Abstract
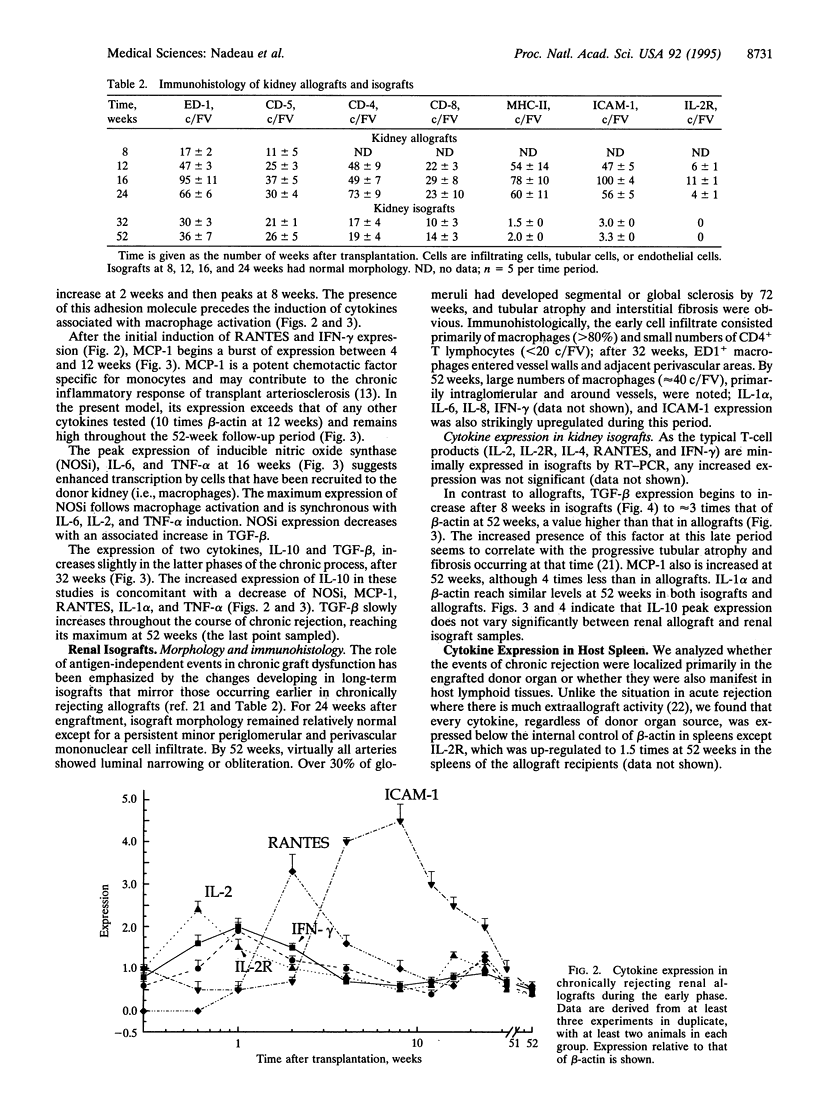
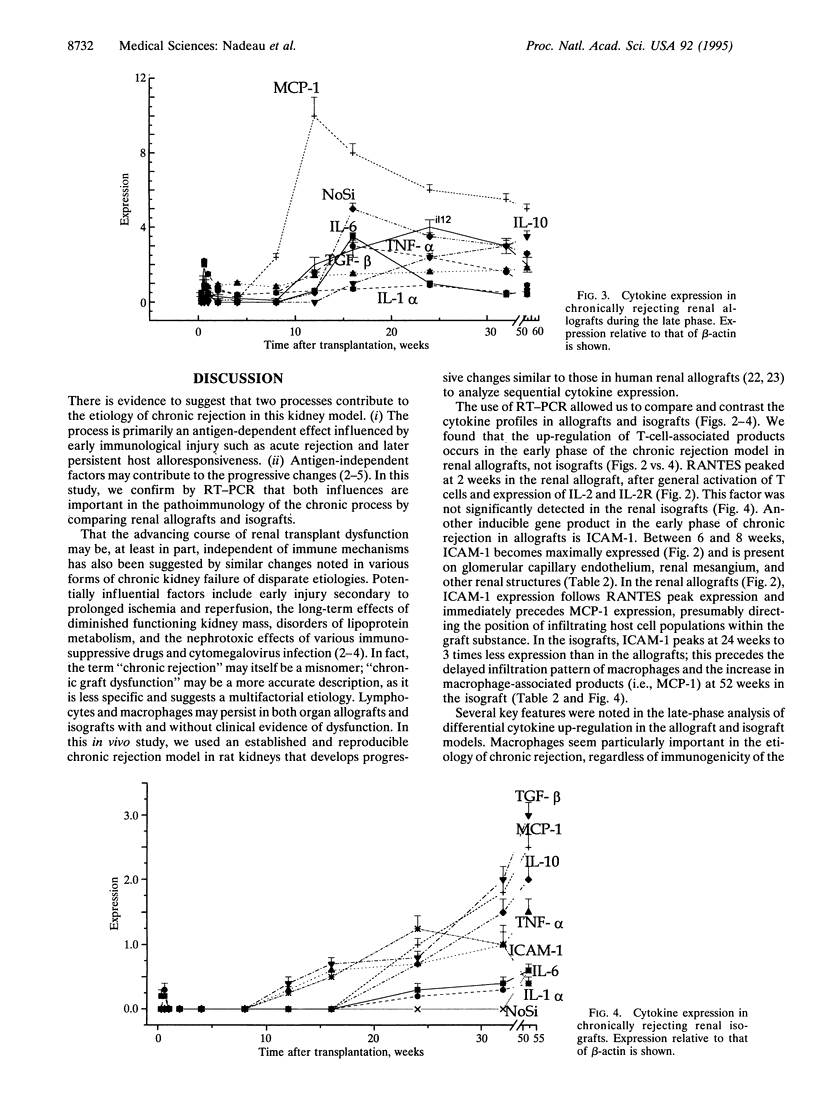
Chronic rejection, the most important cause of long-term graft failure, is thought to result from both alloantigen-dependent and -independent factors. To examine these influences, cytokine dynamics were assessed by semiquantitative competitive reverse transcriptase-PCR and by immunohistology in an established rat model of chronic rejection lf renal allografts. Isograft controls develop morphologic and immunohistologic changes that are similar to renal allograft changes, although quantitatively less intense and at a delayed speed; these are thought to occur secondary to antigen-independent events. Sequential cytokine expression was determined throughout the process. During an early reversible allograft rejection episode, both T-cell associated [interleukin (IL) 2, IL-2 receptor, IL-4, and interferon gamma] and macrophage (IL-1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and IL-6) products were up-regulated despite transient immunosuppression. RANTES (regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted) peaked at 2 weeks; intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) was maximally expressed at 6 weeks. Macrophage products such as monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) increased dramatically (to 10 times), presaging intense peak macrophage infiltration at 16 weeks. In contrast, in isografts, ICAM-1 peaked at 24 weeks. MCP-1 was maximally expressed at 52 weeks, commensurate with a progressive increase in infiltrating macrophages. Cytokine expression in the spleen of allograft and isograft recipients was insignificant. We conclude that chronic rejection of kidney allografts in rats is predominantly a local macrophage-dependent event with intense up-regulation of macrophage products such as MCP-1, IL-6, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. The cytokine expression in isografts emphasizes the contribution of antigen-independent events. The dynamics of RANTES expression between early and late phases of chronic rejection suggest a key role in mediating the events of the chronic process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Border W. A., Noble N. A. Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 10;331(19):1286–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411103311907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G. J., Schamberg J. F., Moretz R. C., Strom T. B., Tilney N. L., Carpenter C. B. T and B cell patterns in irreversibly rejected human renal allografts. Correlation of morphology with surface markers and cytotoxic capacity of the isolated lymphoid infiltrates. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):272–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J. Cytokines as mediators of organ graft rejection and tolerance. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Oct;5(5):788–793. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90138-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J., Wood K. J., Hamano K., Bushell A. R., Morris P. J., Wood M. J., Charlton H. M. Cytokines and peripheral tolerance to alloantigen. Immunol Rev. 1993 Jun;133:5–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devergne O., Marfaing-Koka A., Schall T. J., Leger-Ravet M. B., Sadick M., Peuchmaur M., Crevon M. C., Kim K. J., Schall T. T., Kim T. Production of the RANTES chemokine in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions: involvement of macrophages and endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1689–1694. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. H., Whitley W. D., Tullius S. G., Heemann U. W., Wasowska B., Baldwin W. M., 3rd, Tilney N. L. Cytokines, adhesion molecules, and the pathogenesis of chronic rejection of rat renal allografts. Transplantation. 1993 Sep;56(3):643–650. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199309000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemann U. W., Tullius S. G., Tamatami T., Miyasaka M., Milford E., Tilney N. L. Infiltration patterns of macrophages and lymphocytes in chronically rejecting rat kidney allografts. Transpl Int. 1994 Aug;7(5):349–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00336711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., Mennander A., Yilmaz S., Ustinov J., Räisänen A., Miettinen A., Lautenschlager I., Lemström K., Bruggeman C. A., Paavonen T. Towards understanding the pathophysiology of chronic rejection. Clin Investig. 1992 Sep;70(9):780–790. doi: 10.1007/BF00180748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen A., Cook T., Taylor G. M., Largen P., Riveros-Moreno V., Moncada S., Cattell V. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat immune complex glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1994 Apr;45(4):1215–1219. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer J., Steiniger B., Marquarding E., Vogt P., Lipecz A., Wonigeit K., Günther E. Effects of the RT1.C region in rat allotransplantation. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):713–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matas A. J. Chronic rejection--definition and correlates. Clin Transplant. 