Abstract
Prostaglandin G and H synthases, or cyclooxygenases (COXs), catalyze the formation of prostaglandins (PGs). Whereas COX-1 is diffusely expressed in lymphoid cells in embryonic day 15.5 thymus, COX-2 expression is sparse, apparently limited to stromal cells. By contrast, COX-2 is predominant in a subset of medullary stromal cells in three- to five-week-old mice. The isozymes also differ in their contributions to lymphocyte development. Thus, experiments with selective COX-1 inhibitors in thymic lobes from normal and recombinase-activating gene-1 knockout mice support a role for this isoform in the transition from CD4–CD8– double-negative (DN) to CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP). Concordant data were obtained in COX-1 knockouts. Pharmacological inhibition and genetic deletion of COX-2, by contrast, support its role during early thymocyte proliferation and differentiation and, later, during maturation of the CD4 helper T-cell lineage. PGE2, but not other PGs, can rescue the effects of inhibition of either isoform, although it acts through distinct EP receptor subtypes. COX-dependent PG generation may represent a mechanism of thymic stromal support for T-cell development.
Introduction
Prostaglandins (PGs) are bioactive lipids formed by the sequential actions of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 (COX-1 and COX-2) and specific PG synthases (1). The known functions of the largely constitutive enzyme, COX-1, include generation of proaggregatory TxA2 by platelets, production of gastroprotective PGs, and regulation of water and salt reabsorption in the kidney (1). In contrast, COX-2 expression is induced in macrophages, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells by shear stress, cytokines, and growth factors and accounts for PG formation during inflammatory responses, reproduction, and renal adaptation to systemic stress (2).
PGs have been shown to regulate immune responses mediated by mature B and T lymphocytes. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) shifts the balance within the T lineage of the cellular immune response away from T-helper type 1 cells toward T-helper type 2 cells by inhibiting IL-2 and enhancing IL-4 production (3–8). PGE2 directly regulates the activation of mature B lymphocytes by skewing their differentiation toward IgE production (9). An immunoregulatory role for PGE2 is also suggested by its overproduction, either in vivo or ex vivo, in disorders that feature impaired immunological responses, including AIDS (10, 11), bone marrow or stem cell transplantation (12), atopic dermatitis, and the hyper-IgE syndrome (13).
Several observations implicate PGs in the maturation of the T-cell lineage. Expression of various PG biosynthetic enzymes and receptors has been detected in the thymus (14–17). Furthermore, thymus and nonlymphoid thymic stromal cell lines have been shown to secrete PGs in vitro (18–20). We now report that expression of the COX isoforms in mouse thymus is spatially and temporally distinct. Moreover, the products of these isozymes subserve distinct roles at critical stages in T-cell maturation. COX inhibitors may act, in part, by modulating immune function.
Methods
Mice.
C57Bl/6J wild-type and recombinase-activating gene-1–deficient mice (RAG-1–/–) were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Maine, USA); COX-1– and COX-2–deficient mice were generated as described previously (21, 22). Pregnancies were timed from the first day of plug observation (day 0.5).
Fetal thymic organ cultures.
Fetal thymic organ cultures (FTOCs) were performed according to procedures described previously (23). Cultures were fed daily by complete medium replacement with solvent control or the following drugs (in DMSO or ethanol): indomethacin (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, Missouri, USA), ibuprofen (Sigma Chemical Co.), valeryl salicylate (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA), prostanoids (Cayman Chemical) or prostanoid analogues (Cayman Chemical; Bayer AG, Leverkusen, Germany), NS-398 (Biomol Research Laboratories, Plymouth Meeting, Pennsylvania, USA), L-759,700, and L-745,337 (kindly provided by W. Tanaka, Merck Research Laboratories, Rahway, New Jersey, USA.)
Flow cytometric analyses.
Thymic lobes were mechanically dissociated and stained using standard procedures. The following mAb’s were used: anti-CD4 FITC, anti-CD8 Red 613, and anti-CD3ε phycoerythrin (GIBCO BRL, Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA); or anti-CD4 FITC, anti-CD8 FITC (GIBCO BRL), anti-CD25 phycoerythrin (PharMingen, San Diego, California, USA), biotinylated CD44, and streptavidin Red 670 (GIBCO BRL). Flow cytometric analysis was performed on a FACScan (Becton Dickinson Immunocytometry Systems, San Jose, California, USA) and analyzed using CellQuest software (Becton Dickinson). Aliquots from each cell suspension were removed to determine the total cell number and viability. The relative percentages of various thymocyte subpopulations based on CD4 and CD8 expression were obtained using quadrant statistics in CellQuest. The absolute numbers of each thymocyte subset were calculated by multiplying the total cell number by the percentage of each thymocyte population. The purity of flow-sorted populations of thymocytes was >99%.
RT-PCR analyses.
Total RNA was extracted with an RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN Inc., Valencia, California, USA). RT-PCR analyses were performed using standard procedures with primers specific for COX-1 (sense: 5′-GGTCCTGCTCGCAGATC-CTG-3′; antisense: 5′-CCTCTGGAAAGATGGGTCCT-3′), COX-2 (sense: 5′-CTGTACAAGCA-GTGGCAA-3′; antisense: 5′-TTACAGCTCAGTTGAACGCCT-3′), and the prostaglandin EP4 receptor (24) (sense: 5′-AGCGCCTCAG-CGACTTTCGCC-3′; antisense: 5′-AGGCACTTGATCTTCTCTATG-3′). The mRNA amplifications of other EPs were performed as described (25). PCR products were confirmed by Southern blotting; the filters were hybridized using specific oligonucleotides (COX-1: 5′-TTCTT-TGCACAACACTTCA-3′; COX-2: 5′-CATTAACCCTA-CAGTACTAAT-3′; EP1: 5′-GCTTTGGCAG-TGGCGCTGTGCTGCCA-3′; EP2: 5′-TAATTGAC-CCTTGGGTCTTTGCCA-3′; EP3 isoforms: 5′-ACACAAACTAATGCTTCCAGCTCCA-3′; EP4: 5′-ATCGCCACCTCTCTGGTGGTG-3′) after 5′ end labeling with [32P]ATP.
Immunohistochemistry.
