Abstract
Cystinuria is an autosomal recessive amino-aciduria where three urinary phenotypes have been described (I, II, and III). An amino acid transporter gene, SLC3A1 (formerly rBAT), was found to be responsible for this disorder. To assess whether mutations in SLC3A1 are involved in different cystinuria phenotypes, linkage with this gene and its nearest marker (D2S119) was analyzed in 22 families with type I and/or type III cystinuria. Linkage with heterogeneity was proved (alpha = 0.45; P < 0.008). Type I/I families showed homogeneous linkage to SLC3A1 (Zmax > 3.0 at theta = 0.00; alpha = 1), whereas types I/III and III/III were not linked. Our data suggest that type I cystinuria is due to mutations in the SLC3A1 gene, whereas another locus is responsible for type III. This result establishes genetic heterogeneity for cystinuria, classically considered as a multiallelic monogenic disease.
Full text
PDF
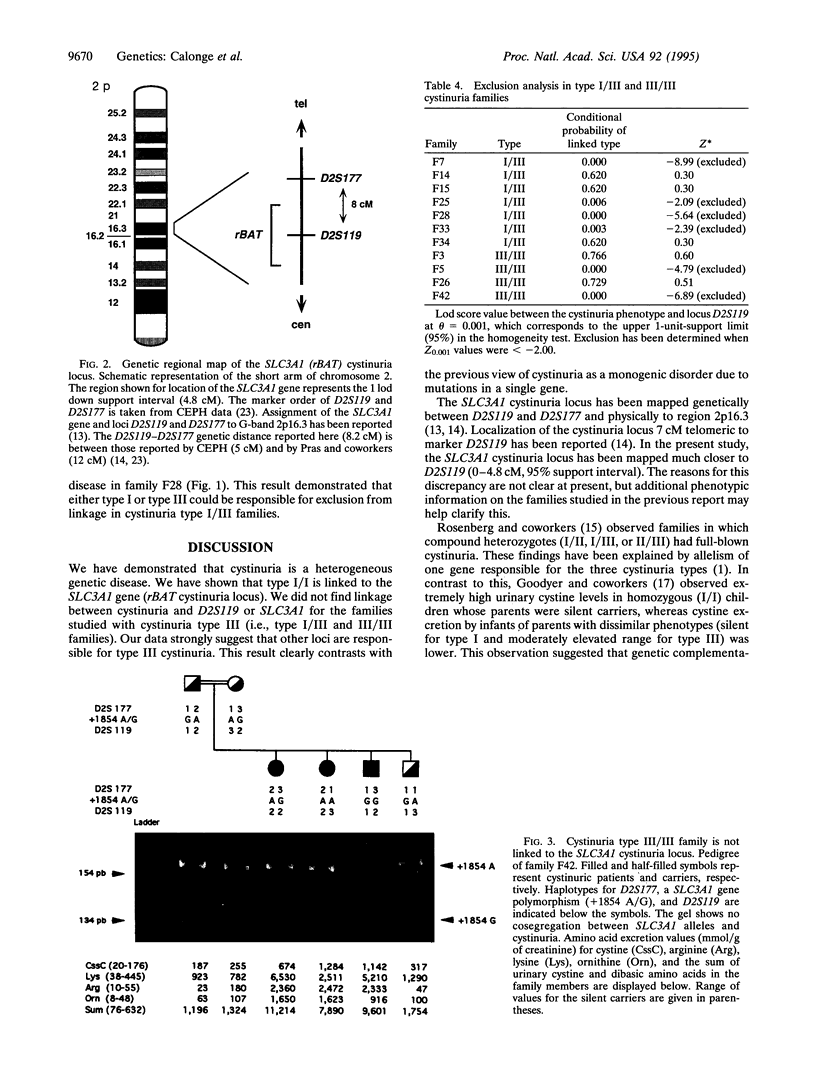

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertran J., Werner A., Chillarón J., Nunes V., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Estivill X., Murer H., Palacín M. Expression cloning of a human renal cDNA that induces high affinity transport of L-cystine shared with dibasic amino acids in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14842–14849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch A. E., Herzer T., Waldegger S., Schmidt F., Palacin M., Biber J., Markovich D., Murer H., Lang F. Opposite directed currents induced by the transport of dibasic and neutral amino acids in Xenopus oocytes expressing the protein rBAT. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25581–25586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calonge M. J., Gasparini P., Chillarón J., Chillón M., Gallucci M., Rousaud F., Zelante L., Testar X., Dallapiccola B., Di Silverio F. Cystinuria caused by mutations in rBAT, a gene involved in the transport of cystine. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):420–425. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calonge M. J., Nadal M., Calvano S., Testar X., Zelante L., Zorzano A., Estivill X., Gasparini P., Palacín M., Nunes V. Assignment of the gene responsible for cystinuria (rBAT) and of markers D2S119 and D2S177 to 2p16 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;95(6):633–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00209478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furriols M., Chillarón J., Mora C., Castelló A., Bertran J., Camps M., Testar X., Vilaró S., Zorzano A., Palacín M. rBAT, related to L-cysteine transport, is localized to the microvilli of proximal straight tubules, and its expression is regulated in kidney by development. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27060–27068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyer P. R., Clow C., Reade T., Girardin C. Prospective analysis and classification of patients with cystinuria identified in a newborn screening program. J Pediatr. 1993 Apr;122(4):568–572. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83537-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. Cystinuria genotypes predicted from excretion patterns. Am J Med Genet. 1978;2(2):175–190. