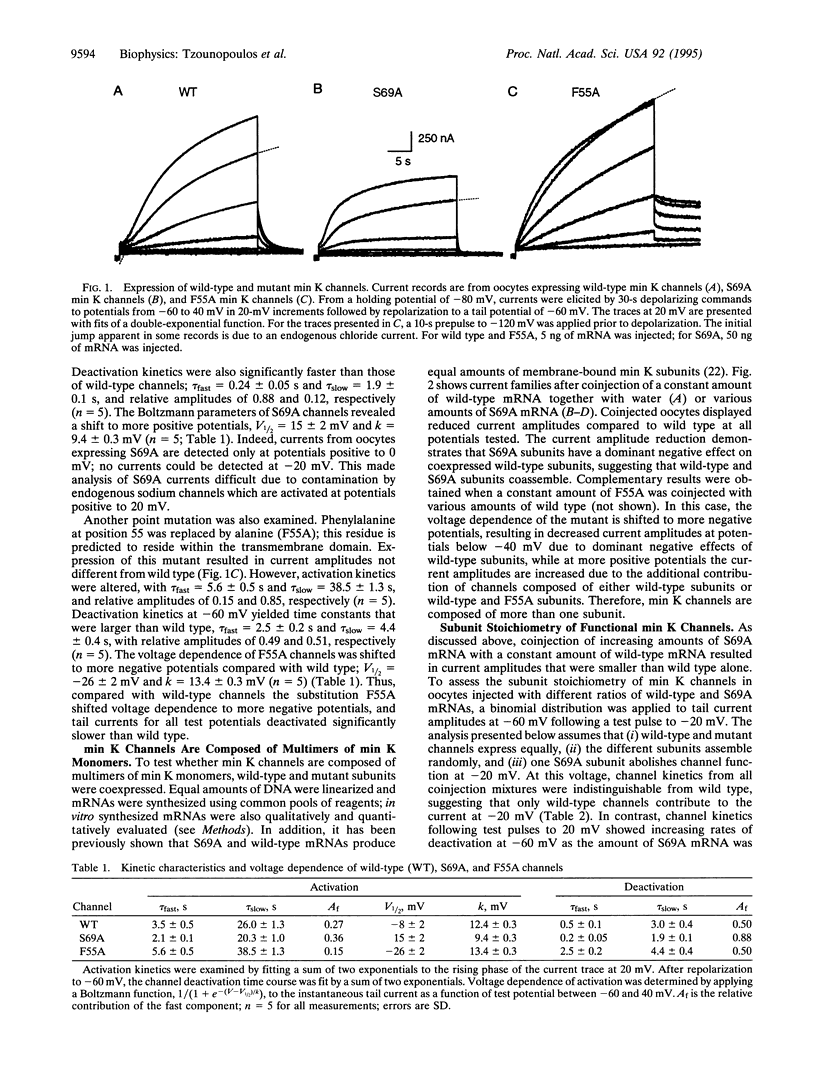
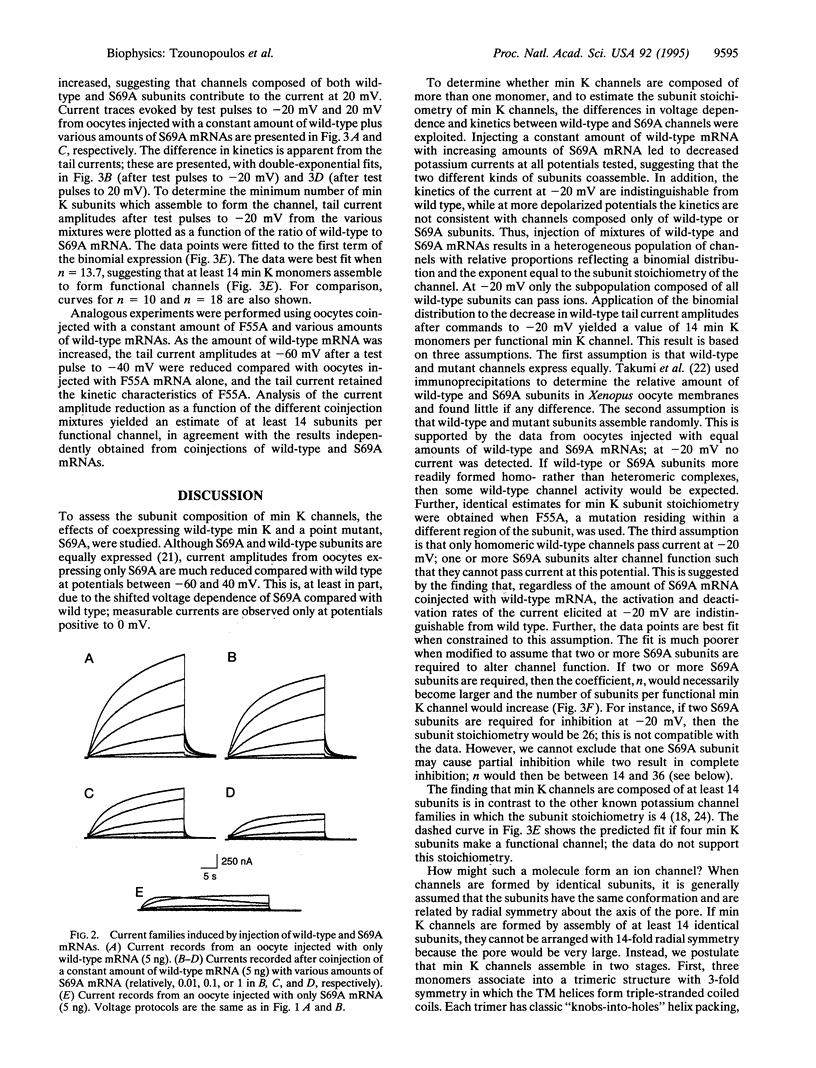
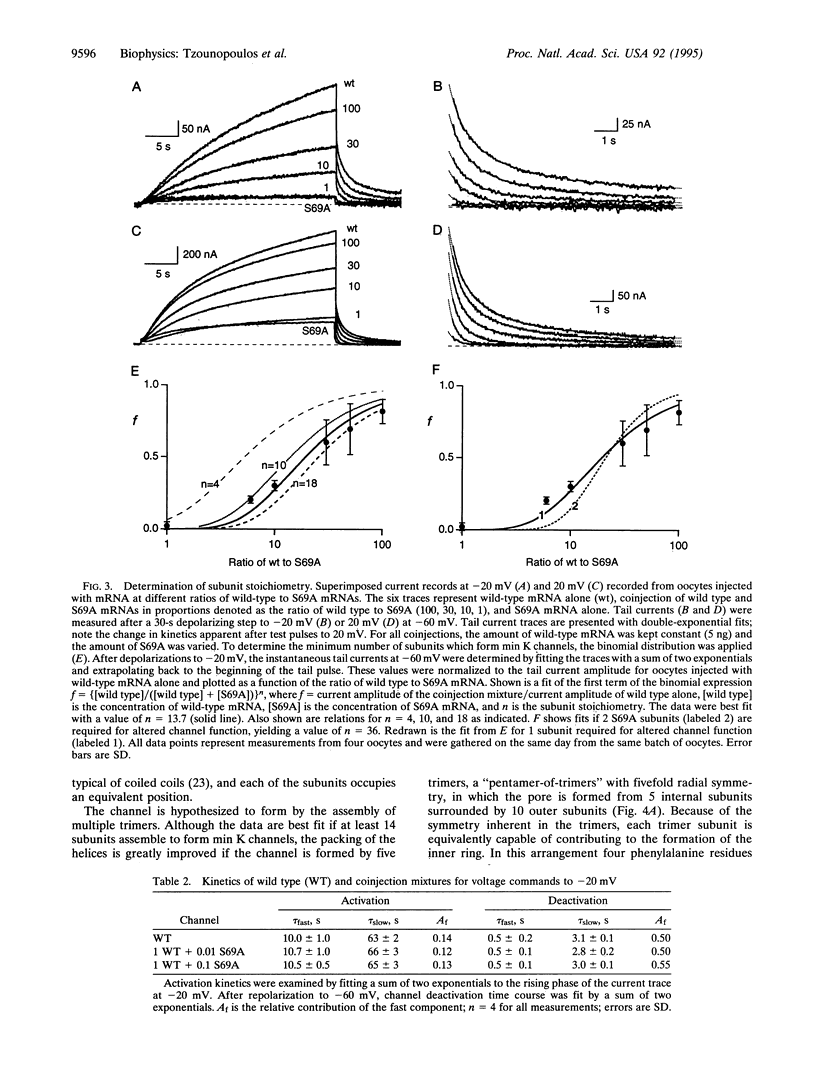
Abstract
Injection of min K mRNA into Xenopus oocytes results in expression of slowly activating voltage-dependent potassium channels, distinct from those induced by expression of other cloned potassium channels. The min K protein also differs in structure, containing only a single predicted transmembrane domain. While it has been demonstrated that all other cloned potassium channels form by association of four independent subunits, the number of min K monomers which constitute a functional channel is unknown. In rat min K, replacement of Ser-69 by Ala (S69A) causes a shift in the current-voltage (I-V) relationship to more depolarized potentials; currents are not observed at potentials negative to 0 mV. To determine the subunit stoichiometry of min K channels, wild-type and S69A subunits were coexpressed. Injections of a constant amount of wild-type mRNA with increasing amounts of S69A mRNA led to potassium currents of decreasing amplitude upon voltage commands to -20 mV. Applying a binomial distribution to the reduction of current amplitudes as a function of the different coinjection mixtures yielded a subunit stoichiometry of at least 14 monomers for each functional min K channel. A model is presented for how min K subunits may form a channel.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Shen K. Z., Kavanaugh M. P., Warren R. A., Wu Y. N., Lagrutta A., Bond C. T., North R. A. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90160-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attali B., Guillemare E., Lesage F., Honoré E., Romey G., Lazdunski M., Barhanin J. The protein IsK is a dual activator of K+ and Cl- channels. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):850–852. doi: 10.1038/365850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond C. T., Pessia M., Xia X. M., Lagrutta A., Kavanaugh M. P., Adelman J. P. Cloning and expression of a family of inward rectifier potassium channels. Receptors Channels. 