Thymic lobes were fixed with sucrose, embedded in OCT compound, and frozen and stained using standard procedures. The primary antibodies were COX-1 antiserum (1:100–1:200 dilution), COX-2 antiserum (1:200-1:400 dilution) (kindly provided by A. Habib and the late J. Maclouf, INSERM, Paris, France; 26), anti–Thy 1.2 (20 μg/mL) mAb, anti–MHC class II (20 μg/mL) mAb(27), ulex europaeus agglutinin-1 (UEA-1) lectin (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, California, USA) (1:100 dilution), anti-6C3 (culture supernatant, undiluted), anti-cytokeratin 8.13 mAb (Sigma Chemical Co.) (1:100 dilution), or anti-CDR1 mAb (1:10 dilution).
Western blot analysis.
Thymi were washed twice with PBS buffer and lysed for Western blotting using standard procedures. Membranes were incubated with specific mAb’s as described previously (26). Chemiluminescent substrates (ECL; Amersham Life Sciences Inc., Arlington Heights, Illinois, USA) were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and bands were observed after a fixed time exposure (1–2 minutes) to Hyperfilm-ECL (Amersham Life Sciences Inc.). Protein bands were quantified using an LKB Ultrascan XL laser densitometer (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, New Jersey, USA). Immunodetection was linear between 15 and 75 μg of COX-1 and COX-2.
Statistical analysis.
The results were evaluated by using ANOVA, with subsequent comparisons using Student’s t test for paired or nonpaired data as appropriate. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05. Values were reported as the mean ± 1 SD. The IC50 was calculated using Biosoft-Dose software (Elsevier-Biosoft, Cambridge, United Kingdom).
Results
Expression of COX-1 and COX-2 in thymi and isolated thymocytes.
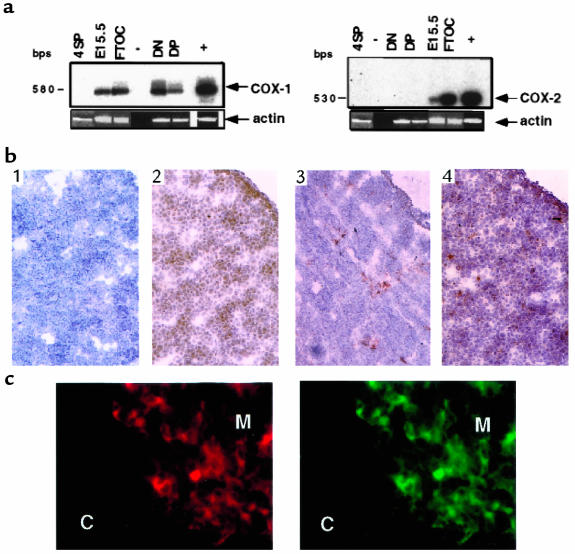
COX-1 and COX-2 products of the expected size were amplified by RT-PCR from total RNA of embryonic day 15.5 (E15.5) thymi, E15.5 cultured thymic lobes, and different thymocyte subpopulations purified by cell sorting, based on CD4 and CD8 expression. COX-1 and COX-2 products of the expected size were amplified from total RNA of E15.5 thymi and from E15.5 FTOCs (Figure 1a). A specific product for COX-1 was amplified from RNA of both CD4–CD8– double-negative (DN) and CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) thymocytes, but not from CD4+ single-positive (SP) mature lymphocytes (Figure 1a). COX-2 transcript was not detectable in purified DN, DP, or CD4+ SP cells (Figure 1a).
Figure 1.
Characterization of COX-1 and COX-2 mRNA and protein expression. (a) Total RNA from indicated tissues or fractions was isolated, and cDNAs were amplified by RT-PCR using primers specific for COX-1 (left), COX-2 (right), or actin (see Methods). The identity of the amplified fragments for COX-1 or COX-2 was confirmed by Southern blot analysis with specific probes. –, negative control; +, positive control (NIH 3T3 cells); DN, CD4–CD8– thymocytes; DP, CD4+CD8+ thymocytes; 4SP, CD4+ lymphocytes; E15.5, embryonic day 15.5 thymus; FTOC, E15.5 thymus cultured for 5 days. (b) Frozen sections of E15.5 thymus were reacted with normal rabbit IgG as a negative control (panel 1), anti–COX-1 (panel 2), anti–COX-2 (panel 3), and anti–Thy 1.2 (panel 4). Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. ×40. (c) Frozen sections of thymus from 3-week-old mice were double stained with UEA-1 lectin (left) and anti–COX-2 (right). C, cortex; M, medulla. ×100.
Sections of E15.5 thymi were immunostained for COX-1 or COX-2 proteins, for the Thy 1.2 antigen, or for the MHC class II molecule. COX-1 staining showed a diffuse pattern of expression in E15.5 thymi similar to that in Thy 1.2 (Figure 1b, panels 2 and 4). The majority of cells positive for COX-1 had lymphoid morphology at higher power (×40–100) (data not shown). Fewer, sparsely distributed cells expressed COX-2 in E15.5 thymus (Figure 1b, panel 3). They demonstrated stromal cell morphology at higher power and were MHC class II positive (data not shown). We also investigated COX-2 expression in the adult (3- to 5-week-old) thymus to characterize further the stromal component expressing COX-2. Thymic sections were stained for COX-2, medulla-specific UEA-1 lectin, cytokeratin, 6C3, or CDR1 (cortex-specific antibodies). The majority of the COX-2–positive cells were positive for UEA-1 and cytokeratin (Figure 1c and data not shown) and were localized near the corticomedullary junction (Figure 1c). Thus, the COX isoforms are differentially expressed in the thymus, and COX-2 is constitutively expressed in thymic medullary stroma.
COX-1 is required for CD4+CD8+ thymocyte formation.
We next investigated T-cell development in the absence of COX activity. We used selective COX inhibitors in FTOCs and analyzed CD4, CD8, and CD3ε expression. More than 90% of thymocytes in normal mice lack CD4, CD8, and CD3ε expression at E15.5, whereas by E17–18.5, the majority of thymocytes (70–80%) have progressed to the DP stage. After E17.5, CD4 and CD8 SP CD3+ thymocytes develop from DP intermediates. This developmental progression is recapitulated in FTOC with a minimal lag (23, 27).
