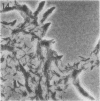
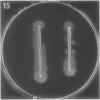
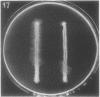
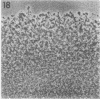
Full text
PDF


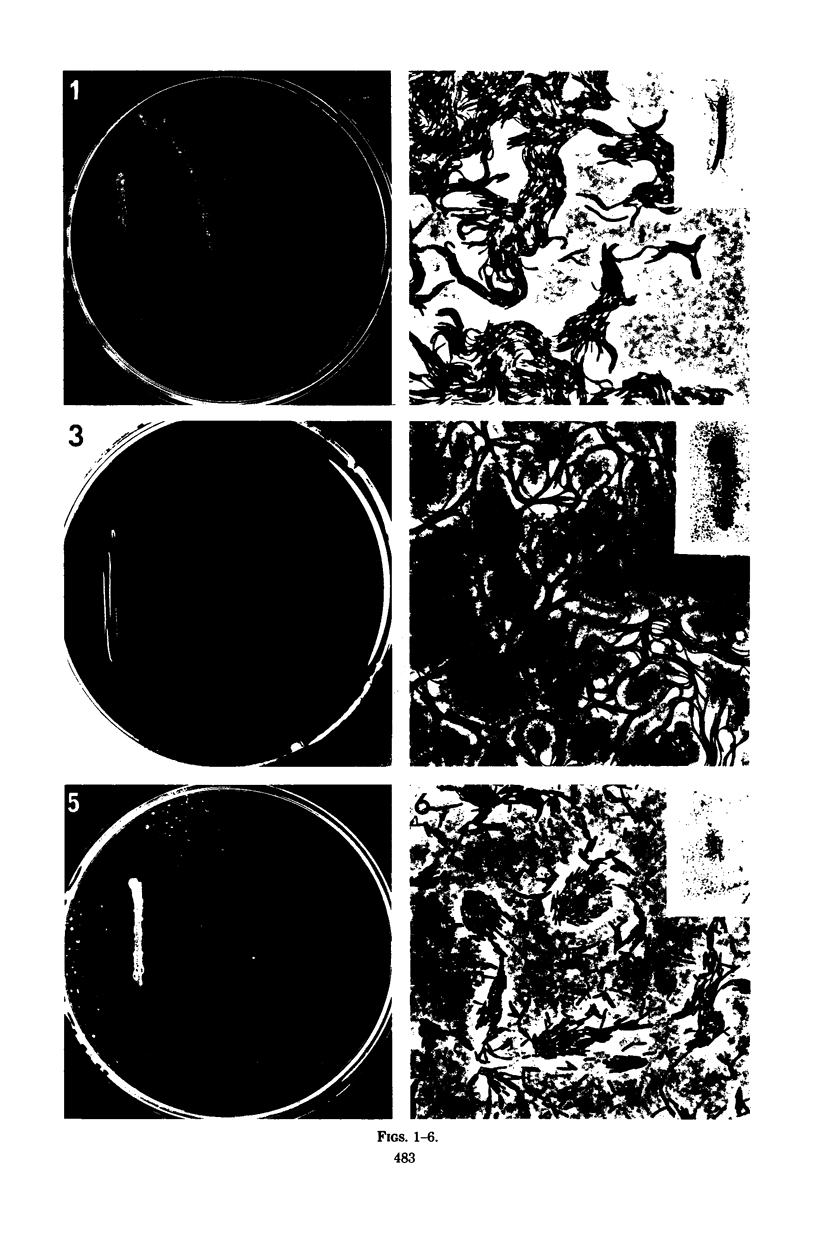


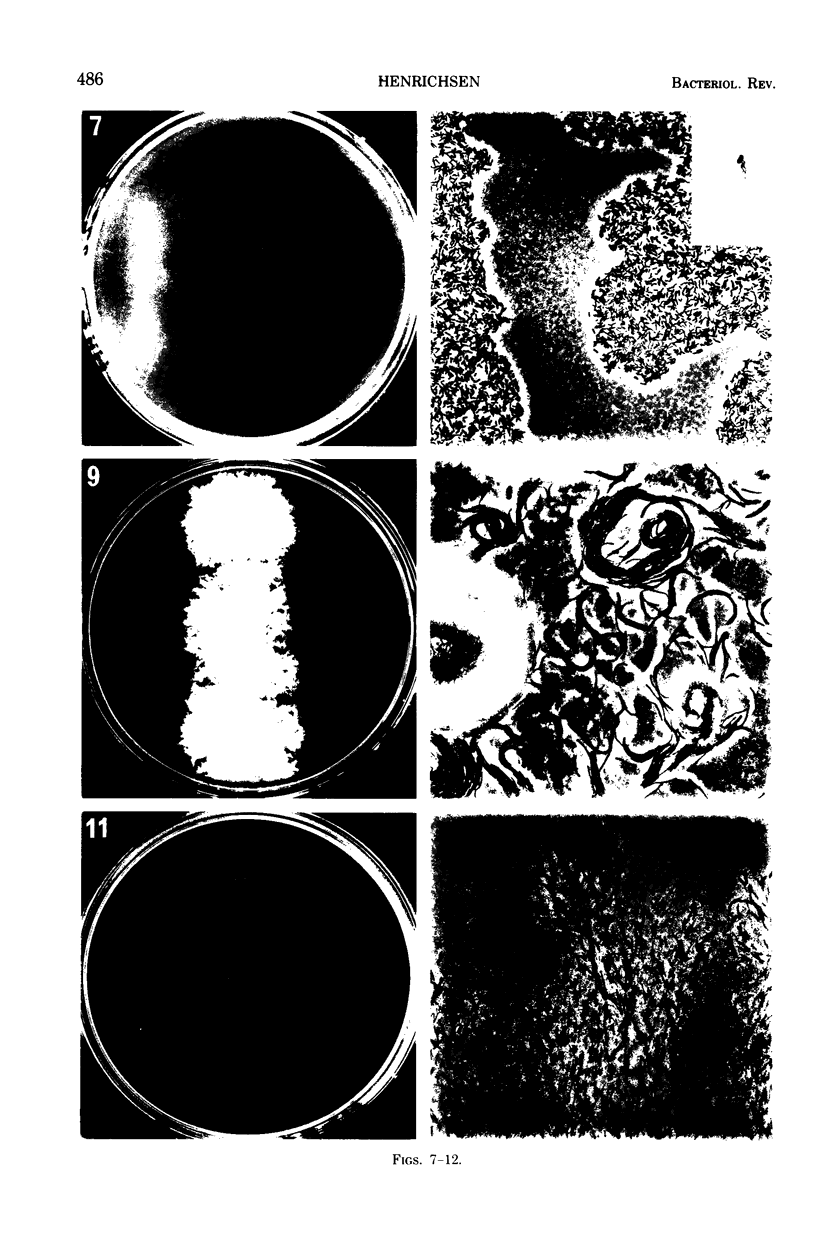



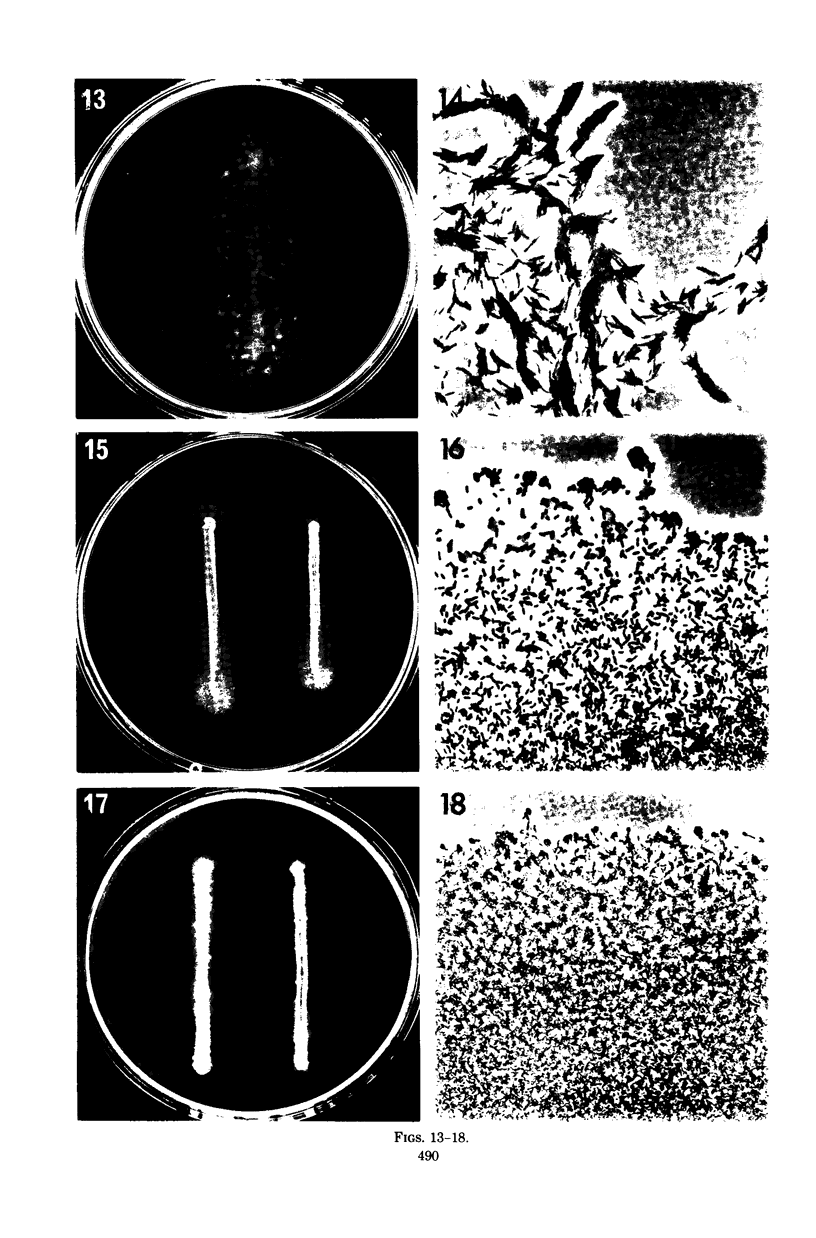





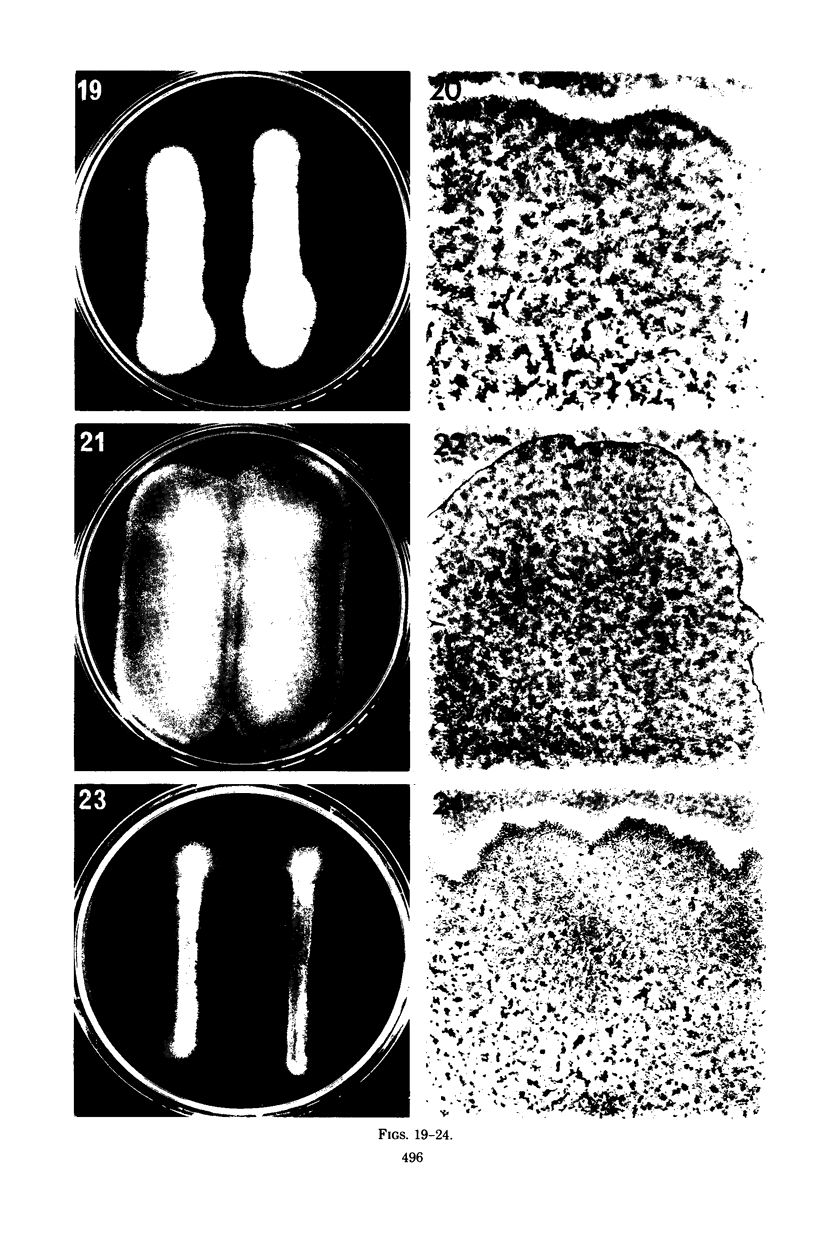

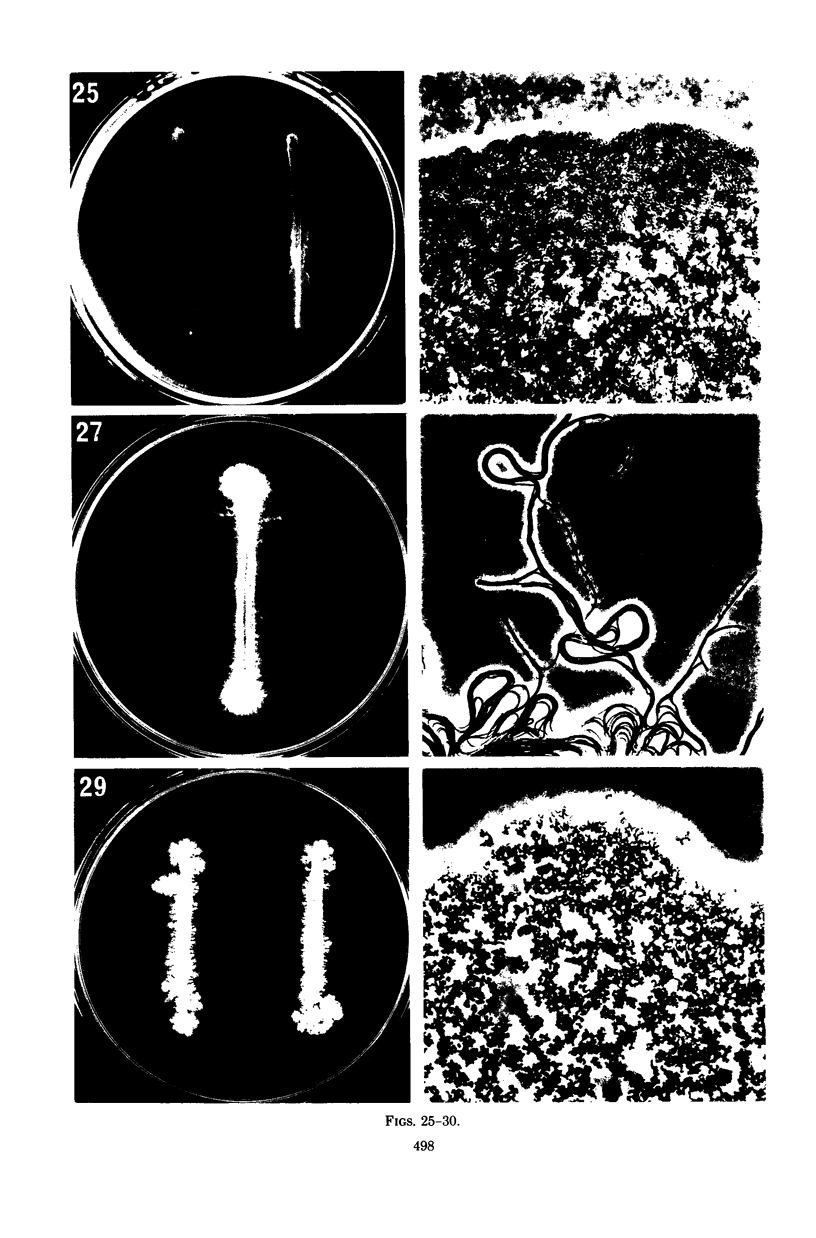





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., ORDAL E. J. Studies on the myxobacterium Chondrococcus columnaris. I. Serological typing. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.25-32.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON R. L., ORDAL E. J. Cytophaga succinicans sp. n., a factaltatively anaerobic, aquatic myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:130–138. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.130-138.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):708–716. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt W., Höfling K. H., Heunert H. H., Milthaler B. Messungen an beweglichen Zellen von Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Z Med Mikrobiol Immunol. 1970;156(1):39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P. Gliding motility mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):940–947. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.940-947.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COETZEE J. N., SACKS T. G. Morphological variants of Proteus hauseri. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Oct;23:209–216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COETZEE J. N. TRANSDUCTION OF SWARMING IN PROTEUS MIRABILIS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:1–7. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTERTON J. W., MURRAY R. G., ROBINOW C. F. Observations on the motility and the structure of Vitreoscilla. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Jun;7:329–339. doi: 10.1139/m61-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. Effects of cytochalasins on mammalian cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 21;213(5073):261–264. doi: 10.1038/213261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. E. Nonmotile Variants of Bacillus alvei. J Bacteriol. 1939 Nov;38(5):491–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.38.5.491-497.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL W. Hemmung des Schwärmens von Proteus-Bakterien durch oberflächenaktive Substanzen (Pril und Rei). Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1956 May;166(1):43–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N., Hageage G. J. Motility in procaryotic organisms: problems, points of view, and perspectives. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Aug;43(3):317–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb00963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. Biology of the myxobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:75–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAUST L., WOLFE R. S. Enrichment and cultivation of Beggiatoa alba. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:99–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.99-106.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner G. A. Physiological and morphological characteristics of Kurthia zopfii isolated from meat products. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;32(3):371–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb00986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianelli F., Cabassi E. Sciamatura di Moraxella. Ig Mod. 1967 Jan-Feb;60(1):81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Characteristics of Alcaligenes odorans var. viridans isolated from human sources. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jul;13(7):895–900. doi: 10.1139/m67-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEAGE G. J., Jr, MURRAY R. G. Random rotation among Vitreoscilla species. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1345–1346. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1345-1346.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSEN J. F. GLIDING MOTILITY IN THE ORGANISMS BACTERIUM ANITRATUM (B5W), MORAXELLA LWOFFI AND ALKALIGENES HAEMOLYSANS, AS COMPARED TO MORAXELLA NONLIQUEFACIENS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:200–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES P. R. Studies on marine flavobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:1–19. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfen L. N., Castenholz R. W. Gliding in a blue-green alga: a possible mechanism. Nature. 1970 Mar 21;225(5238):1163–1165. doi: 10.1038/2251163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J., Froholm L. O., Bovre K. Studies on bacterial surface translocation. 2. Correlation of twitching motility and fimbriation in colony variants of Moraxella nonliquefaciens, M. bovis, and M. kingii. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(3):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Gliding and twitching motility of bacteria unaffected by cytochalasin B. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):623–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn T. L., Bovee E. C. Movement and locomotion of microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:21–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp R., Müller J. Effects of related anionic detergents on flagellation, motility, swarming, and growth of Proteus. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Nov;13(6):950–955. doi: 10.1128/am.13.6.950-955.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautrop H., Bovre K., Frederiksen W. A Moraxella-like microorganism isolated from the genito-urinary tract of man. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(2):255–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Alexander R. H., Sobel H. J. A study of Chromobacterium typhiflavum from the rat. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;32(4):429–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb00993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD J. B., KNOLL M. L., SUTTON R. M. Motility in a species of non-flagellated bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Nov;84(2):459–462. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMeekin T. A., Patterson J. T., Murray J. G. An initial approach to the taxonomy of some gram negative yellow pigmented rods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;34(4):699–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb01007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. G., Clarke S. K. An Alcaligenes species with distinctive properties isolated from human sources. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):343–348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Hendrie M. S., Shewan J. M. The taxonomy, differentiation and identification of Cytophaga species. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;32(1):40–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb02187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. B., Scott A. Swarming of Proteus--a solution to an old problem? Nature. 1966 Jul 16;211(5046):255–257. doi: 10.1038/211255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. G., Elder R. H. THE PREDOMINANCE OF COUNTERCLOCKWISE ROTATION DURING SWARMING OF BACILLUS SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1949 Sep;58(3):351–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.3.351-359.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIECHAUD M. [Motility of the Moraxella]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Feb;104:291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. I. Structure and formation of mesosomes. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):1–13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirt S. J. A kinetic study of the mode of growth of surface colonies of bacteria and fungi. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 May;47(2):181–197. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringsheim E. G. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BACTERIA AND MYXOPHYCEAE. Bacteriol Rev. 1949 Jun;13(2):47–98. doi: 10.1128/br.13.2.47-98.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puttlitz D. H., Seeley H. W., Jr Physiology and nutrition of Lampropedia hyalina. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):931–938. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.931-938.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., PIECHAUD M. ETUDE AU MICROSCOPE 'ELECTRONIQUE DE QUELQUES SOUCHES DE MORAXELLA. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Dec;105:1071–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L. A New Species of the Genus Bacillus Exhibiting Mobile Colonies on the Surface of Nutrient Agar. J Bacteriol. 1935 Mar;29(3):229–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.29.3.229-237.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORIANO S., LEWIN R. A. GLIDING MICROBES: SOME TAXONOMIC RECONSIDERATIONS. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1965;31:66–79. doi: 10.1007/BF02045876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEED P. A. Simonsiellaceae fam.nov.with characterization of Simonsiella crassa and Alysiella filiformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Dec;29:615–624. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-4-615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels S. B., Pittman B., Cherry W. B. Practical physiological schema for the identification of Herellea vaginicola and its differentiation from similar organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Dec;18(6):1015–1024. doi: 10.1128/am.18.6.1015-1024.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Lorenz W., Kühlwein H. Intracelluläre Bewegungsorganellen der Myxobakterien. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;60(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Lorenz W. The fine structure of the swarm cells of myxobacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;32(1):22–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb02184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Kunisawa R., Mandel M., Cohen-Bazire G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):171–205. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.171-205.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. Studies on Nonfruiting Myxobacteria: I. Cytophaga johnsonae, n.sp., a Chitin-decomposing Myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1947 Mar;53(3):297–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. Studies on the Cytophagas. J Bacteriol. 1940 Nov;40(5):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.5.619-635.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. THE CYTOPHAGA GROUP: A CONTRIBUTION TO THE BIOLOGY OF MYXOBACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1942 Sep;6(3):143–196. doi: 10.1128/br.6.3.143-196.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOELZ H., DWORKIN M. Fine structure of Myxococcus xanthus during morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:943–952. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.943-952.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Doetsch R. N. Relationship between cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, and bacterial motility. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):512–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.512-521.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks O. B. Problems concerning the relationships of cytophagas and flavobacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;32(1):13–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb02182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. T., Williams K. Some cultural reactions of Clostridium tetani. J Med Microbiol. 1970 May;3(2):291–301. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-2-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bijsterveld O. P. New Moraxella strain isolated from angular conjunctivitis. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):405–408. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.405-408.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]