Abstract
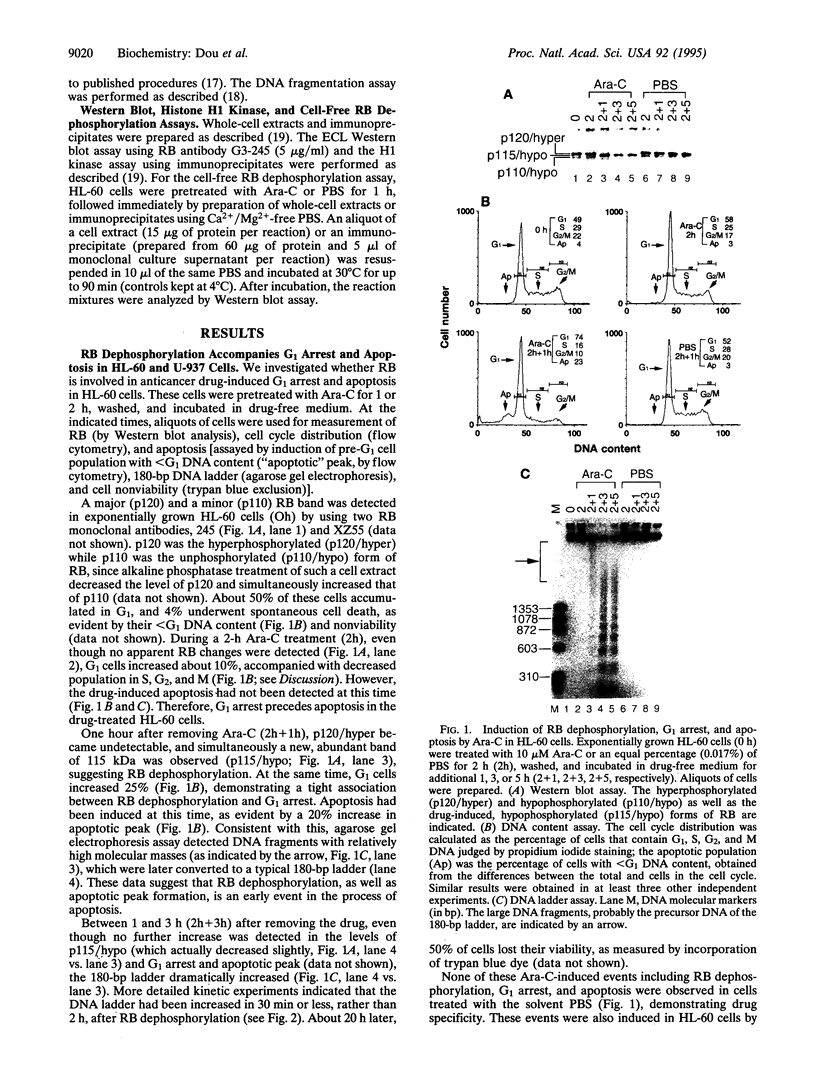
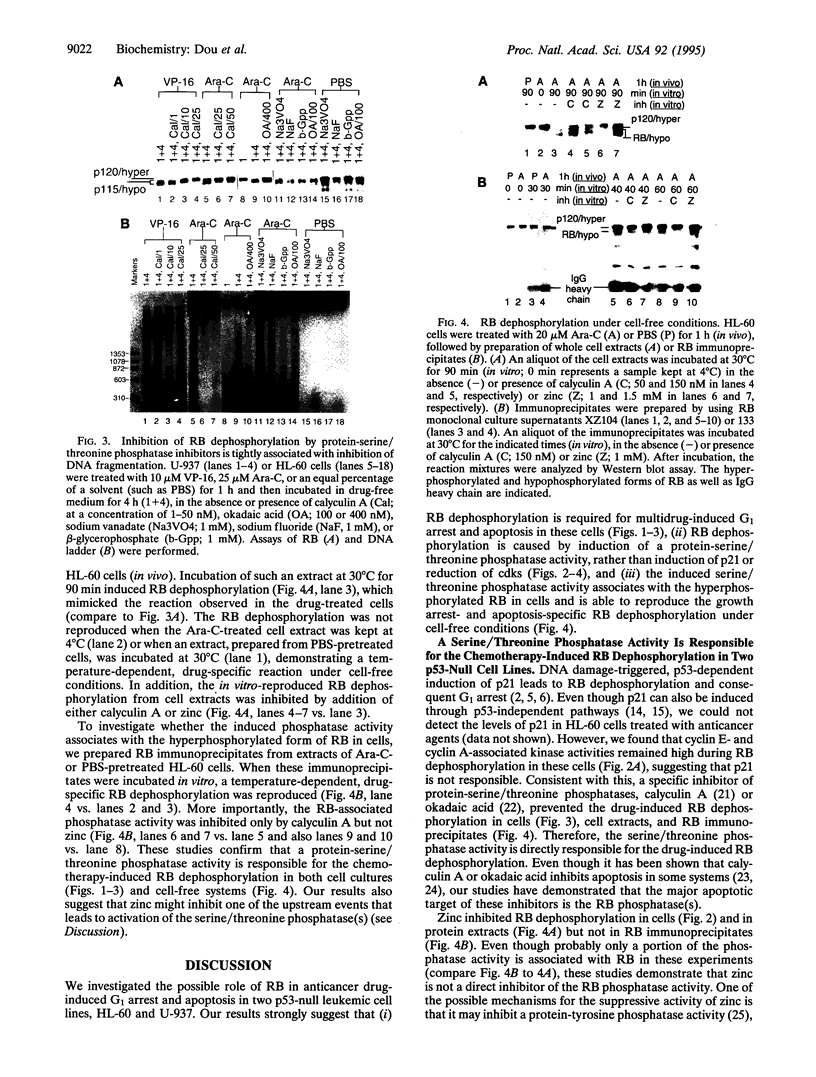
DNA-damaging agents induce accumulation of the tumor suppressor and G1 checkpoint protein p53, leading cells to either growth arrest in G1 or apoptosis (programmed cell death). The p53-dependent G1 arrest involves induction of p21 (also called WAF1/CIP1/SDI1), which prevents cyclin kinase-mediated phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein (RB). Recent studies suggest a p53-independent G1 checkpoint as well; however, little is known about its molecular mechanisms. We report that induction of a protein-serine/threonine phosphatase activity by DNA damage signals is at least one of the mechanisms responsible for p53-independent, RB-mediated G1 arrest and consequent apoptosis. When two p53-null human leukemic cell lines (HL-60 and U-937) were treated with a variety of anticancer agents, RB became hypophosphorylated, accompanied with G1 arrest. This was followed immediately (in less than 30 min) by apoptosis, as determined by the accumulation of pre-G1 apoptotic cells and the internucleosomal fragmentation of DNA. Addition of calyculin A or okadaic acid (specific serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitors) or zinc chloride (apoptosis inhibitor) prevented the G1 arrest- and apoptosis-specific RB dephosphorylation. The levels of cyclin E- and cyclin A-associated kinase activities remained high during RB dephosphorylation, supporting the involvement of a chemotherapy-induced serine/threonine phosphatase(s) rather than p21. Furthermore, the induced phosphatase activity coimmunoprecipitated with the hyperphosphorylated RB and was active in a cell-free system that reproduced the growth arrest- and apoptosis-specific RB dephosphorylation, which was inhibitable by calyculin A but not zinc. We propose that the RB phosphatase(s) might be one of the p53-independent G1 checkpoint regulators.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. S., Thorburn A. M., Shenolikar S., Mumby M. C., Feramisco J. R. Regulation of cell cycle progression and nuclear affinity of the retinoblastoma protein by protein phosphatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danova M., Giordano M., Mazzini G., Riccardi A. Expression of p53 protein during the cell cycle measured by flow cytometry in human leukemia. Leuk Res. 1990;14(5):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers G. W., Foster S. A., Halbert C. L., Galloway D. A. Growth arrest by induction of p53 in DNA damaged keratinocytes is bypassed by human papillomavirus 16 E7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Levin A. H., Zhao S., Pardee A. B. Cyclin E and cyclin A as candidates for the restriction point protein. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1493–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S., Jarvis W. D., Swerdlow P. S., Turner A. J., Traylor R. S., Wallace H. J., Lin P. S., Pettit G. R., Gewirtz D. A. Potentiation of the activity of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine by the protein kinase C activator bryostatin 1 in HL-60 cells: association with enhanced fragmentation of mature DNA. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6270–6278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Kastan M. B. Cell cycle control and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1821–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.7997877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B., Liebermann D. A. Molecular controls of apoptosis: differentiation/growth arrest primary response genes, proto-oncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes as positive & negative modulators. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):1807–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes K. A., Ransom N., Papermaster D. S., Lasudry J. G., Albert D. M., Windle J. J. Apoptosis or retinoblastoma: alternative fates of photoreceptors expressing the HPV-16 E7 gene in the presence or absence of p53. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1300–1310. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Bautista C., Edwards G. M., Defeo-Jones D., Jones R. E., Harlow E. Antibodies specific for the human retinoblastoma protein identify a family of related polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5792–5799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik Y. A., Cole S., Cooke C. A., Nelson W. G., Earnshaw W. C. Nuclear events of apoptosis in vitro in cell-free mitotic extracts: a model system for analysis of the active phase of apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):7–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Christakos S., Small M. B. Apoptosis and signal transduction: clues to a molecular mechanism. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):286–291. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90118-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Glendening C. L., Livingston D. M., DeCarprio J. A. Specific enzymatic dephosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):367–372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenbesser S. D., Williams B. O., Jacks T., DePinho R. A. p53-dependent apoptosis produced by Rb-deficiency in the developing mouse lens. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):72–74. doi: 10.1038/371072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti I., Migliorati G., Pagliacci M. C., Grignani F., Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jun 3;139(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohoka Y., Nakai Y., Mukai M., Iwata M. Okadaic acid inhibits glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in T cell hybridomas at its late stage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):916–921. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. S., Li X. S., Chen J. C., Shao Z. M., Ordonez J. V., Fontana J. A. Mechanisms of regulation of WAF1/Cip1 gene expression in human breast carcinoma: role of p53-dependent and independent signal transduction pathways. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3407–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slebos R. J., Lee M. H., Plunkett B. S., Kessis T. D., Williams B. O., Jacks T., Hedrick L., Kastan M. B., Cho K. R. p53-dependent G1 arrest involves pRB-related proteins and is disrupted by the human papillomavirus 16 E7 oncoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Q., Lavin M. F. Calyculin A, a potent inhibitor of phosphatases-1 and -2A, prevents apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jan 15;190(1):47–55. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. A., Hoffman B., Iro A., Guillouf C., Liebermann D. A., el-Houseini M. E. Induction of p21 (WAF-1/CIP1) during differentiation. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3389–3396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Jacks T., Cory S. DNA damage can induce apoptosis in proliferating lymphoid cells via p53-independent mechanisms inhibitable by Bcl-2. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Furuya-Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Yasumoto S., Kato Y., Fusetani N., Sugimura T. Calyculin A, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases, a potent tumor promoter on CD-1 mouse skin. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3521–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Purification and assay of CD45: an integral membrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:442–451. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