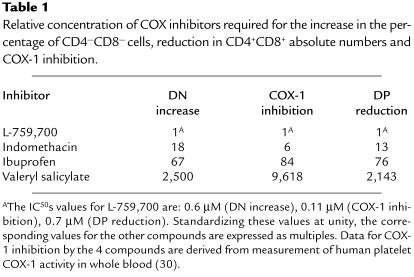
Two highly selective COX-1 inhibitors were used: valeryl salicylate (28) and the more potent L-759,700, which has roughly a 100-fold preference for COX-1 over COX-2 in different cellular systems (ref. 29, and unpublished data) Both inhibitors were provided from Merck Research Laboratories. We also used ibuprofen and indomethacin as nonselective COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors (30, 31). All inhibitors caused dose-dependent, statistically significant increases of 4- to 5-fold in the percentage of DN cells in E15.5 FTOCs, whereas the DP subset was decreased concomitantly (Figure 2a). A dose-dependent increase in the number of DN cells was also observed in the presence of the inhibitors. The IC50 values for the inhibition of DP absolute counts were as follows L-759,700, 0.7 μM; indomethacin, 9 μM; ibuprofen, 53 μM; and valeryl salicylate, 1.5 mM (Figure 2a). These IC50 were similar to the EC50 observed for the increase in the percentage of DN cells. The relative potency of these 4 compounds in FTOCs corresponded to their rank order of potency for inhibition of COX-1 in different systems (30) (Table 1). These effects were reversed by selected PG analogues (see below). Forward- and side-light measurements, as well as propidium iodide staining for fragmented DNA, showed no increase in apoptotic thymocytes in E15.5 inhibitor-treated FTOCs (data not shown).
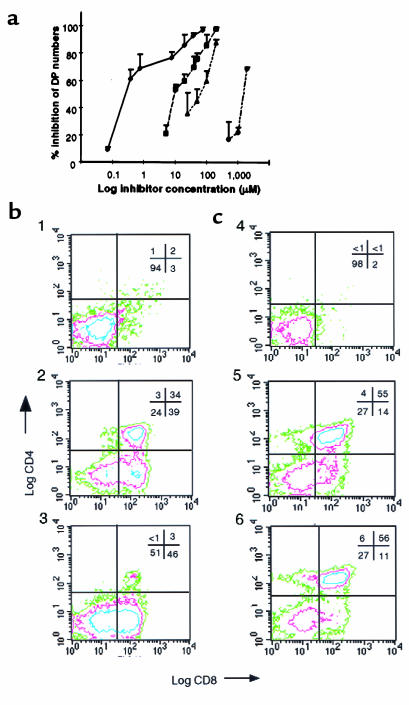
Figure 2.
Effect of COX-1 inhibition on DP formation. (a) E15.5 FTOCs were treated with different concentrations of L-759,700 (filled diamonds), indomethacin (filled squares), ibuprofen (filled triangles), or valeryl salicylate (open circles) for 5 days of culture. The percent inhibition of the DP absolute counts is expressed relative to vehicle-treated FTOCs. Values are means ± SD of 3–6 different experiments, each performed in quadruplicate. (b) Effect of the selective COX-1 inhibitor L-759,700 on E15.5 RAG-1–/– FTOCs. The panels show a representative experiment in which RAG-1–/– thymic lobes were cultured in the presence of vehicle (panel 1), anti-CD3ε mAb (25 μg/mL medium) (panel 2), or anti-CD3ε mAb (25 μg/mL medium) plus L-759,700 (7 μM) (panel 3). (c) Effect of the selective COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 on E15.5 RAG-1–/– FTOCs. RAG-1–/– thymic lobes were cultured for 5 days and analyzed for CD4 and CD8 expression by flow cytometry. Conditions were as follows: vehicle (panel 4), anti-CD3ε mAb (25 μg/mL medium) (panel 5), or anti-CD3ε mAb (25 μg/mL medium) plus NS-398 (40 μM) (panel 6).
Table 1.
Relative concentration of COX inhibitors required for the increase in the percentage of CD4—CD8— cells, reduction in CD4+CD8+ absolute numbers and COX-1 inhibition.
We examined mice with a targeted disruption of the recombinase-activating gene-1 (RAG-1–/–) to clarify further the role of COXs in lymphocyte maturation. Thymocyte development in RAG-1–/– animals is arrested at the DN stage in vivo because of a failure to rearrange the T-cell receptor (TCR) β locus (32). Incubation of RAG-1–/– thymic lobes with anti-CD3ε mAb in FTOCs results in efficient progression of the DN thymocytes to the DP stage (33). DPs were formed in E15.5 RAG-1–/– FTOCs treated with anti-CD3ε mAb alone (Figure 2b, panels 1 and 2). However, when lobes were coincubated with anti-CD3ε mAb and the COX-1–specific inhibitor L-759,700, the development of DP thymocytes was greatly reduced (Figure 2b, panel 3). The selective COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 (34) at concentrations up to 80 μM did not affect the formation of DP thymocytes under the same experimental conditions (Figure 2c). The number of cells recovered in each case was also determined. In the experiments shown in Figure 2, approximately 15 × 104 cells per lobe were recovered from untreated samples. In the presence of anti-CD3ε, cell recovery increased to 76 × 104 cells per lobe. The DN-to-DP transition has been shown previously to be associated with expansion of thymocyte numbers (33). The addition of L-759,700 reduced recovery to 38 × 104 cells per lobe, which is consistent with a developmental block in the DN-to-DP transition. NS-398 also reduced cell numbers by approximately 2-fold in the absence of any change in subset frequency (Figure 2c). This reduction is likely due to an effect of the inhibitor on an earlier stage of thymocyte proliferation (see below).
