| Title: | Mannose Derivatives for Treating Bacterial Infections | ||
| Patent Application Number: | WO 2014/055474 Al | Publication date: | 10 April 2014 |
| Priority Application: | US 61/709,686 | Priority date: | 4 October 2012 |
| Inventors: | Bennani, Y. L.; Liu, B. | ||
| Assignee Company: | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc., 130 Waverly Street, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA | ||
| Disease Area: | Treatment of bacterial infections that cause inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and urinary tract infection (UTI) | Biological Target: | Inhibition of adhesion and FimH, and consequently inhibition of intracellular replication of AlEC in epithelial cells |
| Summary: | The invention in this patent application relates to mannose derivatives represented generally by formula (A). The compounds of the invention inhibit the bacterial adhesin FimH and may potentially treat or prevent bacterial infections that cause inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and urinary tract infection (UTI). | ||
| A combination of causes may contribute to pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD). Such causes include predisposing genetic factors, environmental triggers, dysbiosis of the gastrointestinal microbiota, and an inappropriate inflammatory response. Studies have shown general differences in the levels of microbiota in IBD patients compared to those of healthy subjects. For example, patients with CD show increased numbers of Escherichia coli (E. coli) but highly decreased numbers of Firmicutes compared to healthy subjects. It is not, however, clear if these microbiota changes are causative factors or consequences of inflammation. Studies