Abstract
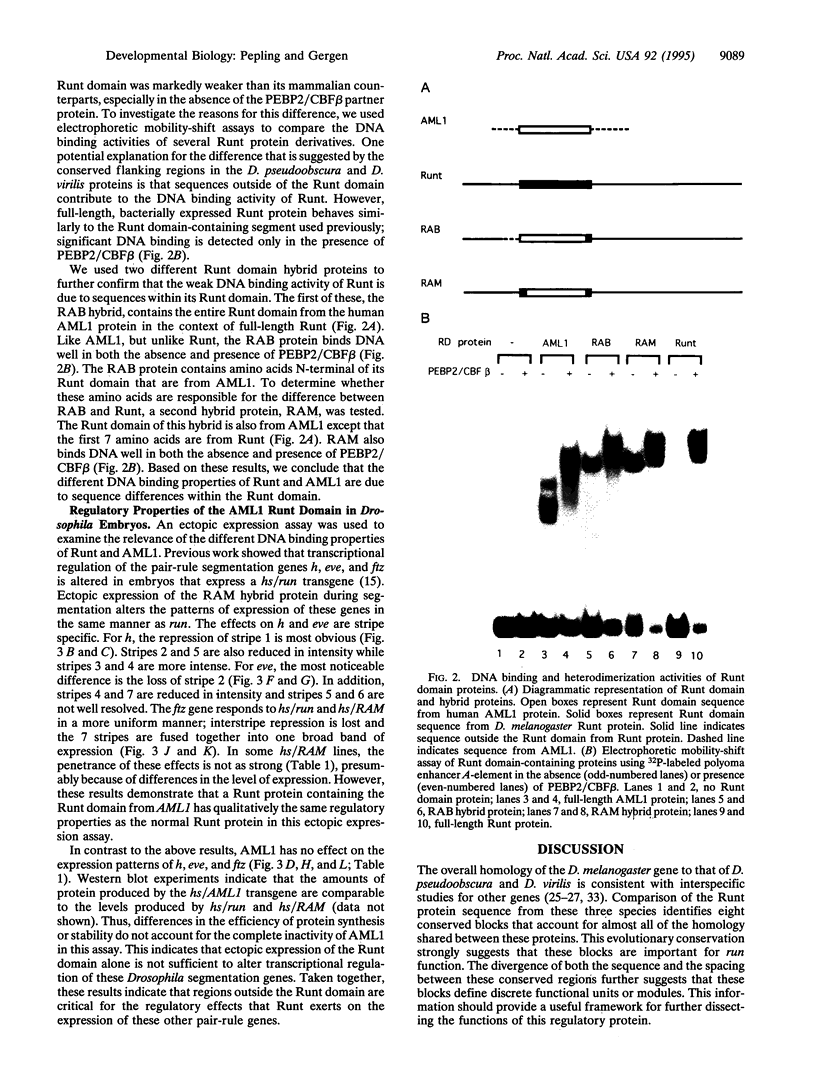
A phylogenetic approach was used to identify conserved regions of the transcriptional regulator Runt. Alignment of the deduced protein sequences from Drosophila melanogaster, Drosophila pseudoobscura, and Drosophila virilis revealed eight blocks of high sequence homology separated by regions with little or no homology. The largest conserved block contains the Runt domain, a DNA and protein binding domain conserved in a small family of mammalian transcription factors. The functional properties of the Runt domain from the D. melanogaster gene and the human AML1 (acute myeloid leukemia 1) gene were compared in vitro and in vivo. Electrophoretic mobility-shift assays with Runt/AML1 chimeras demonstrated that the different DNA binding properties of Runt and AML1 are due to differences within their respective Runt domains. Ectopic expression experiments indicated that proteins containing the AML1 Runt domain function in Drosophila embryos and that sequences outside of this domain are important in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akazawa C., Sasai Y., Nakanishi S., Kageyama R. Molecular characterization of a rat negative regulator with a basic helix-loop-helix structure predominantly expressed in the developing nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21879–21885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae S. C., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Inuzuka M., Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y. Isolation of PEBP2 alpha B cDNA representing the mouse homolog of human acute myeloid leukemia gene, AML1. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Wilson A. C. Molecular evolution in Drosophila and the higher Diptera II. A time scale for fly evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02100622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier E., Vaessin H., Younger-Shepherd S., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. deadpan, an essential pan-neural gene in Drosophila, encodes a helix-loop-helix protein similar to the hairy gene product. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2137–2151. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolwig G. M., Hearing P. Interaction of nuclear factor EF-1A with the polyomavirus enhancer region. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1884–1892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1884-1892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Scott M. P. Zygotically active genes that affect the spatial expression of the fushi tarazu segmentation gene during early Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90543-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delidakis C., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The Enhancer of split [E(spl)] locus of Drosophila encodes seven independent helix-loop-helix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8731–8735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt acts as a position-specific numerator element necessary for the uniform expression of the sex-determining gene Sex-lethal. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2176–2187. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. B., Kania M. A., Gergen J. P. Expression and function of the Drosophila gene runt in early stages of neural development. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1223–1230. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick V. D., Percival-Smith A., Ingles C. J., Krause H. M. Homeodomain-independent activity of the fushi tarazu polypeptide in Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):610–612. doi: 10.1038/356610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Wieschaus E. F. The localized requirements for a gene affecting segmentation in Drosophila: analysis of larvae mosaic for runt. Dev Biol. 1985 Jun;109(2):321–335. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Functional domains of the Drosophila Engrailed protein. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2723–2733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression by the Drosophila even-skipped protein: definition of a minimal repression domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):491–503. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi M., Sasai Y., Nakanishi S., Kageyama R. Molecular characterization of HES-2, a mammalian helix-loop-helix factor structurally related to Drosophila hairy and Enhancer of split. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):645–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagoshima H., Shigesada K., Satake M., Ito Y., Miyoshi H., Ohki M., Pepling M., Gergen P. The Runt domain identifies a new family of heteromeric transcriptional regulators. Trends Genet. 1993 Oct;9(10):338–341. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90026-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Ogawa E., Asano M., Ishida S., Murakami Y., Satake M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Purification of a mouse nuclear factor that binds to both the A and B cores of the polyomavirus enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4808–4819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4808-4819.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kania M. A., Bonner A. S., Duffy J. B., Gergen J. P. The Drosophila segmentation gene runt encodes a novel nuclear regulatory protein that is also expressed in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1701–1713. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A., Poole S. J., Wright D. K., O'Farrell P. H. Sequence conservation in the protein coding and intron regions of the engrailed transcription unit. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3583–3589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingler M., Gergen J. P. Regulation of runt transcription by Drosophila segmentation genes. Mech Dev. 1993 Sep;43(1):3–19. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90019-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Negreanu V., Bernstein Y., Bar-Am I., Avivi L., Groner Y. AML1, AML2, and AML3, the human members of the runt domain gene-family: cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal localization. Genomics. 1994 Sep 15;23(2):425–432. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnikova I. N., Crute B. E., Wang S., Speck N. A. Sequence specificity of the core-binding factor. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2408–2411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2408-2411.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Downing J. R., Hiebert S. W. Identification of AML-1 and the (8;21) translocation protein (AML-1/ETO) as sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins: the runt homology domain is required for DNA binding and protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6336–6345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi H., Shimizu K., Kozu T., Maseki N., Kaneko Y., Ohki M. t(8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10431–10434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Inuzuka M., Maruyama M., Satake M., Naito-Fujimoto M., Ito Y., Shigesada K. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEBP2 beta, the heterodimeric partner of a novel Drosophila runt-related DNA binding protein PEBP2 alpha. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):314–331. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa E., Maruyama M., Kagoshima H., Inuzuka M., Lu J., Satake M., Shigesada K., Ito Y. PEBP2/PEA2 represents a family of transcription factors homologous to the products of the Drosophila runt gene and the human AML1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6859–6863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paroush Z., Finley R. L., Jr, Kidd T., Wainwright S. M., Ingham P. W., Brent R., Ish-Horowicz D. Groucho is required for Drosophila neurogenesis, segmentation, and sex determination and interacts directly with hairy-related bHLH proteins. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):805–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Hogan A., Pinchin S. M., Howe K. M., Lardelli M., Ish-Horowicz D. The Drosophila hairy protein acts in both segmentation and bristle patterning and shows homology to N-myc. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3095–3103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasai Y., Kageyama R., Tagawa Y., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Two mammalian helix-loop-helix factors structurally related to Drosophila hairy and Enhancer of split. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2620–2634. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Inuzuka M., Shigesada K., Oikawa T., Ito Y. Differential expression of subspecies of polyomavirus and murine leukemia virus enhancer core binding protein, PEBP2, in various hematopoietic cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jul;83(7):714–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger M. A., Kaufman T. C. Molecular analysis of the bicoid gene from Drosophila pseudoobscura: identification of conserved domains within coding and noncoding regions of the bicoid mRNA. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2977–2987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer R. J., Tautz D. Involvement of an orthologue of the Drosophila pair-rule gene hairy in segment formation of the short germ-band embryo of Tribolium (Coleoptera) Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):448–450. doi: 10.1038/361448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treier M., Pfeifle C., Tautz D. Comparison of the gap segmentation gene hunchback between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila virilis reveals novel modes of evolutionary change. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1517–1525. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C., Gergen J. P. Gap gene properties of the pair-rule gene runt during Drosophila segmentation. Development. 1994 Jun;120(6):1671–1683. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C., Gergen P. Pair-rule expression of the Drosophila fushi tarazu gene: a nuclear receptor response element mediates the opposing regulatory effects of runt and hairy. Development. 1995 Feb;121(2):453–462. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright S. M., Ish-Horowicz D. Point mutations in the Drosophila hairy gene demonstrate in vivo requirements for basic, helix-loop-helix, and WRPW domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2475–2483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Speck N. A. Purification of core-binding factor, a protein that binds the conserved core site in murine leukemia virus enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):89–102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




