Abstract
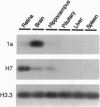
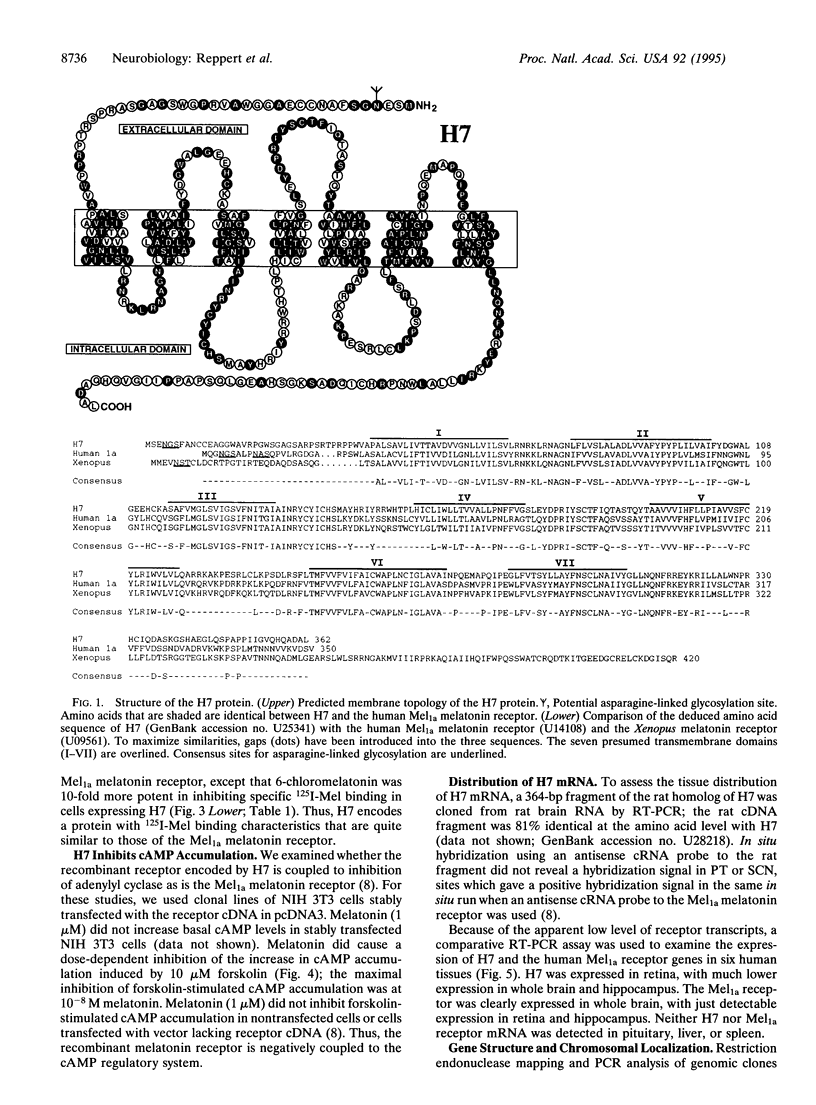
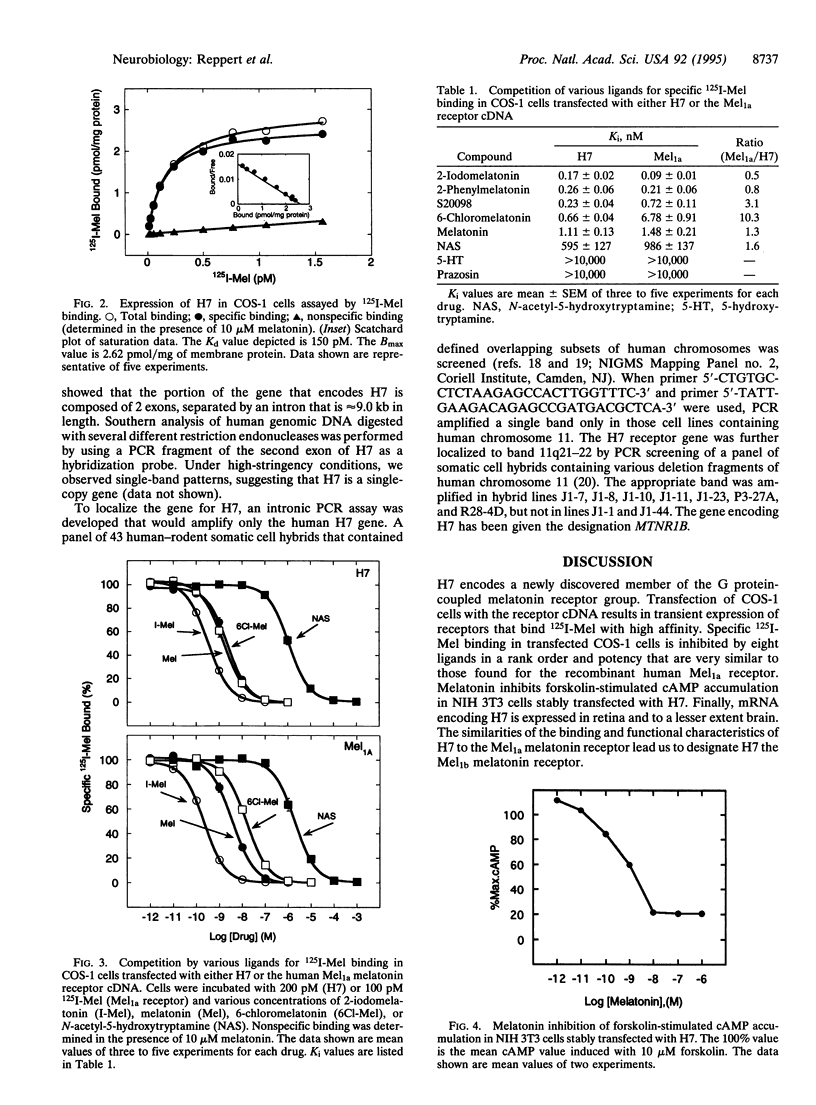
A G protein-coupled receptor for the pineal hormone melatonin was recently cloned from mammals and designated the Mel1a melatonin receptor. We now report the cloning of a second G protein-coupled melatonin receptor from humans and designate it the Mel1b melatonin receptor. The Mel1b receptor cDNA encodes a protein of 362 amino acids that is 60% identical at the amino acid level to the human Mel1a receptor. Transient expression of the Mel1b receptor in COS-1 cells results in high-affinity 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding (Kd = 160 +/- 30 pM). In addition, the rank order of inhibition of specific 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding by eight ligands is similar to that exhibited by the Mel1a melatonin receptor. Functional studies of NIH 3T3 cells stably expressing the Mel1b melatonin receptor indicate that it is coupled to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. Comparative reverse transcription PCR shows that the Mel1b melatonin receptor is expressed in retina and, to a lesser extent, brain. PCR analysis of human-rodent somatic cell hybrids maps the Mel1b receptor gene (MTNR1B) to human chromosome 11q21-22. The Mel1b melatonin receptor may mediate the reported actions of melatonin in retina and participate in some of the neurobiological effects of melatonin in mammals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besharse J. C., Dunis D. A. Methoxyindoles and photoreceptor metabolism: activation of rod shedding. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1341–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.6828862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. M., Grace M. S., Besharse J. C. Rhythmic regulation of retinal melatonin: metabolic pathways, neurochemical mechanisms, and the ocular circadian clock. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1991 Oct;11(5):529–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00734814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone V. M. Effects of melatonin on vertebrate circadian systems. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Nov;13(11):457–464. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90099-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubocovich M. L. Melatonin is a potent modulator of dopamine release in the retina. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):782–784. doi: 10.1038/306782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubocovich M. L., Takahashi J. S. Use of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin to characterize melatonin binding sites in chicken retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisawa T., Karne S., Lerner M. R., Reppert S. M. Expression cloning of a high-affinity melatonin receptor from Xenopus dermal melanophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6133–6137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Liao M., Brook J. D., Martin F. H., Zsebo K. M., Housman D. E., Galli S. J. Stem cell factor (SCF), a novel hematopoietic growth factor and ligand for c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor, maps on human chromosome 12 between 12q14.3 and 12qter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1991 Mar;17(2):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01232978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Housman D., Lewis W. H., Gerhard D., Jones C. A fine-structure deletion map of human chromosome 11p: analysis of J1 series hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Nov;15(6):477–501. doi: 10.1007/BF01534910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsborough A. S., Healy L. E., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Willison K. R., Ashworth A. Cloning, chromosomal localization and expression pattern of the POU domain gene Oct-11. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):127–134. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiramand J., Montmayeur J. P., Ceraline J., Bhatia M., Borrelli E. Alternative splicing of the dopamine D2 receptor directs specificity of coupling to G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7354–7358. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. R., Jurgens J. K., Tentler J., Emanuele N. V., Blutt S. E., Emanuele M. A. Coupled reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique is comparative, quantitative, and rapid: uses in alcohol research involving low abundance mRNA species such as hypothalamic LHRH and GRF. Alcohol. 1993 May-Jun;10(3):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(93)90033-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews F. S. The structure, function and evolution of cytochromes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;45(1):1–56. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzveig D. R., Mathew S., Gershengorn M. C. Alternative splicing of a 48-nucleotide exon generates two isoforms of the human calcitonin receptor. Endocrinology. 1995 May;136(5):2047–2051. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.5.7720653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Brook J. D., Housman D. E. Assignment of two of the translation initiation factor-4E (EIF4EL1 and EIF4EL2) genes to human chromosomes 4 and 20. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):1079–1082. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90203-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter R. J. Pineal melatonin: cell biology of its synthesis and of its physiological interactions. Endocr Rev. 1991 May;12(2):151–180. doi: 10.1210/edrv-12-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R., Ebisawa T. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian melatonin receptor that mediates reproductive and circadian responses. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1177–1185. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R., Rivkees S. A., Stopa E. G. Putative melatonin receptors in a human biological clock. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):78–81. doi: 10.1126/science.2845576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R., Stehle J. H., Rivkees S. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a rat A1-adenosine receptor that is widely expressed in brain and spinal cord. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1037–1048. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-8-1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin M. F., Saunders A. M., Rochelle J. M., Howard T. A. A proximal mouse chromosome 9 linkage map that further defines linkage groups homologous with segments of human chromosomes 11, 15, and 19. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):678–685. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90361-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaugenhaupt S. A., Roca A. L., Liebert C. B., Altherr M. R., Gusella J. F., Reppert S. M. Mapping of the gene for the Mel1a-melatonin receptor to human chromosome 4 (MTNR1A) and mouse chromosome 8 (Mtnr1a). Genomics. 1995 May 20;27(2):355–357. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood H., Goldman B. D. Vertebrate circadian and photoperiodic systems: role of the pineal gland and melatonin. J Biol Rhythms. 1987 Winter;2(4):279–315. doi: 10.1177/074873048700200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanecek J. Melatonin binding sites. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1436–1440. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Chen Y., Gilbert D. J., Moore K. J., Yu L., Simon M. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Identification, chromosomal location, and genome organization of mammalian G-protein-coupled receptors. Genomics. 1993 Nov;18(2):175–184. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]