Abstract
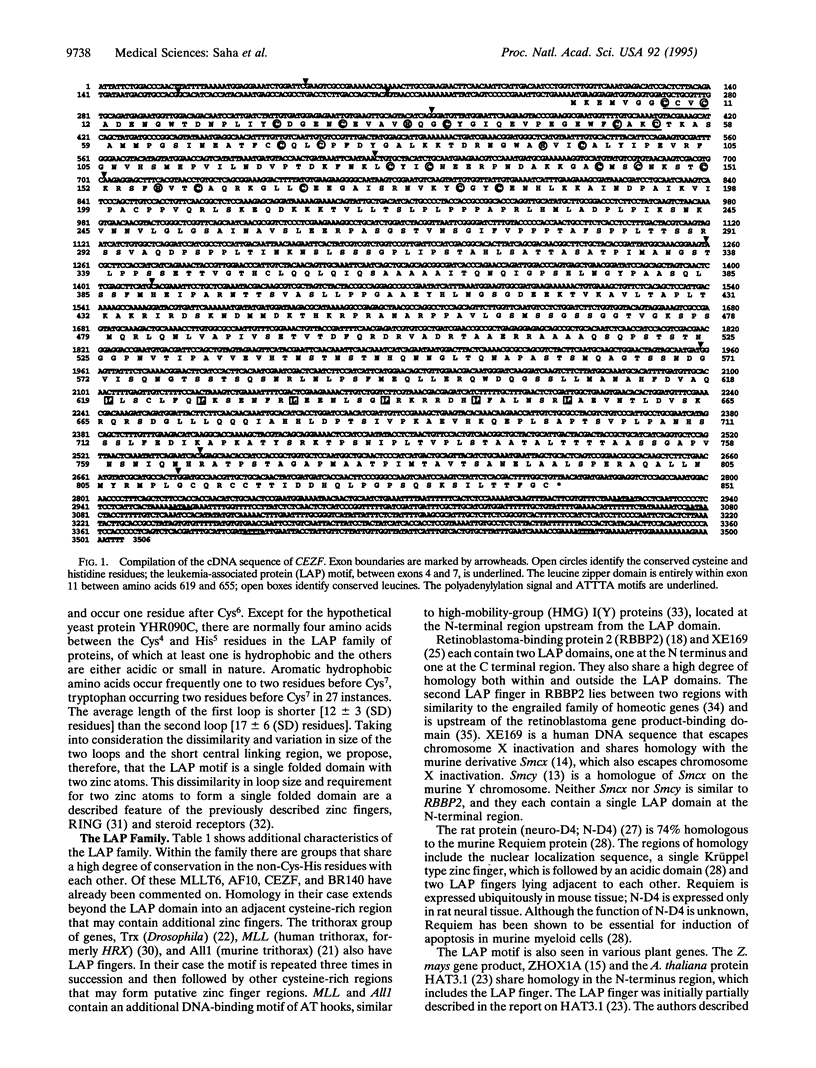
We have identified and further characterized a Caenorhabditis elegans gene, CEZF, that encodes a protein with substantial homology to the zinc finger and leucine zipper motifs of the human gene products AF10, MLLT6, and BR140. The first part of the zinc finger region of CEZF has strong similarity to the corresponding regions of AF10 (66%) and MLLT6 (64%) at the cDNA level. As this region is structurally different from previously described zinc finger motifs, sequence homology searches were done. Twenty-five other proteins with a similar motif were identified. Because the functional domain of this motif is potentially disrupted in leukemia-associated chromosomal translocations, we propose the name of leukemia-associated protein (LAP) finger. On the basis of these comparisons, the LAP domain consensus sequence is Cys1-Xaa1-2-Cys2-Xaa9-21-Cys3-Xaa2-4 -Cys4-Xaa4-5-His5-Xaa2-Cys6-Xaa12-46 - Cys7-Xaa2-Cys8, where subscripted numbers represent the number of amino acid residues. We review the evidence that this motif binds zinc, is the important DNA-binding domain in this group of regulatory proteins, and may be involved in leukemogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasland R., Gibson T. J., Stewart A. F. The PHD finger: implications for chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Feb;20(2):56–59. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88957-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agulnik A. I., Mitchell M. J., Lerner J. L., Woods D. R., Bishop C. E. A mouse Y chromosome gene encoded by a region essential for spermatogenesis and expression of male-specific minor histocompatibility antigens. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):873–878. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agulnik A. I., Mitchell M. J., Mattei M. G., Borsani G., Avner P. A., Lerner J. L., Bishop C. E. A novel X gene with a widely transcribed Y-linked homologue escapes X-inactivation in mouse and human. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jun;3(6):879–884. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.6.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellmann R., Werr W. Zmhox1a, the product of a novel maize homeobox gene, interacts with the Shrunken 26 bp feedback control element. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3367–3374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O. A., Berger R. Molecular basis of 11q23 rearrangements in hematopoietic malignant proliferations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995 Jun;13(2):75–85. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870130202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besansky N. J., Bedell J. A., Mukabayire O. Q: a new retrotransposon from the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol Biol. 1994 Feb;3(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.1994.tb00150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besansky N. J. Evolution of the T1 retroposon family in the Anopheles gambiae complex. Mol Biol Evol. 1990 May;7(3):229–246. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Foroni L., Kaneko Y., Perutz M. F., Rabbitts T. H. The rhombotin family of cysteine-rich LIM-domain oncogenes: distinct members are involved in T-cell translocations to human chromosomes 11p15 and 11p13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4367–4371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman V. L., Ninkina N. N., Bogdanov Y. D., Bortvin A. L., Akopian H. N., Kiselev S. L., Krylova OYu, Anokhin K. V., Georgiev G. P. Differential splicing creates a diversity of transcripts from a neurospecific developmentally regulated gene encoding a protein with new zinc-finger motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5579–5585. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin T., Ayton P., Bernard O. A., Saha V., Della Valle V., Hillion J., Gregorini A., Lillington D., Berger R., Young B. D. A novel class of zinc finger/leucine zipper genes identified from the molecular cloning of the t(10;11) translocation in acute leukemia. Blood. 1995 Mar 15;85(6):1435–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Brand N. J., Chen A., Chen S. J., Tong J. H., Wang Z. Y., Waxman S., Zelent A. Fusion between a novel Krüppel-like zinc finger gene and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha locus due to a variant t(11;17) translocation associated with acute promyelocytic leukaemia. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1161–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Coulson A. F. Significance of protein sequence similarities. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:474–487. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattaey A. R., Helin K., Dembski M. S., Dyson N., Harlow E., Vuocolo G. A., Hanobik M. G., Haskell K. M., Oliff A., Defeo-Jones D. Characterization of the retinoblastoma binding proteins RBP1 and RBP2. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3149–3156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S. The RING finger. A novel protein sequence motif related to the zinc finger. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 11;684:174–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb32280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., Mantel P. L., Rosli R., Crean C. D. Requiem: a novel zinc finger gene essential for apoptosis in myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29515–29519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadereit S., Gewert D. R., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G., Meurs E. F. Molecular cloning of two new interferon-induced, highly related nuclear phosphoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24432–24441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakizuka A., Miller W. H., Jr, Umesono K., Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Murty V. V., Dmitrovsky E., Evans R. M. Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RAR alpha with a novel putative transcription factor, PML. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90112-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfhage U., Trezzini G. F., Meier I., Hahlbrock K., Somssich I. E. Plant homeodomain protein involved in transcriptional regulation of a pathogen defense-related gene. Plant Cell. 1994 May;6(5):695–708. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A consideration of alternative models for the initiation of translation in eukaryotes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(4-5):385–402. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonie A., D'Andrea R., Paro R., Saint R. Molecular characterisation of the Polycomblike gene of Drosophila melanogaster, a trans-acting negative regulator of homeotic gene expression. Development. 1994 Sep;120(9):2629–2636. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.9.2629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovering R., Hanson I. M., Borden K. L., Martin S., O'Reilly N. J., Evan G. I., Rahman D., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J., Freemont P. S. Identification and preliminary characterization of a protein motif related to the zinc finger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Q., Alder H., Nelson K. K., Chatterjee D., Gu Y., Nakamura T., Canaani E., Croce C. M., Siracusa L. D., Buchberg A. M. Analysis of the murine All-1 gene reveals conserved domains with human ALL-1 and identifies a motif shared with DNA methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6350–6354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazo A. M., Huang D. H., Mozer B. A., Dawid I. B. The trithorax gene, a trans-acting regulator of the bithorax complex in Drosophila, encodes a protein with zinc-binding domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad R., Leshkowitz D., Gu Y., Alder H., Nakamura T., Saito H., Huebner K., Berger R., Croce C. M., Canaani E. Leucine-zipper dimerization motif encoded by the AF17 gene fused to ALL-1 (MLL) in acute leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8107–8111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Langan T. A., Nissen M. S. Phosphorylation of the DNA-binding domain of nonhistone high-mobility group I protein by cdc2 kinase: reduction of binding affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1671–1675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Beckmann H., Cashmore A. R. HAT3.1, a novel Arabidopsis homeodomain protein containing a conserved cysteine-rich region. Plant J. 1993 Jul;4(1):137–150. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04010137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R. Octamania: the POU factors in murine development. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90422-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedkov Y., Tillib S., Mizrokhi L., Mazo A. The bithorax complex is regulated by trithorax earlier during Drosophila embryogenesis than is the Antennapedia complex, correlating with a bithorax-like expression pattern of distinct early trithorax transcripts. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):1907–1917. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.1907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg M. J. PROMOT: a FORTRAN program to scan protein sequences against a library of known motifs. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Apr;7(2):257–260. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. A., Wang B., Argraves W. S., Giancotti F. G., Schranck D. P., Ruoslahti E. BR140, a novel zinc-finger protein with homology to the TAF250 subunit of TFIID. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 15;198(3):1143–1152. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida H., Kawano S., Sato N., Kuroiwa T. Isolation and characterization of novel genes which are expressed during the very early stage of zygote formation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1993 Oct;24(4):296–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00336779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winicov I. cDNA encoding putative zinc finger motifs from salt-tolerant alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cells. Plant Physiol. 1993 Jun;102(2):681–682. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.2.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Ellison J., Salido E., Yen P., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. Isolation and characterization of XE169, a novel human gene that escapes X-inactivation. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):153–160. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



