Abstract
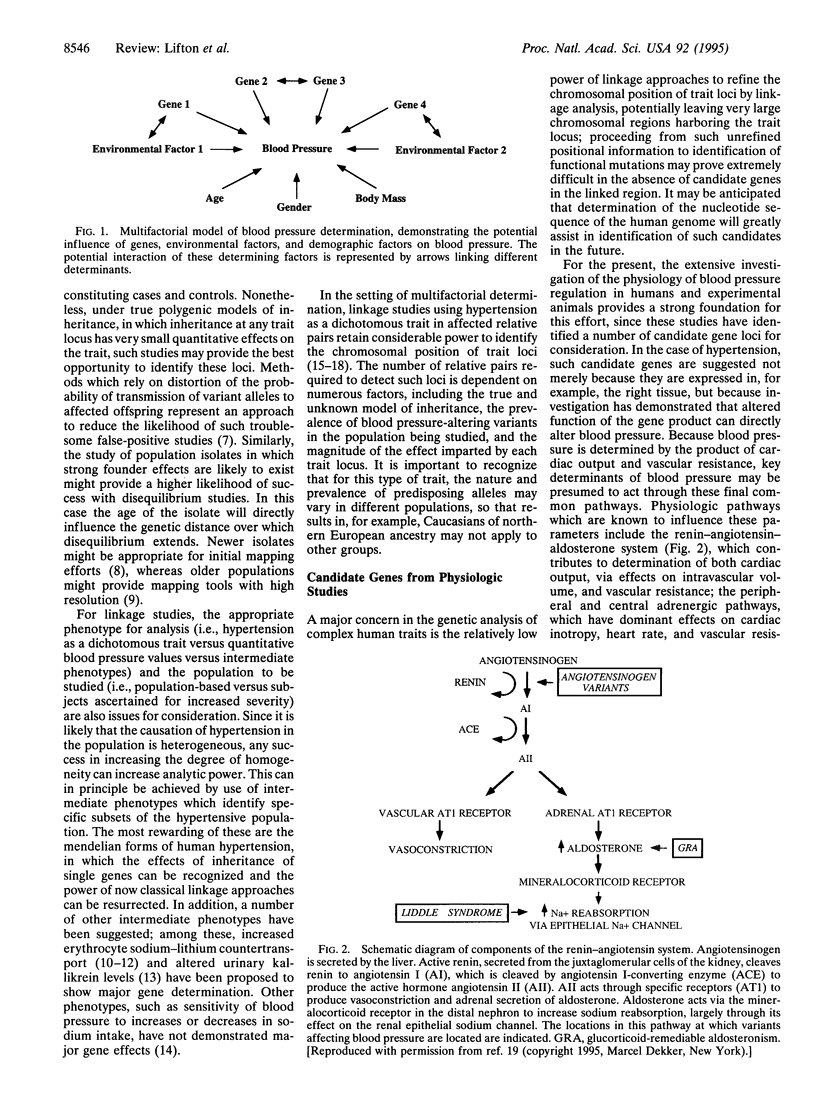
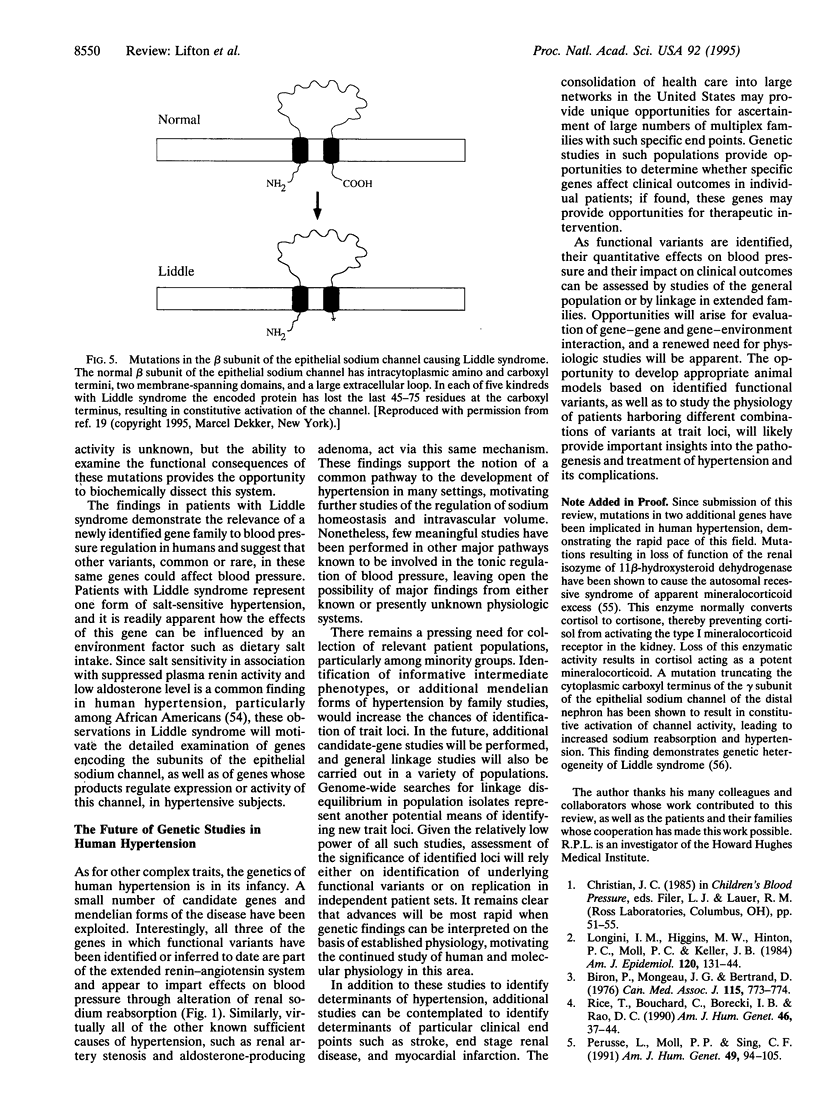
Hypertension is a common trait of multifactorial determination imparting an increased risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and end-stage renal disease. The primary determinants of hypertension, as well as the factors which determine specific morbid sequelae, remain unknown in the vast majority of subjects. Knowledge that a large fraction of the interindividual variation in this trait is genetically determined motivates the application of genetic approaches to the identification of these primary determinants. Success in this effort will afford insights into pathophysiology, permit preclinical identification of subjects with specific inherited susceptibility, and provide opportunities to tailor therapy to specific underlying abnormalities. To date, mutations in three genes have been implicated in the pathogenesis of human hypertension: mutations resulting in ectopic expression of aldosterone synthase enzymatic activity cause a mendelian form of hypertension known as glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism; mutations in the beta subunit of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel cause constitutive activation of this channel and the mendelian form of hypertension known as Liddle syndrome; finally, common variants at the angiotensinogen locus have been implicated in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension in Caucasian subjects, although the nature of the functional variants and their mechanism of action remain uncertain. These early findings demonstrate the feasibility and utility of the application of genetic analysis to dissection of this trait.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry T. D., Hasstedt S. J., Hunt S. C., Wu L. L., Smith J. B., Ash K. O., Kuida H., Williams R. R. A gene for high urinary kallikrein may protect against hypertension in Utah kindreds. Hypertension. 1989 Jan;13(1):3–8. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron P., Mongeau J. G., Bertrand D. Familial aggregation of blood pressure in 558 adopted children. Can Med Assoc J. 1976 Oct 23;115(8):773–774. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwelder W. C., Elston R. C. A comparison of sib-pair linkage tests for disease susceptibility loci. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(1):85–97. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnardeaux A., Davies E., Jeunemaitre X., Féry I., Charru A., Clauser E., Tiret L., Cambien F., Corvol P., Soubrier F. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms in human essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1994 Jul;24(1):63–69. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.24.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botero-Velez M., Curtis J. J., Warnock D. G. Brief report: Liddle's syndrome revisited--a disorder of sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 20;330(3):178–181. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401203300305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M., Lavender P., Farrall M., Munroe P., Lawson M., Turner P., Clark A. J. Linkage of the angiotensinogen gene to essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 9;330(23):1629–1633. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406093302301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C. Evidence for HL-A-linked genes in "juvenile" diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 19;3(5976):133–135. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5976.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Sanchez C. E., Montgomery M., Ganguly A., Holland O. B., Gomez-Sanchez E. P., Grim C. E., Weinberger M. H. Elevated urinary excretion of 18-oxocortisol in glucocorticoid-suppressible aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):1022–1024. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould A. B., Green D. Kinetics of the human renin and human substrate reaction. Cardiovasc Res. 1971 Jan;5(1):86–89. doi: 10.1093/cvr/5.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Wu L. L., Ash K. O., Kuida H., Williams R. R. Hypertension and sodium-lithium countertransport in Utah pedigrees: evidence for major-locus inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):14–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeunemaitre X., Lifton R. P., Hunt S. C., Williams R. R., Lalouel J. M. Absence of linkage between the angiotensin converting enzyme locus and human essential hypertension. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):72–75. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeunemaitre X., Rigat B., Charru A., Houot A. M., Soubrier F., Corvol P. Sib pair linkage analysis of renin gene haplotypes in human essential hypertension. Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;88(3):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00197264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeunemaitre X., Soubrier F., Kotelevtsev Y. V., Lifton R. P., Williams C. S., Charru A., Hunt S. C., Hopkins P. N., Williams R. R., Lalouel J. M. Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90275-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawainoto T., Mitsuuchi Y., Ohnishi T., Ichikawa Y., Yokoyama Y., Sumimoto H., Toda K., Miyahara K., Kuribayashi I., Nakao K. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for human cytochrome P-450aldo as related to primary aldosteronism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):309–316. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K. A test statistic for the affected-sib-set method. Ann Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;50(Pt 3):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1986.tb01049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
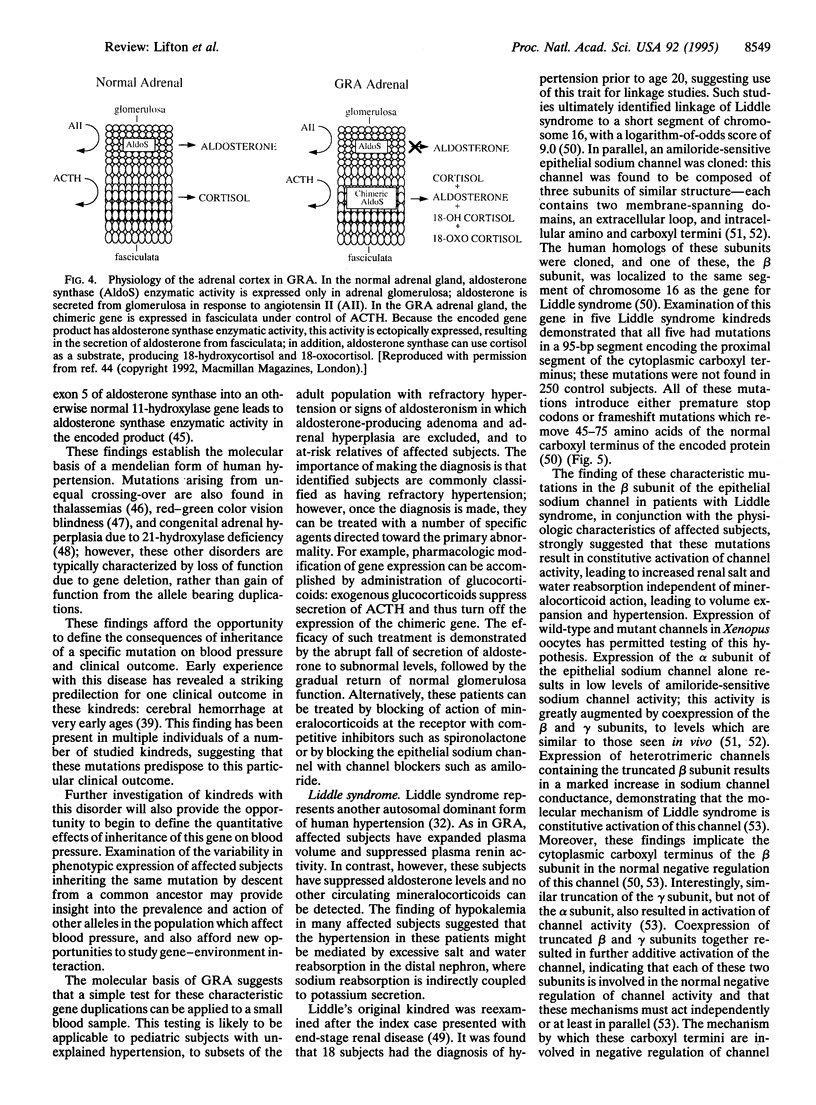
- Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G., Powers M., Rich G. M., Cook S., Ulick S., Lalouel J. M. A chimaeric 11 beta-hydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):262–265. doi: 10.1038/355262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G., Powers M., Rich G. M., Gutkin M., Fallo F., Gill J. R., Jr, Feld L., Ganguly A., Laidlaw J. C. Hereditary hypertension caused by chimaeric gene duplications and ectopic expression of aldosterone synthase. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):66–74. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longini I. M., Jr, Higgins M. W., Hinton P. C., Moll P. P., Keller J. B. Environmental and genetic sources of familial aggregation of blood pressure in Tecumseh, Michigan. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Jul;120(1):131–144. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Fritsch E. F., Lauer J., Lawn R. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobins. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:145–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet E., Dupont J., Vitek A., White P. C. Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta). J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20961–20967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky A. G., Burke W., Billings P. R., Ward R. H. Hypertension and the genetics of red cell membrane abnormalities. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;130:150–166. doi: 10.1002/9780470513507.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mune T., Rogerson F. M., Nikkilä H., Agarwal A. K., White P. C. Human hypertension caused by mutations in the kidney isozyme of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Nat Genet. 1995 Aug;10(4):394–399. doi: 10.1038/ng0895-394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabika T., Bonnardeaux A., James M., Julier C., Jeunemaitre X., Corvol P., Lathrop M., Soubrier F. Evaluation of the SA locus in human hypertension. Hypertension. 1995 Jan;25(1):6–13. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Sung C. H., Weitz C. J., Davenport C. M., Merbs S. L., Wang Y. Visual pigments and inherited variation in human vision. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1992;47:109–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. F., McCusker J. H., Sander M. A., Kee Y., Modrich P., Brown P. O. Genomic mismatch scanning: a new approach to genetic linkage mapping. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):11–18. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I., Peterson R. E. A new form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):300–305. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogishima T., Shibata H., Shimada H., Mitani F., Suzuki H., Saruta T., Ishimura Y. Aldosterone synthase cytochrome P-450 expressed in the adrenals of patients with primary aldosteronism. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10731–10734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascoe L., Curnow K. M., Slutsker L., Connell J. M., Speiser P. W., New M. I., White P. C. Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism results from hybrid genes created by unequal crossovers between CYP11B1 and CYP11B2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8327–8331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. H., Jones J. J., Miller J. Z., Wagner M. A., Fineberg N. S. Racial differences in aldosterone excretion and plasma aldosterone concentrations in children. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 26;321(17):1152–1157. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910263211703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérusse L., Moll P. P., Sing C. F. Evidence that a single gene with gender- and age-dependent effects influences systolic blood pressure determination in a population-based sample. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):94–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice T., Bouchard C., Borecki I. B., Rao D. C. Commingling and segregation analysis of blood pressure in a French-Canadian population. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):37–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich G. M., Ulick S., Cook S., Wang J. Z., Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G. Glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism in a large kindred: clinical spectrum and diagnosis using a characteristic biochemical phenotype. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 15;116(10):813–820. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-10-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits. III. The effect of marker polymorphism on analysis of affected relative pairs. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):242–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Kramer P., Almasy L., Singer B., Fahn S., Breakefield X., Bressman S. Genetic analysis of idiopathic torsion dystonia in Ashkenazi Jews and their recent descent from a small founder population. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):152–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild L., Canessa C. M., Shimkets R. A., Gautschi I., Lifton R. P., Rossier B. C. A mutation in the epithelial sodium channel causing Liddle disease increases channel activity in the Xenopus laevis oocyte expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets R. A., Warnock D. G., Bositis C. M., Nelson-Williams C., Hansson J. H., Schambelan M., Gill J. R., Jr, Ulick S., Milora R. V., Findling J. W. Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Maeda N. Gene targeting approaches to complex genetic diseases: atherosclerosis and essential hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5266–5272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman R. S., McGinnis R. E., Ewens W. J. Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;52(3):506–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. J., Ruse J. L., Laidlaw J. C. Hypertension, increased aldosterone secretion and low plasma renin activity relieved by dexamethasone. Can Med Assoc J. 1966 Nov 26;95(22):1109–1119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulick S., Chan C. K., Gill J. R., Jr, Gutkin M., Letcher L., Mantero F., New M. I. Defective fasciculata zone function as the mechanism of glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Nov;71(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-5-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulick S., Chu M. D., Land M. Biosynthesis of 18-oxocortisol by aldosterone-producing adrenal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5498–5502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward K., Hata A., Jeunemaitre X., Helin C., Nelson L., Namikawa C., Farrington P. F., Ogasawara M., Suzumori K., Tomoda S. A molecular variant of angiotensinogen associated with preeclampsia. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):59–61. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. C., Harrap S. B., Foy C. J., Holton D. W., Edwards H. V., Davidson H. R., Connor J. M., Lever A. F., Fraser R. Abnormalities of glucocorticoid metabolism and the renin-angiotensin system: a four-corners approach to the identification of genetic determinants of blood pressure. J Hypertens. 1992 May;10(5):473–482. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199205000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Vitek A., Dupont B., New M. I. Characterization of frequent deletions causing steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4436–4440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]