1994;2(3):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Wei A. G., Baker K., Salkoff L. A family of putative potassium channel genes in Drosophila. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):943–947. doi: 10.1126/science.2493160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., North R. A. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.2539643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Guy H. R. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81809-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Bond C., Glowatzki E., König C., Adelman J. P., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. A structural determinant of differential sensitivity of cloned inward rectifier K+ channels to intracellular spermine. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folander K., Smith J. S., Antanavage J., Bennett C., Stein R. B., Swanson R. Cloning and expression of the delayed-rectifier IsK channel from neonatal rat heart and diethylstilbestrol-primed rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowatzki E., Fakler G., Brändle U., Rexhausen U., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P., Fakler B. Subunit-dependent assembly of inward-rectifier K+ channels. Proc Biol Sci. 1995 Aug 22;261(1361):251–261. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1995.0145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. A., Miller C. Site-specific mutations in a minimal voltage-dependent K+ channel alter ion selectivity and open-channel block. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. W., North R. A. Two types of neurone in the rat ventral tegmental area and their synaptic inputs. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:455–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liman E. R., Tytgat J., Hess P. Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cDNAs. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90239-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R. Determination of the subunit stoichiometry of a voltage-activated potassium channel. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):232–235. doi: 10.1038/350232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., Snay K. J., Trimmer J. S., MacLusky N. J., Naftolin F., Kaczmarek L. K., Boyle M. B. Estrogen induction of a small, putative K+ channel mRNA in rat uterus. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):807–812. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90207-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., Lagrutta A., Davies N. W., Standen N. B., Adelman J. P., North R. A. Tetraethylammonium block of Slowpoke calcium-activated potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes: evidence for tetrameric channel formation. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Mar;426(5):440–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00388308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Tanabe Y., Shigemoto R., Iwai M., Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Immunohistochemical study of a rat membrane protein which induces a selective potassium permeation: its localization in the apical membrane portion of epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jan;113(1):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01869604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T., Moriyoshi K., Aramori I., Ishii T., Oiki S., Okada Y., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Alteration of channel activities and gating by mutations of slow ISK potassium channel. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22192–22198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning of a membrane protein that induces a slow voltage-gated potassium current. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.3194754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker locus of Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):770–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2441471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnum M. D., Busch A. E., Bond C. T., Maylie J., Adelman J. P. The min K channel underlies the cardiac potassium current IKs and mediates species-specific responses to protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11528–11532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]