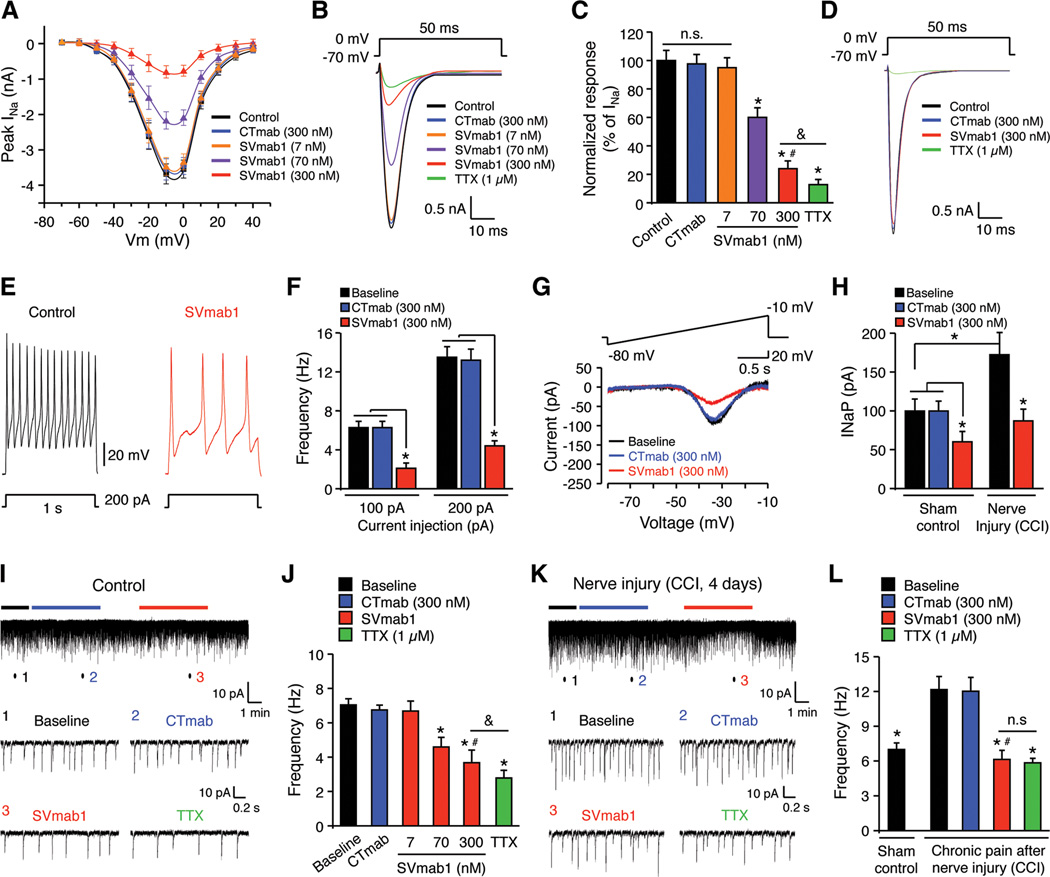
Figure 6. SVmab1 suppresses transient and persistent sodium currents and action potentials in small-sized DRG neurons and nociceptive synaptic transmission in spinal cord slices.
(A–D) SVmab1 suppresses transient sodium currents (INaT) in dissociated DRG neurons. (A) Current-voltage relationship of INaT and the effects of SVmab1 (7, 70, and 300 nM) and CTmab (300 nM), n = 15–20 neurons/group. (B) Traces of INaT and the effects of SVmab1, CTmab (300 nM), and TTX (1 µM). (C) Percentage inhibition of INaT by SVmab1 and TTX (1 µM). *P < 0.05, vs. control (no treatment); #P < 0.05, vs. CTmab (300 nM), &P < 0.05, n = 15–20 neurons/group. Note that TTX (1 µM) further inhibits INaT compared with SVmab1 (300 nM). (D) TTX (1 µM) but not SVmab1 (300 nM) inhibits INaT in large-sized DRG neurons. n = 10 neurons/group.
(E, F) SVmab1 inhibits the action potential frequency in dissociated small-sized DRG neurons. (E) Traces of action potentials. (F) Action potential frequencies following current injection (100 and 200 pA). *P < 0.05, n = 15–20 neurons/group.
(G, H) SVmab1 inhibits persistent sodium currents (INaP) in small-sized neurons of whole mount DRGs from naïve mice and mice with nerve injury (CCI). (G) Traces of INaP before treatment (control) and after treatment with CTmab (300 nM) and SVmab1 (300 nM). (H) Amplitudes of INaP in DRG neurons, which are increased after CCI. Note that SVmab1 (300 nM) produces a greater inhibition of INaP after CCI. *P < 0.05, n = 6–7 neurons/group.
(I, J) SVmab1 inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in IIo neurons of spinal cord slices of normal mice. (I) Traces of spontaneous EPSCs (sEPSCs). Low panel, enlargements of traces (1,2, 3) before and during the CTmab and SVmab1 treatment (300 nM). (J) Frequency of sEPSCs. *P < 0.05, vs. baseline; #P < 0.05, vs. CTmab (300 nM); &P < 0.05, n = 5–6 neurons/group.
(K, L) SVmab1 inhibits chronic pain-potentiated excitatory nociceptive synaptic transmission in lamina IIo neurons of spinal cord slices 4 days after CCI. (K) Traces of sEPSCs. Low panel, enlargements of traces (1, 2, 3) before and during the CTmab and SVmab1 treatment (300 nM). (L) Frequency of sEPSCs. *P < 0.05, vs. no treatment baseline after CCI; #P < 0.05, vs. CTmab (300 nM), n = 5 neurons/group. Note that SVmab1 is as effectively as TTX in suppressing synaptic transmission in chronic pain. n.s., no significance. All the data are shown as means ± SEM.