have also determined that adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) has been associated with Crohn’s disease (CD). AlEC is capable of adhering to and invading epithelial cells. It is believed that the binding of adhesins expressed on the bacterial cell surface to defined glycosylated receptors on the host tissue surface is an initial and critical step in pathogenesis of CD. Therefore, blocking the interaction between type 1 pili and CEACAM6, a known host receptor for FimH (a mannose-specific adhesin located on the tip of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli) may then provide a new opportunity for treatment of CD. In addition to their potential CD therapy, recent studies have demonstrated the potential of FimH antagonists as effective treatment of urinary tract infections. | |||
| Important Compound Classes: | 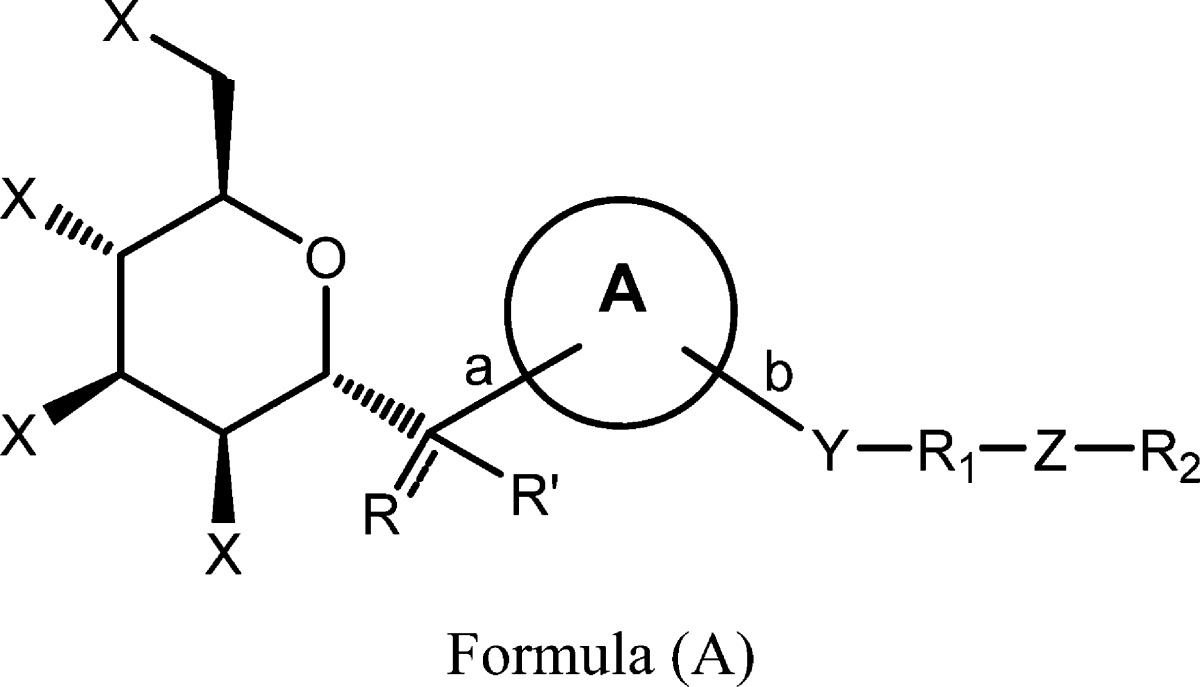 |
||
| Key Structures: | The inventors reported the structures of 15 examples of formula (A) including compounds 1, 12, and 15 seen here: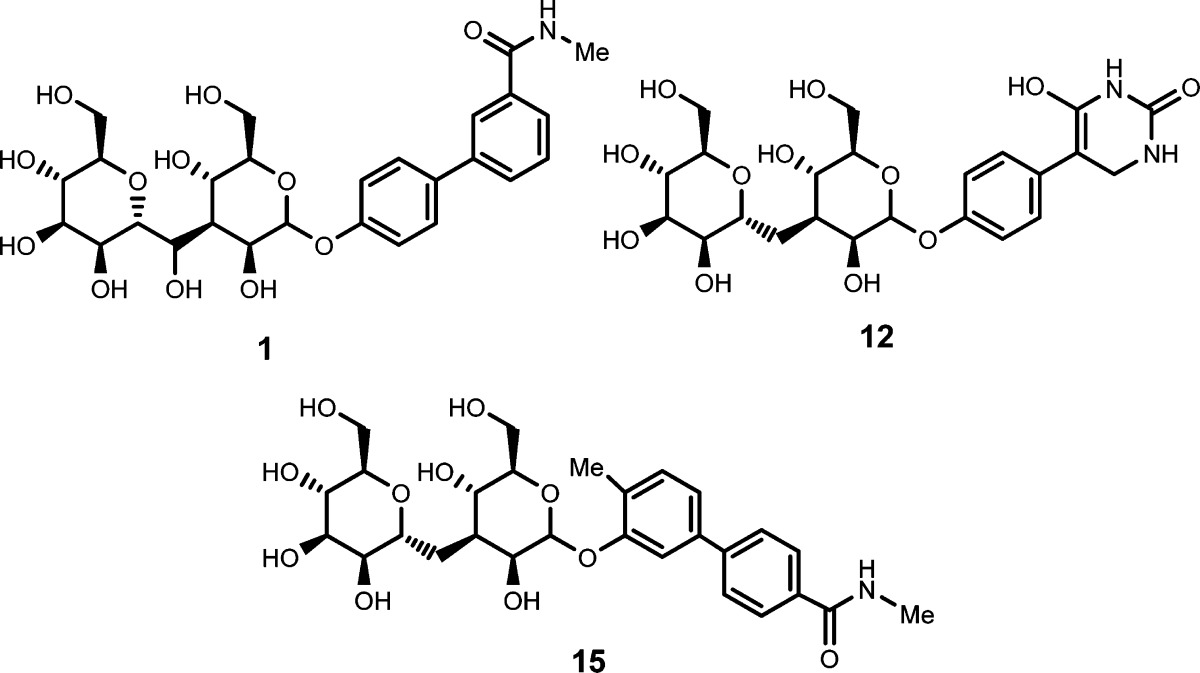
|
||
| Biological Assay: | Competitive Binding Assay | ||
| Biological Data: | The inventors reported the Kd (equilibrium dissociation constant) values for 15 examples of formula (A); the data for the above representative examples 1, 12, and 15 are reported in the following table: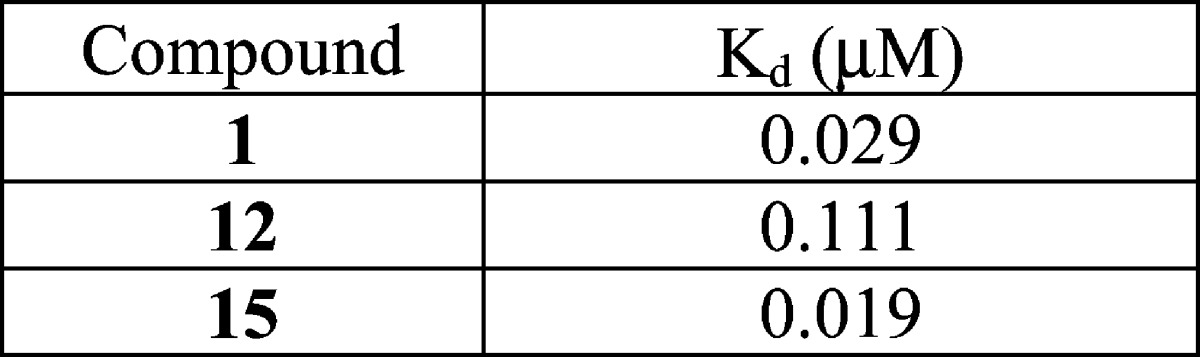
|
||
| Recent Review Articles: | 1. Hartmann M.; Lindhorst T. K.. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011 (20–21), 3583–3609. | ||
| 2. Tadema H.; Heeringa P.; Kallenberg C. G. M.. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23 (4), 366–371. | |||
The authors declare no competing financial interest.


