Abstract
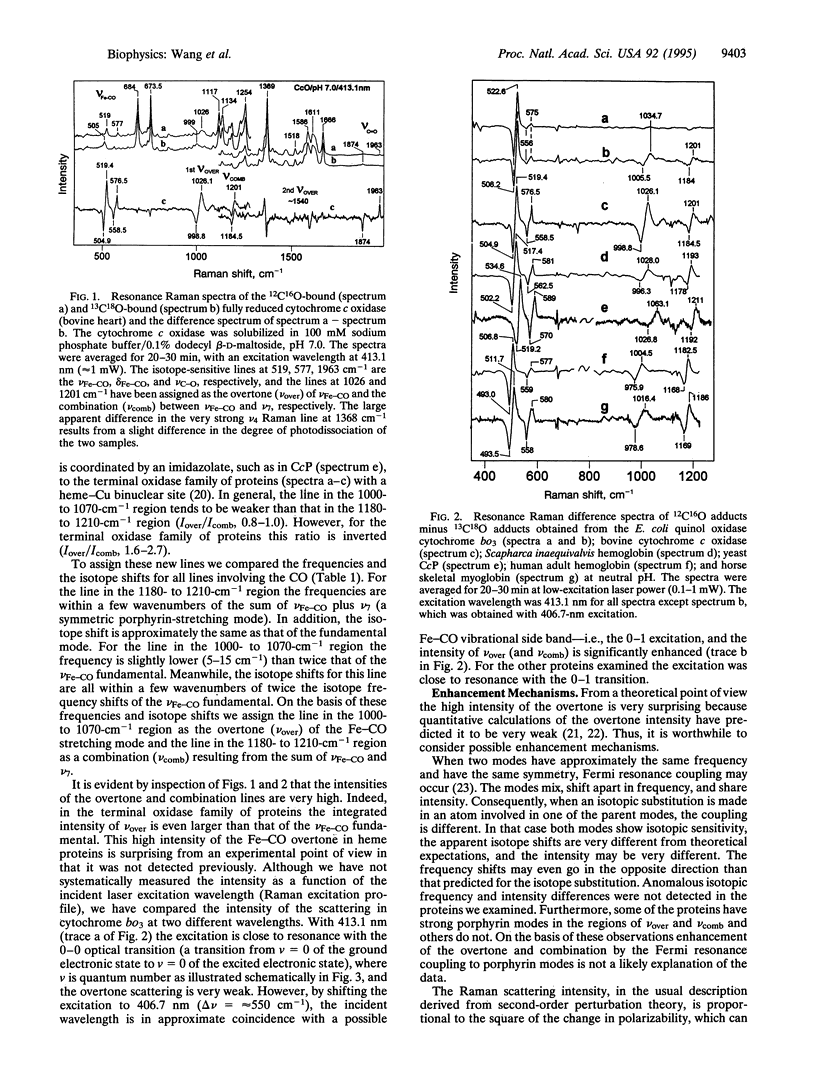
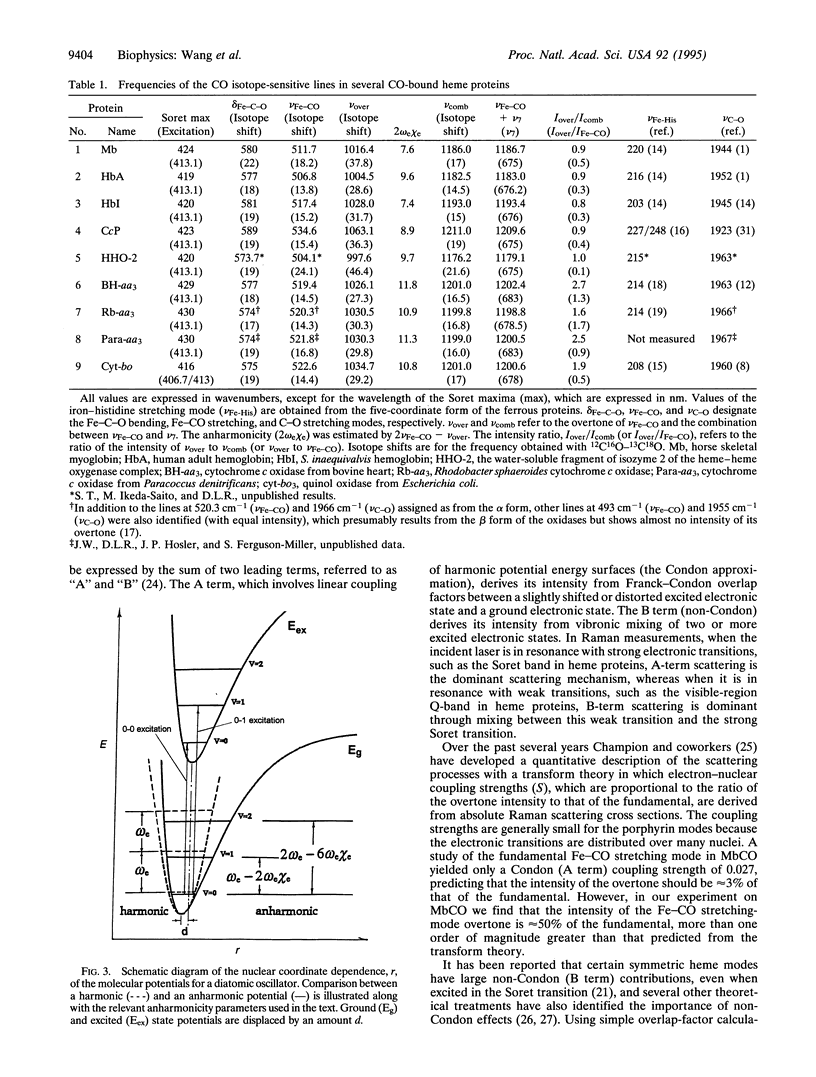
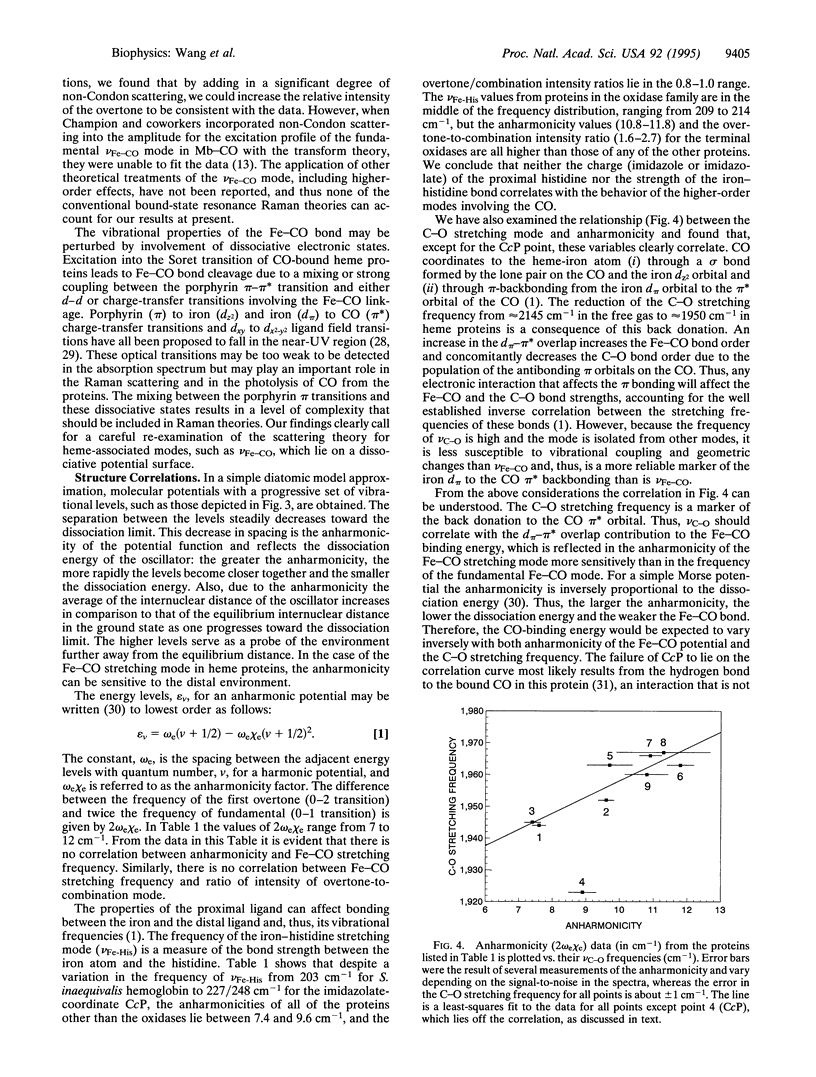
Two CO-isotope sensitive lines have been detected in the overtone region of the resonance Raman spectra of CO-bound hemeproteins. One line is assigned as the overtone of the Fe-CO stretching mode and is located in the 1000- to 1070-cm-1 region. The other line is found in the 1180- to 1210-cm-1 region and is assigned as a combination between a porphyrin mode, nu 7, and the Fe-CO stretching mode. The high intensities of these lines, which in the terminal oxidase class of proteins are of the same order as those of the fundamental stretching mode, indicate that the mechanism of enhancement for modes involving the Fe-CO moiety is different from that for the modes of the porphyrin macrocycle and call for reexamination of Raman theory of porphyrins as applied to axial ligands. The anharmonicity of the electronic potential function was evaluated, revealing that in the terminal oxidases the anharmonicity is greater than in the other heme proteins that were examined, suggesting a distinctive interaction of the bound CO with its distal environment in this family. Furthermore, the anharmonicity correlates with the frequency of the C-O stretching mode, demonstrating that both of these parameters are sensitive to the Fe-CO bond energy. The overtone and combination lines involving the bound CO promise to be additional probes of heme protein structural properties.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argade P. V., Ching Y. C., Rousseau D. L. Cytochrome a3 structure in carbon monoxide-bound cytochrome oxidase. Science. 1984 Jul 20;225(4659):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.6330890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Hofrichter J. Polarized absorption and linear dichroism spectroscopy of hemoglobin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:175–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Sligar S. G., Wolynes P. G. The energy landscapes and motions of proteins. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1598–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.1749933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Teraoka J., Inubushi T., Yonetani T., Kitagawa T. Resonance Raman study on cytochrome c peroxidase and its intermediate. Presence of the Fe(IV) = O bond in compound ES and heme-linked ionization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11110–11118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J., Goswitz V. C., Calhoun M., Garcia-Horsman J. A., Lemieux L., Alben J. O., Gennis R. B. Demonstration by FTIR that the bo-type ubiquinol oxidase of Escherichia coli contains a heme-copper binuclear center similar to that in cytochrome c oxidase and that proper assembly of the binuclear center requires the cyoE gene product. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 24;31(46):11435–11440. doi: 10.1021/bi00161a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosler J. P., Fetter J., Tecklenburg M. M., Espe M., Lerma C., Ferguson-Miller S. Cytochrome aa3 of Rhodobacter sphaeroides as a model for mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase. Purification, kinetics, proton pumping, and spectral analysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24264–24272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau D. L., Ching Y., Wang J. Proton translocation in cytochrome c oxidase: redox linkage through proximal ligand exchange on cytochrome a3. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1993 Apr;25(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00762858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmeen I., Rimai L., Babcock G. Raman spectra of heme a, cytochrome oxidase-ligand complexes, and alkaline denatured oxidase. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):800–806. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song S., Boffi A., Chiancone E., Rousseau D. L. Protein-heme interactions in hemoglobin from the mollusc Scapharca inaequivalvis: evidence from resonance Raman scattering. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 29;32(25):6330–6336. doi: 10.1021/bi00076a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubaki M., Mogi T., Hori H., Hirota S., Ogura T., Kitagawa T., Anraku Y. Molecular structure of redox metal centers of the cytochrome bo complex from Escherichia coli. Spectroscopic characterizations of the subunit I histidine mutant oxidases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30861–30868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., Boldt N. J., Ondrias M. R. Formation and photolability of low-spin ferrous cytochrome c peroxidase at alkaline pH. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 28;31(3):867–878. doi: 10.1021/bi00118a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Rousseau D. L., Abu-Soud H. M., Stuehr D. J. Heme coordination of NO in NO synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10512–10516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Takahashi S., Hosler J. P., Mitchell D. M., Ferguson-Miller S., Gennis R. B., Rousseau D. L. Two conformations of the catalytic site in the aa3-type cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1995 Aug 8;34(31):9819–9825. doi: 10.1021/bi00031a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. I. Absolute and difference absorption spectra. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa S., Choc M. G., O'Toole M. C., Caughey W. S. An infrared study of CO binding to heart cytochrome c oxidase and hemoglobin A. Implications re O2 reactions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5498–5508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



