Abstract
Different autoantigens are thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and they may account for the variation in the clinical presentation of the disease. Sera from patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I contain autoantibodies against the beta-cell proteins glutamate decarboxylase and an unrelated 51-kDa antigen. By screening of an expression library derived from rat insulinoma cells, we have identified the 51-kDa protein as aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.28). In addition to the previously published full-length cDNA, forms coding for a truncated and an alternatively spliced version were identified. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-5-hydroxytryptophan to serotonin and that of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine to dopamine. Interestingly, pyridoxal phosphate is the cofactor of both aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase and glutamate decarboxylase. The biological significance of the neurotransmitters produced by the two enzymes in the beta cells remains largely unknown.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahonen P., Myllärniemi S., Sipilä I., Perheentupa J. Clinical variation of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) in a series of 68 patients. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 28;322(26):1829–1836. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006283222601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A. Isolated mouse pancreatic islets in culture: effects of serum and different culture media on the insulin production of the islets. Diabetologia. 1978 Jun;14(6):397–404. doi: 10.1007/BF01228134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Bowman M. A., Campbell L., Darrow B. L., Kaufman D. L., Maclaren N. K. Cellular immunity to a determinant common to glutamate decarboxylase and coxsackie virus in insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):2125–2129. doi: 10.1172/JCI117567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Kaufman D. L., Campbell L., Gibbs K. A., Shah S. C., Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J., Maclaren N. K. Response of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells to glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1992 Feb 22;339(8791):458–459. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91061-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Riley W. J. 64,000 Mr autoantibodies as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jun 9;335(8702):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Landin M., Kristensen J. K., Srikanta S., Bruining G. J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., de Beaufort C., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G., Lindgren F. Antibodies to a 64,000 Mr human islet cell antigen precede the clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):926–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI112903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk E., Velloso L. A., Kämpe O., Karlsson F. A. GAD autoantibodies in IDDM, stiff-man syndrome, and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I recognize different epitopes. Diabetes. 1994 Jan;43(1):161–165. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK C. T., WEISSBACH H., UDENFRIEND S. 5-Hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase: preparation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1954 Sep;210(1):139–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christenson J. G., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. On the identity of DOPA decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase (immunological titration-aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-serotonin-dopamine-norepinephrine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):343–347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Honeyman M. C., DeAizpurua H. J., Schmidli R. S., Colman P. G., Tait B. D., Cram D. S. Inverse relation between humoral and cellular immunity to glutamic acid decarboxylase in subjects at risk of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1993 May 29;341(8857):1365–1369. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90940-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger C. B., Teitelman G., Joh T. H., Albert V. R., Park D. H., Reis D. J. Some neurons of the rat central nervous system contain aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase but not monoamines. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1233–1235. doi: 10.1126/science.6131537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang U. J., Joh T. H. Deduced amino acid sequence of bovine aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase: homology to other decarboxylases. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Jun;8(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Coge F., Gros F., Thibault J. Different mRNAs code for dopa decarboxylase in tissues of neuronal and nonneuronal origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2161–2165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpe O., Andersson A., Björk E., Hallberg A., Karlsson F. A. High-glucose stimulation of 64,000-Mr islet cell autoantigen expression. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1326–1328. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I., Panagiotidis G., Stenström A. Effect of L-dopa administration on islet monoamine oxidase activity and glucose-induced insulin release in the mouse. Pancreas. 1991 Sep;6(5):522–527. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199109000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Regulated splicing produces different forms of dopa decarboxylase in the central nervous system and hypoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3335–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld M., Maclaren N., Blizzard R. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Pediatr Ann. 1980 Apr;9(4):154–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Weir G. C., Baylin S. B. Clonal analysis of insulin and somatostatin secretion and L-dopa decarboxylase expression by a rat islet cell tumor. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):1070–1075. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R., Wesslau C., William-Olsson T., Zettergren L. Elevated aminotransferases and alkaline phosphatases in unstable diabetes mellitus without ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;11(5):541–545. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198910000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman M. K., Nagatsu T., Kato T. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase activity in central and peripheral tissues and serum of rats with L-DOPA and L-5-hydroxytryptophan as substrates. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 15;30(6):645–649. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reetz A., Solimena M., Matteoli M., Folli F., Takei K., De Camilli P. GABA and pancreatic beta-cells: colocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA with synaptic-like microvesicles suggests their role in GABA storage and secretion. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1275–1284. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siow Y. L., Dakshinamurti K. Effect of pyridoxine deficiency on aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in adult rat brain. Exp Brain Res. 1985;59(3):575–581. doi: 10.1007/BF00261349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solimena M., Folli F., Aparisi R., Pozza G., De Camilli P. Autoantibodies to GABA-ergic neurons and pancreatic beta cells in stiff-man syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 31;322(22):1555–1560. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005313222202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y. H., Connor E., Li Y., Zorovich B., Balducci P., Maclaren N. The role of tyrosinase in autoimmune vitiligo. Lancet. 1994 Oct 15;344(8929):1049–1052. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91709-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. L., Garry D. G., Brelje T. C. Structural and functional considerations of GABA in islets of Langerhans. Beta-cells and nerves. Diabetes. 1991 Nov;40(11):1365–1374. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.11.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies in pathology and cell biology. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):841–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Horio Y., Taketoshi M., Imamura I., Ando-Yamamoto M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kuroda M., Wada H. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA of rat dopa decarboxylase: partial amino acid homologies with other enzymes synthesizing catecholamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8142–8146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian J., Lehmann P. V., Kaufman D. L. T cell cross-reactivity between coxsackievirus and glutamate decarboxylase is associated with a murine diabetes susceptibility allele. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1979–1984. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velloso L. A., Kämpe O., Hallberg A., Christmanson L., Betsholtz C., Karlsson F. A. Demonstration of GAD-65 as the main immunogenic isoform of glutamate decarboxylase in type 1 diabetes and determination of autoantibodies using a radioligand produced by eukaryotic expression. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2084–2090. doi: 10.1172/JCI116431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
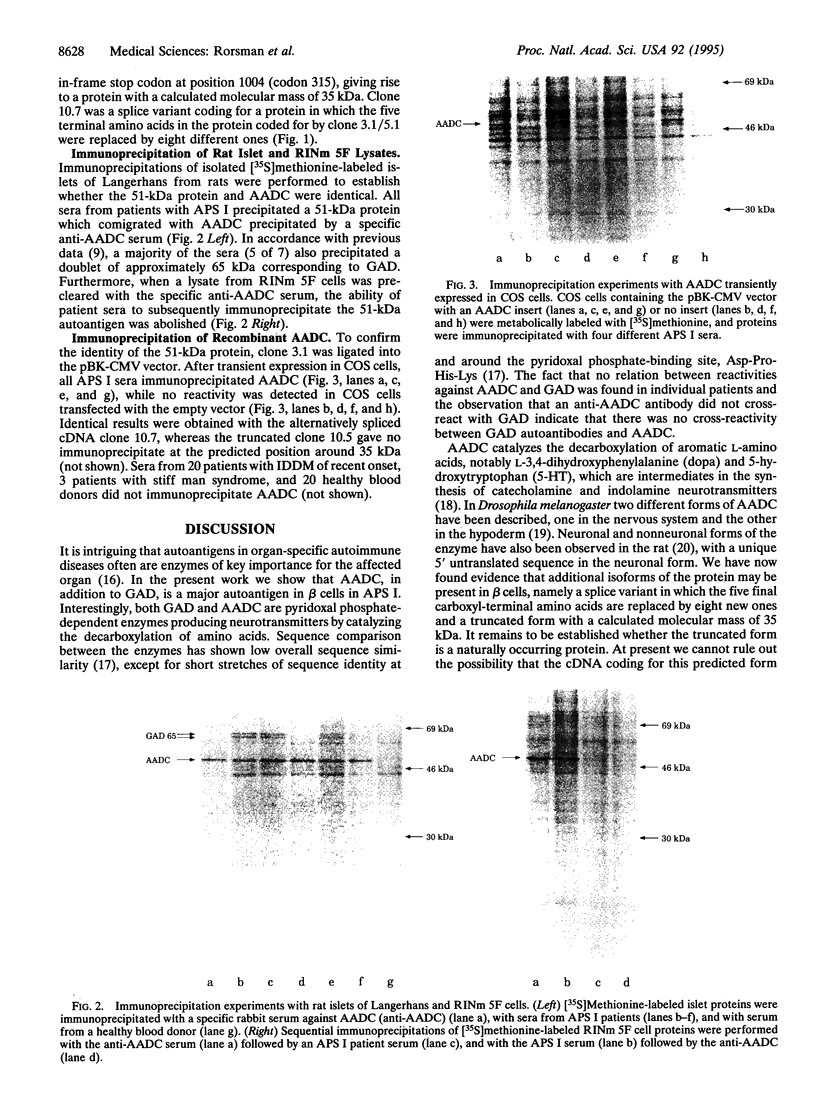
- Velloso L. A., Winqvist O., Gustafsson J., Kämpe O., Karlsson F. A. Autoantibodies against a novel 51 kDa islet antigen and glutamate decarboxylase isoforms in autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. Diabetologia. 1994 Jan;37(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00428779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winqvist O., Gebre-Medhin G., Gustafsson J., Ritzén E. M., Lundkvist O., Karlsson F. A., Kämpe O. Identification of the main gonadal autoantigens in patients with adrenal insufficiency and associated ovarian failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 May;80(5):1717–1723. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.5.7745025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winqvist O., Gustafsson J., Rorsman F., Karlsson F. A., Kämpe O. Two different cytochrome P450 enzymes are the adrenal antigens in autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I and Addison's disease. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2377–2385. doi: 10.1172/JCI116843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]