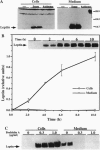
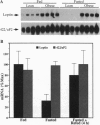
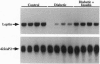
Abstract
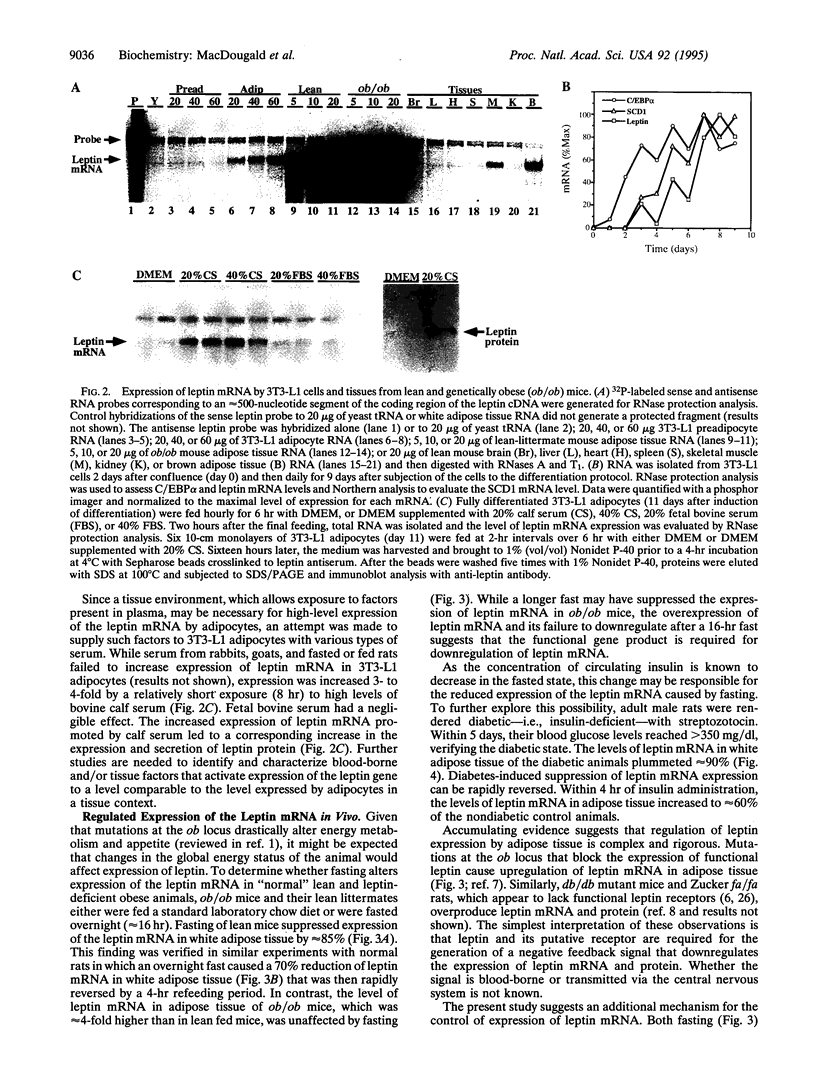
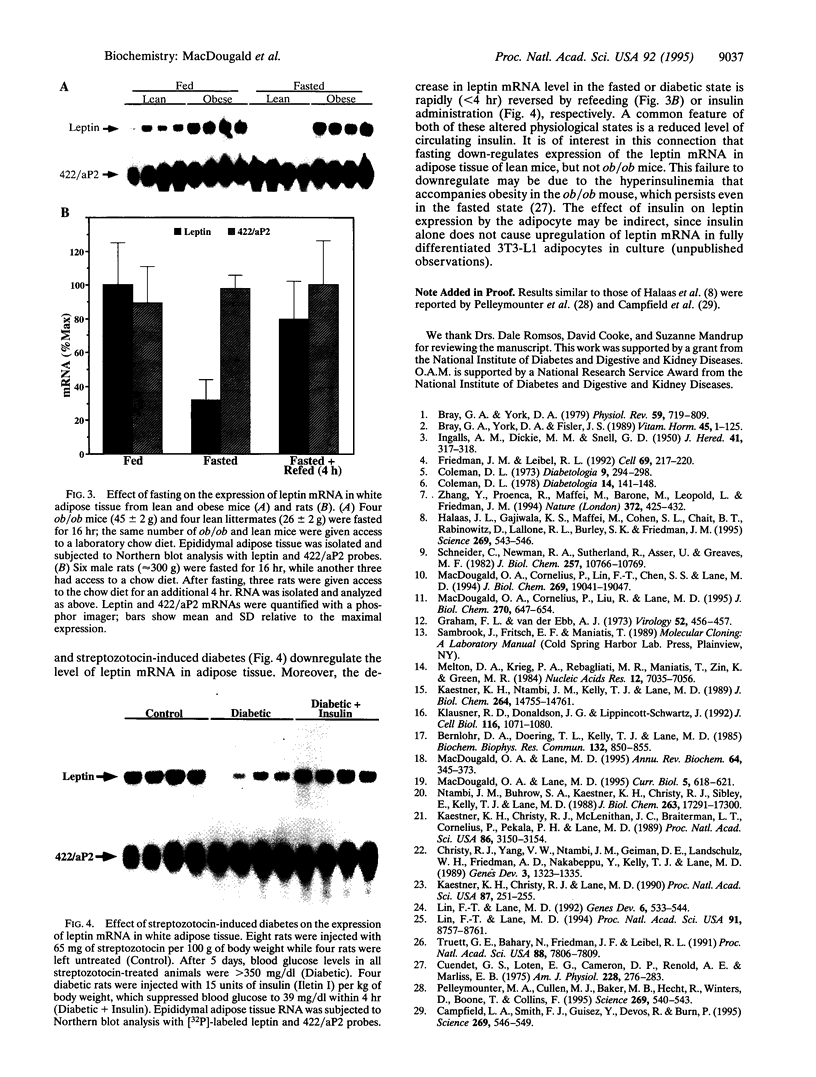
A mutation within the obese gene was recently identified as the genetic basis for obesity in the ob/ob mouse. The obese gene product, leptin, is a 16-kDa protein expressed predominantly in adipose tissue. Consistent with leptin's postulated role as an extracellular signaling protein, human embryonic kidney 293 cells transfected with the obese gene secreted leptin with minimal intracellular accumulation. Upon differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes into adipocytes, the leptin mRNA was expressed concomitant with mRNAs encoding adipocyte marker proteins. A factor(s) present in calf serum markedly activated expression of leptin by fully differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. A 16-hr fast decreased (by approximately 85%) the leptin mRNA level of adipose tissue of lean (ob/+ or +/+) mice but had no effect on the approximately 4-fold higher level in obese (ob/ob) littermates. Since the mutation at the ob locus fails to produce the functional protein, yet its cognate mRNA is overproduced, it appears that leptin is necessary for its own downregulation. Leptin mRNA was also suppressed in adipose tissue of rats during a 16-hr fast and was rapidly induced during a 4-hr refeeding period. Insulin deficiency provoked by streptozotocin also markedly down-regulated leptin mRNA and this suppression was rapidly reversed by insulin. These results suggest that insulin may regulate the expression of leptin.
