In Table S2, column #13 (‘BETA') is incorrect. A corrected version of Table S2 can be viewed below.
Supporting Information
eQTL SNP replication table. Summary of eQTL findings and replication across all included studies. eQTL SNPs were included in the table if, from a given study, they were the most highly associated cis-linked SNP within an LD block and if their 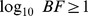 . eQTL SNPs are listed in separate rows and associated data are in columns, as labeled in the first row and denote the following:
. eQTL SNPs are listed in separate rows and associated data are in columns, as labeled in the first row and denote the following:
1. REF STUDY. eQTL discovery study.
2. GENE. RefSeq gene identifier.
3. CHR. Chromosome of the eQTL SNP and associated gene expression trait.
4. STRAND. Annotated strand of the associated transcript.
5. TSS. Genomic coordinate of the transcription start site.
6. TES. Genomic coordinate of the transcription end site.
7. RSID. Identity of the eQTL SNP.
8. HS INDEX. Identity of the LD block containing the SNP.
9. RSCOORD. Genomic coordinate of the SNP.
10. TIER. Tier of the SNP with respect the associated gene.
11. UBF. Univariate 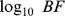 of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association.
of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association.
12. MBF. Multivariate 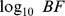 of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association, controlling for all SNPs in lower tiers.
of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association, controlling for all SNPs in lower tiers.
13. BETA. Estimate of the effect size per minor allele of the SNP.
14. GEX. Mean gene expression level across all samples in the discovery study.
15. PROBE MAF. Maximum minor allele frequency of SNPs overlapping the coordinates of the gene expression probe.
16. NALN. Number of high quality alignments between the gene expression probe and hg18.
Reference
- 1. Brown CD, Mangravite LM, Engelhardt BE (2013) Integrative Modeling of eQTLs and Cis-Regulatory Elements Suggests Mechanisms Underlying Cell Type Specificity of eQTLs. PLoS Genet 9(8): e1003649 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eQTL SNP replication table. Summary of eQTL findings and replication across all included studies. eQTL SNPs were included in the table if, from a given study, they were the most highly associated cis-linked SNP within an LD block and if their 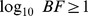 . eQTL SNPs are listed in separate rows and associated data are in columns, as labeled in the first row and denote the following:
. eQTL SNPs are listed in separate rows and associated data are in columns, as labeled in the first row and denote the following:
1. REF STUDY. eQTL discovery study.
2. GENE. RefSeq gene identifier.
3. CHR. Chromosome of the eQTL SNP and associated gene expression trait.
4. STRAND. Annotated strand of the associated transcript.
5. TSS. Genomic coordinate of the transcription start site.
6. TES. Genomic coordinate of the transcription end site.
7. RSID. Identity of the eQTL SNP.
8. HS INDEX. Identity of the LD block containing the SNP.
9. RSCOORD. Genomic coordinate of the SNP.
10. TIER. Tier of the SNP with respect the associated gene.
11. UBF. Univariate 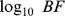 of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association.
of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association.
12. MBF. Multivariate 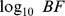 of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association, controlling for all SNPs in lower tiers.
of the eQTL SNP-gene expression trait association, controlling for all SNPs in lower tiers.
13. BETA. Estimate of the effect size per minor allele of the SNP.
14. GEX. Mean gene expression level across all samples in the discovery study.
15. PROBE MAF. Maximum minor allele frequency of SNPs overlapping the coordinates of the gene expression probe.
16. NALN. Number of high quality alignments between the gene expression probe and hg18.


