Full text
PDF
























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M. I., Haque R. Identification of staphylococcal epsilon hemolysin. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Apr;18(4):535–536. doi: 10.1139/m72-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Bernheimer A. W. Physical states of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1170-1177.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Billcliffe B. Lipid-induced polymerization of staphylococcal -toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):309–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. EFFECT OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND OTHER BACTERIAL TOXINS ON PLATELETS IN VITRO. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:209–223. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
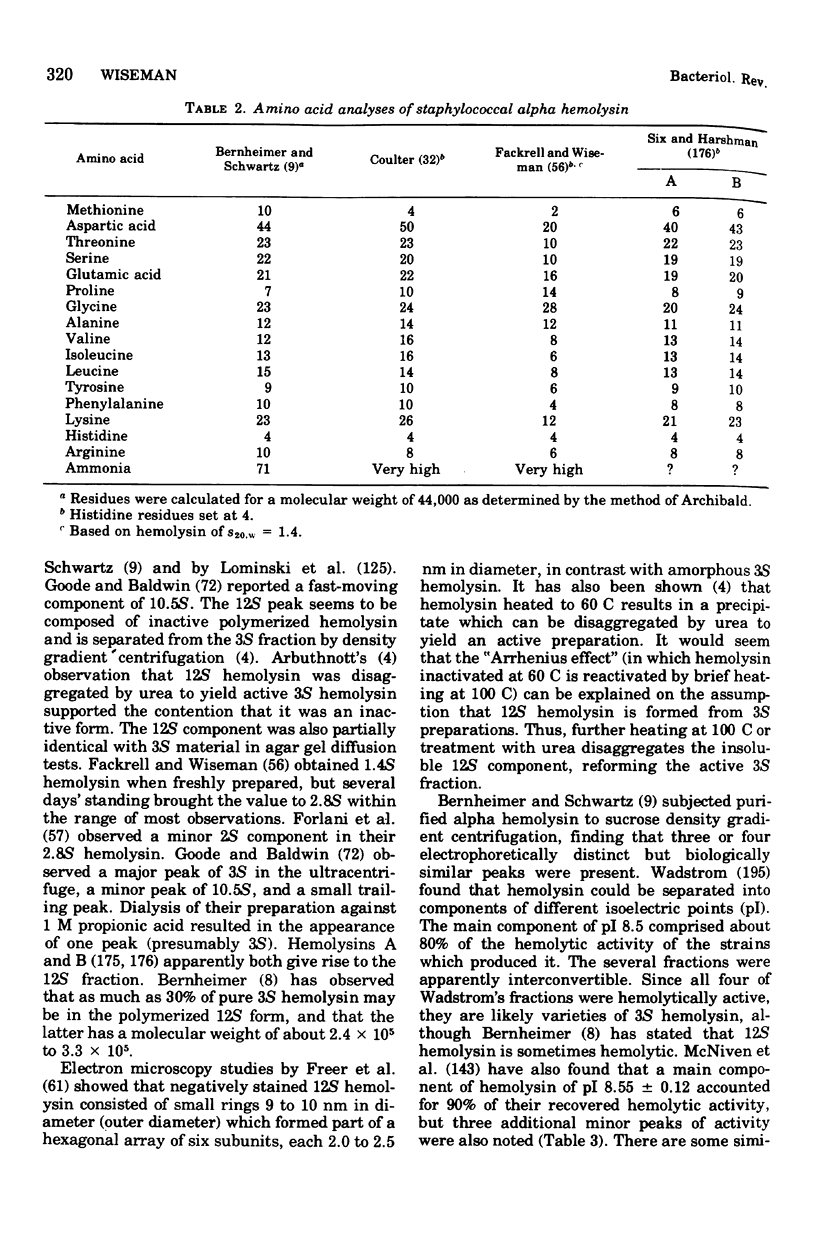
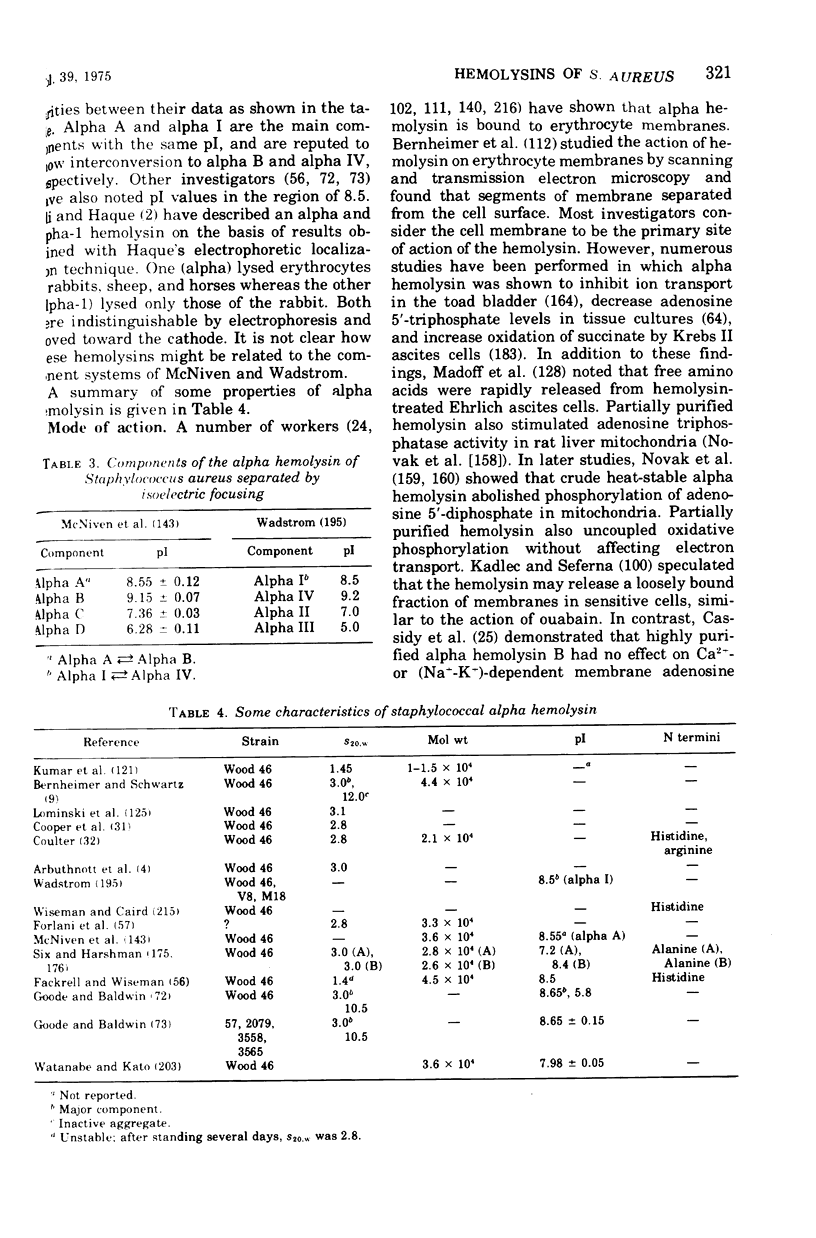
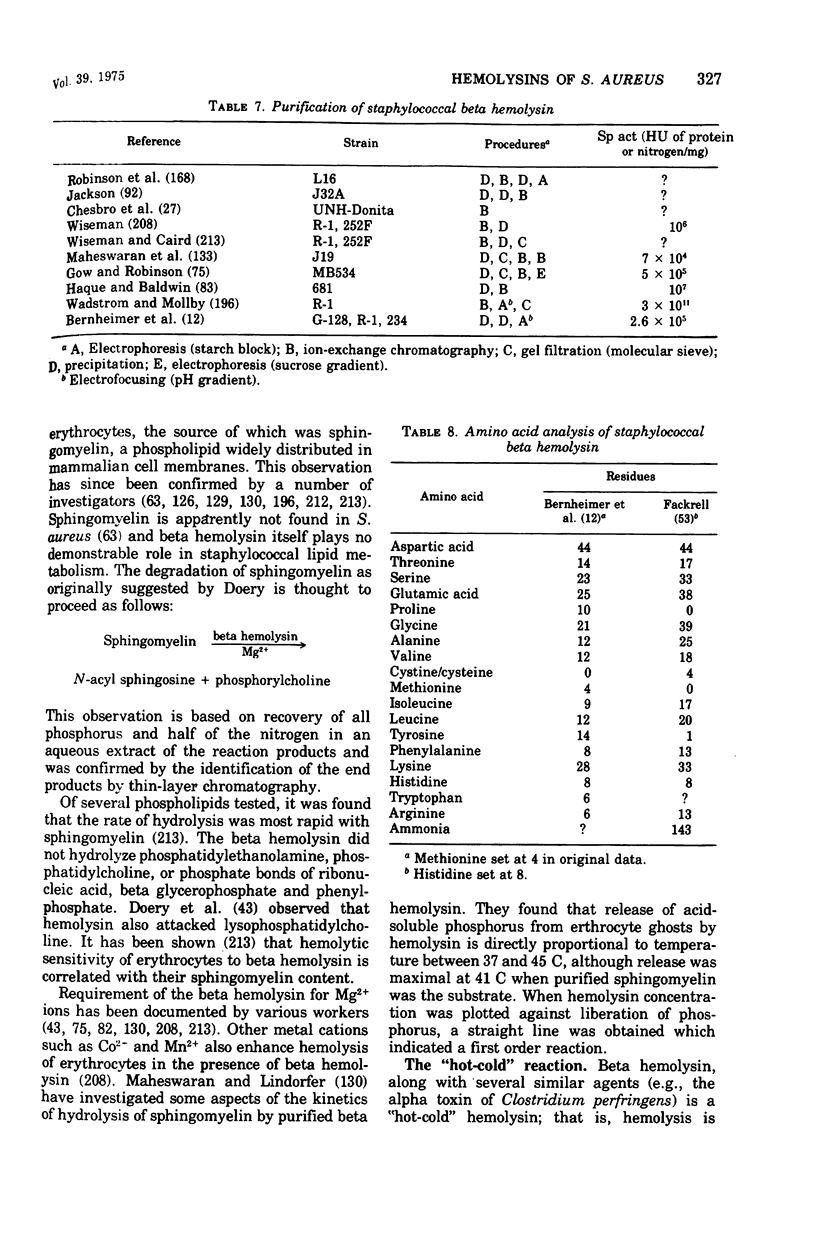
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMANN J., NORLIN G. A factor in yeast dialysate of significance in the formation of staphylococcus toxin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1951;29(2):127–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS J., HOLTMAN D. F. Biochemical properties of virulent and avirulent staphylococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1115–1124. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartell P. F., Orr T. E., Geffen A., Iorio P. Experimental infection of mice with Staphylococcus aureus: evidence against alpha toxin and the terminal size of the bacterial population as determinants of lethality. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):481–490. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Kim K. S. Staphylococcal sphingomyelinase (beta-hemolysin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):292–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Kim K. S., Remsen C. C., Antanavage J., Watson S. W. Factors affecting interaction of staphylococcal alpha toxin with membranes. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):636–642. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.636-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskaran C. S., Jayakar P. A. Biochemical activity of coagulase positive Staphylococci isolated from cases and carriers. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1969;33(1):39–43. doi: 10.1159/000162085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckelew A. R., Jr, Colacicco G. Lipid monolayers. Interactions with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHESBRO W. R., HEYDRICK F. P., MARTINEAU R., PERKINS G. N. PURIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL BETA-HEMOLYSIN AND ITS ACTION ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:378–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.378-389.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caird J. D., Wiseman G. M. Purification of the delta toxin os Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):703–708. doi: 10.1139/m70-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Colacicco G., Rapport M. M. Lipid monolayers: interactions with the apoprotein of high density plasma lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):562–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P. S., Harshman S. The binding of staphylococcal 125I-alpha-toxin (B) to erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5545–5546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesbro W., Kucic V. Beta hemolysin: a persistent impurity in preparations of staphylococcal nuclease and enterotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):233–241. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.233-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacicco G., Buckelew A. R., Jr Lipid monolayers: influence of lipid film and urea on the surface activity of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Lipids. 1971 Aug;6(8):546–553. doi: 10.1007/BF02531134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley C. M., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., van Deenen L. L. Lytic and non-lytic degradation of phospholipids in mammalian erythrocytes by pure phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 25;307(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. Z., Madoff M. A., Weinstein L. Heat stability and species range of purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1686–1692. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1686-1692.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter J. R., Mukherjee T. M. Electron microscopic localization of alpha toxin within the staphylococcal cell by ferritin-labeled antibody. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):650–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.650-655.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter J. R. Production, purification, and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1655–1662. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1655-1662.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulska J., Jeljaszewicz J. Staphylococcal interference. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969;211(2):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerski P., Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Zak C. Blastoid transformation of rabbit lymphocytes by staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin and leukocidin. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1968;90(4):328–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOERY H. M., MAGNUSSON B. J., CHEYNE I. M., SULASEKHARAM J. A phospholipase in staphylococcal toxin which hydrolyses sphingomyelin. Nature. 1963 Jun 15;198:1091–1092. doi: 10.1038/1981091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOERY H. M., NORTH E. A. The interaction of staphylococcal toxin and ganglioside. I. Inactivation of the lethal effect of staphylococcal toxin in mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1961 Aug;39:333–344. doi: 10.1038/icb.1961.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen A. B. Production of staphylococcal -toxin in a defined medium and identification of a stimulating factor from yeast extract. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):53–60. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen A. B. The induction of staphylococcal -toxin by histidine. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):61–69. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen A. B. The influence of pH and histidine dipeptides on the production of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Dec;79(2):265–274. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doery H. M., Magnusson B. J., Gulasekharam J., Pearson J. E. The properties of phospholipase enzymes in staphylococcal toxins. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Aug;40(2):283–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. A. Antistaphylococcal hemolysins and delta hemolysin inhibitor in adult human serum. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Aug;15(8):957–959. doi: 10.1139/m69-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Cho G. J. Production of staphylococcal alpha toxin. I. Relationship between cell growth and toxin formation. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):456–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.456-461.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Cho G. J. Production of staphylococcal alpha toxin. II. Glucose repression of toxin formation. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):689–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.689-694.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., CONEN P. E. The virulence of Staphylococcus pyogenes for man; a study of the problems of wound infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Dec;38(6):573–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D. Experimental staphylococcal infections in the skin of man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):85–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. Distribution of haemolysins in pathogenic and non-pathogenic staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):541–554. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER W. D. THE ROLE OF ALPHA-HAEMOLYSIN IN THE PATHOGENICITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:535–541. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fackrell H. B., Wiseman G. M. Immunogenicity of the delta-haemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Nov;7(4):411–414. