Abstract
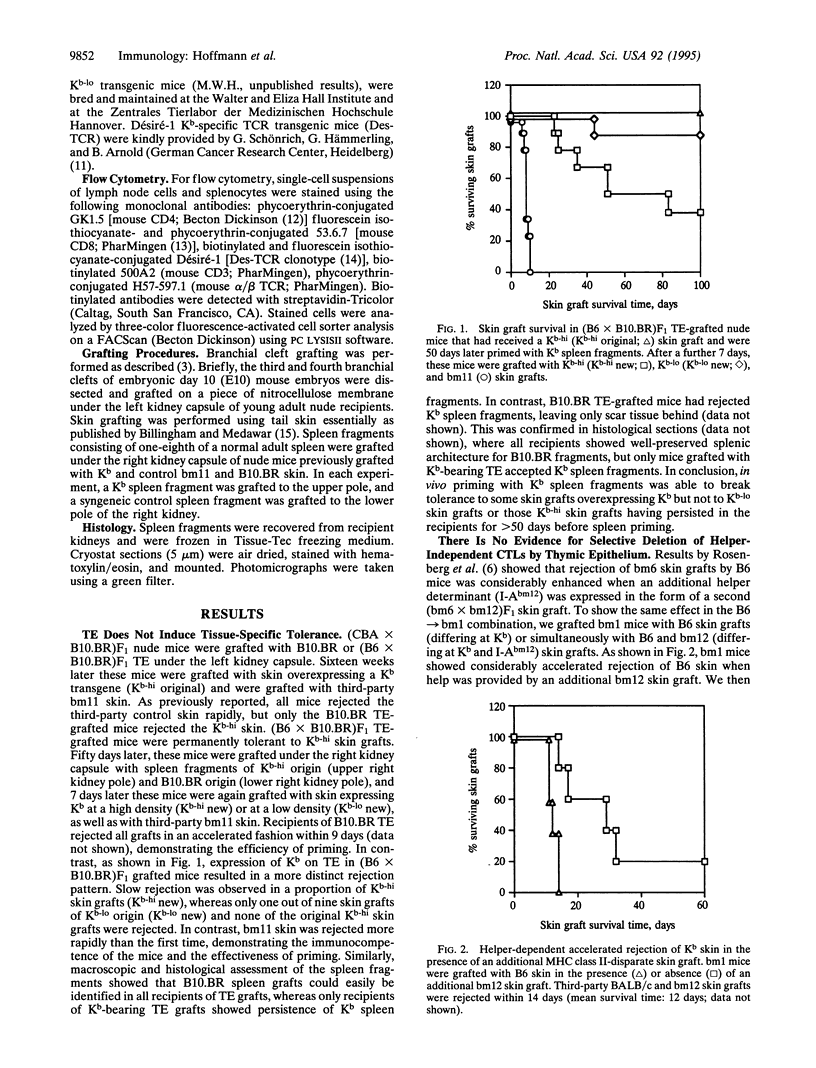
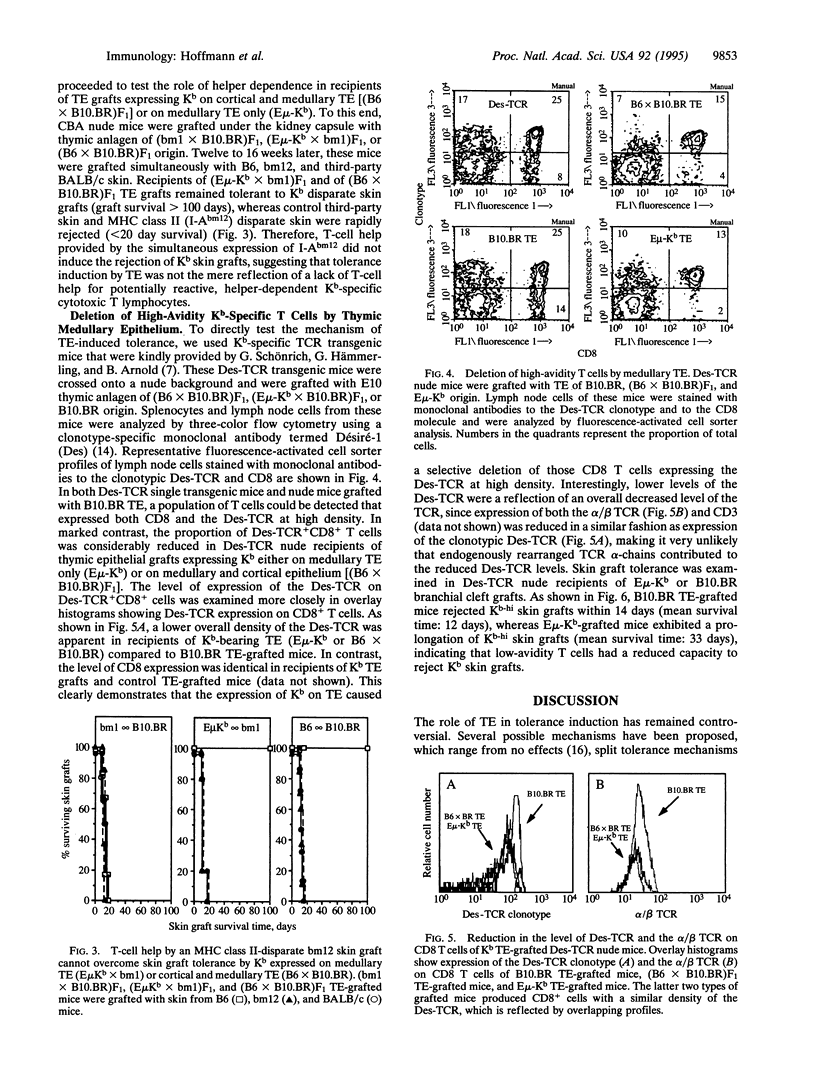
Tolerance induction by thymic epithelium induces a state of so-called "split tolerance," characterized in vivo by tolerance and in vitro by reactivity to a given thymically expressed antigen. Using a model major histocompatibility complex class I antigen, H-2Kb (Kb), three mechanisms of thymic epithelium-induced tolerance were tested: induction of tolerance of tissue-specific antigens exclusively, selective inactivation of T helper cell-independent cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and deletion of high-avidity T cells. To this end, thymic anlagen from Kb-transgenic embryonic day 10 mouse embryos, taken before colonization by cells of hemopoietic origin, were grafted to nude mice. Tolerance by thymic epithelium was not tissue-specific, since Kb-bearing skin and spleen grafts were maintained indefinitely. Only strong priming in vivo could partially overcome the tolerant state and induce rejection of some skin grafts overexpressing transgenic Kb. Furthermore, the hypothesis that thymic epithelium selectively inactivates those T cells that reject skin grafts in a T helper-independent fashion could not be supported. Thus, when T-cell help was provided by a second skin graft bearing an additional major histocompatibility complex class II disparity, tolerance to the Kb skin graft was not broken. Finally, direct evidence could be obtained for the avidity model of thymic epithelium-induced negative selection, using Kb-specific T-cell receptor (TCR) transgenic mice. Thymic epithelium-grafted TCR transgenic mice showed a selective deletion of those CD8+ T cells with the highest density of the clonotypic TCR. These cells presumably represent the T cells with the highest avidity for Kb. We conclude that split tolerance induced by thymic epithelium was mediated by the deletion of those CD8+ T lymphocytes that have the highest avidity for antigen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J., Müllbacher A., Cox K., Morahan G., Boyd R., Scollay R., Blanden R. V., Miller J. F. Selection of the T-cell repertoire in transgenic mice expressing a transplantation antigen in distinct thymus subsets. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Sep 22;241(1302):170–178. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonomo A., Matzinger P. Thymus epithelium induces tissue-specific tolerance. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1153–1164. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley G., Benson M. T., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Factors affecting the acceptance of deoxyguanosine-treated thymus allografts. Transplantation. 1988 Jan;45(1):202–205. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198801000-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkly L. C., Degermann S., Longley J., Hagman J., Brinster R. L., Lo D., Flavell R. A. Clonal deletion of V beta 5+ T cells by transgenic I-E restricted to thymic medullary epithelium. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):3954–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degermann S., Surh C. D., Glimcher L. H., Sprent J., Lo D. B7 expression on thymic medullary epithelium correlates with epithelium-mediated deletion of V beta 5+ thymocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3254–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Quan Z. S., Wall K. A., Pierres A., Quintáns J., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Fitch F. W. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2445–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao E. K., Lo D., Sprent J. Strong T cell tolerance in parent----F1 bone marrow chimeras prepared with supralethal irradiation. Evidence for clonal deletion and anergy. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1101–1121. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Pyke K. W., Nossal G. J. Functional clonal deletion of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte precursors in chimeric thymus produced in vitro from embryonic Anlagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. R., Allison J., Hoffmann M. W., Schönrich G., Hämmerling G., Arnold B., Miller J. F. Autoimmune diabetes as a consequence of locally produced interleukin-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):547–549. doi: 10.1038/359547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. R., Kjer-Nielsen L., Hoffmann M. W. Avidity for antigen can influence the helper dependence of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):5993–6001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. W., Allison J., Miller J. F. Tolerance induction by thymic medullary epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2526–2530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua C., Boyer C., Buferne M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Monoclonal antibodies against an H-2Kb-specific cytotoxic T cell clone detect several clone-specific molecules. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):1937–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson E. J., Anderson G., Owen J. J. Studies on T cell maturation on defined thymic stromal cell populations in vitro. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):845–853. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Sprent J. Tolerance of CD8+ T cells developing in parent-->F1 chimeras prepared with supralethal irradiation: step-wise induction of tolerance in the intrathymic and extrathymic environments. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):367–378. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell F., Lantz T., Fowlkes B. J. A nondeletional mechanism of thymic self tolerance. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1038–1041. doi: 10.1126/science.2511629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. S., Mizuochi T., Singer A. Evidence for involvement of dual-function T cells in rejection of MHC class I disparate skin grafts. Assessment of MHC class I alloantigens as in vivo helper determinants. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):33–45. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaün J., Bandeira A., Khazaal I., Burlen-Defranoux O., Thomas-Vaslin V., Coltey M., Le Douarin N. M., Coutinho A. Transplantation tolerance is unrelated to superantigen-dependent deletion and anergy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10420–10424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaün J., Bandeira A., Khazaal I., Calman F., Coltey M., Coutinho A., Le Douarin N. M. Thymic epithelium tolerizes for histocompatibility antigens. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1471–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönrich G., Kalinke U., Momburg F., Malissen M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Malissen B., Hämmerling G. J., Arnold B. Down-regulation of T cell receptors on self-reactive T cells as a novel mechanism for extrathymic tolerance induction. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90163-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönrich G., Momburg F., Hämmerling G. J., Arnold B. Anergy induced by thymic medullary epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1687–1691. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser D. E., Pircher H., Ohashi P. S., Kyburz D., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Clonal deletion induced by either radioresistant thymic host cells or lymphohemopoietic donor cells at different stages of class I-restricted T cell ontogeny. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1277–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Lo D., Gao E. K., Ron Y. T cell selection in the thymus. Immunol Rev. 1988 Jan;101:173–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Boehmer H., Schubiger K. Thymocytes appear to ignore class I major histocompatibility complex antigens expressed on thymus epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Nov;14(11):1048–1052. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