We also considered the possibility that the COX-1 inhibitors could reduce the survival of DP thymocytes, thereby decreasing their numbers and increasing the frequency of DN thymocytes. To test this possibility, we allowed fetal development to proceed in vivo to E17.5 and 18.5, and then initiated 5-day FTOCs in the presence or absence of L-759,700. By E17.5, DP thymocytes are already formed in vivo, and they transit to the CD4 SP mature stage during 5 days of organ culture (23). L-759,700 was much less effective in reducing the percentages and absolute numbers of the DP thymocytes in E17.5 and 18.5 relative to E15.5 thymi (Figure 3, a and b). Some reductions in DP cell numbers were observed at higher doses (Figure 3c). These reductions could reflect an inhibitor-mediated block of the remaining DN cells in the older thymi undergoing the DP transition during the culture period. In addition, L-759,700 did not affect the percentage or number of CD4 or CD8 SP CD3ε+ thymocytes (Figure 3). Taken together, these observations support the hypothesis that the COX-1 inhibitor interferes with the DN-to-DP transition by blocking either differentiation, proliferation, or survival of differentiating cells. Our data argue against the possibility that the COX-1 inhibitor is directly toxic to preformed DP thymocytes.
Figure 3.
Flow cytometry analysis of thymocytes from E17.5 and E18.5 FTOCs treated with selective COX-1 inhibitor. Thymocytes from E17.5 plus 5 days culture in FTOCs were examined for CD4 and CD8 expression. (a) Vehicle. (b) L-759,700, 10 μM. The percentage of cells in each quadrant are indicated in the corners of each graph. (c) E15.5 (filled circles), E17.5 (filled squares), and E18.5 (filled triangles) FTOCs were treated with different concentrations of L-759,700. The percent inhibition of the DP absolute counts is expressed relative to vehicle-treated FTOCs. Values are means ± SD of 3–6 different experiments, each performed in quadruplicate.
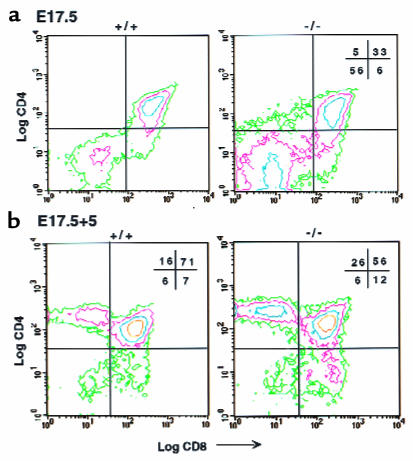
We confirmed these results in COX-1–deficient mice (COX-1–/–). E15.5 thymi isolated from COX-1–/– and wild-type embryos showed no differences in the total cell number or the phenotype of thymocytes (>90% were in the DN stage; data not shown). However, by E17.5, a significantly higher percentage of DN and lower percentage of DP thymocytes were consistently observed in E17.5 COX-1–/– embryos compared with wild-type embryos (Figure 4a). Therefore, we investigated the DN-to-DP transition by culturing E15.5 thymi. Again, thymi from COX-1–/– mice showed a significantly (P < 0.001) reduced percentage and number of DP cells, with a concomitant increase in DN cells. DN percentages were increased 2-fold in COX-1–/– mice relative to wild-type littermates (28 ± 8% in COX-1–/– vs. 12 ± 3% in wild-type mice), as were DN absolute numbers (19 ± 4 × 104 cells per lobe in COX-1–/– vs. 11 ± 4 × 104 in wild-type mice). DP percentages were slightly but significantly (P < 0.001) decreased in COX-1–/– mice relative to wild-type littermates (54 ± 8% in COX-1–/– vs. 70 ± 5% in wild-type), as were absolute numbers (40 ± 16 × 104 cells per lobe in COX-1–/– vs. 58 ± 14 × 104 in wild-type mice).
Figure 4.
Flow cytometry analysis of thymocytes from E17.5 thymi and from E17.5 cultured COX-1–/– and control thymi. Thymocytes from COX-1–/– and control mice were examined for CD4 and CD8 expression. (a) E17.5 thymi. (b) E17.5 thymi in culture 5 days. +/+, controls; –/–, COX-1–/– mice. The percentage of cells in each quadrant is indicated in the corners of each graph.
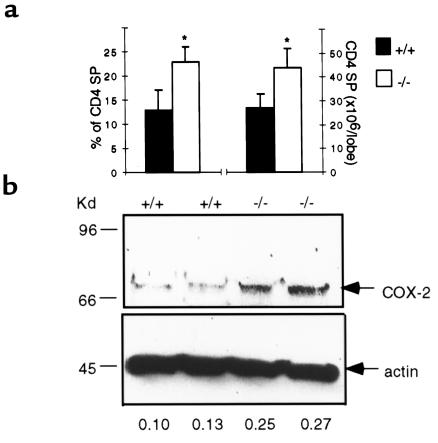
Clearly, the requirement for COX-1 is not absolute in the knockout mice because many DP thymocytes are formed, and these thymocytes can continue differentiation to the SP stage. In fact, although the percentage of DP cells was still significantly lower in COX-1–/– compared with wild-type organs in embryonic and adult mice (5 weeks, data not shown), a significant increase in both the relative percentage and absolute number of CD4 SP lymphocytes was observed in null thymi (Figures 4b and 5a). Because our further results (see below) indicate that COX-2 plays a role in CD4 SP formation, we investigated whether increased COX-2 expression might compensate for the absence of COX-1. COX-2 protein was increased approximately 2.4-fold in COX-1–/– thymi (Figure 5b).
Figure 5.
CD4 SP cells and COX-2 protein levels in COX-1–/– and wild-type thymi. (a) Thymocytes were isolated from adult (5-week-old) thymi, counted, and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage and absolute counts of CD4 SP cells are shown in the graphs. *P < 0.01 vs. controls; n = 4 each group. (b) Western blot analysis using proteins (50 μg) extracted from 5-week-old thymi and using antibodies specific for COX-2 or β-actin as controls. The numbers indicate the actin/COX-2 ratios of the densitometric values of the bands. +/+, wild-type mice; –/–, COX-1–/– mice.
COX-2 is required at 2 steps of T-cell development.
