
Aim—To correlate immunohistochemical staining with single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis of the p53 gene in colorectal cancer in order to understand how the findings provided by the two techniques complement each other in defining p53 functional status.
Methods—Frozen tumour tissue from 94 patients with colorectal cancer was studied for p53 protein accumulation and gene mutations. Accumulation of p53 protein was detected by immunohistochemistry using PAb1801 and BP53-12-1 monoclonal antibodies. The findings were then compared with SSCP analysis of exons 5 to 8 of the p53 gene. All cases with a positive result by SSCP analysis were confirmed by sequencing.
Results—Nuclear staining was observed in 51 (54.2%) cases. SSCP analysis of the DNA amplified by PCR revealed that the electrophoretic pattern had shifted in 30 cases; sequence analysis confirmed the occurrence of a mutation in 29 cases and of a polymorphism in one. In 27 cases both assays gave a positive result, and in 40 both were negative; therefore, concordance between PCR-SSCP and immunohistochemistry was seen in 72% of cases.
Conclusion—The data indicate that positive immunostaining corresponds with the presence of a mutation in most, but not all, cases studied; other mechanisms could be responsible for stabilisation and accumulation of p53 protein in the nucleus. Nonsense mutations which do not confer stability on the protein will not be detected by immunohistochemistry and false negative results can also occur with SSCP analysis.
Keywords: p53
Keywords: colorectal cancer
Keywords: immunohistochemistry
Keywords: PCR-SSCP
Full text
PDF


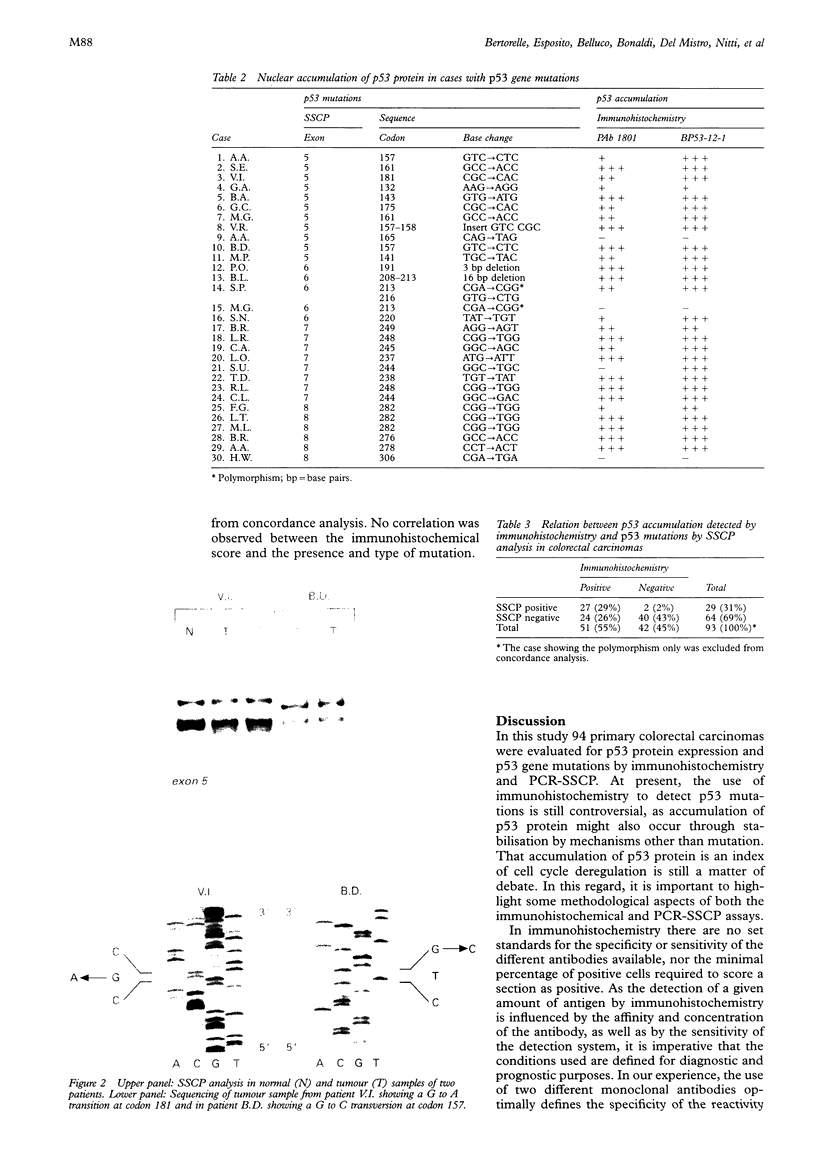


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison C., Jenkins J. R., Stürzbecher H. W. The p53 nuclear localisation signal is structurally linked to a p34cdc2 kinase motif. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allred D. C., Clark G. M., Elledge R., Fuqua S. A., Brown R. W., Chamness G. C., Osborne C. K., McGuire W. L. Association of p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Feb 3;85(3):200–206. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.3.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas I. O., Mulder J. W., Offerhaus G. J., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. An evaluation of six antibodies for immunohistochemistry of mutant p53 gene product in archival colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol. 1994 Jan;172(1):5–12. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorelle R., Esposito G., Del Mistro A., Belluco C., Nitti D., Lise M., Chieco-Bianchi L. Association of p53 gene and protein alterations with metastases in colorectal cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Apr;19(4):463–471. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199504000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bártek J., Bártková J., Vojtesek B., Stasková Z., Lukás J., Rejthar A., Kovarík J., Midgley C. A., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Aberrant expression of the p53 oncoprotein is a common feature of a wide spectrum of human malignancies. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1699–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone D., Chiba I., Mitsudomi T. Polymorphism at codon 213 within the p53 gene. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1691–1692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron de Fromentel C., Soussi T. TP53 tumor suppressor gene: a model for investigating human mutagenesis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jan;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie A., Eeles R., Borresen A. L., Coles C., Cooper C., Prosser J. Detection of point mutations in the p53 gene: comparison of single-strand conformation polymorphism, constant denaturant gel electrophoresis, and hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide techniques. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(1):58–66. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Dalbagni G., Saez G. T., Oliva M. R., Zhang Z. F., Rosai J., Reuter V. E., Pellicer A. p53 mutations in human bladder cancer: genotypic versus phenotypic patterns. Int J Cancer. 1994 Feb 1;56(3):347–353. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps K. J., Purdie C. A., Carder P. J., White S., Komine K., Bird C. C., Wyllie A. H. A study of stabilisation of p53 protein versus point mutation in colorectal carcinoma. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2739–2743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas E. C., Bateman A. C., Wilkins B. S., Johnson P. A., Williams J. H., Lee A. H., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Microwave antigen retrieval in immunocytochemistry: a study of 80 antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;47(5):448–452. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix B., Robbins P., Carrello S., House A., Iacopetta B. Comparison of p53 gene mutation and protein overexpression in colorectal carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1994 Oct;70(4):585–590. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esrig D., Spruck C. H., 3rd, Nichols P. W., Chaiwun B., Steven K., Groshen S., Chen S. C., Skinner D. G., Jones P. A., Cote R. J. p53 nuclear protein accumulation correlates with mutations in the p53 gene, tumor grade, and stage in bladder cancer. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1389–1397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt M. S., Bennett W. P., Hollstein M., Harris C. C. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4855–4878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann A., Blaszyk H., McGovern R. M., Schroeder J. J., Cunningham J., De Vries E. M., Kovach J. S., Sommer S. S. p53 gene mutations inside and outside of exons 5-8: the patterns differ in breast and other cancers. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 16;10(4):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Yandell D. W. How sensitive is PCR-SSCP? Hum Mutat. 1993;2(5):338–346. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. I., Hong W. S., Jang J. J., Lee D. S., Cho N. S., Jung M. E., Kim H. B., Ha G. W., Park I. C., Cho D. S. Alterations of p53 gene in primary gastric cancer tissues. Anticancer Res. 1994 May-Jun;14(3B):1251–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi-Yanoshita R., Konishi M., Ito S., Seki M., Tanaka K., Maeda Y., Iino H., Fukayama M., Koike M., Mori T. Genetic changes of both p53 alleles associated with the conversion from colorectal adenoma to early carcinoma in familial adenomatous polyposis and non-familial adenomatous polyposis patients. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 15;52(14):3965–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. The regulation of p53 function: Steiner Award Lecture. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jun 1;57(5):623–627. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Urbano-Ispizua A., Gill R., Thomas D. M., Gilbertson J., Foster C., Marshall C. J. Multiple K-ras codon 12 mutations in cholangiocarcinomas demonstrated with a sensitive polymerase chain reaction technique. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 1;51(13):3497–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Park S. H., Thompson T. C., Lane D. P. Ras-induced hyperplasia occurs with mutation of p53, but activated ras and myc together can induce carcinoma without p53 mutation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90541-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyret C., Theillet C., Puig P. L., Molés J. P., Thomas G., Hamelin R. Relative efficiency of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and single strand conformation polymorphism in the detection of mutations in exons 5 to 8 of the p53 gene. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1739–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokocimer M., Rotter V. Structure and function of p53 in normal cells and their aberrations in cancer cells: projection on the hematologic cell lineages. Blood. 1994 Oct 15;84(8):2391–2411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa A., Capelli P., Mukai K., Zamboni G., Oda T., Iacono C., Hirohashi S. Pancreatic adenocarcinomas frequently show p53 gene mutations. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1534–1543. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Ben-Ze'ev A., Rotter V. Nuclear accumulation of p53 protein is mediated by several nuclear localization signals and plays a role in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6565–6577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Beck J. S., Kwitek A. E., Sandstrom D. W., Stone E. M. The sensitivity of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis for the detection of single base substitutions. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):325–332. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umekita Y., Kobayashi K., Saheki T., Yoshida H. Nuclear accumulation of p53 protein correlates with mutations in the p53 gene on archival paraffin-embedded tissues of human breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1994 Aug;85(8):825–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1994.tb02954.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynford-Thomas D. P53 in tumour pathology: can we trust immunocytochemistry? J Pathol. 1992 Apr;166(4):329–330. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