Full text
PDF
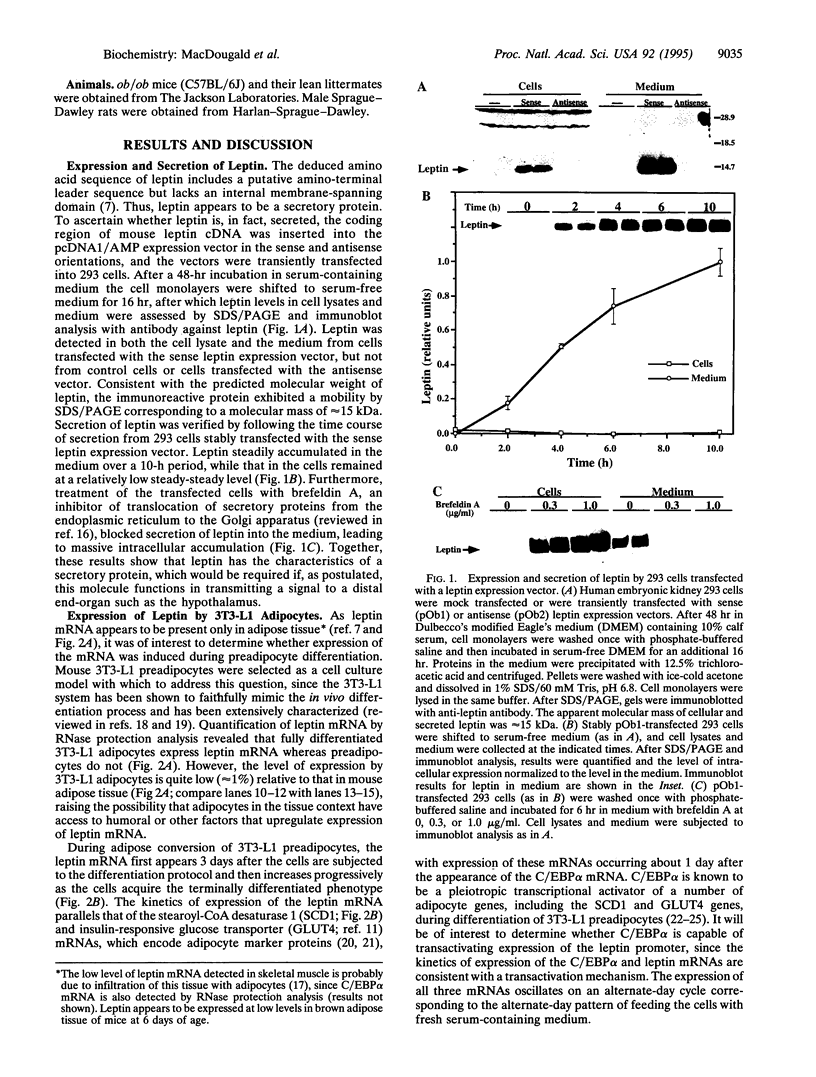
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernlohr D. A., Doering T. L., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lane M. D. Tissue specific expression of p422 protein, a putative lipid carrier, in mouse adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):850–855. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., York D. A., Fisler J. S. Experimental obesity: a homeostatic failure due to defective nutrient stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Vitam Horm. 1989;45:1–125. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., York D. A. Hypothalamic and genetic obesity in experimental animals: an autonomic and endocrine hypothesis. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):719–809. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campfield L. A., Smith F. J., Guisez Y., Devos R., Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.7624778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Effects of parabiosis of obese with diabetes and normal mice. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01221857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuendet G. S., Loten E. G., Cameron D. P., Renold A. E., Marliss E. B. Hormone-substrate responses to total fasting in lean and obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jan;228(1):276–283. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.1.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Leibel R. L. Tackling a weighty problem. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaas J. L., Gajiwala K. S., Maffei M., Cohen S. L., Chait B. T., Rabinowitz D., Lallone R. L., Burley S. K., Friedman J. M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.7624777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGALLS A. M., DICKIE M. M., SNELL G. D. Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered. 1950 Dec;41(12):317–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Lane M. D. Mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter gene: characterization of the gene and trans-activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., McLenithan J. C., Braiterman L. T., Cornelius P., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D. Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Ntambi J. M., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. A second differentially expressed gene encoding stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14755–14761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., Lane M. D. Antisense CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein RNA suppresses coordinate gene expression and triglyceride accumulation during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):533–544. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha is sufficient to initiate the 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8757–8761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Cornelius P., Lin F. T., Chen S. S., Lane M. D. Glucocorticoids reciprocally regulate expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha and delta genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and white adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19041–19047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Cornelius P., Liu R., Lane M. D. Insulin regulates transcription of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) alpha, beta, and delta genes in fully-differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):647–654. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Adipocyte differentiation. When precursors are also regulators. Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):618–621. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Transcriptional regulation of gene expression during adipocyte differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:345–373. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ntambi J. M., Buhrow S. A., Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Sibley E., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Characterization of a differentially expressed gene encoding stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17291–17300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleymounter M. A., Cullen M. J., Baker M. B., Hecht R., Winters D., Boone T., Collins F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):540–543. doi: 10.1126/science.7624776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett G. E., Bahary N., Friedman J. M., Leibel R. L. Rat obesity gene fatty (fa) maps to chromosome 5: evidence for homology with the mouse gene diabetes (db). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7806–7809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J. M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):425–432. doi: 10.1038/372425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]