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-4-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forlani L., Bernheimer A. W., Chiancone E. Ultracentrifugal analysis of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):138–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.138-142.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. A. Hemolysin production in the development of staphylococcal lesions. Science. 1965 Sep 17;149(3690):1395–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3690.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. A. Tissue injury by toxins in experimental staphylococcal infections. Effect of polyvalent antitoxin on developing renal lesions. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):913–928. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Bernheimer A. W. Interaction of staphylococcal alpha-toxin with artificial and natural membranes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1153–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1153-1168.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B. Effects of staphylococcal -toxin on the structure of erythrocyte membranes: a biochemical and freeze-etching study. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):321–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche D. Untersuchungen zur Funktion des beta-Hämolysins von Staphylococcus aureus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970 Apr;213(3):348–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLADSTONE G. P., GLENCROSS E. J. Growth and toxin production of staphylococci in cellophane sacs in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Jun;41:313–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLADSTONE G. P., VAN HEYNINGEN W. E. Staphylococcal leucocidins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Apr;38(2):123–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSHI K., CLUFF L. E., NORMAN P. S. Studies on the pathogenesis of staphylococcal infection. V. Purification and characterization of staphylococcal alpha hemolysin. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1963 Jan;112:15–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanti B., Paradisi F., Mancini A., Giusti G. An early effect of Staphylococcus alpha-toxin on cells growing in culture: ATP levels in normal and intoxicated cells. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1968;32(5):277–284. doi: 10.1159/000162068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone G. P., Yoshida A. The cytopathic action of purified staphylococcal delta-hemolysin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Feb;48(1):11–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode R. L., Baldwin J. N. Comparison of purified alpha-toxins from various strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):86–90. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.86-90.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode R. L., Baldwin J. N. Purification of staphylococcal alpha toxin by electrofocusing. Prep Biochem. 1973;3(4):349–361. doi: 10.1080/00327487308061520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow J. A., Robinson J. Properties of purified staphylococcal beta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1026–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1026-1032.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyonnet F., Plommet M. Hémolysine gamma de staphylococcus aureus: purification et propriétés. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Jan;118(1):19–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLANDER H. O. FRACTIONATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXINS BY GEL-FILTRATION. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:543–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAQUE R. U., BALDWIN J. N. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL BETA-HEMOLYSIN. I. PRODUCTION OF BETA-HEMOLYSIN. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1304–1309. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1304-1309.