Abstract
Using SDS/polyacrylamide gels that contained myelin basic protein, we identified a 46-kDa protein kinase in tobacco that is transiently activated by cutting. Although the activity of the kinase was rarely detectable in mature leaves, marked activity became apparent within several minutes after isolation of leaf discs and subsided within 30 min. In the presence of cycloheximide (CHX), the kinase activity did not diminish after the isolation over the course of 2 hr, suggesting that protein synthesis was not required for the activation of the kinase. A second cutting of leaf discs between 30 min and 60 min after the isolation failed to activate the kinase, whereas a second cutting given 3 hr after isolation apparently activated the kinase. These results suggest that the 46-kDa protein kinase is desensitized immediately after the first activation, which can be blocked by CHX, but the response ability recovers with time. When protein extracts containing the active kinase were treated with serine/threonine-specific or tyrosine-specific protein phosphatase, the kinase activity was abolished. After immunoprecipitation with antibody against phosphotyrosine, activity of the kinase was recovered in the immunoprecipitate. These results suggest that the active form of the kinase is phosphorylated at both serine/threonine and tyrosine residues. It seems likely that the 46-kDa protein kinase can be activated by dual phosphorylation. The activity of a 46-kDa protein kinase was also detected in leaves of a wide variety of plant species including dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. We propose the name PMSAP (plant multisignal-activated protein) kinase for this kinase because the kinase was also activated by various signals other than cutting.
Full text
PDF
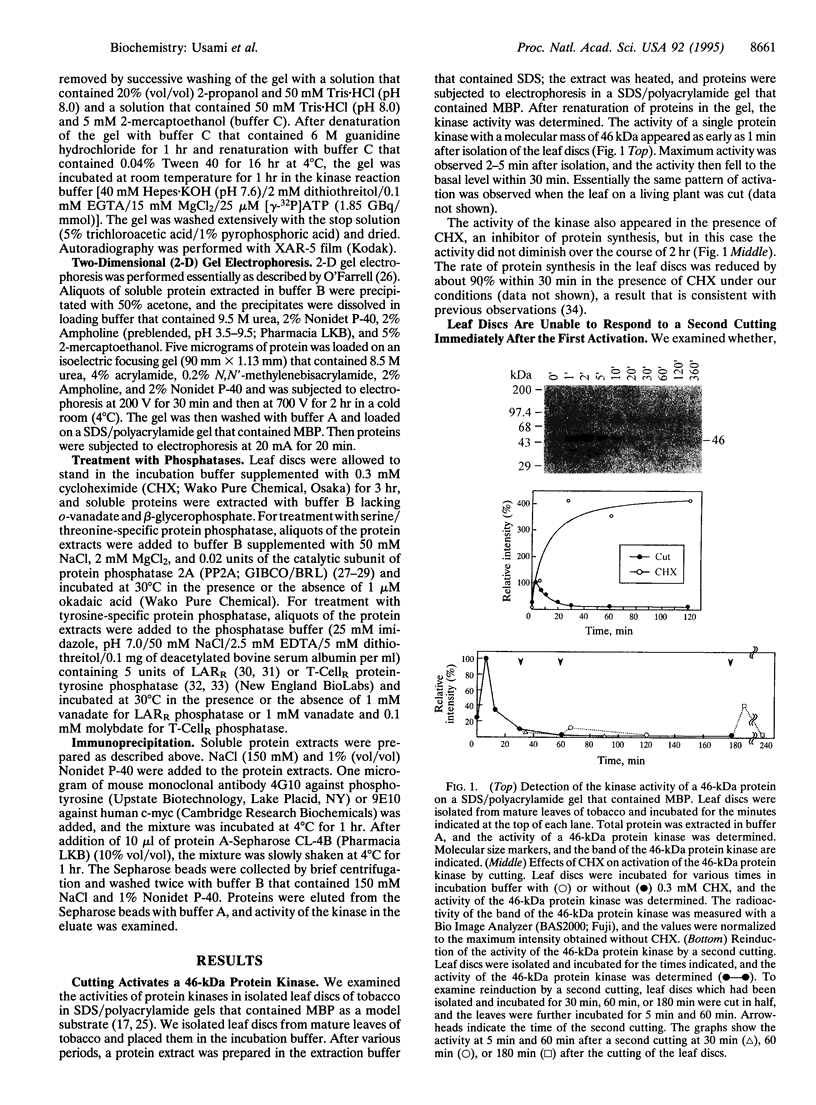



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi D. R., Smythe C., Keyse S. M. The human CL100 gene encodes a Tyr/Thr-protein phosphatase which potently and specifically inactivates MAP kinase and suppresses its activation by oncogenic ras in Xenopus oocyte extracts. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):2015–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno H., Hirano K., Nakamura T., Irie K., Nomoto S., Matsumoto K., Machida Y. NPK1, a tobacco gene that encodes a protein with a domain homologous to yeast BCK1, STE11, and Byr2 protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4745–4752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. Diversity in function and regulation of MAP kinase pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jun;19(6):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles D. J. Local and systemic signals in the wound response. Semin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;4(2):103–111. doi: 10.1006/scel.1993.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kwok S. F., Bleecker A. B., Meyerowitz E. M. Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.8211181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ramer S. E., Itoh M., Winkler D. G., Kitas E., Bannwarth W., Burn P., Saito H., Walsh C. T. Purification and characterization of a soluble catalytic fragment of the human transmembrane leukocyte antigen related (LAR) protein tyrosine phosphatase from an Escherichia coli expression system. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6210–6216. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich A., Mayer J. E., Hahlbrock K. Fungal elicitor triggers rapid, transient, and specific protein phosphorylation in parsley cell suspension cultures. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6360–6368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi K., Gartner A., Ammerer G., Errede B., Shinkawa H., Sugimoto K., Matsumoto K. MSG5, a novel protein phosphatase promotes adaptation to pheromone response in S. cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):61–70. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr B., Gawienowski M., Ropp T., Jacobs T. MsERK1: a mitogen-activated protein kinase from a flowering plant. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):87–96. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Weinberg R. A. The pathway to signal achievement. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):781–783. doi: 10.1038/365781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. In vitro phosphorylation of plant plasma membrane proteins in response to the proteinase inhibitor inducing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1539–1542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix G., Grosskopf D. G., Regenass M., Boller T. Rapid changes of protein phosphorylation are involved in transduction of the elicitor signal in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8831–8834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Banno H., Moribe T., Hinata K., Machida Y. NPK15, a tobacco protein-serine/threonine kinase with a single hydrophobic region near the amino-terminus. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Oct 17;245(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00279745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak C., Heberle-Bors E., Hirt H. MAP kinases: universal multi-purpose signaling tools. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Feb;24(3):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00024109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak C., Páy A., Bögre L., Hirt H., Heberle-Bors E. The plant homologue of MAP kinase is expressed in a cell cycle-dependent and organ-specific manner. Plant J. 1993 Apr;3(4):611–617. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.03040611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. A sensitive method for detection of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieber J. J., Rothenberg M., Roman G., Feldmann K. A., Ecker J. R. CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the raf family of protein kinases. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):427–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90119-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Green P. J., Wong M., Chua N. H. Phytochrome activation of two nuclear genes requires cytoplasmic protein synthesis. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2777–2783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. Y., Dailey D., Martin G. S., Thorner J. Yeast MCK1 protein kinase autophosphorylates at tyrosine and serine but phosphorylates exogenous substrates at serine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21155–21164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. B., Brommonschenkel S. H., Chunwongse J., Frary A., Ganal M. W., Spivey R., Wu T., Earle E. D., Tanksley S. D. Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1432–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.7902614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer-Jaekel R. E., Hemmings B. A. Protein phosphatase 2A--a 'ménage à trois'. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;4(8):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Hayashida N., Iwasaki T., Kamada H., Shinozaki K. Characterization of two cDNAs that encode MAP kinase homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana and analysis of the possible role of auxin in activating such kinase activities in cultured cells. Plant J. 1994 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.5010111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi T., Hayashida N., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Kamada H., Shinozaki K. ATMPKs: a gene family of plant MAP kinases in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80852-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M. Conservation and reiteration of a kinase cascade. Trends Genet. 1993 Nov;9(11):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A. The search for the proteinase inhibitor-inducing factor, PIIF. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):123–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00015610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata W., Banno H., Ito Y., Hirano K., Irie K., Usami S., Machida C., Machida Y. A tobacco protein kinase, NPK2, has a domain homologous to a domain found in activators of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKKs). Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Feb 20;246(4):401–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00290443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda N., Toyoda-Yamamoto A., Nagamine J., Usami S., Katayama M., Sakagami Y., Machida Y. Control of expression of Agrobacterium vir genes by synergistic actions of phenolic signal molecules and monosaccharides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6684–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh T. J. Insulin receptor serine kinase activation by casein kinase 2 and a membrane tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 Apr 21;121(2):167–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00925976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafstrom J. P., Altschuler M., Anderson D. H. Molecular cloning and expression of a MAP kinase homologue from pea. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Apr;22(1):83–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00038997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Charles C. H., Lau L. F., Tonks N. K. MKP-1 (3CH134), an immediate early gene product, is a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase in vivo. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Shinshi H. Transient Activation and Tyrosine Phosphorylation of a Protein Kinase in Tobacco Cells Treated with a Fungal Elicitor. Plant Cell. 1995 May;7(5):639–647. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.5.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai A. Y., Itoh M., Streuli M., Thai T., Saito H. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive and thermostable mutants of the human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase LAR. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10534–10543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Eller N., Gartner A., Vicente O., Heberle-Bors E. Isolation and characterization of a tobacco cDNA clone encoding a putative MAP kinase. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Nov;23(3):543–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00019302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa T., Muto S. Ca(2+)-dependent protein kinase from the halotolerant green alga Dunaliella tertiolecta: partial purification and Ca(2+)-dependent association of the enzyme to the microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jul;296(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90560-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zander N. F., Lorenzen J. A., Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Daum G., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Purification and characterization of a human recombinant T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase from a baculovirus expression system. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6964–6970. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Dephosphorylation and inactivation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase by a mitogen-induced Thr/Tyr protein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16116–16119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]