Abstract
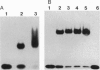
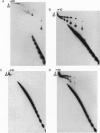
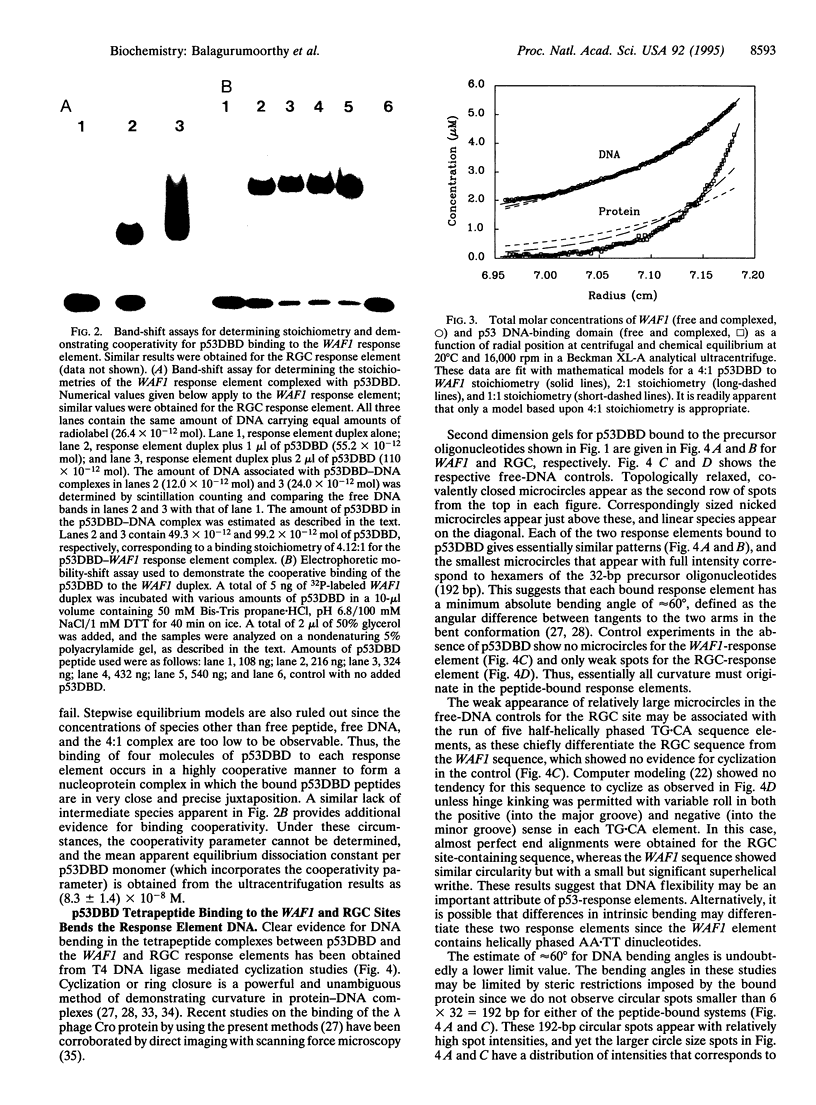
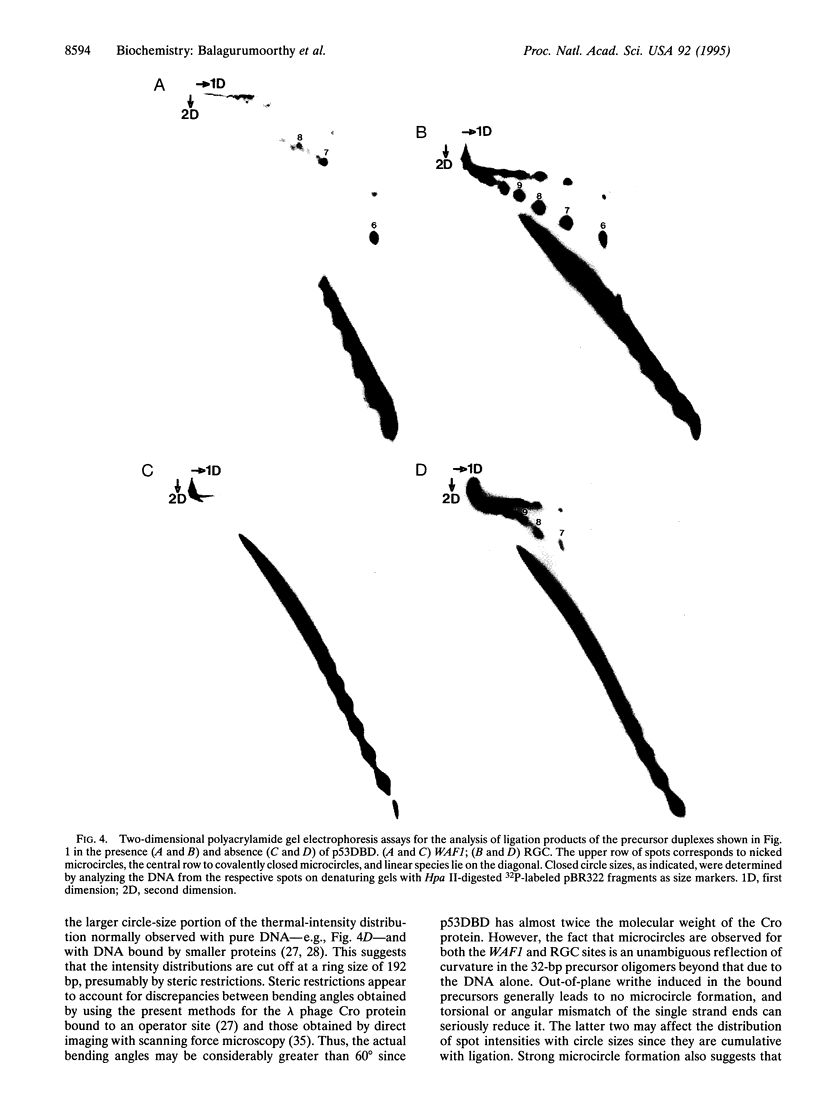
Recent structural studies of the minimal core DNA-binding domain of p53 (p53DBD) complexed to a single consensus pentamer sequence and of the isolated p53 tetramerization domain have provided valuable insights into their functions, but many questions about their interacting roles and synergism remain unanswered. To better understand these relationships, we have examined the binding of the p53DBD to two biologically important full-response elements (the WAF1 and ribosomal gene cluster sites) by using DNA circularization and analytical ultracentrifugation. We show that the p53DBD binds DNA strongly and cooperatively with p53DBD to DNA binding stoichiometries of 4:1. For the WAF1 element, the mean apparent Kd is (8.3 +/- 1.4) x 10(-8) M, and no intermediate species of lower stoichiometries can be detected. We show further that complex formation induces an axial bend of at least 60 degrees in both response elements. These results, taken collectively, demonstrate that p53DBD possesses the ability to direct the formation of a tight nucleoprotein complex having the same 4:1 DNA-binding stoichiometry as wild-type p53 which is accompanied by a substantial conformational change in the response-element DNA. This suggests that the p53DBD may play a role in the tetramerization function of p53. A possible role in this regard is proposed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Giant leap for p53, small step for drug design. Bioessays. 1995 Jan;17(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Reynisdóttir I., Friedman P. N., Prives C. Site-specific binding of wild-type p53 to cellular DNA is inhibited by SV40 T antigen and mutant p53. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1886–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brukner I., Susic S., Dlakic M., Savic A., Pongor S. Physiological concentration of magnesium ions induces a strong macroscopic curvature in GGGCCC-containing DNA. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):26–32. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y., Gorina S., Jeffrey P. D., Pavletich N. P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):346–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8023157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Omichinski J. G., Sakaguchi K., Zambrano N., Sakamoto H., Appella E., Gronenborn A. M. High-resolution structure of the oligomerization domain of p53 by multidimensional NMR. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):386–391. doi: 10.1126/science.8023159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Omichinski J. G., Sakaguchi K., Zambrano N., Sakamoto H., Appella E., Gronenborn A. M. Interhelical angles in the solution structure of the oligomerization domain of p53: correction. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1515–1516. doi: 10.1126/science.7878474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erie D. A., Yang G., Schultz H. C., Bustamante C. DNA bending by Cro protein in specific and nonspecific complexes: implications for protein site recognition and specificity. Science. 1994 Dec 2;266(5190):1562–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.7985026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Chen X., Bargonetti J., Prives C. The p53 protein is an unusually shaped tetramer that binds directly to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt M. S., Bennett W. P., Hollstein M., Harris C. C. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4855–4878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Davis L. J., Kandil A. N. Wild-type p53 adopts a 'mutant'-like conformation when bound to DNA. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Conformational shifts propagate from the oligomerization domain of p53 to its tetrameric DNA binding domain and restore DNA binding to select p53 mutants. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5057–5064. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. R., Milner J. Structural and kinetic analysis of p53-DNA complexes and comparison of human and murine p53. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 2;10(3):561–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R. E. DNA curving and bending in protein-DNA recognition. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2549–2555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R. E. Studies of DNA bending and flexibility using gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 1993 Aug;14(8):732–746. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501401116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Kastan M. B. Cell cycle control and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1821–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.7997877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D., Gorina S., Pavletich N. P. Crystal structure of the tetramerization domain of the p53 tumor suppressor at 1.7 angstroms. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1498–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.7878469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Crothers D. M. Protein-induced bending and DNA cyclization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Tsukiyama T., Lewis M. S., Wu C. Interaction of the DNA-binding domain of Drosophila heat shock factor with its cognate DNA site: a thermodynamic analysis using analytical ultracentrifugation. Protein Sci. 1994 Jul;3(7):1040–1051. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Harvey T. S., Yin Y., Yau P., Litchfield D., Arrowsmith C. H. Solution structure of the tetrameric minimum transforming domain of p53. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;1(12):877–890. doi: 10.1038/nsb1294-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The tumor suppressor genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:623–651. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y., Shlyakhtenko L., Chernov B., Harrington R. E. DNA bending induced by Cro protein binding as demonstrated by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5331–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. Forms and functions of p53. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Jun;5(3):211–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Chambers K. A., Pabo C. O. The DNA-binding domain of p53 contains the four conserved regions and the major mutation hot spots. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2556–2564. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. How loops, beta sheets, and alpha helices help us to understand p53. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):543–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Manfredi J. J. The p53 tumor suppressor protein: meeting review. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):529–534. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Lewis M. S., Kodama H., Appella E., Sakaguchi K. Specific sequences from the carboxyl terminus of human p53 gene product form anti-parallel tetramers in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8974–8978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger J. E., Tegtmeyer P., Mayr G. A., Reed M., Wang Y., Wang P., Hough P. V., Mastrangelo I. A. p53 oligomerization and DNA looping are linked with transcriptional activation. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6011–6020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06947.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokino T., Thiagalingam S., el-Deiry W. S., Waldman T., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. p53 tagged sites from human genomic DNA. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Sep;3(9):1537–1542. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.9.1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Schwedes J. F., Parks D., Mann K., Tegtmeyer P. Interaction of p53 with its consensus DNA-binding site. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):2157–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman J. L., Shenk J. L., Halazonetis T. D. The dihedral symmetry of the p53 tetramerization domain mandates a conformational switch upon DNA binding. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):512–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Direct evidence for DNA bending at the lambda replication origin. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):416–422. doi: 10.1126/science.2951850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]