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN E. M., STREITFELD M. M. THE ANTIBIOTIC ACTIVITY ASSOCIATED WITH PREPARATIONS OF DELTA HEMOLYSIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:203–211. doi: 10.1139/m65-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUSER E. D., BERRY L. J. The pathogenesis of staphylococcus infections. I. The use of diffusion chambers in establishing the role of staphylococcus toxins. J Infect Dis. 1961 Jul-Aug;109:24–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallander H. O. Characterization and partial purification of staphylococcal delta-lysin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;72(4):586–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb00471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallanger H. O., Bengtsson S. Studies on the cell toxicity and species specificity of purified staphylococcal toxins. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;70(1):107–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque R. U., Baldwin J. N. Purification and properties of staphylococcal beta hemolysin. II. Purification of beta hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):751–759. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.751-759.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvie N. R. De-esterification of cholesteryl esters in human plasma alpha-lipoprotein (HDL) by preparations of staphylococcal alpha toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1283–1288. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley N. G. A new method for the preparation and some properties of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):269–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holme T., Wadström T. A continuous process for the production of extracellular proteins by Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):414–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON A. W., LITTLE R. M. Leucocidal effect of staphylococcal delta-lysin. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Feb;3(1):101–102. doi: 10.1139/m57-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON A. W., LITTLE R. M. Staphylococcal toxins. II. Factors affecting hemolysis by delta-lysin. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Oct;4(5):435–444. doi: 10.1139/m58-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON A. W., LITTLE R. M. Staphylococcal toxins. III. Partial purification and some properties of delta-lysin. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Oct;4(5):453–461. doi: 10.1139/m58-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Korbecki M., Zak C. Histochemical demonstration of changes in enzymatic activity of KB cells produced by staphylococcal alpha and beta hemolysins. J Infect Dis. 1965 Dec;115(5):421–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.5.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Zak C. Distribution of 131-I-labelled staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin in the rabbit. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969;209(3):310–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPRAL F. A., KEOGH A. M., TAUBLER J. H. THE NATURE OF ALPHA TOXIN PRODUCTION BY STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS GROWN IN VIVO. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:74–77. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAYSER A., RAYNAUD M. ETUDE D'UNE DEUXI'EME H'EMOLYSINE (DISTINCTE DE L'H'EMOLYSINE-ALPHA) PR'ESENTE DANS LES FILTRATS DE CULTURE DE LA SOUCHE WOOD 46 DE STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (H'EMOLYSINE G OU DELTA) Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Feb;108:215–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAINER A. S., MADOFF M. A., COOPER L. Z., WEINSTEIN L. STAPHYLOCOCCAL ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN: DETECTION ON THE ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):714–715. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORBECKI M., JELJASZESICZ J. ACTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXINS IN CELL CULTURES. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:205–213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR S., LINDORFER R. K. The characterization of staphylococcal toxins. I. The electrophoretic migration of the alpha hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal, and leucocidal activities of crude toxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1095–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec O., Seferna I. Analysis of staphylococcal alpha toxin action in the taenia coli of the guinea pig. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):465–472. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Temples B., Shaw W. V. Staphylococcal delta hemolysin: purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):142–156. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. T. Specific and nonspecific staining in detecting staphylococcal alpha toxin on erythrocytes by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):831–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.831-832.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus delta hemolysin by phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):519–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Staphylococcus aureus: some host-parasite interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):267–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. The phagocytosis and intracellular fate of staphylococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):285–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Chang T. W., Weinstein L. Effects of purified staphylococcal alpha toxin on the ultrastructure of human and rabbit erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):808–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.808-813.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleck J. L., Donahue J. A. Production of thermostable hemolysin by cultures of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1968 Jun;118(3):317–323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Bernheimer A. W. Disruption of bacterial protoplasts and spheroplasts by staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):603–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.603-605.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK C. H., TOWERS A. G. Serological tests for staphylococcal infection. Br Med J. 1962 Nov 10;2(5314):1227–1231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5314.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK C. H., WAILLING D. G. A study of 435 strains of Staphylococcus pyogenes with reference to factors which may contribute to pathogenicity. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Oct;68(2):431–443. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low D. K., Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Möllby R., Wadström T. Consequences of spingomyelin degradation in erythrocyte ghost membranes by staphylococcal beta-toxin (sphingomyelinase C). Toxicon. 1974 May;12(3):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAARUCCI A. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF STAPHYLOCCAL ALPHA-HEMOLYSIN. II. ANALYSIS OF THE KINETIC CURVE AND INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTIBODY. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1189–1195. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1189-1195.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF M. A., WEINSTEIN L. Purification of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:914–918. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.914-918.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J. Recognition of pathogenic staphylococci: with notes on non-specific staphylococcal haemolysin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):175–186. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J., VAUGHAN A. C. T. Staphylococcal delta-haemolysin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):597–615. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEOD J. W. Thermostable staphylococcal toxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:35–53. doi: 10.1002/path.1700860106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. L., NEURATH H. Proteolytic enzymes of the formed elements of human blood. I. Erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUDD S. Practicability of enhancing specific resistance to staphylococcic infection. JAMA. 1960 Jul 23;173:1360–1361. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03020300072023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Frommes S. P., Lindorfer R. K. Ultrastructural changes in neutrophils treated with staphylococcal alpha toxin. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jan;15(1):128–129. doi: 10.1139/m69-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Lindorfer R. K. Staphylococcal beta-hemolysin. II. Phospholipase C activity of purified beta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1313–1319. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1313-1319.