Abstract
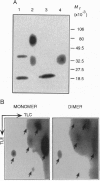
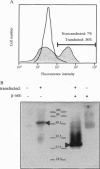
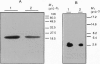
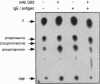
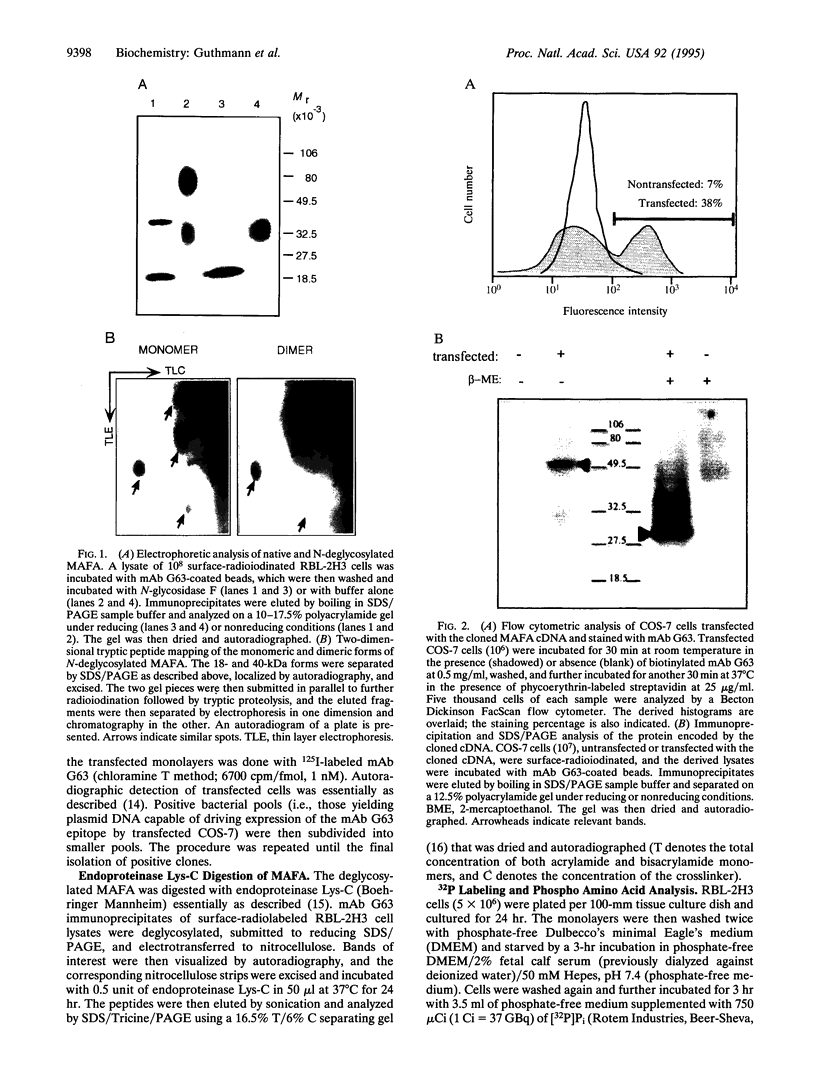
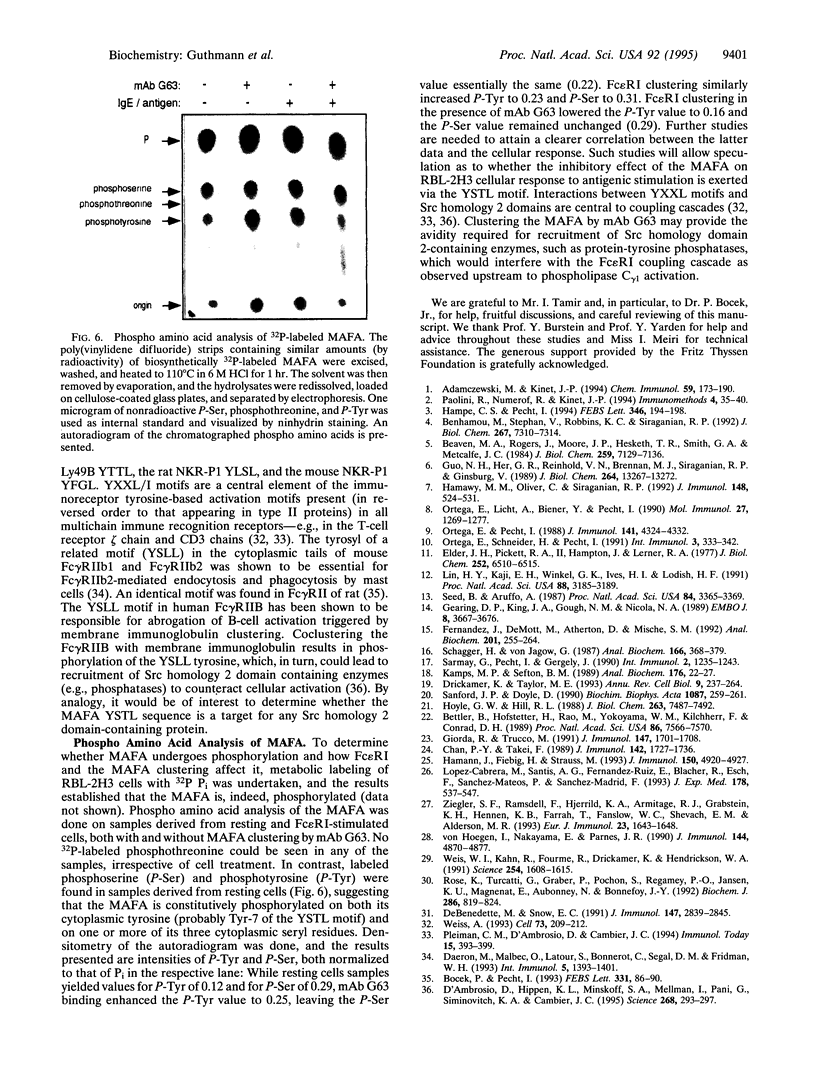
Secretion of inflammatory mediators by rat mast cells (line RBL-2H3) was earlier shown to be inhibited upon clustering a membrane glycoprotein by monoclonal antibody G63. This glycoprotein, named mast cell function-associated antigen (MAFA), was also shown to interfere with the coupling cascade of the type 1 Fc epsilon receptor upstream to phospholipase C gamma 1 activation by protein-tyrosine kinases. Here we report that the MAFA is expressed as both a monomer and a homodimer. Expression cloning of its cDNA shows that it contains a single open reading frame, encoding a 188-amino acid-long type II integral membrane protein. The 114 C-terminal amino acids display sequence homology with the carbohydrate-binding domain of calcium-dependent animal lectins, many of which have immunological functions. The cytoplasmic tail of MAFA contains a YXXL (YSTL) motif, which is conserved among related C-type lectins and is an essential element in the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. Finally, changes in the MAFA tyrosyl- and seryl-phosphorylation levels are observed in response to monoclonal antibody G63 binding, antigenic stimulation, and a combination of both treatments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamczewski M., Kinet J. P. The high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E. Chem Immunol. 1994;59:173–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A., Rogers J., Moore J. P., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. The mechanism of the calcium signal and correlation with histamine release in 2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7129–7136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou M., Stephan V., Robbins K. C., Siraganian R. P. High-affinity IgE receptor-mediated stimulation of rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells induces early and late protein-tyrosine phosphorylations. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7310–7314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Hofstetter H., Rao M., Yokoyama W. M., Kilchherr F., Conrad D. H. Molecular structure and expression of the murine lymphocyte low-affinity receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon RII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7566–7570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocek P., Pecht I. Cloning and sequence of the cDNA coding for rat type II Fc gamma receptor of mast cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 27;331(1-2):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80302-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. Y., Takei F. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel murine T cell surface antigen, YE1/48. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1727–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio D., Hippen K. L., Minskoff S. A., Mellman I., Pani G., Siminovitch K. A., Cambier J. C. Recruitment and activation of PTP1C in negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling by Fc gamma RIIB1. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):293–297. doi: 10.1126/science.7716523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M., Malbec O., Latour S., Bonnerot C., Segal D. M., Fridman W. H. Distinct intracytoplasmic sequences are required for endocytosis and phagocytosis via murine Fc gamma RII in mast cells. Int Immunol. 1993 Nov;5(11):1393–1401. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.11.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBenedette M., Snow E. C. Induction and regulation of casein kinase II during B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2839–2845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., Taylor M. E. Biology of animal lectins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:237–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J., DeMott M., Atherton D., Mische S. M. Internal protein sequence analysis: enzymatic digestion for less than 10 micrograms of protein bound to polyvinylidene difluoride or nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1992 Mar;201(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorda R., Trucco M. Mouse NKR-P1. A family of genes selectively coexpressed in adherent lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1701–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo N. H., Her G. R., Reinhold V. N., Brennan M. J., Siraganian R. P., Ginsburg V. Monoclonal antibody AA4, which inhibits binding of IgE to high affinity receptors on rat basophilic leukemia cells, binds to novel alpha-galactosyl derivatives of ganglioside GD1b. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13267–13272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann J., Fiebig H., Strauss M. Expression cloning of the early activation antigen CD69, a type II integral membrane protein with a C-type lectin domain. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):4920–4927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamawy M. M., Oliver C., Siraganian R. P. Inhibition of IgE binding to RBL-2H3 cells by a monoclonal antibody (BD6) to a surface protein other than the high affinity IgE receptor. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):524–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe C. S., Pecht I. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity enhancement is induced upon Fc epsilon receptor activation of mast cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 13;346(2-3):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00471-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle G. W., Hill R. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for a carbohydrate binding receptor unique to rat Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7487–7492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Kaji E. H., Winkel G. K., Ives H. E., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression of a vascular smooth muscle endothelin 1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Santis A. G., Fernández-Ruiz E., Blacher R., Esch F., Sánchez-Mateos P., Sánchez-Madrid F. Molecular cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of the human earliest lymphocyte activation antigen AIM/CD69, a new member of the C-type animal lectin superfamily of signal-transmitting receptors. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):537–547. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega Soto E., Pecht I. A monoclonal antibody that inhibits secretion from rat basophilic leukemia cells and binds to a novel membrane component. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4324–4332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega E., Licht A., Biener Y., Pecht I. A glycolipid-specific monoclonal antibody modulates Fc epsilon receptor stimulation of mast cells. Mol Immunol. 1990 Dec;27(12):1269–1277. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90031-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega E., Schneider H., Pecht I. Possible interactions between the Fc epsilon receptor and a novel mast cell function-associated antigen. Int Immunol. 1991 Apr;3(4):333–342. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolini R., Numerof R., Kinet J. P. Kinase activation through the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E. Immunomethods. 1994 Feb;4(1):35–40. doi: 10.1006/immu.1994.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleiman C. M., D'Ambrosio D., Cambier J. C. The B-cell antigen receptor complex: structure and signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1994 Sep;15(9):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K., Turcatti G., Graber P., Pochon S., Regamey P. O., Jansen K. U., Magnenat E., Aubonney N., Bonnefoy J. Y. Partial characterization of natural and recombinant human soluble CD23. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj2860819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J. P., Doyle D. Mouse asialoglycoprotein receptor cDNA sequence: conservation of receptor genes during mammalian evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 23;1087(2):259–261. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90216-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmay G., Pecht I., Gergely J. Phosphorylation of type II Fc gamma receptor on activated human B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1990;2(12):1235–1243. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.12.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hoegen I., Nakayama E., Parnes J. R. Identification of a human protein homologous to the mouse Lyb-2 B cell differentiation antigen and sequence of the corresponding cDNA. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4870–4877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W. I., Kahn R., Fourme R., Drickamer K., Hendrickson W. A. Structure of the calcium-dependent lectin domain from a rat mannose-binding protein determined by MAD phasing. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1608–1615. doi: 10.1126/science.1721241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Ramsdell F., Hjerrild K. A., Armitage R. J., Grabstein K. H., Hennen K. B., Farrah T., Fanslow W. C., Shevach E. M., Alderson M. R. Molecular characterization of the early activation antigen CD69: a type II membrane glycoprotein related to a family of natural killer cell activation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1643–1648. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]