Abstract
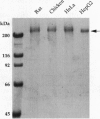
Fatty acid synthase (FAS; EC 2.3.1.85) was purified to near homogeneity from a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. The HepG2 FAS has a specific activity of 600 nmol of NADPH oxidized per min per mg, which is about half that of chicken liver FAS. All the partial activities of human FAS are comparable to those of other animal FASs, except for the beta-ketoacyl synthase, whose significantly lower activity is attributable to the low 4'-phosphopantetheine content of HepG2 FAS. We cloned the human brain FAS cDNA. The cDNA sequence has an open reading frame of 7512 bp that encodes 2504 amino acids (M(r), 272,516). The amino acid sequence of the human FAS has 79% and 63% identity, respectively, with the sequences of the rat and chicken enzymes. Northern analysis revealed that human FAS mRNA was about 9.3 kb in size and that its level varied among human tissues, with brain, lung, and liver tissues showing prominent expression. The nucleotide sequence of a segment of the HepG2 FAS cDNA (bases 2327-3964) was identical to that of the cDNA from normal human liver and brain tissues, except for a 53-bp sequence (bases 3892-3944) that does not alter the reading frame. This altered sequence is also present in HepG2 genomic DNA. The origin and significance of this sequence variance in the HepG2 FAS gene are unclear, but the variance apparently does not contribute to the lower activity of HepG2 FAS.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amy C. M., Witkowski A., Naggert J., Williams B., Randhawa Z., Smith S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of cDNAs encoding the entire rat fatty acid synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3114–3118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian S. A., Arslanian M. J., Wakil S. J. Comparative studies on the kinetic parameters and product analyses of chicken and rat liver and yeast fatty acid synthetase. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;71(4):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90465-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arslanian M. J., Wakil S. J. Fatty acid synthase from chicken liver. Methods Enzymol. 1975;35:59–65. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)35138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirala S. S., Kasturi R., Pazirandeh M., Stolow D. T., Huang W. Y., Wakil S. J. A novel cDNA extension procedure. Isolation of chicken fatty acid synthase cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3750–3757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G. E., Andres H., Weiss L., Kreisel C., Sander R. Properties and organ distribution of ATP citrate (pro-3S)-lyase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 6;620(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. Y., Chirala S. S., Wakil S. J. Amino-terminal blocking group and sequence of the animal fatty acid synthase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Oct;314(1):45–49. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar A., Chirala S. S., Chinault A. C., Baldini A., Abu-Elheiga L., Wakil S. J. Isolation and chromosomal mapping of genomic clones encoding the human fatty acid synthase gene. Genomics. 1994 Sep 15;23(2):420–424. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. K., Smith S. Construction, expression, and characterization of a mutated animal fatty acid synthase deficient in the dehydrase function. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22508–22513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda K., Goodridge A. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the gene for goose fatty acid synthase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):419–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhajda F. P., Jenner K., Wood F. D., Hennigar R. A., Jacobs L. B., Dick J. D., Pasternack G. R. Fatty acid synthesis: a potential selective target for antineoplastic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazirandeh M., Chirala S. S., Wakil S. J. Site-directed mutagenesis studies on the recombinant thioesterase domain of chicken fatty acid synthase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20946–20952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncari D. A., Mack E. Y. Mammalian fatty acid synthetase. III. Characterization of human liver synthetase products and kinetics of methylmalonyl-CoA inhibition. Can J Biochem. 1976 Nov;54(11):923–926. doi: 10.1139/o76-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncari D. A. Mammalian fatty acid synthetase. I. Purification and properties of human liver complex. Can J Biochem. 1974 Mar;52(3):221–230. doi: 10.1139/o74-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncari D. A. Mammalian fatty acid synthetase. II. Modification of purified human liver complex activity. Can J Biochem. 1975 Feb;53(2):135–142. doi: 10.1139/o75-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer M., Takabayashi K., Laux T., Beck K. F., Schreglmann R. Rat mammary gland fatty acid synthase: localization of the constituent domains and two functional polyadenylation/termination signals in the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):567–586. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenkovich C. F., Coleman T., Goforth R. Physiologic concentrations of glucose regulate fatty acid synthase activity in HepG2 cells by mediating fatty acid synthase mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):6961–6970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrago E., Spennetta T., Gordon E. Fatty acid synthesis in human adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 25;244(10):2761–2766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. B., Jordan P. M. Purification and properties of 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase from Penicillium patulum. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):839–846. doi: 10.1042/bj2880839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoops J. K., Awad E. S., Arslanian M. J., Gunsberg S., Wakil S. J., Oliver R. M. Studies on the yeast fatty acid synthetase. Subunit composition and structural organization of a large multifunctional enzyme complex. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4464–4475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoops J. K., Ross P., Arslanian M. J., Aune K. C., Wakil S. J., Oliver R. M. Physicochemical studies of the rat liver and adipose fatty acid synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7418–7426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoops J. K., Wakil S. J. Animal fatty acid synthetase. A novel arrangement of the beta-ketoacyl synthetase sites comprising domains of the two subunits. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5128–5133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoops J. K., Wakil S. J. The isolation of the two subunits of yeast fatty acid synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 14;84(1):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90286-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai M. H., Chirala S. S., Wakil S. J. Roles of Ser101, Asp236, and His237 in catalysis of thioesterase II and of the C-terminal region of the enzyme in its interaction with fatty acid synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1852–1856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. J., Stern A., Smith S. Purification and properties of fatty acid synthetase from a human breast cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 13;662(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweto J., Larrabee A. R. The effect of fasting on synthesis and 4'-phosphopantetheine exchange in rat liver fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4900–4904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweto J., Liberati M., Larrabee A. R. Protein turnover and 4'-phosphopantetheine exchange in rat liver fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2468–2471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Vagelos P. R. Fatty acid synthetase of mammalian brain, liver and adipose tissue. Regulation by prosthetic group turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakil S. J. Fatty acid synthase, a proficient multifunctional enzyme. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4523–4530. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Hoffmann G. E., Schreiber R., Andres H., Fuchs E., Körber E., Kolb H. J. Fatty-acid biosynthesis in man, a pathway of minor importance. Purification, optimal assay conditions, and organ distribution of fatty-acid synthase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Sep;367(9):905–912. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H., Mattick J. S., Wakil S. J. The architecture of the animal fatty acid synthetase. III. Isolation and characterization of beta-ketoacyl reductase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15305–15311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelewski M., Swierczyński J. Comparative studies on lipogenic enzyme activities in the liver of human and some animal species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;95(3):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(90)90004-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]