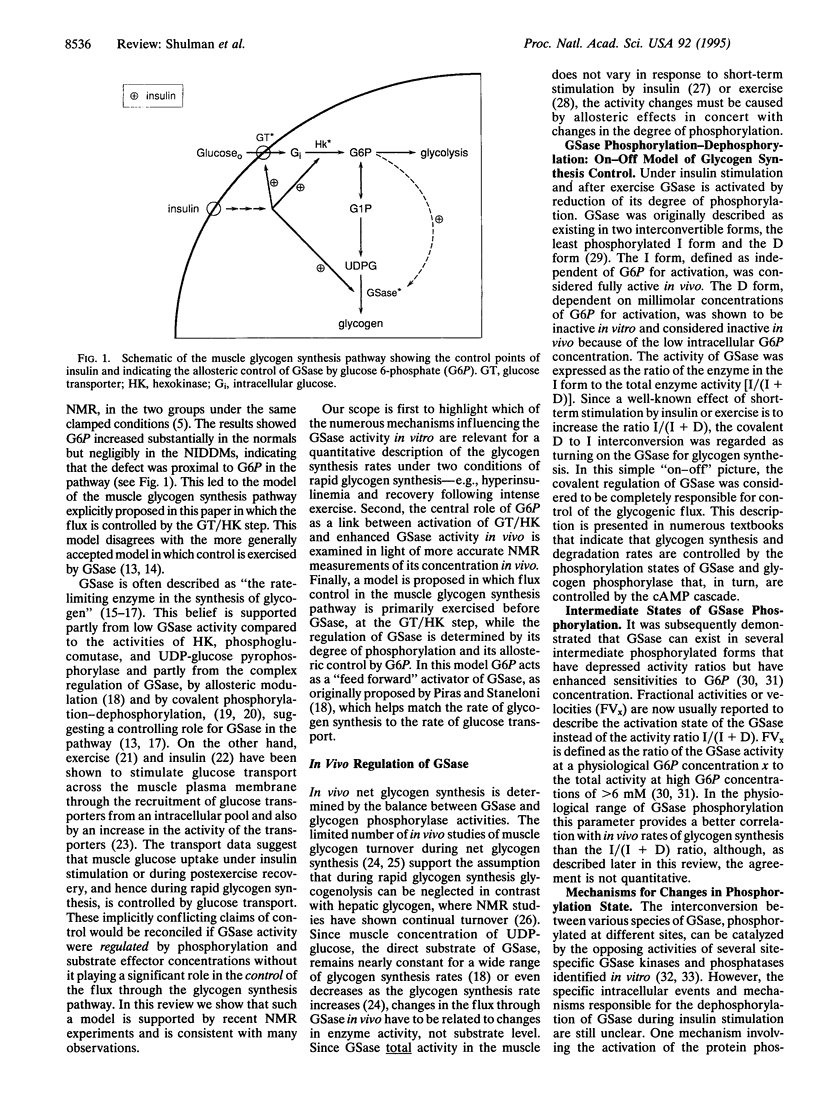
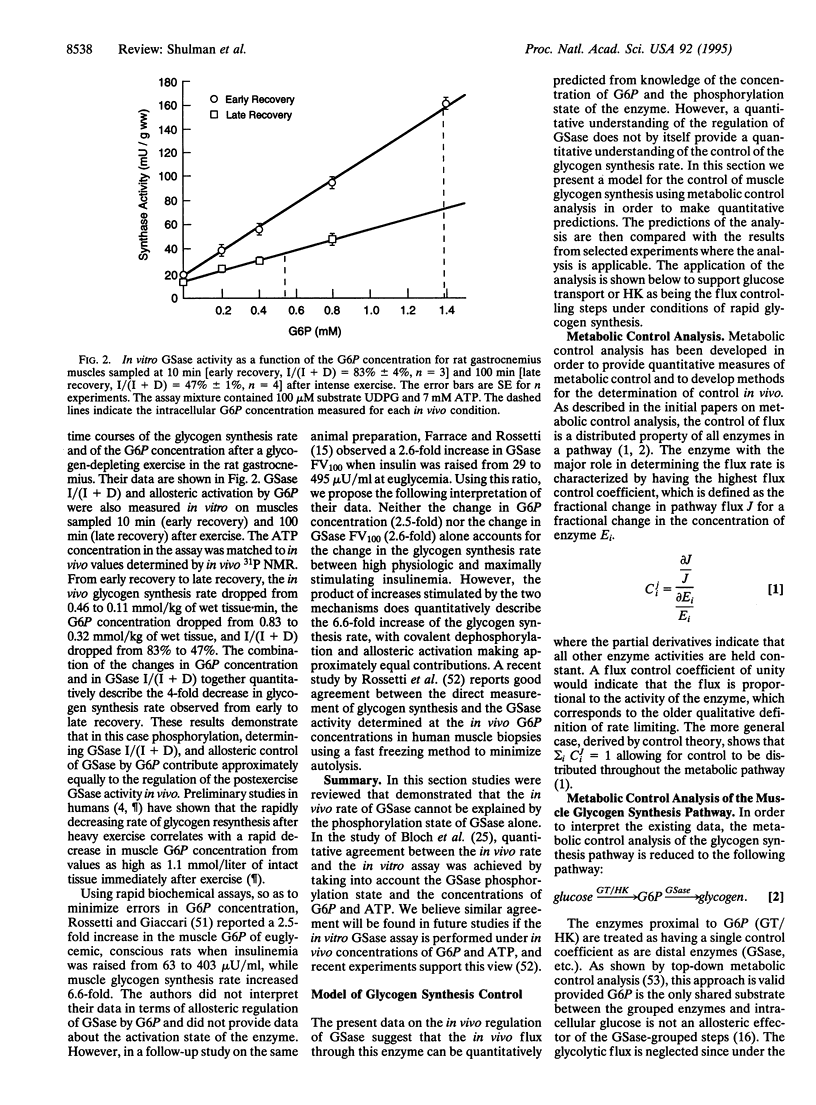
Abstract
The activity of glycogen synthase (GSase; EC 2.4.1.11) is regulated by covalent phosphorylation. Because of this regulation, GSase has generally been considered to control the rate of glycogen synthesis. This hypothesis is examined in light of recent in vivo NMR experiments on rat and human muscle and is found to be quantitatively inconsistent with the data under conditions of glycogen synthesis. Our first experiments showed that muscle glycogen synthesis was slower in non-insulin-dependent diabetics compared to normals and that their defect was in the glucose transporter/hexokinase (GT/HK) part of the pathway. From these and other in vivo NMR results a quantitative model is proposed in which the GT/HK steps control the rate of glycogen synthesis in normal humans and rat muscle. The flux through GSase is regulated to match the proximal steps by "feed forward" to glucose 6-phosphate, which is a positive allosteric effector of all forms of GSase. Recent in vivo NMR experiments specifically designed to test the model are analyzed by metabolic control theory and it is shown quantitatively that the GT/HK step controls the rate of glycogen synthesis. Preliminary evidence favors the transporter step. Several conclusions are significant: (i) glucose transport/hexokinase controls the glycogen synthesis flux; (ii) the role of covalent phosphorylation of GSase is to adapt the activity of the enzyme to the flux and to control the metabolite levels not the flux; (iii) the quantitative data needed for inferring and testing the present model of flux control depended upon advances of in vivo NMR methods that accurately measured the concentration of glucose 6-phosphate and the rate of glycogen synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak J. F., Pedersen O. Exercise-enhanced activation of glycogen synthase in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):E957–E963. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.6.E957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R. J., Youngren J. F. Regulation of glucose transport in skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3238–3244. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch G., Chase J. R., Avison M. J., Shulman R. G. In vivo 31P NMR measurement of glucose-6-phosphate in the rat muscle after exercise. Magn Reson Med. 1993 Sep;30(3):347–350. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910300311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch G., Chase J. R., Meyer D. B., Avison M. J., Shulman G. I., Shulman R. G. In vivo regulation of rat muscle glycogen resynthesis after intense exercise. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):E85–E91. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.266.1.E85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Stone K., Mott D. Correlation between muscle glycogen synthase activity and in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonadonna R. C., Del Prato S., Saccomani M. P., Bonora E., Gulli G., Ferrannini E., Bier D., Cobelli C., DeFronzo R. A. Transmembrane glucose transport in skeletal muscle of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):486–494. doi: 10.1172/JCI116592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonadonna R. C., Saccomani M. P., Seely L., Zych K. S., Ferrannini E., Cobelli C., DeFronzo R. A. Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle. The in vivo response to insulin. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):191–198. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carabaza A., Ciudad C. J., Baqué S., Guinovart J. J. Glucose has to be phosphorylated to activate glycogen synthase, but not to inactivate glycogen phosphorylase in hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 20;296(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80381-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANFORTH W. H. GLYCOGEN SYNTHETASE ACTIVITY IN SKELETAL MUSCLE. INTERCONVERSION OF TWO FORMS AND CONTROL OF GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:588–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Lavoinne A., Nakielny S., Caudwell F. B., Watt P., Cohen P. The molecular mechanism by which insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis in mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):302–308. doi: 10.1038/348302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Vranic M., Holloszy J. O., Klip A. Exercise induces recruitment of the "insulin-responsive glucose transporter". Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13427–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrace S., Rossetti L. Hyperglycemia markedly enhances skeletal muscle glycogen synthase activity in diabetic, but not in normal conscious rats. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1453–1463. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furler S. M., Jenkins A. B., Storlien L. H., Kraegen E. W. In vivo location of the rate-limiting step of hexose uptake in muscle and brain tissue of rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):E337–E347. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.3.E337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goncharova N. Iu, Zelenina E. V. Vliianie insulina na kataliticheskuiu éffektivnost' II izozima geksokinazy skeletnykh myshts krysy. Biokhimiia. 1991 May;56(5):913–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyear L. J., Hirshman M. F., Smith R. J., Horton E. S. Glucose transporter number, activity, and isoform content in plasma membranes of red and white skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):E556–E561. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.5.E556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyear L. J., King P. A., Hirshman M. F., Thompson C. M., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Contractile activity increases plasma membrane glucose transporters in absence of insulin. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):E667–E672. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.4.E667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriou M., Trayer I. P., Cornish-Bowden A. Isotope-exchange evidence that glucose 6-phosphate inhibits rat-muscle hexokinase II at an allosteric site. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter R., Prolla T. A., Shulman R. G. 13C NMR visibility of rabbit muscle glycogen in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Aug;20(2):327–332. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910200216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinovart J. J., Salavert A., Massagué J., Ciudad C. J., Salsas E., Itarte E. Glycogen synthase: a new activity ratio assay expressing a high sensitivity to the phosphorylation state. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80515-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. Regulation of protein phosphatase-1G from rabbit skeletal muscle. 2. Catalytic subunit translocation is a mechanism for reversible inhibition of activity toward glycogen-bound substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):711–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy J. L., Costill D. L., Fink W. J., Lower R. W. Influence of caffeine and carbohydrate feedings on endurance performance. Med Sci Sports. 1979 Spring;11(1):6–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacser H., Burns J. A. The control of flux. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:65–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Pâquet M. R. Glucose transport and glucose transporters in muscle and their metabolic regulation. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):228–243. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan R. G., Lamb D. R., Reimann E. M., Schlender K. K. Modified assays to detect activation of glycogen synthase following exercise. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):E197–E202. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.2.E197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynska Y. T., Home P. D., Alberti K. G. In vivo regulation of liver and skeletal muscle glycogen synthase activity by glucose and insulin. Diabetes. 1986 Jun;35(6):662–667. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.6.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo K., Foley J. E. Rate-limiting steps for insulin-mediated glucose uptake into perfused rat hindlimb. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):E100–E102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.1.E100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J. Insulin and the stimulation of glycogen synthesis. The road from glycogen structure to glycogen synthase to cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase to insulin mediators. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:173–231. doi: 10.1002/9780470123096.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin M. R., Petit W. A., Jr, Shulman R. G., Barrett E. J. Measurement of myocardial glycogen synthesis in diabetic and fasted rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):E184–E190. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.1.E184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueck J. D., Fromm H. J. Kinetics, mechanism, and regulation of rat skeletal muscle hexokinase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1341–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maehlum S., Høstmark A. T., Hermansen L. Synthesis of muscle glycogen during recovery after prolonged severe exercise in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;37(4):309–316. doi: 10.3109/00365517709092634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L. J., Consoli A., Jain A., Kelley D. E. Differential regulation of intracellular glucose metabolism by glucose and insulin in human muscle. Am J Physiol. 1993 Dec;265(6 Pt 1):E898–E905. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.265.6.E898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellgren R. L., Coulson M. Coordinated feedback regulation of muscle glycogen metabolism: inhibition of purified phosphorylase phosphatase by glycogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munger R., Temler E., Jallut D., Haesler E., Felber J. P. Correlations of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase activities with glycogen concentration in human muscle biopsies. Evidence for a double-feedback mechanism regulating glycogen synthesis and breakdown. Metabolism. 1993 Jan;42(1):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90169-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras R., Rothman L. B., Cabib E. Regulation of muscle glycogen synthetase by metabolites. Differential effects on the I and D forms. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):56–66. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras R., Staneloni R. In vivo regulation of rat muscle glycogen synthetase activity. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2153–2160. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug T., Galbo H., Ohkuwa T., Tranum-Jensen J., Vinten J. Kinetics of glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle membrane vesicles: effects of insulin and contractions. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E700–E711. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug T., Wojtaszewski J., Kristiansen S., Hespel P., Galbo H., Richter E. A. Glucose transport and transporters in muscle giant vesicles: differential effects of insulin and contractions. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):E270–E278. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.2.E270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price T. B., Rothman D. L., Taylor R., Avison M. J., Shulman G. I., Shulman R. G. Human muscle glycogen resynthesis after exercise: insulin-dependent and -independent phases. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 Jan;76(1):104–111. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quant P. A. Experimental application of top-down control analysis to metabolic systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):26–30. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90084-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Control of glycogen synthase by hierarchal protein phosphorylation. FASEB J. 1990 Sep;4(12):2961–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J., Larner J. Rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase. II. Enzyme phosphorylation state and effector concentrations as interacting control parameters. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1920–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J., Takeda Y., Larner J. Rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase. I. Relationship between phosphorylation state and kinetic properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1913–1919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Giaccari A. Relative contribution of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis to insulin-mediated glucose uptake. A dose-response euglycemic clamp study in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Hu M. Skeletal muscle glycogenolysis is more sensitive to insulin than is glucose transport/phosphorylation. Relation to the insulin-mediated inhibition of hepatic glucose production. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2963–2974. doi: 10.1172/JCI116919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Lee Y. T., Ruiz J., Aldridge S. C., Shamoon H., Boden G. Quantitation of glycolysis and skeletal muscle glycogen synthesis in humans. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):E761–E769. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.265.5.E761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Magnusson I., Cline G., Gerard D., Kahn C. R., Shulman R. G., Shulman G. I. Decreased muscle glucose transport/phosphorylation is an early defect in the pathogenesis of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Shulman R. G., Shulman G. I. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of muscle glucose-6-phosphate. Evidence for reduced insulin-dependent muscle glucose transport or phosphorylation activity in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1172/JCI115686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Rothman D. L., Jue T., Stein P., DeFronzo R. A., Shulman R. G. Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):223–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillerud L. O., Shulman R. G. Structure and metabolism of mammalian liver glycogen monitored by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1087–1094. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. K., Katz A. Role of glycogen in control of glycolysis and IMP formation in human muscle during exercise. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):E859–E864. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.6.E859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R., Price T. B., Rothman D. L., Shulman R. G., Shulman G. I. Validation of 13C NMR measurement of human skeletal muscle glycogen by direct biochemical assay of needle biopsy samples. Magn Reson Med. 1992 Sep;27(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910270103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten D. R., Davis J. M., Meyers D. M., Durstine J. L. Altered cellular distribution of hexokinase in skeletal muscle after exercise. Int J Sports Med. 1992 Jul;13(5):436–438. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardanis A., Hudson A. J. Regulation of glycogen synthesis in human skeletal muscle: does cellular glycogen control glycogen synthase phosphatase activity? Biochem Int. 1991 Sep;25(2):289–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar-Palasi C. Substrate specific activation by glucose 6-phosphate of the dephosphorylation of muscle glycogen synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 12;1095(3):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90109-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Z., Spencer M. K., Katz A. Effect of low glycogen on glycogen synthase in human muscle during and after exercise. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Aug;145(4):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Mott D., Young A. A., Stone K., Bogardus C. Regulation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase activities by glucose and insulin in human skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):95–100. doi: 10.1172/JCI113069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Sahlin K., Ren J. M., Koivisto V. A. Localization of rate-limiting defect for glucose disposal in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant type I diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):157–167. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Young A. A., Lamkin C., Foley J. E. Kinetics of glucose disposal in whole body and across the forearm in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1713–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI113011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. A., Bogardus C., Stone K., Mott D. M. Insulin response of components of whole-body and muscle carbohydrate metabolism in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):E231–E236. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.2.E231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachwieja J. J., Costill D. L., Pascoe D. D., Robergs R. A., Fink W. J. Influence of muscle glycogen depletion on the rate of resynthesis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1991 Jan;23(1):44–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]