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Smith K. L., Lindorfer R. K. Saphylococcal beta-hemolysin. I. Purification of beta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):300–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.300-305.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniar A. C., Weslake C., Warner P. Prevalence of staphylococcal anti-delta lysin in man. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Aug;13(8):925–929. doi: 10.1139/m67-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar M., Maheswaran S. K., Frommes S. P., Lindorfer R. K. Platelet damaging factor, a fifth activity of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):224–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.224-231.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNiven A. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Cell-associated alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Feb;5(1):123–127. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNiven A. C., Owen P., Arbuthnott J. P. Multiple forms of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Feb;5(1):113–122. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meduski J. W., Hochstein P. Hot-cold hemolysis: the role of positively charged membrane phospholipids. Experientia. 1972 May 15;28(5):565–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01931879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. L., Kocholaty W. F., Cooper D. A., Gray J. L., Robinson S. L. A proteinase from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 15;212(1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S., Gladstone G. P., Lenhart N. A. The antigenicity in man of staphlylococcal leucocidin toxoid, with notes on therapeutic immunization in chronic osteomyelits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Aug;46(4):455–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Haque R. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta-hemolysin. I. Production of delta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1327–1333. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1327-1333.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Wadström T. Separation of Gamma Hemolysin from Staphylococcus aureus Smith 5R. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):633–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.633-635.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOGRADY G., BURTON A. L. [The effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on chick embryo cells in tissue cultures]. Pathol Biol. 1961 Apr;9:831–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble W. C. Virulence and the biochemical characters of staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):181–193. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H. Chain initiation and control of protein synthesis. Science. 1966 Mar 11;151(3715):1241–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3715.1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosál R., Rasková H., Masek K. Comparative study on the effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on erythrocytes and thrombocytes. Toxicon. 1969 Dec;7(4):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(69)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novák E., Seifert J., Buchar E., Rasková H. Effect of staphylococcal -toxin on the phosphorylation of ADP by rat liver mitochondria. II. Effect of staphylococcal -toxin upon electron transport. Toxicon. 1971 Oct;9(4):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(71)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novák E., Seifert J., Rasková H. Effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on mitochondrial Mg2+ (Na+, K+) activated adenosine triphosphatase. Toxicon. 1970 Nov;8(4):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(70)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHOU R. Recherches sur l'immunité antistaphylococcique beta naturellement acquise chez l'homme et chez différentes espèces animales. Bull Acad Natl Med. 1953 Jul 7;137(25-26-27):446–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J., THATCHER F. S., GAGNON J. Studies with staphylococcal toxins. IV. The purification and metallic requirements of specific hemolysins. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Aug;4(4):345–361. doi: 10.1139/m58-037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr Comparative effects of purified staphylococcal alpha and delta toxins on mitochondrial metabolism. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):96–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Plaut M. E., Rosen H., Weinstein L. Purified staphylococcal alpha toxin: effect on epithelial ion transport. Science. 1967 Mar 3;155(3766):1118–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3766.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Bernheimer A. W. Evidence for an ordered arrangement in erythrocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1297–1304. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. E., Melly M. A. Speculations on the immunology of staphylococcal infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):274–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLANETZ L. W., BARTLEY C. H. The diagnosis of staphylococcal mastitis, with special reference to the characteristics of mastitis staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1953 Mar-Apr;92(2):139–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/92.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONEA S., DE REPENTIGNY J., FRAPPIER A. A REVERSIBLE METABOLIC CONTROL OF VIRULENCE CHARACTERISTICS OF A TOXINOGENIC STAPHLOCOCCUS AUREUS STRAIN. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:383–385. doi: 10.1139/m65-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Ultrastructure of membrane lesions in immune lysis, osmotic lysis and drug-induced lysis. Fed Proc. 1974 Oct;33(10):2116–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. S., Haque R. A chemically defined medium for the production of staphylococcal beta hemolysin. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Oct;19(10):1319–1323. doi: 10.1139/m73-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. S., Haque R. Effect of tryptophan analogues on synthesis of staphylococcal beta-haemolysin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jul;77(1):221–224. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-1-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Harshman S. Physical and chemical studies on staphylococcal -toxins A and B . Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Harshman S. Purification and properties of two forms of staphylococcal toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2672–2677. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soucková A., Soucek A. Inhibition of the hemolytic action of and lysins of Staphylococcus pyogenes by Corynebacterium hemolyticum, C. ovis and C. ulcerans. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth V., Wallach D. F., Weidekamm E., Knüfermann H. Micromorphologic consequences following perturbation of erythrocyte membranes by trypsin, phospholipase A, lysolecithin, sodium dodecyl sulfate and saponin. A correlated freeze-etching and biochemical study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):386–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington D. A., Arbuthnott J. P. Effects of staphylococcus alpha-toxin and streptolysin S on the oxidation of succinate by ascites tumour cells. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):495–505. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBLER J. H., KAPRAL F. A., MUDD S. ROLE OF ALPHA-TOXIN IN LESION FORMATION BY STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS ON SUTURES SUBCUTANEOUSLY IMPLANTED IN MICE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:51–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.51-57.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A. P., EGNER W. The site of action of the Staphylococcus alpha toxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:67–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A., EGNER W. Local effect of staphylococcal toxin; studies on blood vessels with particular reference to phenomenon dermonecrosis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954 May;57(5):392–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. G., Plommet M. Anti-gamma haemolysin as a diagnostic test in staphylococcal osteomyelitis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jun;26(6):409–412. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.6.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R., Wadström T. Effects of staphylococcal alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-hemolysins on human diploid fibroblasts and HeLa cells: evaluation of a new quantitative as say for measuring cell damage. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.938-946.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turgeon P., Grimard S., de Repentigny J. Inhibitions produites par la 8-azaguanine chez une souche toxinogène de staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):588–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda C. T., Gerstl B., Smith J. K., Carr W. T. Anti-staphylococcal beta-hemolysin antibodies in humans with neurological disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Oct;123(1):143–146. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEGERSHAUSEN B. [On some pharmacological properties of staphylolysin]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1960;238:144–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEGERSHAUSEN B. [On the pharmacology of staphylococcal toxin (Wood 46). V. The effect of staphylococcal toxin on the isolated heart, auricles and vessels of various species]. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1962;9:517–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISEMAN G. M. FACTORS AFFECTING THE SENSITIZATION OF SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES TO STAPHYLOCOCCAL BETA LYSIN. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:463–471. doi: 10.1139/m65-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISEMAN G. M. SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BETA-HAEMOLYSIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:187–207. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Biological properties of extracellular proteins from staphylococcus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):343–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Some biological properties of purified staphylococcal haemolysins. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. VI. Production and purification of -haemolysin in large scale. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):288–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. VII. Studies on -haemolysin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):308–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. IV. Separation of alpha-toxin by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):228–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Kato I. Purification and properties of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1974 Apr;27(2):86–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Sessa G., Bernheimer A. W. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: effects on artificial lipid spherules. Science. 1966 Nov 11;154(3750):772–774. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3750.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D., Fackrell H. B. Trypsin-mediated activation of the alpha-haemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):29–38. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Further observations on the mode of action of the alpha toxin of Staphylococcus aureus "Wood-46". Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):987–992. doi: 10.1139/m72-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Mode of action of the alpha toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):47–50. doi: 10.1139/m70-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Phospholipase activity of the delta hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):428–430. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. The nature of staphylococcal beta hemolysin. I. Mode of action. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Apr;13(4):369–376. doi: 10.1139/m67-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M. The nature of staphylococcal beta hemolysin. II. Effect on mammalian cells. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Feb;14(2):179–181. doi: 10.1139/m68-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurzel M., Bernheimer A. W., Zweifach B. W. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced contraction of isolated arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1966 Feb;210(2):360–364. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA A. Staphylococcal delta-hemolysin. I. Purification and chemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 4;71:544–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]