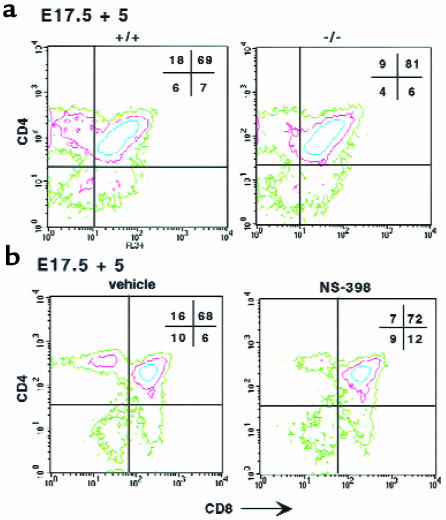
We next investigated the role of COX-2 in T-cell formation. The relative distribution of DN vs. DP subsets in E17.5 COX-2–/– thymi was similar to that in wild-type embryos, indicating that, in contrast to COX-1, COX-2 is not involved in DN-to-DP transition (data not shown and Figure 6a). However, CD4 SP lymphocyte formation was impaired in COX-2–/– E17.5 thymi cultured for 5 days (Figure 6a). There was a 50% reduction in the relative percentage and number of CD4 SP cells in COX-2–/– embryos (P < 0.001) (Figure 6a). Although the relative percentage of the DP cells was increased by roughly 10% in the COX-2–/– thymi (Figure 6a), their absolute counts were not significantly different from controls. No significant differences in percentage or absolute counts were observed for the CD8 SP subset. Furthermore, the DN counts were reduced by approximately 45% in E17.5 COX-2–/– cultured thymic lobes compared with controls (P < 0.01). COX-1 protein was not upregulated in COX-2–/– thymi (data not shown).
Figure 6.
Flow cytometric analyses of thymocytes from COX-2–/– E17.5 FTOCs and wild-type E17.5 FTOCs in the presence of COX-2 inhibitors. (a) E17.5 thymi were isolated from COX-2–/– embryos (–/–) and control siblings (+/+) and cultured for 5 days. Thymocytes were analyzed for CD4 and CD8 expression by flow cytometry. The contour plots are shown. Percentages are indicated in the corner of each quadrant. (b) The same experiments and analyses were performed in wild-type E17.5 FTOCs in the presence of the selective COX-2 inhibitor NS-398 (40 μM) or vehicle.
The results with the COX-2–/– mice were confirmed by pharmacological inhibition of COX-2. NS-398 and L-745,337 are reportedly 160- and 245-fold more potent on average as COX-2 and COX-1 inhibitors, respectively (34). Neither NS-398 nor L-745,337 caused any change in the relative proportions of DN and DP subsets in E15.5 FTOCs. These data and the observation that NS-398 did not impair the DP formation in anti-CD3ε–treated RAG-1–/– FTOCs (Figure 2c) confirmed that, in contrast to COX-1, COX-2 is not involved in this transition. However, in E17.5 FTOCs, NS-398 caused a dose-dependent decrease in the percentage and number of CD4 SP cells, with an IC50 of 30 μM (Figure 6b and data not shown). No such decrease was observed with the specific COX-1 inhibitor L-759,700 (Figure 3). No significant change in CD8 SP thymocytes was observed, even when the cells were gated, based on expression of CD3ε (data not shown). In addition, the DN cell counts were also dose dependently reduced by NS-398 (IC50 of 30 μM). The DP percentages were slightly increased (Figure 6b), but their absolute numbers were not significantly affected. L-745,337 showed effects similar to NS-398 in E17.5 FTOCs, with an IC50 of 82 μM. The relative difference in the IC50 between NS-398 and L-745,337 is consistent with their respective potencies in inhibiting COX-2 in a different cellular system (34).
We further investigated the effects of selective COX-2 inhibition on the different DN thymocyte subsets by staining for CD44 and CD25 antigens (35). NS-398 caused a concentration-dependent decrease in the total cell counts per lobe in E15.5 RAG-1–/– FTOCs (IC50 of 31 μM). The percentages and absolute counts of the CD44–CD25+ subset were reduced with the same IC50. On the other hand, the proportions of the 2 most immature subsets of DN thymocytes (CD44+CD25– and CD44+CD25+) showed a parallel increase, but their counts were not significantly affected by NS-398 (data not shown). Similar results were obtained with E15.5 wild-type FTOCs. The selective COX-1 inhibitor L-759,700 showed no effect on the DN subsets in the same experimental conditions (data not shown). These data are consistent with a role for COX-2 in the maturation of CD4 SP cells and in the survival or further differentiation of thymocytes at the CD44–CD25+ stage.
PGE2 regulates development by different receptor subtypes.
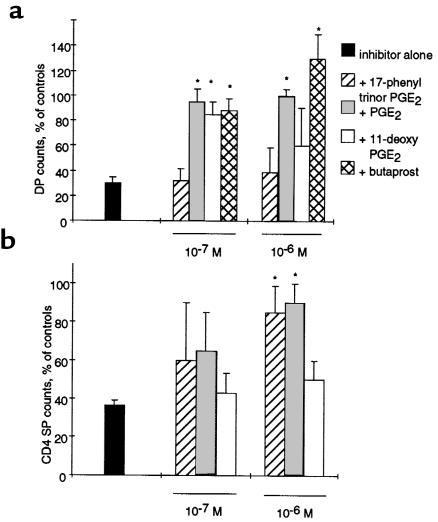
To determine which PGs might be involved in the maturation of DN thymocytes, we rescued the impairment in development by adding back prostanoids or their synthetic analogues to inhibitor-treated FTOCs. E15.5 FTOCs were incubated in the presence of indomethacin (40 μM), with increasing concentrations of PGE2 or one of its synthetic analogues: PGF2α, U46619 (a stable PGH2/TXA2 analogue), iloprost (a stable PGI2 analogue), or 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 (a putative metabolite of PGD2). PGE2, but none of the other prostanoids, overcame the inhibitory effect of indomethacin in E15.5 FTOCs (Figure 7a). In addition, neutralizing antibodies to PGE2 (kindly provided by P. Isakson, Monsanto, Skokie, Illinois, USA; ref. 36) caused a block in the DN-to-DP transition (data not shown). Four different subtypes of PGE2 receptors (EP1–EP4) have been described in the mouse (15), and we detected all of them in the mouse embryonic thymus using RT-PCR (data not shown). Among the EP agonists, butaprost (an EP2 agonist) and 11-deoxy PGE2 (an EP2/EP4 agonist) rescued the inhibition on DP cells (Figure 7a), whereas sulprostone (an EP1/EP3 agonist) and 17-phenyl-trinor PGE2 (an EP1 agonist) did not show any effect (data not shown). Therefore, the EP2 receptor subtype is most likely to mediate the effects of PGE2 on DP thymocyte formation.
