Abstract
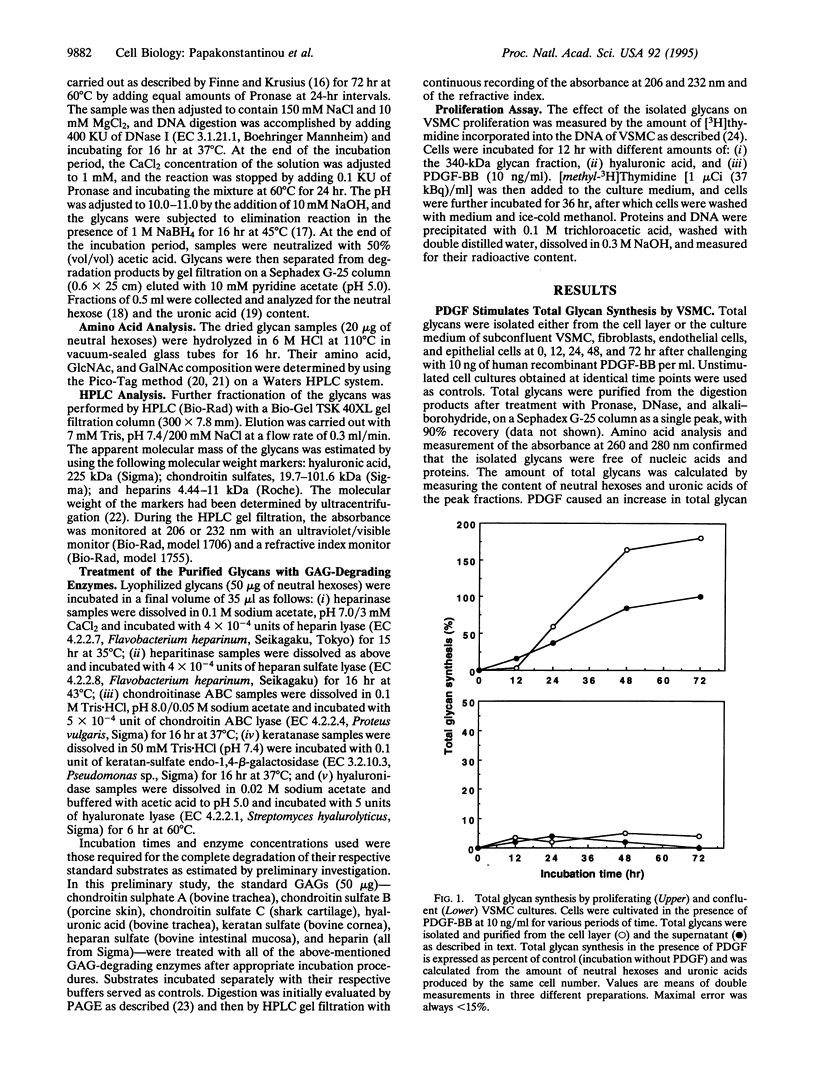
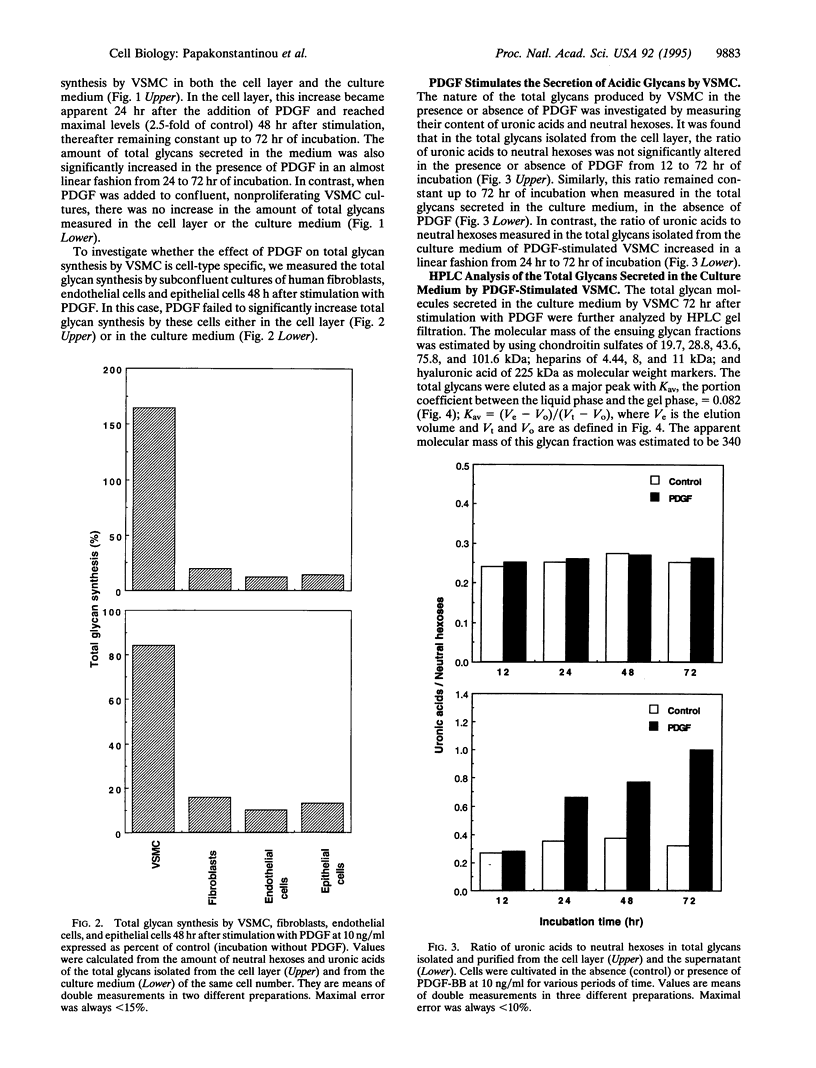
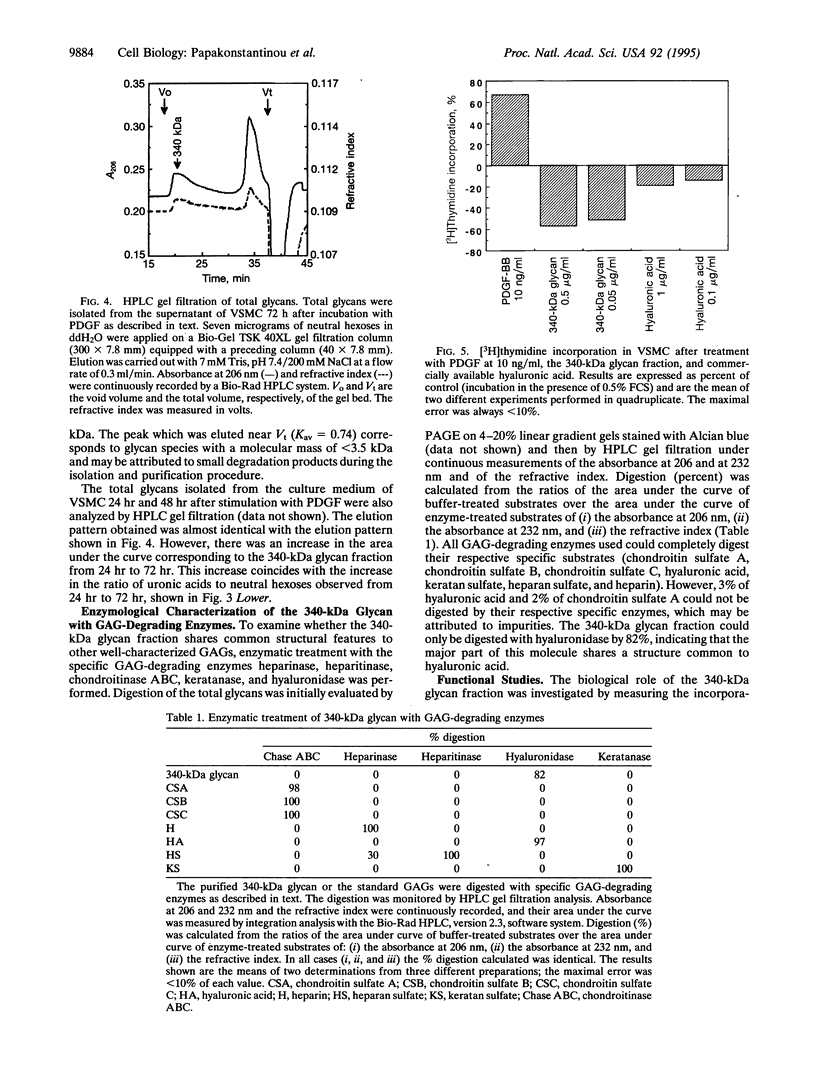
Total glycans from the cell layer and the culture medium of human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) that had been cultivated in the presence of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) were isolated and purified by gel filtration after Pronase and DNase digestion and alkaliborohydride treatment. Measurements of the content of neutral hexoses and uronic acids revealed that PDGF stimulates total glycan synthesis by proliferating VSMC in a linear fashion from 24 h to 72 h of incubation. In contrast, total glycan synthesis by human fibroblasts, epithelial cells, or endothelial cells was not affected by PDGF, indicating cell-type specificity. Chemical, biochemical, and enzymological characterization of the total glycans synthesized by VSMC showed that PDGF stimulates the secretion of a 340-kDa glycan molecule in a time-dependent manner from 24 h to 72 h. This molecule is highly acidic, shares a common structure with hyaluronic acid, and exhibits a potent antiproliferative activity on VSMC. These results suggest that VSMC in response to PDGF are capable of controlling their own growth and migration by the synthesis of a specific form of hyaluronic acid with antiproliferative potency, which may be involved in the regulation of the local inflammatory responses associated with atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caniggia I., Post M. Differential effect of platelet-derived growth factor on glycosaminoglycan synthesis by fetal rat lung cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):L495–L500. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.4.L495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Addonizio M. L., Rosenberg R., Karnovsky M. J. Cultured endothelial cells produce a heparinlike inhibitor of smooth muscle cell growth. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):372–379. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Favreau L. V., Karnovsky M. J., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by endothelial cell-derived heparin. Possible role of a platelet endoglycosidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11256–11260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Karnowsky M. J. Suppression by heparin of smooth muscle cell proliferation in injured arteries. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):625–626. doi: 10.1038/265625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalferes E. R., Jr, Radhakrishnamurthy B., Ruiz H. A., Berenson G. S. Composition of proteoglycans from human atherosclerotic lesions. Exp Mol Pathol. 1987 Dec;47(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(87)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fager G., Camejo G., Bondjers G. Heparin-like glycosaminoglycans influence growth and phenotype of human arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. I. Evidence for reversible binding and inactivation of the platelet-derived growth factor by heparin. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1992 Mar;28A(3 Pt 1):168–175. doi: 10.1007/BF02631087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Krusius T. Preparation and fractionation of glycopeptides. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:269–277. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritze L. M., Reilly C. F., Rosenberg R. D. An antiproliferative heparan sulfate species produced by postconfluent smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1041–1049. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Chang T., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor is a chemoattractant for vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Nov;113(2):261–266. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3669–3672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. E., Forstrom J. W., Kelly J. D., Seifert R. A., Smith R. A., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two classes of PDGF receptor recognize different isoforms of PDGF. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1529–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.2836952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papakonstantinou E., Karakiulakis G., Aletras A. J., Misevic G. N. A novel class of adhesion acidic glycans in sea urchin embryos. Isolation, characterization and immunological studies during early embryonal development. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Sep 15;224(3):1067–1077. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.01067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papakonstantinou E., Misevic G. N. Isolation and characterization of a new class of acidic glycans implicated in sea urchin embryonal cell adhesion. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Oct;53(2):98–113. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. F., Vande Berg J., Rudolph R., Tarpley J., Mustoe T. A. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB and transforming growth factor beta 1 selectively modulate glycosaminoglycans, collagen, and myofibroblasts in excisional wounds. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):629–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. George Lyman Duff Memorial Lecture. Atherosclerosis: a problem of the biology of arterial wall cells and their interactions with blood components. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):293–311. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.5.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Masuda J., Raines E. W., Gown A. M., Katsuda S., Sasahara M., Malden L. T., Masuko H., Sato H. Localization of PDGF-B protein in macrophages in all phases of atherogenesis. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1009–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2343305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Emmons L. R., Perruchoud A., Block L. H. Expressions of the low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes are stimulated by recombinant platelet-derived growth factor isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1888–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Solèr M., Hornung M., Emmons L. R., Stulz P., Perruchoud A. P. Cell cultures from cryopreserved human lung tissue. Tissue Cell. 1992;24(4):455–459. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(92)90061-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin K., Tingström A., Hansson G. K., Larsson E., Rönnstrand L., Klareskog L., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H., Fellström B., Terracio L. Induction of B-type receptors for platelet-derived growth factor in vascular inflammation: possible implications for development of vascular proliferative lesions. Lancet. 1988 Jun 18;1(8599):1353–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtschabel D. O., Freudenstein G. Verminderte Stimulierbarkeit der Hyaluronsäuresynthese durch PDGF, IGF-I oder Serum in der Alterungsphase von Hautfibroblasten in vitro. Z Gerontol. 1994 May-Jun;27(3):177–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Fredman P. A procedure for the quantitative isolation of brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 18;617(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziesche R., Roth M., Papakonstantinou E., Nauck M., Hörl W. H., Kashgarian M., Block L. H. A granulocyte inhibitory protein overexpressed in chronic renal disease regulates expression of interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):301–305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