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Wells R. G., Sabbag R. V., Mohandas T. K., Hediger M. A. Cloning and chromosomal localization of a human kidney cDNA involved in cystine, dibasic, and neutral amino acid transport. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):1959–1963. doi: 10.1172/JCI116415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matise T. C., Perlin M., Chakravarti A. Automated construction of genetic linkage maps using an expert system (MultiMap): a human genome linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):384–390. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacín M. A new family of proteins (rBAT and 4F2hc) involved in cationic and zwitterionic amino acid transport: a tale of two proteins in search of a transport function. J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:123–137. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Nirenberg M. J., Chan J., Mosckovitz R., Udenfriend S., Tate S. S. Ultrastructural localization of a neutral and basic amino acid transporter in rat kidney and intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7779–7783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras E., Arber N., Aksentijevich I., Katz G., Schapiro J. M., Prosen L., Gruberg L., Harel D., Liberman U., Weissenbach J. Localization of a gene causing cystinuria to chromosome 2p. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):415–419. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras E., Raben N., Golomb E., Arber N., Aksentijevich I., Schapiro J. M., Harel D., Katz G., Liberman U., Pras M. Mutations in the SLC3A1 transporter gene in cystinuria. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1297–1303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Downing S., Durant J. L., Segal S. Cystinuria: biochemical evidence for three genetically distinct diseases. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):365–371. doi: 10.1172/JCI105351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Durant J. L., Albrecht I. Genetic heterogeneity in cystinuria: evidence for allelism. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1966;79:284–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Durant J. L., Holland J. M. Intestinal absorption and renal extraction of cystine and cysteine in cystinuria. N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 2;273(23):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512022732303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharland M., Jones M., Bain M., Chalmers R., Hammond J., Patton M. A. Balanced translocation (14;20) in a mentally handicapped child with cystinuria. J Med Genet. 1992 Jul;29(7):507–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnell D. C., Cooper J. D. Rapid assay for amino acids in serum or urine by pre-column derivatization and reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):527–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan N., Mosckovitz R., Gerber L. D., Mathew S., Murty V. V., Tate S. S., Udenfriend S. Characterization of the promoter region of the gene for the rat neutral and basic amino acid transporter and chromosomal localization of the human gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7548–7552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]