Figure 7.
Effect of PGE2 and its analogues in inhibitor-treated FTOCs. (a) E15.5 FTOCs were treated with indomethacin (40 μM) in the presence or absence of different concentrations of PGE2 or its synthetic analogues. After 5 days of culture, thymic lobes were dissociated, and the thymocytes were counted and stained for CD4 and CD8. DP counts are expressed in the graphs as the percentage of vehicle-treated FTOCs (100%). (b) The same experiments were performed with E17.5 FTOCs in the presence of 40 μM NS-398, and the CD4 SP cells were considered for the analyses. *P < 0.01 vs. inhibitor-treated FTOCs.
We next attempted to rescue impaired CD4 SP maturation caused by selective COX-2 inhibitors in E17.5 FTOCs treated with 40 μM of NS-398. PGE2 and 17-phenyl trinor PGE2 (an EP1 agonist) dose dependently rescued the effect of the selective COX-2 inhibitor on CD4 SP formation, whereas 11-deoxy PGE2 (an EP2/EP4 agonist) was ineffective (Figure 7b). Therefore, the EP1 receptor subtype is most likely to mediate the effects of PGE2 on CD4 SP thymocyte formation.
Discussion
To our knowledge, the present studies provide the first direct genetic and pharmacological evidence that both COX isozymes are required for the efficient maturation of the T-cell lineage in the fetal thymus. A model based on our data for the distinct function of the COX isozymes in fetal T-cell development is depicted in Figure 8.
Figure 8.
Simplified model of the possible role of COX-1, COX-2, PGs, and PG receptors during T-cell development. COX-1–dependent PGE2 synthesis is required for an efficient transition of thymocytes from DN to DP. In this model, an autocrine effect of PGE2 acting on the EP2 receptor of immature thymocytes is hypothesized. However, we cannot exclude an effect of COX-1 in stromal cells. COX-2–dependent PG production positively affects the DN population, and it is also required for CD4 SP formation. We hypothesize a paracrine effect of PGE2 formed by stromal cell COX-2 acting on thymocyte EP1 receptors in positive selection. It is also possible that COX-2–dependent PG production may also act on the stromal cells in an autocrine fashion.
Previous workers have noted the existence of PG synthases in the thymus (14–18, 37). We have extended these descriptive observations. Both COX isoforms are present in the fetal thymus. Furthermore, they differ in both the spatial and temporal aspects of their expression. Thus, COX-1, but not COX-2, is present in immature thymocytes, whereas COX-2 expression changes as the thymus matures. As a result, COX-2 is sparsely expressed in the fetal thymus, whereas it becomes highly expressed and localized to the medulla when the thymus is fully developed. In addition to varied patterns of expression, we report distinct functions for the 2 COXs in lymphocyte development. Spatial segregation of expression of these isozymes within a single organ is also observed in the kidney, where COX-1 is present in the collecting ducts, microvasculature, and glomeruli, and COX-2 is expressed in the macula densa and in a subset of medullary interstitial stroma cells (1, 2). Although distinct roles for the COX isozymes in renal function seem to be likely, these roles remain to be established.
Both genetic and pharmacological evidence from the present study supports a role for COX-1 in the transition of immature DN thymocytes to DP thymocytes. Furthermore, the presence of COX-1 in the most immature thymocytes, and its downregulation in the mature CD4 SP cells, also supports this role, although indirectly. The DN-to-DP transition depends upon productive TCR-β gene rearrangements and the assembly of a pre-TCR complex (38, 39). However, because COX-1 inhibitors blocked the DN-to-DP transition following CD3ε cross-linking in RAG-1–/– thymus, it is likely that the requirement for PG synthesis follows signaling by the pre-TCR. Furthermore, COX-1 inhibitors did not block the anti-CD3ε–induced transition of RAG-1–/– thymocytes to the intermediate CD8 SP subset, although they reduced the level of expression of CD8 on this subset (data not shown). Interestingly, overexpression of the transcription factor Egr-1 induces T-cell development in RAG-1–/– mice to the immature CD8 SP stage, but the cells remain blocked prior to CD4 upregulation (40). Presently, it is unknown whether or how the COX-1 and Egr-1 pathways might interact to control this step of T-cell differentiation. Our experiments support a role for COX-1 in the transition of immature DN thymocytes to DP thymocytes. Although it remains to be determined whether COX-1 is required for survival, proliferation, or differentiation of thymocytes, COX-1 inhibition does not cause a general increase in thymocyte apoptosis. Other groups reported conflicting effects on apoptosis by PGs, either protecting (41) or inducing (42) programmed cell death. This conflict may reflect the different experimental conditions used by other investigators. In fact, these previous reports studied isolated thymocytes incubated with PGs for relatively short periods. FTOCs, on the other hand, represent a more integrated environment where the anatomy of the thymus is preserved. Therefore, an isolated cell system may fail to reflect the interactions operating in the intact whole organ.
Selective COX-1 inhibition did not affect the positive selection of CD4 SP lymphocytes. However, there was an increased percentage and increased absolute numbers of the CD4 SP cells in COX-1–/– thymi. Expression of COX-2 was increased in COX-1–/– thymi. Compensatory expression of the alternate isozyme has been reported in COX-deficient lung fibroblasts (43), whereas compensatory expression was not observed in colonic adenomes of patients treated with a COX-2 inhibitor (DuBois, R., personal communication). In the thymus, it is likely that the COX-2–dependent PG production may partially compensate for the absence of COX-1. Indeed, the block in transition to DP cells is more complete in the presence of inhibitors (Figure 5b) than following gene deletion (Figure 2a). COX-2 overexpression may also cause the increase in formation of CD4 SP cells in COX-1–/– thymi.
