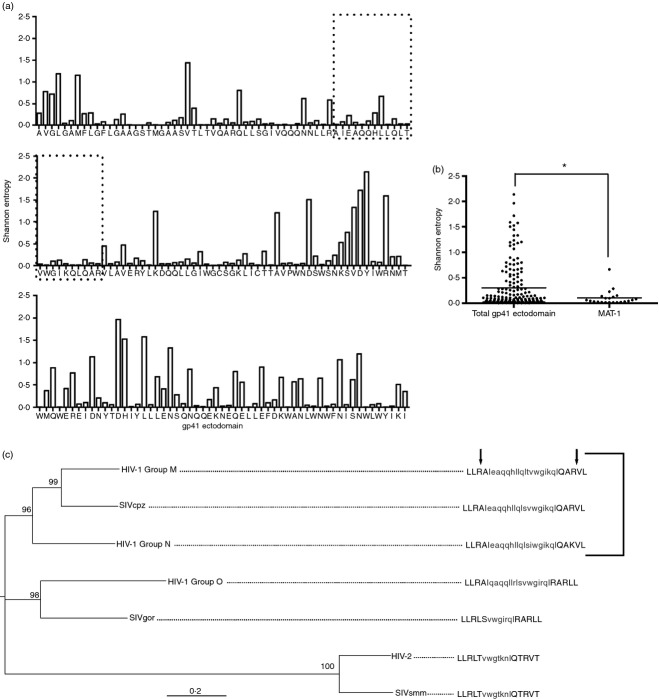
Figure 3.
Matriptase cleavage sites in gp41 are conserved across diverse HIV clades. HIV-1 Group M subtype B amino acid sequences from 173 taxa were aligned using MUSCLE. (a) Shannon Entropy was calculated for each amino acid spanning the gp41 ectodomain. Low values correspond to low variation and so more conserved residues. The area enclosed in dotted boxes represents the MAT-1 peptide. (b) Average Entropy values for each amino acid were plotted and the median values for MAT-1 and the entire gp41 ectodomain were compared (*P < 0·05). (c) DNA sequences from representative strains of diverse HIV and SIV clades were aligned with ClustalW. Maximum likelihood was used to generate a phylogeny. Nodal support is represented as bootstrap values. Consensus amino acid sequences were generated for each taxa and matriptase cut sites are shown for the N and C terminals of MAT-1 as indicated by arrows. The bracketed taxa represent those containing conserved matriptase recognition sites.