1994 Apr;8(2 Pt 2):162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDiarmid S. V., Farmer D. G., Kuniyoshi J. S., Robert M., Khadavi A., Shaked A., Busuttil R. W. The correlation of intragraft cytokine expression with rejection in rat small intestine transplantation. Transplantation. 1994 Sep 27;58(6):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., O'Garra A., de Waal Malefyt R., Vieira P., Mosmann T. R. Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:165–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. E. Renal transplantation before Starzl. Transplant Proc. 1988 Feb;20(1 Suppl 1):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J., Nelson P. J., Huie P., von Leuttichau I., Farshid G., Sibley R. K., Krensky A. M. RANTES chemokine expression in cell-mediated transplant rejection of the kidney. Lancet. 1994 Jan 22;343(8891):209–211. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90992-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. E., Adams D. H., Wyner L. R., Yamashita Y., Halnon N. J., Karnovsky M. J. Early and persistent induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in rat cardiac allografts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6086–6090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney N. L., Kupiec-Weglinski J. W., Heidecke C. D., Lear P. A., Strom T. B. Mechanisms of rejection and prolongation of vascularized organ allografts. Immunol Rev. 1984;77:185–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney N. L., Whitley W. D., Diamond J. R., Kupiec-Weglinski J. W., Adams D. H. Chronic rejection--an undefined conundrum. Transplantation. 1991 Sep;52(3):389–398. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199109000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius S. G., Heemann U., Hancock W. W., Azuma H., Tilney N. L. Long-term kidney isografts develop functional and morphologic changes that mimic those of chronic allograft rejection. Ann Surg. 1994 Oct;220(4):425–435. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199410000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanOtteren G. M., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Paine R., 3rd, Greenberger M. J., Danforth J. M., Burdick M. D., Standiford T. J. Compartmentalized expression of RANTES in a murine model of endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 15;154(4):1900–1908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk H. D., Müller S., Yarkoni S., Diamantstein T., Lorberboum-Galski H. Mechanisms of dichotomous action of IL-2-Pseudomonas exotoxin 40 (IL-2-PE40) on cell-mediated and humoral immune response. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2497–2505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