Both mutation of the COX-2 gene and pharmacological inhibition of the enzyme limited the fetal development of CD4 SP thymocytes. Moreover, COX-2 protein was upregulated in COX-1–/– thymi, coinciding with a significant increase of CD4 SP thymocytes. Inhibition of COX-2 failed to affect negative selection by deletion (our unpublished data). Thus, COX-2–dependent PG synthesis appears to influence CD4 SP differentiation. Although the existence of such a system has previously been hypothesized (44, 45), PGs would represent the first family of mediators, aside from the TCR, its coreceptors, and their ligands, that modulates the CD4 SP development in intact thymic organs. As COX-2 is only expressed in stromal cells, it seems likely that PGs act as stromal cofactors to influence developing thymocytes (Figure 8). Indeed, we have shown that COX-2–dependent formation of PGs enhanced adherence of DP and CD4 SP thymocytes to medullary stromal cell lines (29). Because we saw no effect of COX-2 deficiency on CD8 generation, it is possible that COX-2 may function specifically in the CD4 lineage.
Genetic deletion or inhibition of COX-2 negatively influenced the DN cells, especially the CD44–CD25+ subpopulation, which represents the majority (>70%) of DN thymocytes (35). Subsequent proliferation may amplify the progenitors that slip past the CD44–CD25+ stage. CD25 upregulation coincides with the initiation of TCR-β rearrangement, and CD44 downregulation is associated with the acquisition of TCR-β cytoplasmic expression (46). Therefore, it is possible that COX-2 may be required in some aspect of the initiation or progression of TCR-β rearrangements.
Finally, our data support a predominant role for PGE2 in mediating both the effect of COX-1 during DN-to-DP transition and the effect of COX-2 in CD4 SP formation, although through 2 distinct EP subtypes: EP2 and EP1, respectively. Both are G protein–coupled receptors: EP2 activates adenylyl cyclase, and EP1 is coupled to phospholipase C (15). A potential mechanism by which PGE2 may act through the EP2 subtype is the modulation of cellular adhesion, because cAMP analogues and PGE2 both enhance the binding of immature DN and DP thymocytes to extracellular matrix proteins (47). Alternatively, a transient elevation of cAMP is necessary for the initiation of S phase in mouse lymphocytes (48), suggesting that PGE2, acting through EP2, may modulate cellular proliferation.
In summary, we report evidence that COX isozymes play functionally distinct roles in lymphocyte development, in addition to their recognized importance in the regulation of inflammation and of mature B- and T-helper cells. COX-1–dependent formation of PGE2, acting through EP2 receptors, plays an important role in DN-to-DP transition, while COX-2 expression in the stroma influences positive selection of thymocytes through EP1 receptors.
Immunomodulatory effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the induction and maintenance of central tolerance have been reported previously (49–51). Interestingly, indomethacin prevents induction of thymic tolerance in vivo in mice, while administration of PGE2 rescues this effect (49). Although an analysis of immune function has yet to be reported receptors or in mice deficient in either COX isoform or in prostanoid receptors, idiopathic chronic suppurative peritonitis and bowel inflammation were both unexpected findings in the COX-2 knockout mice (21). Given the emergence of selective inhibitors of COX isozymes into clinical application, assessment of their effects on immune function and immune cell development would seem timely.
Acknowledgments
Supported by grants HL-57847 and HL-54500 from the National Institutes of Health.
References
- 1.Smith WL, DeWitt DL. Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases -1 and -2. Adv Immunol. 1996;62:167–215. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60430-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Herschman HR, Reddy ST, Xie W. Function and regulation of prostaglandin synthase-2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;407:61–66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1813-0_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Betz M, Fox BS. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits production of Th1 lymphokines but not of Th2 lymphokines. J Immunol. 1991;146:108–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anastassiou ED, Paliogianni F, Balow JP, Yamada H, Boumpas DT. Prostaglandin E2 and other cyclic AMP-elevating agents modulate IL-2 and IL-2R alpha gene expression at multiple levels. J Immunol. 1992;148:2845–2852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Paliogianni F, Kincaid RL, Boumpas DT. Prostaglandin E2 and other cyclic AMP elevating agents inhibit interleukin 2 gene transcription by counteracting calcineurin-dependent pathways. J Exp Med. 1993;178:1813–1817. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hilkens CMU, et al. Differential modulation of T helper type 1 (Th1) and T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokine secretion by prostaglandin E2 critically depends on interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:59–63. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Katamura K, et al. Prostaglandin E2, at priming doses of naive CD4+ T-cells inhibits acquisition of ability to produce IFN-γ and IL-2, but not IL-4 and IL-5. J Immunol. 1995;155:4604–4612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Van der Pouw Kraan TCTM, Boeije LCM, Smeenk RJT, Wijdenes J, Aarden LA. Prostaglandin E2 is a potent inhibitor of human interleukin 12 production. J Exp Med. 1995;181:775–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fedyk ER, Phipps RP. Prostaglandin E2 receptors of the EP2 and EP4 subtypes regulate activation and differentiation of mouse B lymphocytes to IgE-secreting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:10978–10983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.20.10978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mastino A, et al. Correlation between induction of lymphocyte apoptosis and prostaglandin E2 production by macrophages infected with HIV. Cell Immunol. 1993;152:120–130. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Delemarre FG, et al. Reduced toxoplasmatic activity of monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophage from AIDS patients is mediated via prostaglandin E2. AIDS. 1995;9:441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cayeux SJ, Beverly PC, Schulz R, Dorken B. Elevated plasma prostaglandin E2 levels found in 14 patients undergoing autologous bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1993;12:603–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis: the skin as a window into the pathogenesis of chronic allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96:302–318. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nusing R, et al. Localization of thromboxane synthase in human tissues by monoclonal antibody Tu 300. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421:249–254. doi: 10.1007/BF01611182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ushikubi F, Hirata M, Narumiya S. Molecular biology of prostanoid receptors: an overview. J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal. 1995;12:343–359. doi: 10.1016/0929-7855(95)00022-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Appasamy PM, et al. Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase (cyclooxygenase) during murine fetal thymic development. Cell Immunol. 1991;137:341–357. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90084-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Milicevic NM, Appasamy PM, Colic M, Milicevic Z. Immunocytochemical demonstration of prostaglandin synthase (cyclooxygenase) in thymic macrophages of normal and cyclosporin-treated rats. Immunobiology. 1994;190:376–384. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(11)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sun L, Piltch AS, Liu P, Johnson A, Hayashi J. Thymocytes stimulate metabolism of arachidonic acid in rat epithelial cells. Cell Immunol. 1990;131:86–97. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90236-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McCormack JE, Kappler J, Marrack P, Westcott JY. Production of prostaglandin E2 and prostacyclin by thymic nurse cells in culture. J Immunol. 1991;146:239–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pendino KJ, Chepenik KP, Schmidt RR. Differential eicosanoid synthesis by murine fetal thymic non-lymphoid cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 1992;70:237–252. doi: 10.1038/icb.1992.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Morham SF, et al. Prostaglandin synthase gene disruption causes severe renal pathology in the mouse. Cell. 1995;83:473–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Langenbach R, et al. Prostaglandin synthase-1 gene disruption in mice reduce arachidonic acid-induced inflammation and indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration. Cell. 1995;83:483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kisielow, P. 1990. Applications of fetal thymus organ cultures in studies of T-cell development. In Immunological methods, volume 4. I. Lefkovits and B. Pernis, editors. Academic Press. San Diego, CA. 292–309.
