Abstract
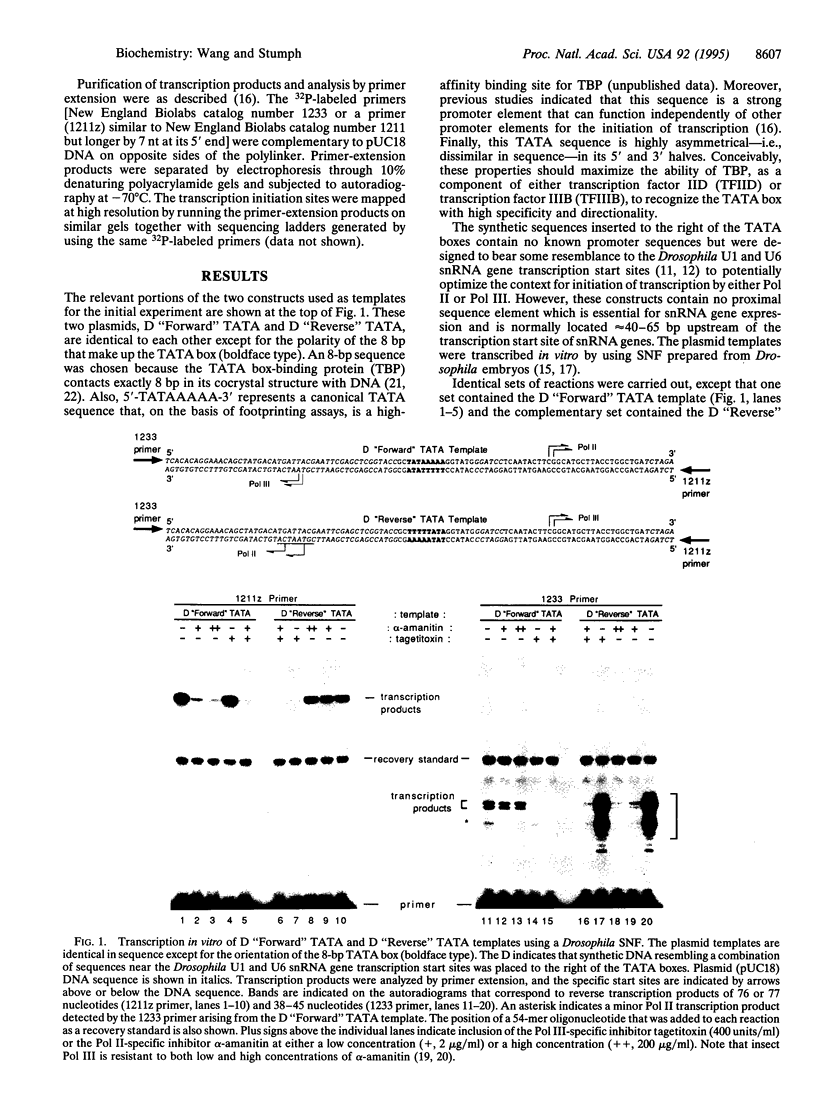
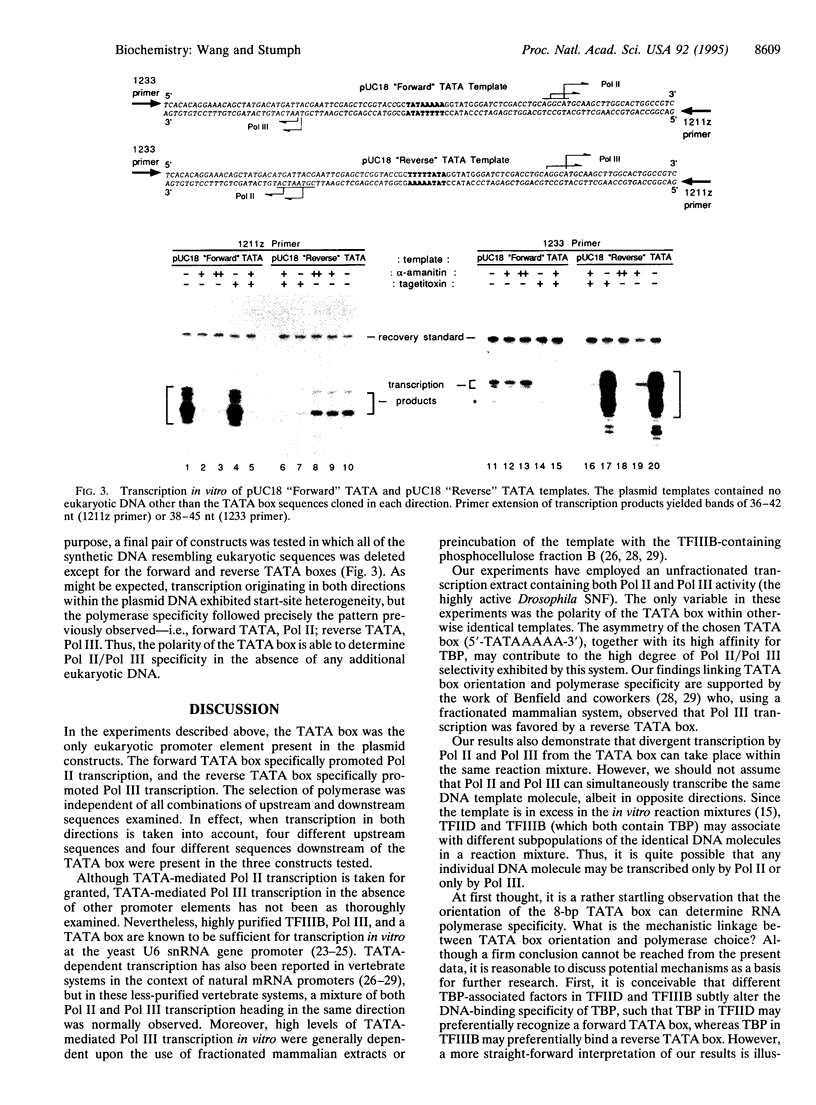
The TATA box sequence in eukaryotes is located about 25 bp upstream of many genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and some genes transcribed by RNA polymerase III (Pol III). The TATA box is recognized in a sequence-specific manner by the TATA box-binding protein (TBP), an essential factor involved in the initiation of transcription by all three eukaryotic RNA polymerases. We have investigated the recognition of the TATA box by the Pol II and Pol III basal transcription machinery and its role in establishing the RNA polymerase specificity of the promoter. Artificial templates were constructed that contained a canonical TATA box as the sole promoter element but differed in the orientation of the 8-bp TATA box sequence. As expected, Pol II initiated transcription in unfractionated nuclear extracts downstream of the "forward" TATA box. In distinct contrast, transcription that initiated downstream of the "reverse" TATA box was carried out specifically by Pol III. Importantly, this effect was observed regardless of the source of the DNA either upstream or downstream of the TATA sequence. These findings suggest that TBP may bind in opposite orientations on Pol II and Pol III promoters and that opposite, yet homologous, surfaces of TBP may be utilized by the Pol II and Pol III basal machinery for the initiation of transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Brown W. L., Groudine M. Accurate, TATA box-dependent polymerase III transcription from promoters of the c-myc gene in injected Xenopus oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1179–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sussman D. J., Zeller R., Leder P. The c-myc gene encodes superimposed RNA polymerase II and III promoters. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. How does III x II make U6? Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1462–1463. doi: 10.1126/science.1962205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Reddy R. Structure, organization, and transcription of Drosophila U6 small nuclear RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1187–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. D., O'Connell A. M., Sharp S. J. Formation of an active transcription complex in the Drosophila melanogaster 5S RNA gene is dependent on an upstream region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2046–2051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach V. L., Whitehall S. K., Geiduschek E. P., Brow D. A. TFIIIB placement on a yeast U6 RNA gene in vivo is directed primarily by TFIIIC rather than by sequence-specific DNA contacts. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1455–1466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Conesa C., Manaud N., Chaussivert N., Sentenac A. Interactions between yeast TFIIIB components. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jun 25;22(12):2282–2288. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.12.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R. Genomic footprinting of a yeast tRNA gene reveals stable complexes over the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3244–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joazeiro C. A., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Identical components of yeast transcription factor IIIB are required and sufficient for transcription of TATA box-containing and TATA-less genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2798–2808. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Kadonaga J. T. The soluble nuclear fraction, a highly efficient transcription extract from Drosophila embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;44:225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60916-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Tyree C. M., Kadonaga J. T. Accurate and efficient RNA polymerase II transcription with a soluble nuclear fraction derived from Drosophila embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann J., Smale S. T. Direct recognition of initiator elements by a component of the transcription factor IID complex. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):821–829. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo B., Brophy B., Jackson S. P. Conserved functional domains of the RNA polymerase III general transcription factor BRF. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 1;8(23):2879–2890. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.23.2879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Maser R. L., Calvet J. P., Pederson T. U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8575–8579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D., Bradford-Wilcox J., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A short 5' flanking region containing conserved sequences is required for silkworm alanine tRNA gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3416–3420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo P. C., Mount S. M. Drosophila melanogaster genes for U1 snRNA variants and their expression during development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6971–6979. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Human U1 loci: genes for human U1 RNA have dramatically similar genomic environments. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Chiang C. M., Ge H., Roeder R. G. TATA-binding protein-associated factor(s) in TFIID function through the initiator to direct basal transcription from a TATA-less class II promoter. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3115–3126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. TATA box-mediated in vitro transcription by RNA polymerase III. Evidence for TATA-binding protein in a polymerase III type complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1141–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. T., Hobson G. M., Benfield P. A. TATA box-mediated polymerase III transcription in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1995–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. G., Sprague K. U. In vitro transcription of a silkworm 5S RNA gene requires an upstream signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5519–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov D. B., Hu S. H., Lin J., Gasch A., Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Chua N. H., Roeder R. G., Burley S. K. Crystal structure of TFIID TATA-box binding protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):40–46. doi: 10.1038/360040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S., Colbert T., Hahn S. TFIIIC determines RNA polymerase III specificity at the TATA-containing yeast U6 promoter. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 1;9(7):832–842. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.7.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Stevens J. N., Metzenberg R. L. An upstream signal is required for in vitro transcription of Neurospora 5S RNA genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):189–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02428052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Gage L. P., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase III from the posterior silk gland of Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3794–3800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Mathews D. E., Durbin R. D., Burgess R. R. Tagetitoxin: a new inhibitor of eukaryotic transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Yokomori K., Chen J. L., Tjian R. Drosophila TAFII150: similarity to yeast gene TSM-1 and specific binding to core promoter DNA. Science. 1994 May 13;264(5161):933–941. doi: 10.1126/science.8178153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamrod Z., Tyree C. M., Song Y., Stumph W. E. In vitro transcription of a Drosophila U1 small nuclear RNA gene requires TATA box-binding protein and two proximal cis-acting elements with stringent spacing requirements. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5918–5927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]