Abstract
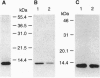
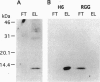
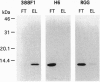
Murine suppressor T-cell hybridoma cells (231F1) secrete not only bioactive glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF) but also an inactive peptide comparable to bioactive GIF peptide in its molecular size and reactivity with anti-GIF; the amino acid sequence of the inactive peptide is identical to that of the bioactive homologue. The inactive GIF peptide in culture supernatant of both the 231F1 cells and a stable transfectant of human GIF cDNA in the murine suppressor T hybridoma selectively bound to Affi-Gel 10, whereas bioactive GIF peptides from the same sources failed to bind to the gel. The inactive cytosolic human GIF from the stable transfectant and Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human GIF also had affinity for Affi-Gel 10. Both the bioactive murine GIF peptide from the suppressor T hybridoma and bioactive recombinant human GIF from the stable transfectant bound to the anti-I-J monoclonal antibody H6 coupled to Affi-Gel. However, bioactive hGIF produced by a stable transfectant of human GIF cDNA in BMT10 cells failed to be retained in H6-coupled Affi-Gel. These results indicate that the I-J specificity is determined by the cell source of the GIF peptide and that the I-J determinant recognized by monoclonal antibody H6 does not represent a part of the primary amino acid sequence of GIF. It appears that the epitope is generated by a posttranslational modification of the peptide.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhagen J., Calandra T., Mitchell R. A., Martin S. B., Tracey K. J., Voelter W., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):756–759. doi: 10.1038/365756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Bernhagen J., Mitchell R. A., Bucala R. The macrophage is an important and previously unrecognized source of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1895–1902. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Suppressor cells and immunoregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:127–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi H., Tagaya Y., Nakano T., Mikayama T., Ishizaka K. Antigen-binding glycosylation inhibiting factor from a human T-cell hybridoma specific for bee venom phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Regulation of IgE synthesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:159–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamatsu A. S-carboxymethylation of proteins transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes followed by in situ protease digestion and amino acid microsequencing. Electrophoresis. 1992 Mar;13(3):142–147. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150130129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Ishizaka K. Construction of antigen-specific suppressor T cell hybridomas from spleen cells of mice primed for the persistent IgE antibody formation. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3270–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Akasaki M., Ishizaka K. Carrier-specific suppression of antibody responses by antigen-specific glycosylation-inhibiting factors. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1494–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Uede T., Ishizaka K. IgE-binding factors from mouse T lymphocytes. III. Role of antigen-specific suppressor T cells in the formation of IgE-suppressive factor. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3266–3273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno M., Kobayashi S., Tokuhisa T., Takei I., Shinohara N., Taniguchi M. Monoclonal antibodies that recognize the product controlled by a gene in the I-J subregion of the mouse H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1290–1304. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Steinmetz M., Kobori J., Kraig E., Kapp J. A., Pierce C. W., Sorensen C. M., Suzuki G., Tada T., Hood L. RNA transcripts for I-J polypeptides are apparently not encoded between the I-A and I-E subregions of the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. C., Nakano T., Elly C., Ishizaka K. Requirement of posttranslational modifications for the generation of biologic activity of glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11227–11231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikayama T., Nakano T., Gomi H., Nakagawa Y., Liu Y. C., Sato M., Iwamatsu A., Ishii Y., Weiser W. Y., Ishizaka K. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10056–10060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Herzenberg L. A., Okumura K., Herzenberg L. A., McDevitt H. O. A new I subregion (I-J) marked by a locus (Ia-4) controlling surface determinants on suppressor T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):699–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Kubo R. T., Kishimoto H., Asano Y., Tada T. Biochemical identification of I-J as a novel dimeric surface molecule on mouse helper and suppressor T cell clones. Int Immunol. 1989;1(1):50–58. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara R. M., Jr, Byrne M. C., Kuchroo V. K., Nagelin A., Whitters M. J., Jayaraman S., Henderson S. L., Dorf M. E., Collins M. T cell receptor alpha-chain defines the antigen specificity of antigen-specific suppressor factor but does not impart genetic restriction. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2075–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. K., Kuchroo V. K., Kawasaki H., Jayaraman S., Iwata M., Ishizaka K., Dorf M. E. A monoclonal antibody raised to lipomodulin recognizes T suppressor factors in two independent hapten-specific suppressor networks. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2213–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumida T., Sado T., Kojima M., Ono K., Kamisaku H., Taniguchi M. I-J as an idiotype of the recognition component of antigen-specific suppressor T-cell factor. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):738–741. doi: 10.1038/316738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., David C. S. Properties of the antigen-specific suppressive T-cell factor in the regulation of antibody response of the mouse. IV. Special subregion assignment of the gene(s) that codes for the suppressive T-cell factor in the H-2 histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):713–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Uracz W., Abe R., Asano Y. I-J as an inducible T cell receptor for self. Immunol Rev. 1985 Apr;83:105–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb00472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Gomi H., Takeuchi T., Carini C., Tagaya Y., Ishizaka K. Glycosylation-inhibiting factor from human T cell hybridomas constructed from peripheral blood lymphocytes of a bee venom-sensitive allergic patient. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):729–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uracz W., Asano Y., Abe R., Tada T. I-J epitopes are adaptively acquired by T cells differentiated in the chimaeric condition. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):741–743. doi: 10.1038/316741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser W. Y., Temple P. A., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Remold H. G., Clark S. C., David J. R. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a human macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7522–7526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]