- 24.Arakawa T, et al. Prostanoid receptors of murine NIH 3T3 and RAW 264.7 cells. Structure and expression of the murine prostaglandin EP4 receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:29569–29575. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.47.29569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fedyk ER, Ripper JM, Brown DM, Phipps RP. A molecular analysis of the PGE receptor (EP) expression on normal and transformed B lymphocytes: coexpression of the EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4. Mol Immunol. 1996;33:33–45. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(95)00130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Habib A, et al. Demonstration of an inducible cyclooxygenase in human endothelial cells using antibodies raised against the carboxyl-terminal region of the cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23448–23454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jenkinson EJ, Owen JJ. T-cell differentiation in thymus organ cultures. Semin Immunol. 1990;2:51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bhattacharyya DK, Lecomte M, Dunn J, Morgans DJ, Smith WL. Selective inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-1 (cyclooxygenase-1) by valeryl salicylic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995;317:19–24. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rocca B, Spain LM, Ciabattoni G, Patrono C, FitzGerald GA. Differential expression and regulation of cyclooxygenase enzymes in thymic stromal cells. J Immunol. 1999;162:4589–4597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Patrignani P, et al. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of the cyclooxygenase activity of human blood prostaglandin endoperoxide synthases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;271:1705–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Smith WL, DeWitt DL. Biochemistry of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-1 and synthase -2 and their differential susceptibility to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Semin Nephrol. 1995;15:179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mombaerts P, et al. RAG-1 deficient mice have no mature B and T-lymphocytes. Cell. 1992;68:869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Levelt CN, Mombaerts P, Iglesias A, Tonegawa S, Eichmann K. Restoration of early thymocyte differentiation in T-cell receptor β-chain deficient mutant mice by transmembrane signaling through CD3ε. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:11410–11415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Panara MR, et al. Effects of the novel anti-inflammatory compounds, N-[2-(cyclohexyloxy)-4-nitrophenyl] merthanesulphonamide (NS-398) and 5-methane-sulphonamido-6-(2,4-difluorothio-phenyl)-1-indanone (L-745,337), on the cyclooxygenase activity of human blood prostaglandin endoperoxide synthases. Br J Pharmacol. 1995;116:2429–2434. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Godfrey DI, Kennedy J, Suda T, Zlotnik A. A developmental pathway involving four phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets of CD3–DN triple negative adult mouse thymocytes defined by CD44 and CD25 expression. J Immunol. 1993;150:4244–4252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mnich SJ, et al. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes the activity of prostaglandin E2. J Immunol. 1995;155:4437–4444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.O’Neill GP, Ford-Hutchinson AW. Expression of mRNA for cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human tissues. FEBS Lett. 1993;330:156–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80263-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Saint-Ruf C, et al. Analysis and expression of a cloned pre-T-cell receptor gene. Science. 1994;266:1208–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Berger MA, et al. Subunit composition of pre-T-cell receptor complexes expressed by primary thymocytes: CD3ε is physically associated but not functionally required. J Exp Med. 1997;186:1461–1467. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.9.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Miyazaki T. Two distinct steps during thymocyte maturation from CD4–CD8– to CD4+CD8+ distinguished in the early growth response (Egr)-1 transgenic mice with a recombinase-activating gene-deficient background. J Exp Med. 1997;186:877–885. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.6.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Goetzl EJ, Songzhu A, Zeng L. Specific suppression by prostaglandin E2 of activation-induced apoptosis of human DP T lymphoblasts. J Immunol. 1995;154:1041–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Saiagh S, Rigal D, Monier JC. Effects of PGE2 upon differentiation and programmed cell death of suspension cultured CD4–CD8– thymocytes. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1994;16:775–786. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kirtikara K, et al. Compensatory prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis in cyclooxygenase 1 or 2 null cells. J Exp Med. 1998;187:517–523. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.4.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Anderson G, Owen J, Moore NC, Jenkinson EJ. Thymic epithelial cells provide unique signals for positive selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes in vitro. J Exp Med. 1994;179:2027–2031. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pénit C, Lucas B, Vasseur F. Cell expansion and growth arrest phase from precursor (CD4-8-) to immature (CD4+8+) thymocytes in normal and genetically modified mice. J Immunol. 1995;154:5103–5113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Falk I, Biro J, Kohler H, Eichmann K. Proliferation kinetics associated with T-cell receptor-beta chain selection of fetal murine thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1996;184:2327–2339. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.6.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Halvorson MJ, Coligan JE. Enhancement of VLA integrin receptor function on thymocytes by cAMP is dependent on the maturation stage of the thymocytes. J Immunol. 1995;155:4567–4574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang T, Sheppard JR, Foker JE. Rise and fall of cyclic AMP is required for onset of lymphocyte A synthesis. Science. 1978;211:155–157. doi: 10.1126/science.208147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Scheuer WV, Hobbs MV, Weigle WO. Interference with tolerance induction in vivo by inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis. Cell Immunol. 1987;104:409–418. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ruiz P, Woodson C, Rey L. Modification of rat skin allograft rejection by inhibition of thromboxane synthesis. Transplantation. 1992;54:385–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Remuzzi G, et al. Thromboxane A2 receptor blocking abrogates donor specific unresponsiveness to renal allografts induced by thymic recognition of major histocompatibility allopeptides. J Exp Med. 1994;180:1967–1972. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]